Novel manganese superoxide dismutase regulatory elements and uses therefore
a technology of manganese superoxide dismutase and regulatory elements, applied in the field of new transcriptional regulatory elements, can solve the problems of inability to adapt to and control the expression of foreign genes, lack of specificity, repeated administration of recombinant ad based vectors, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the transcription/expression level of heterologous polynucleotides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Characterization of the Rat MnSOD Promoter
[0224] The following studies were performed to characterize the region of the rat MnSOD gene responsible for induction of gene expression in response to inflammatory mediators.
The Rat MnSOD Promoter does not Contain all the DNA Elements Necessary for Cytokine-Inducible Expression
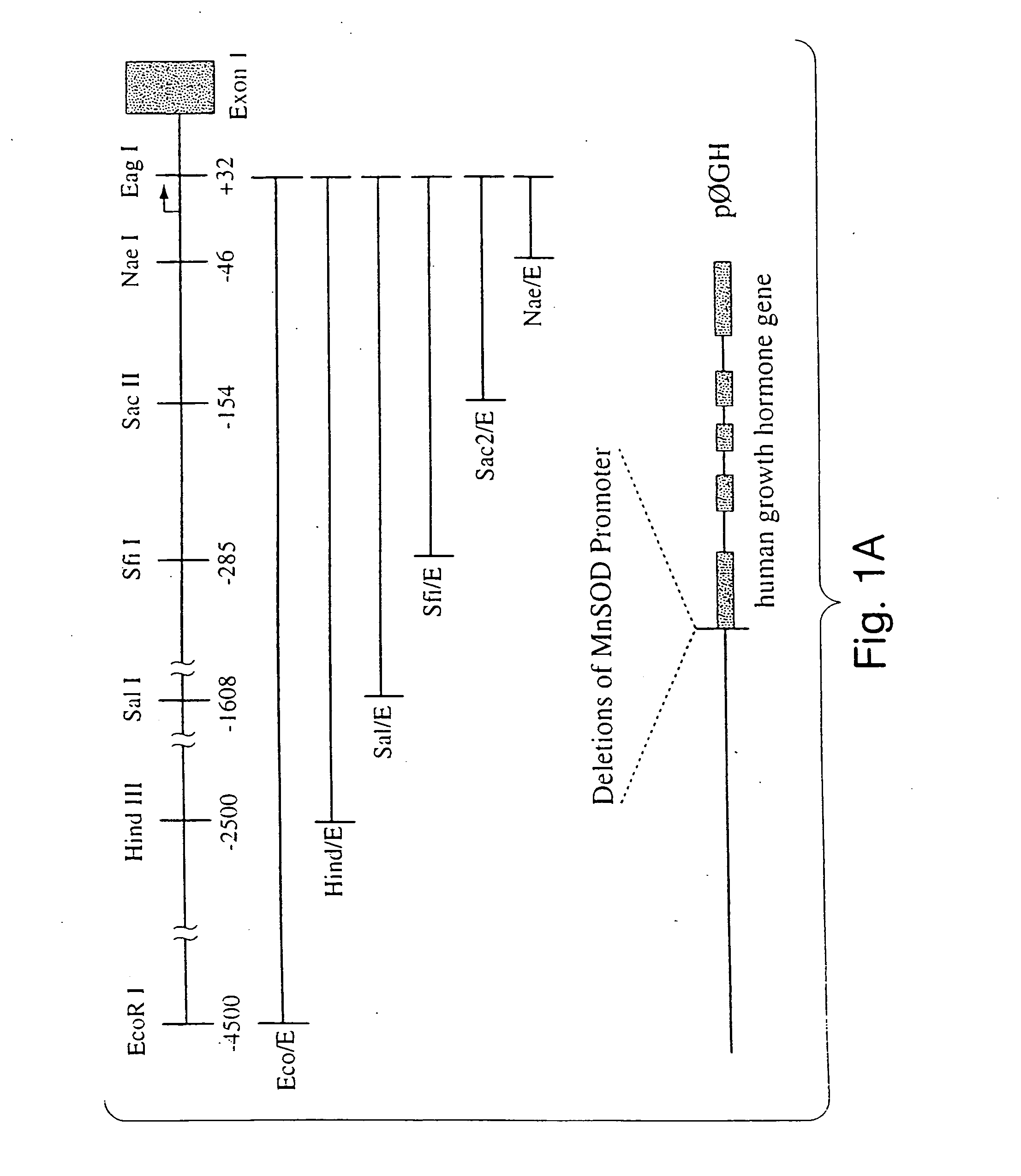
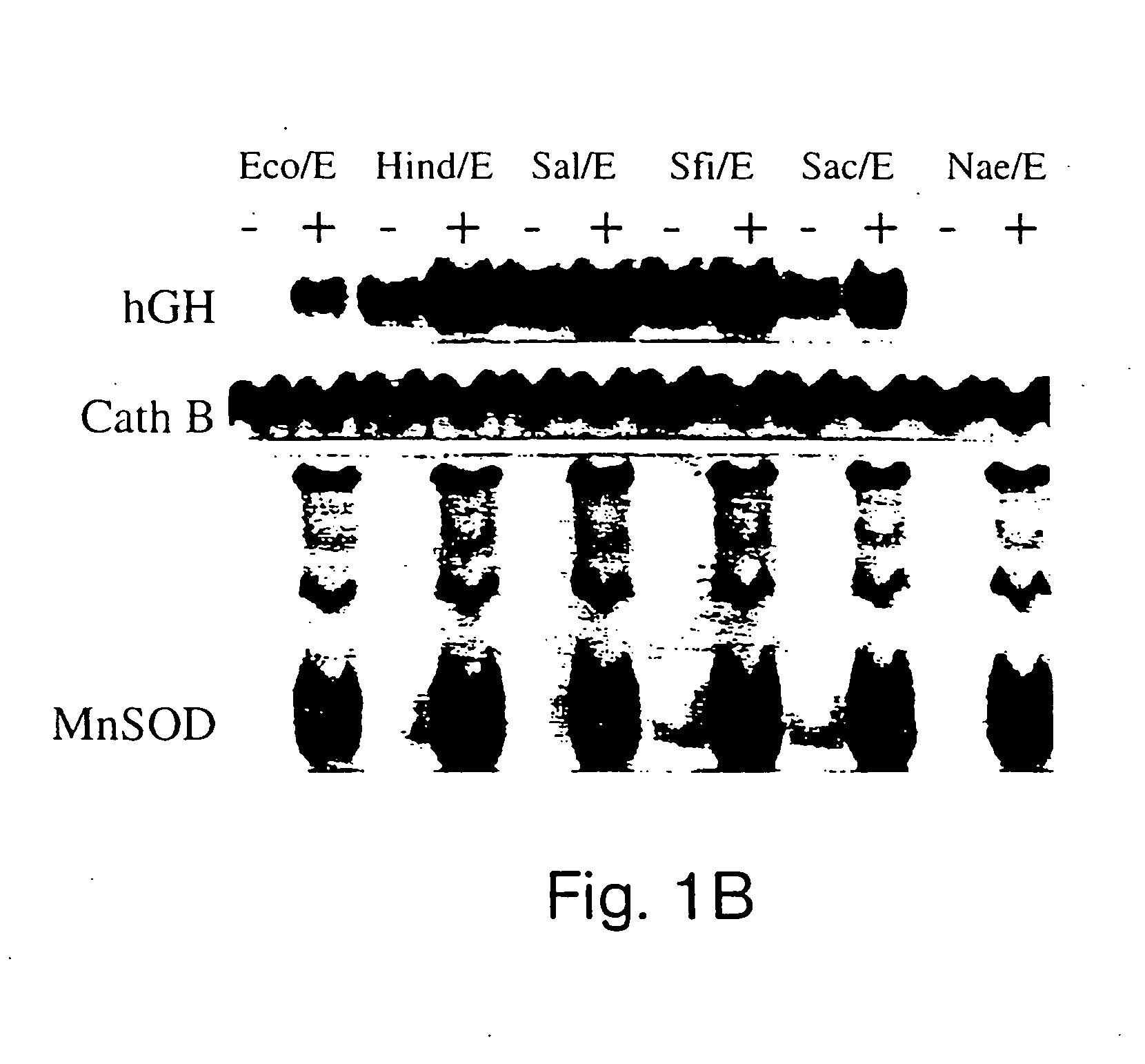
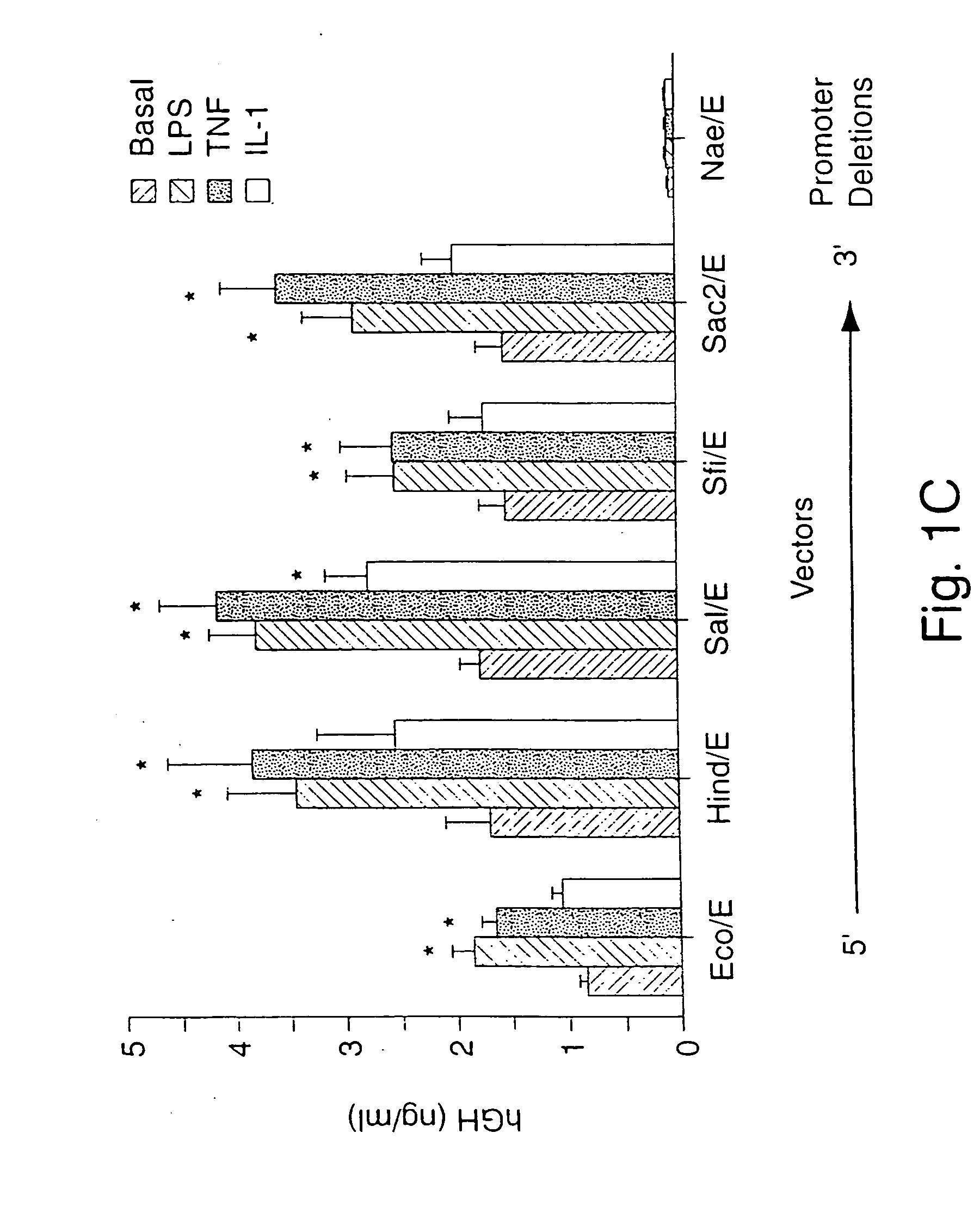
[0225] MnSOD gene expression is stimulated by inflammatory mediators, including LPS, TNF-α, and IL-1β, and is due at least in part to de novo gene transcription. To identify sequences in rat MnSOD which confer specificity for LPS-, TNF-α- and IL-1β-dependent gene induction, a series of MnSOD promoter deletion constructs were generated using the promoterless human growth hormone vector pØGH (FIG. 1A). Unique restriction sites within the rat MnSOD 5′ flanking sequence were used to create vectors containing the promoter deletions. Each 5′ promoter deletion construct contained sequences which incorporated the MnSOD transcriptional start site. Cells transfected with a...
example 2
Characterization of MnSOD Enhancer Elements
[0227] The studies described in Example 1 showed that the rat MnSOD gene 5′ proximal promoter was not solely responsible for inducible gene expression. Accordingly, the following studies were performed to identify and characterize further transcriptional regulatory elements within the MnSOD gene itself (e.g., within intron sequences).
A Novel Inducible Cis-Acting Enhancer Element Exists within the Rat and Human MnSOD Genes
[0228] To determine whether the remaining DNaseI hypersensitive sites described in Example 1 (within the MnSOD gene) contained regulatory function, pØGH expression vectors were created that contained both a 2.5 Kb fragment of the MnSOD promoter (Hind / E) and a 6.1 kb HindIII internal fragment of the MnSOD gene which contains all of the other Dnase I hypersensitive sites (FIG. 2A). Expression of hGH mRNA in cells transfected with this vector was compared to expression of hGH in cells transfected with a pØGH construct cont...
example 3
Construction of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vectors Containing MnSOD Prohancer Elements
[0244] The novel MnSOD prohancer elements of the invention can also be used to generate delivery vectors suitable for inducible heterologous gene expression. A series of AAV vectors can be engineered containing the MnSOD prohancer element. To do this, the PCMV promoter is removed from pTR-UF2 using KpnI and XhaI, and the MnSOD prohancer, either alone or coupled to a minimal promoter, is inserted (FIG. 10). The recombinant AAV plasmids are packaged using the current method for isolating rAAV as developed by Hermonat and Muzyczka (1984). Human cells (e.g., 293 cells) are transfected with the plasmid which consists of a transgene flanked by the AAV terminal repeats (TR), the only AAV sequences required for viral DNA replication, packaging and integration. The cells are also transfected with a complementing plasmid that is defective for packaging, but supplies the wild type AAV rep and c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com