Radioactive multiplexing analytical methods for biomarkers discovery
a biomarker and radioactive multiplexing technology, applied in the field of radioactive multiplexing analytical methods for biomarker discovery, can solve the problems of label interference with the analyte, protein cannot be used for protein array analysis, and dye may alter the structure of dna or rna significantly, so as to achieve the effect of higher sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Biomarker Discovery and High-Throughput Assay Development
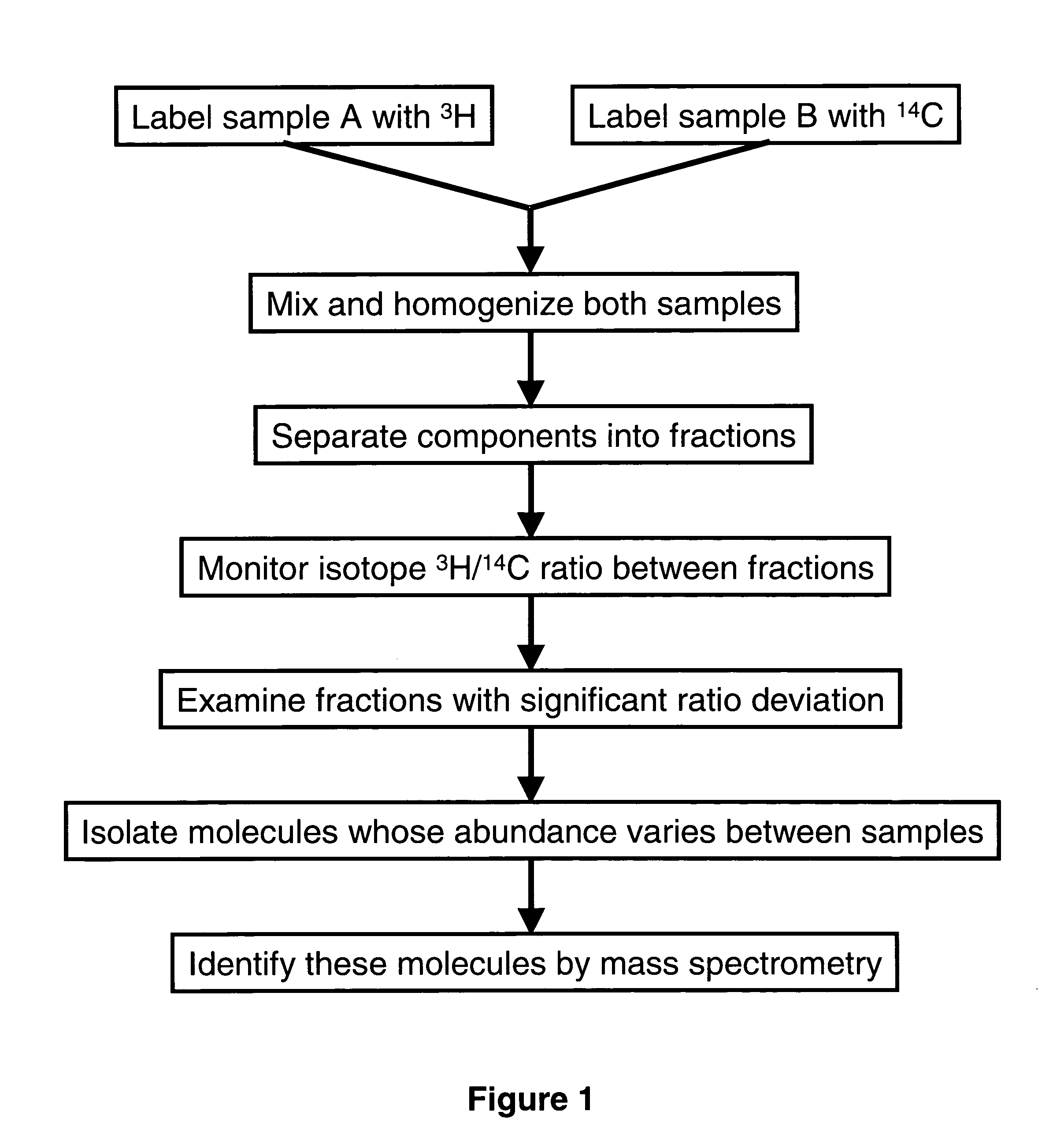
[0058] Because of the limited antibodies availability, biomarkers must first be discovered and then antibodies are made against them to build useful antibody arrays for high throughput screening. Current methods use 2-D gel electrophoresis to separate proteins. This example presents an alternative to 2-D gel electrophoresis.
[0059] Samples from two sources such as drug-treated and vehicle treated cells are used to look for biomarkers. These samples are prepared so that one is labeled with 3H while the other is labeled with 14C by chemically similar labels or by metabolic incorporation and then mixed together for analysis. A small aliquot is counted on scintillation counter capable of distinguishing between 3H and 14C to establish the ratio of samples mixture. The mixture is then separated by tandem chromatography. The fractions resulting from one type of chromatography are further separated by another form of chromatography....
example 2
Post-Translational Modification Studies
Protein Phosphorylation Study
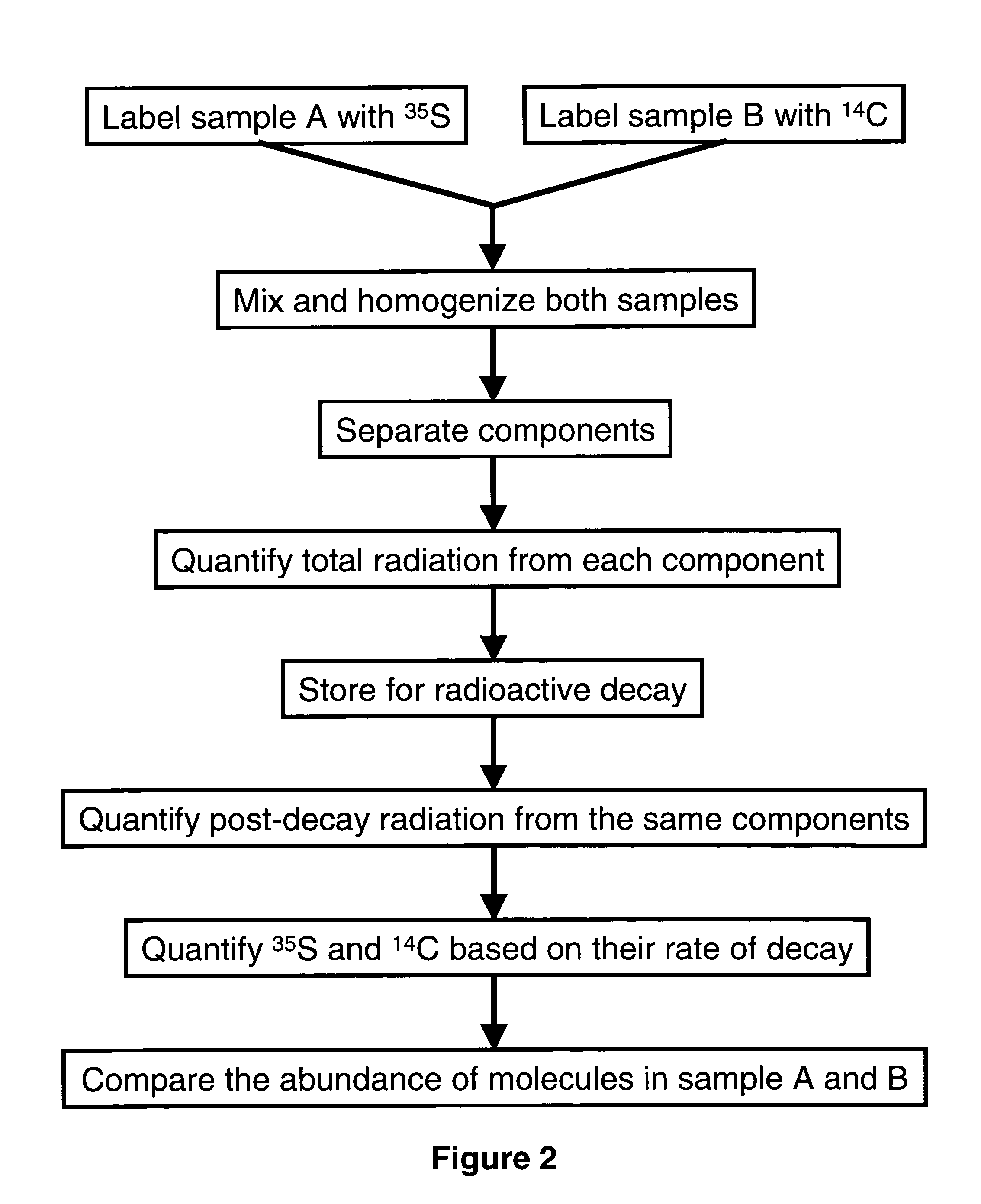
[0061] Post-translational modifications of proteins are very important regulatory mechanism in eukaryotic organisms. One such important modification is phosphorylation: a phosphate added to an enzyme or receptor can turn it on or off depending on the type of enzyme or receptor. Thus a system that enables the comparison of protein phosphorylation with high degree of sensitivity can be a very powerful tool for research and diagnostic use. A dual labeling system using chemically similar labeling agents that comprises either 32P or 33P is used to determine the degree of phosphorylation in two set of cells or cells undergoing two different treatments.
[0062] Cellular drug response can be studied as followed: (1) Cells are grown equally in two culture dishes. Prior to labeling, the cells are starved of phosphate by washing and replacing growth media with phosphate-deficient media for 1 hour. (2) Labeling media are add...
example 3
Genomic / RNA Expression Studies
[0068] For tissue samples where RNA is readily extracted, the RNA can be labeled with either 32P or 33P at their end terminals and then applied to a complementary DNA array. The array is then exposed to the two-screen phosphorescent imaging system so signals specific to either 32P or 33P could be quantified and compared after normalized with internal controls' signals. Alternatively, total signals can be quantified before and after a few days and used to calculate signal unique to 32P or 33P. The half-life of 32P is shorter than that of 33P (14.3 days compared to 25.3 days) thus makes the calculation possible. For higher sensitivity in smaller tissue sample, a Reverse Transcriptase reaction can be performed with either 32P or 33P labeled poly dT or labeled nucleotides. The poly dT is hybridized to the poly A tail of mRNA and reverse transcriptase synthesizes the rest of the complementary sequence to form a single stranded cDNA. The RNA is then digeste...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radioactive | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com