Plating method, plating apparatus and a method of forming fine circuit wiring
a plating apparatus and wire technology, applied in the field of copper plating methods, can solve the problems of reducing the electric conductivity of copper plating films, affecting the production efficiency of printed circuits, so as to reduce the amount of chlorine ions incorporated, improve the electromigration resistance, and reduce the possibility of corrosion and deterioration of copper-plated wiring.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
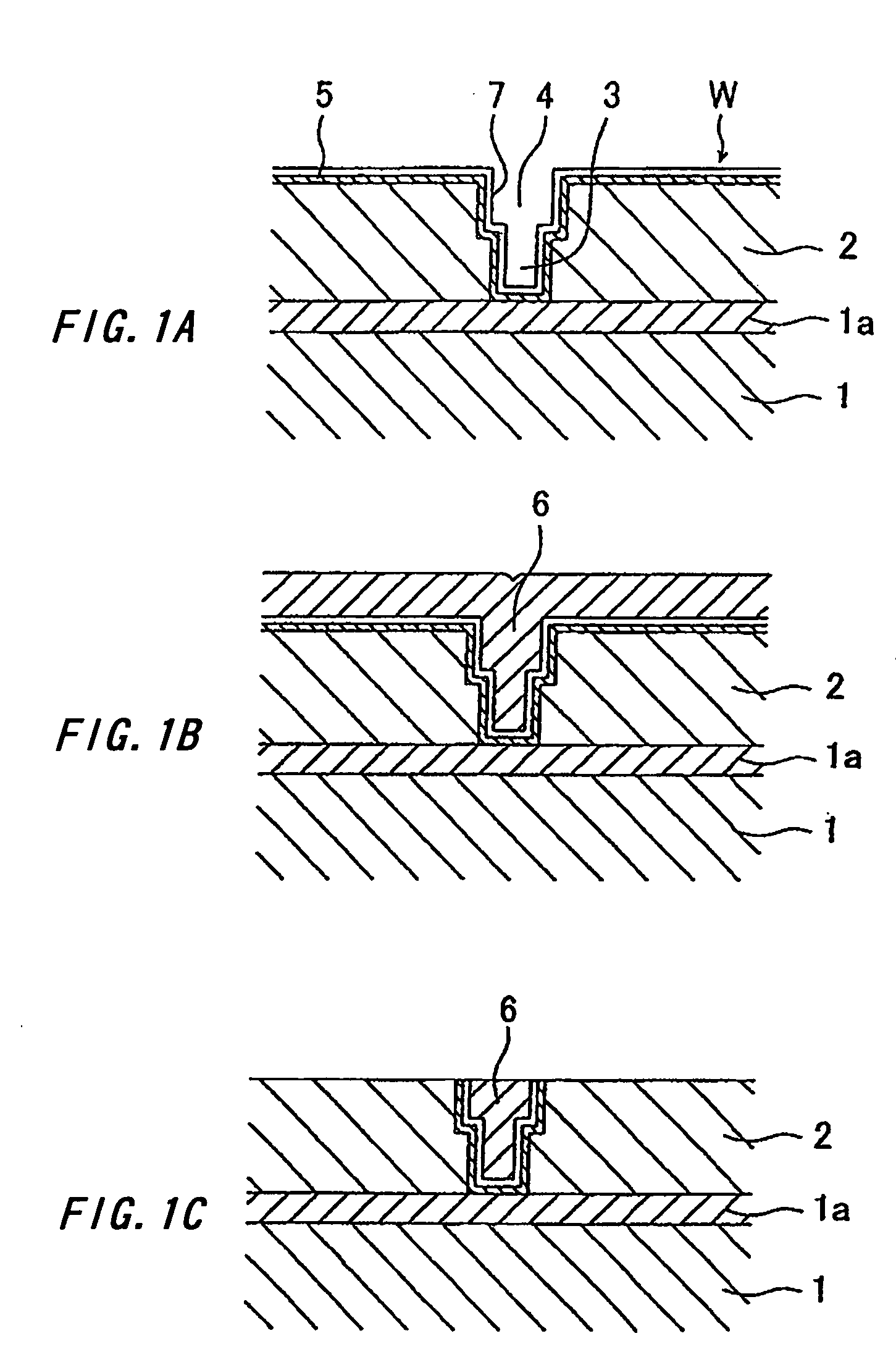
[0079] A test was conducted to ascertain that chlorine ions incorporated into a plating film were of a leveler.
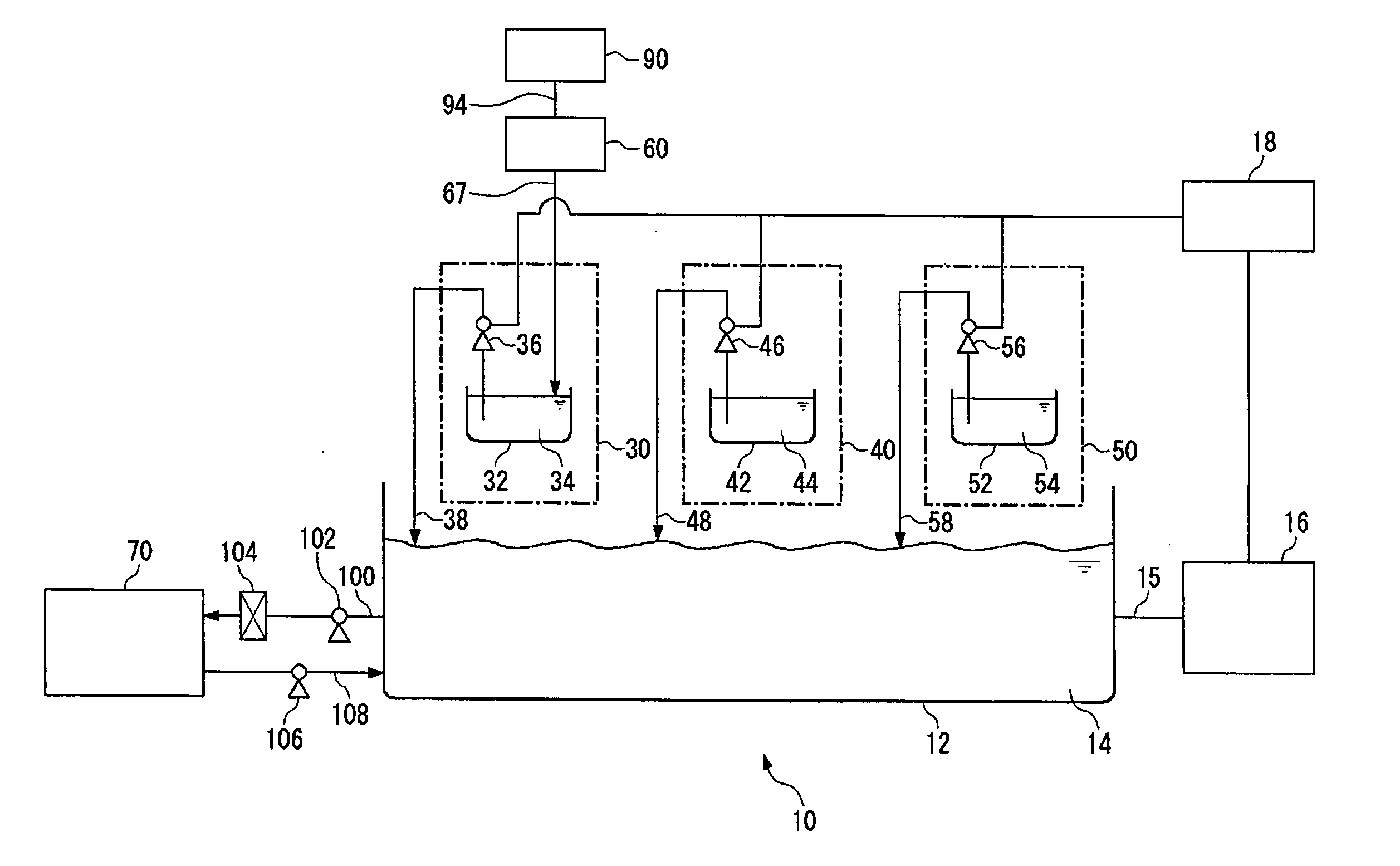
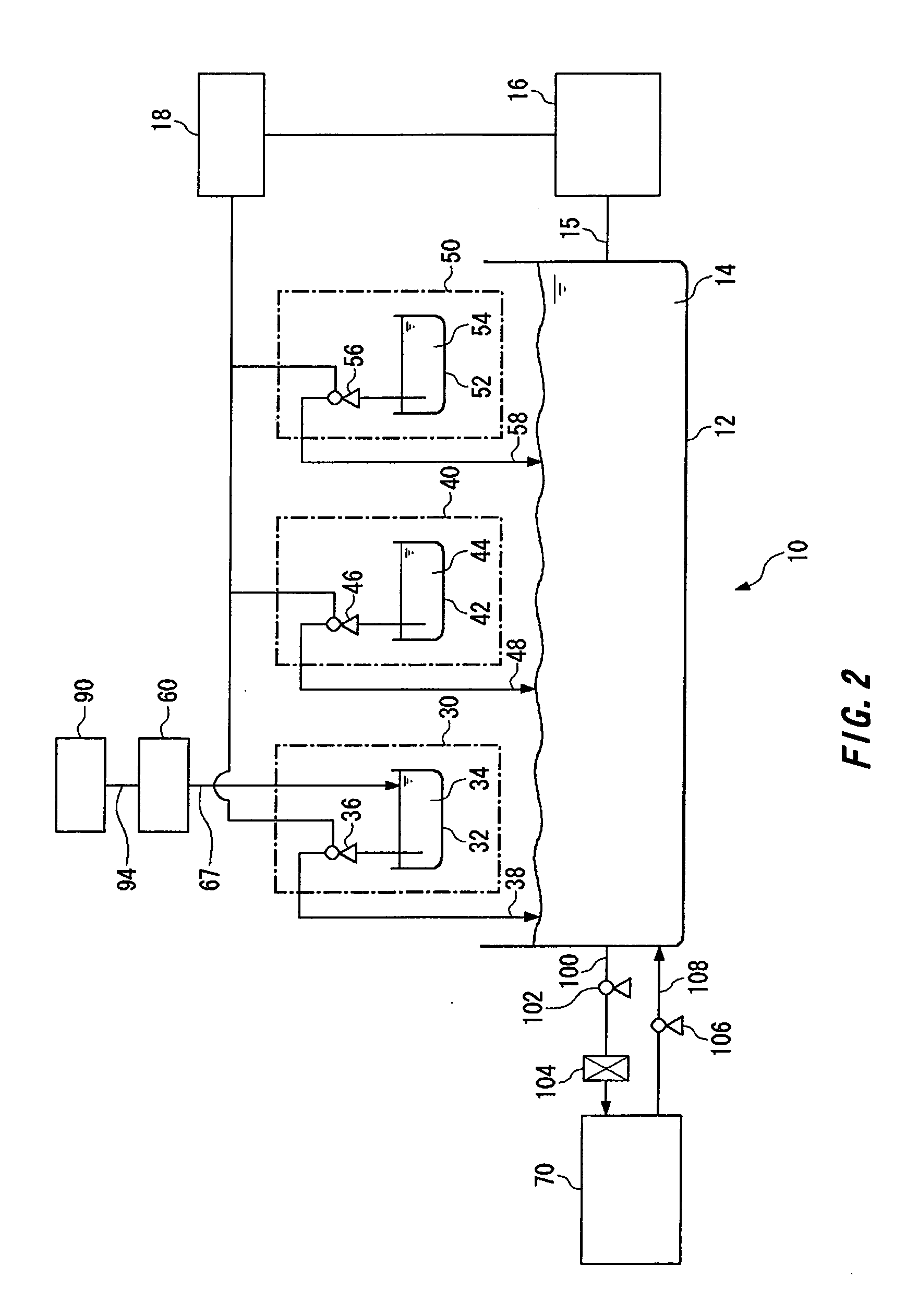
[0080] One liter of a plating solution was so prepared as to contain 200 g of CuSO4.5H2O, 10 g of H2SO4, 60 mg of chlorine ions, 200 mg of polyethylene glycol having a molecular weight of about 3000 and 5 mg of bis(3-sulfopropyl)disulfide.
[0081] A quaternary ammonium hydrochloride salt of polyvinyl pyridine yet to be dechlorinated was employed as a leveler and was so added to the plating solution that the plating solution might contain 10 mg of polyvinyl pyridine per liter. The leveler yet to be dechlorinated contained 16 g of polyvinyl pyridine and 4 g of chlorine ions per liter. The plating solution was used for the copper plating of a silicon wafer. The plating solution to which no leveler had been added was also used for the copper plating of a silicon wafer.
[0082] The copper-plated silicon wafers were examined by a secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) for the chlo...
example 2
[0084] The leveler used in Example 1 was dechlorinated to prepare a leveler having a chlorine ion concentration reduced to 1 g / l.
[0085] The dechlorinated leveler and the same plating solution as in Example 1 were used for the copper plating of a silicon wafer.
[0086] The examination of the wafer by SIMS as in Example 1 can confirm a reduction in the amount of chlorine ions incorporated in its copper plating film.
example 3
[0087] A phosphorus-doped copper plating solution was prepared by adding 5 ml of 50% phosphoric acid to one liter of a copper sulfate plating solution (basic solution) having the composition shown below. The plating solution was used for one minute of phosphorus-doped copper plating at a temperature of 25° C. and a current density of 30 mA / cm2 on a semiconductor wafer in which via holes having a width of 150 nm and an aspect ratio of 5 had been formed. The semiconduct or wafer had a barrier and a seed layer formed by customary methods.
[0088] Composition of the Copper Sulfate Plating Solution:
Copper sulfate pentahydrate200 g / lSulfuric acid 50 g / lChlorine ion 50 mg / lPhosphorus compound100 mg / l(as phosphoric acid ion)Polymer component 30 ml / lCarrier component 10 ml / lLeveler component 10 ml / l
[0089] There was obtained a phosphorus -doped copper plating film having a phosphorus content of 1×10−6 atom % or more along its depth. Its examination by a scanning electron microscope did not r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com