Method of inhibiting stenosis and restenosis
a technology of stenosis and restraint, which is applied in the field of inhibiting stenosis and restraint, can solve the problems of inability to inability to effectively inhibit stenosis and restraint, etc., to achieve the effect of inhibiting adhesion and/or recruitment, and inhibiting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
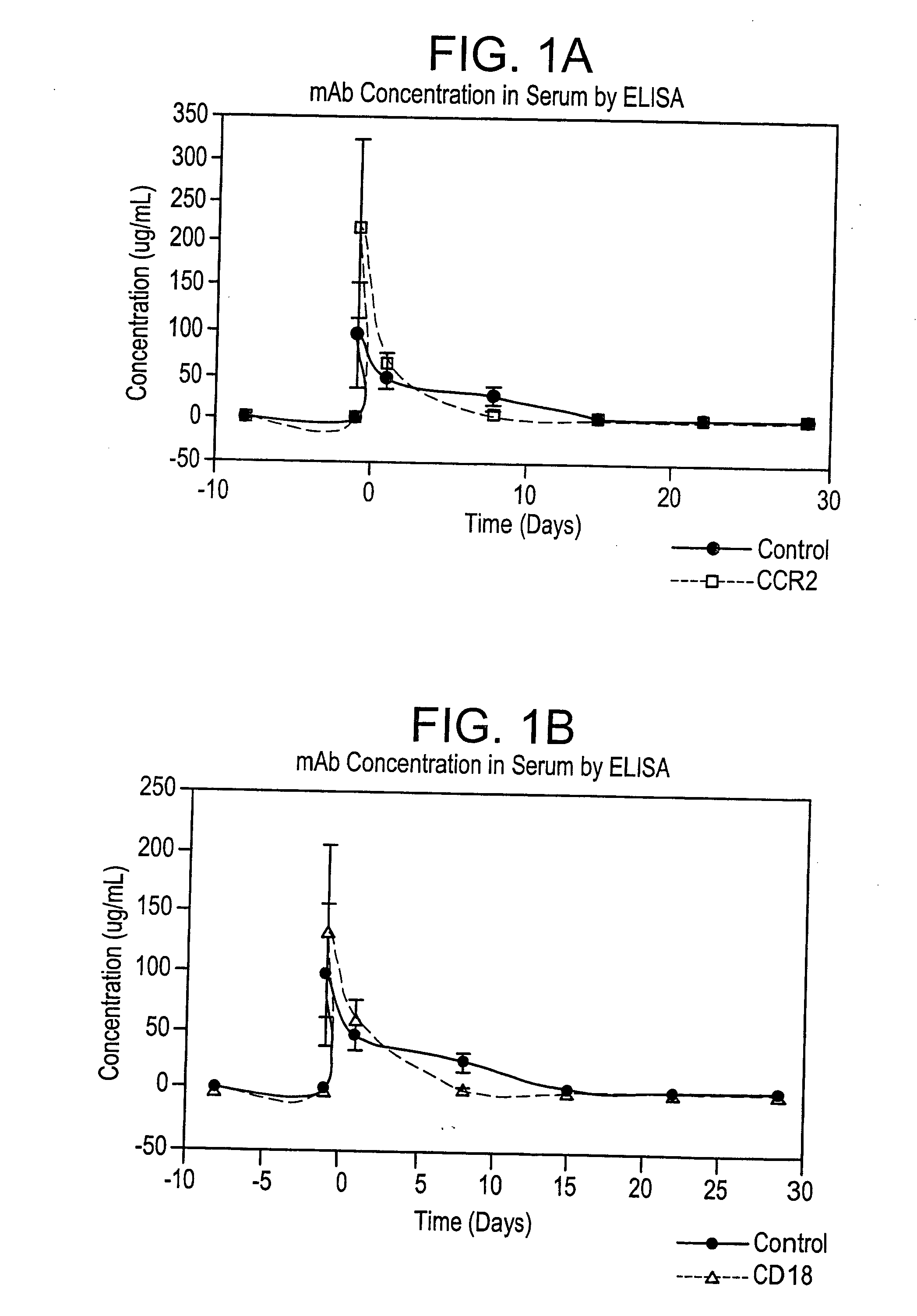
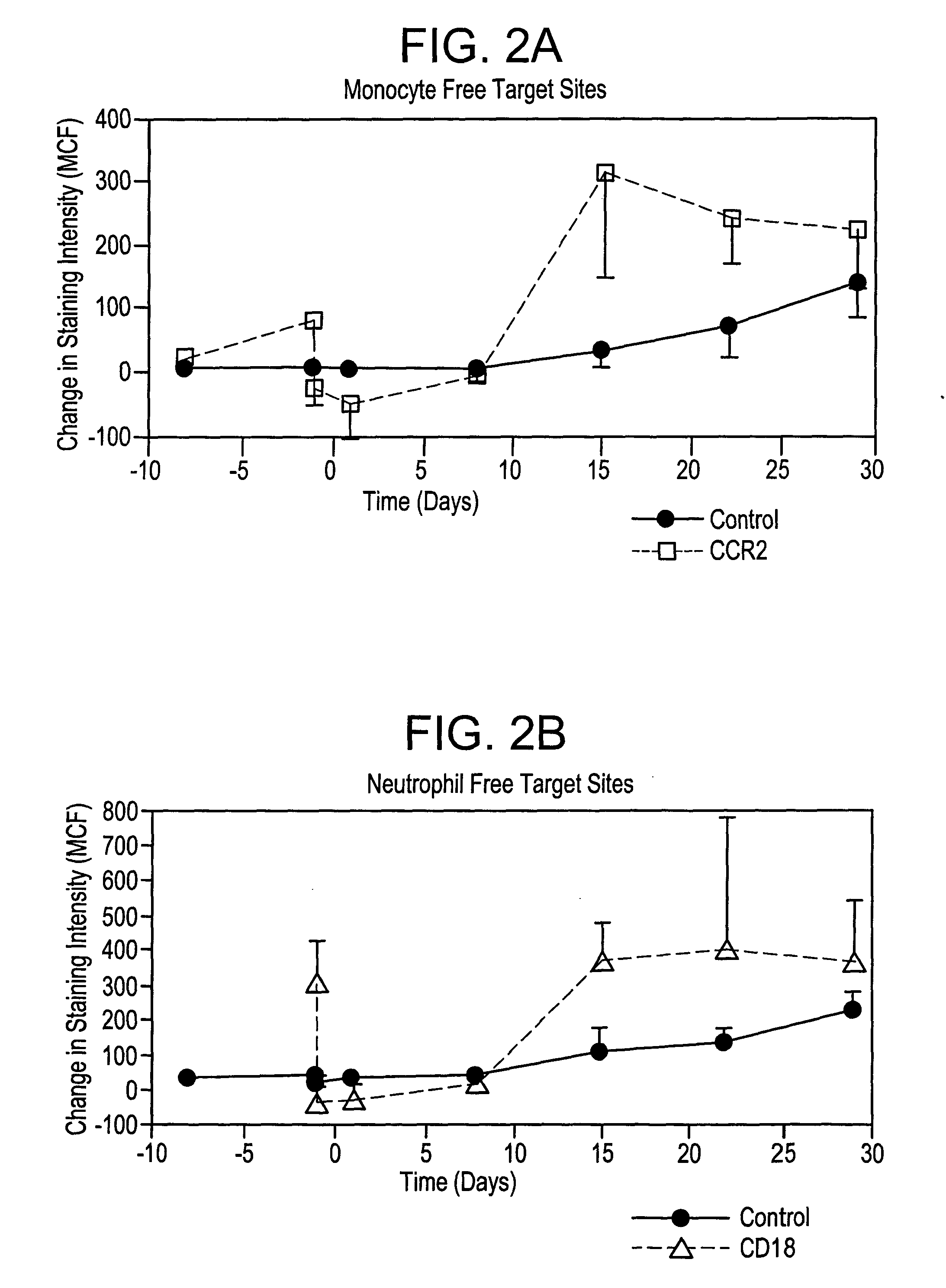
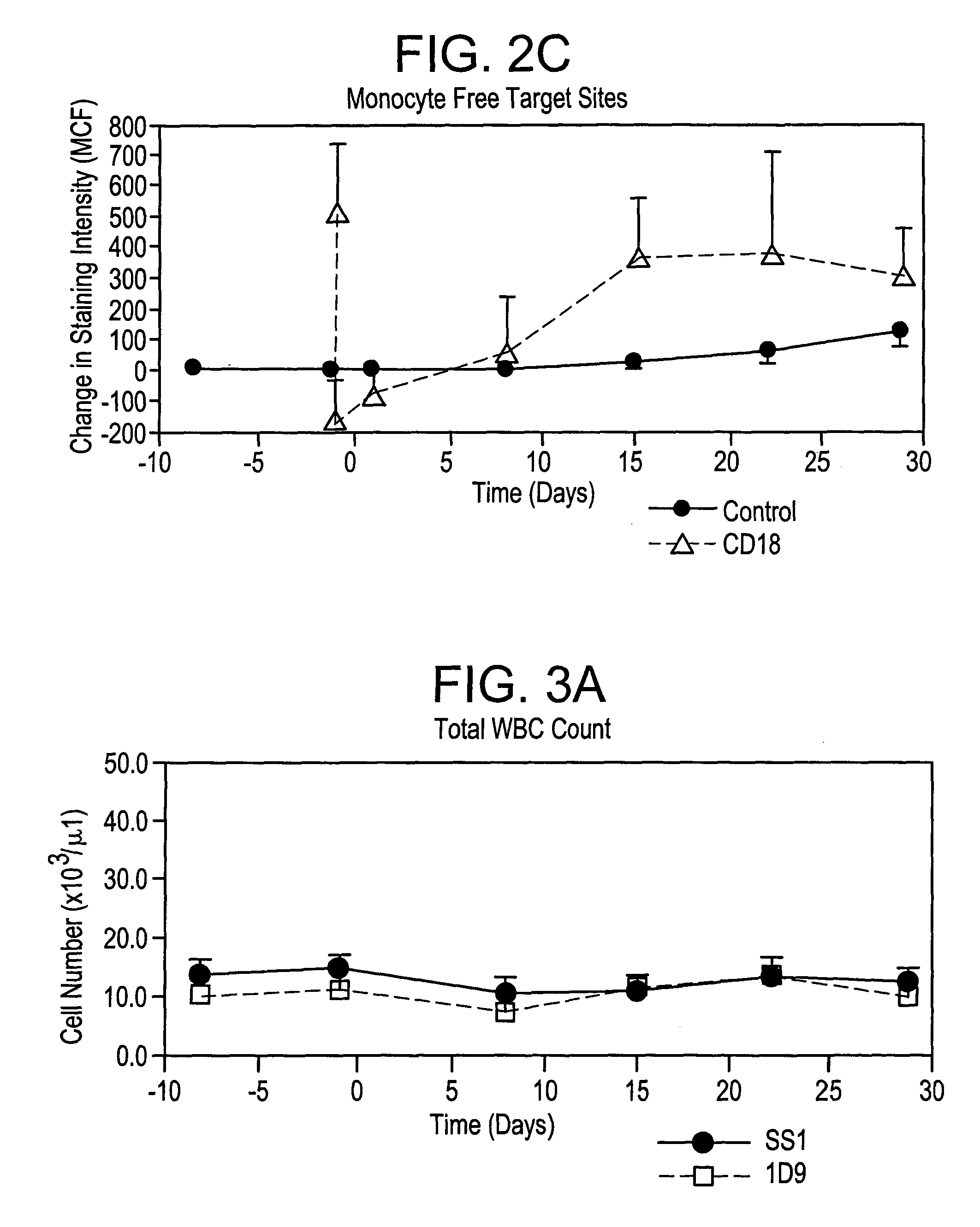
[0101] The effects of murine monoclonal antibodies which bind human integrin CD18 or human chemokine receptor CCR2 in a model of restenosis in cynomolgus monkeys was evaluated.
Study Design
[0102] Cynomolgus monkeys were randomized on the basis of body weight to groups to receive treatment with either an irrelevant murine monoclonal antibody (mAb) as an IgG2a isotype control (S-S.1), an anti-human CCR2 mAb (1D9) or an anti-human CD18 mAb (1B4). Animals were administered a loading dose of mAb intravenously (IV) on Day −1, followed by daily SC injections on Days 1-13. On Day 1, all animals underwent bilateral balloon angioplasty-induced iliac artery endothelial denudation, followed by intravascular stent placement, as a model of restenosis. Animals were euthanized at the end of the test period to allow perfusion fixation and collection of the iliac arteries and other tissue samples (see Table A).
[0103] Efficacy of treatment was evaluated by use of quantitative angiography at the tim...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adhesion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com