Polyglutamate-amino acid conjugates and methods
a technology of polyglutamate and amino acid, applied in the field of biocompatible watersoluble polymers, can solve the problems of/or drug, poor bioavailability of the relative hydrophobic imaging agent, and poor so as to achieve the effect of effective solubility of the imaging agent and/or drug, increasing functionality and/or bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
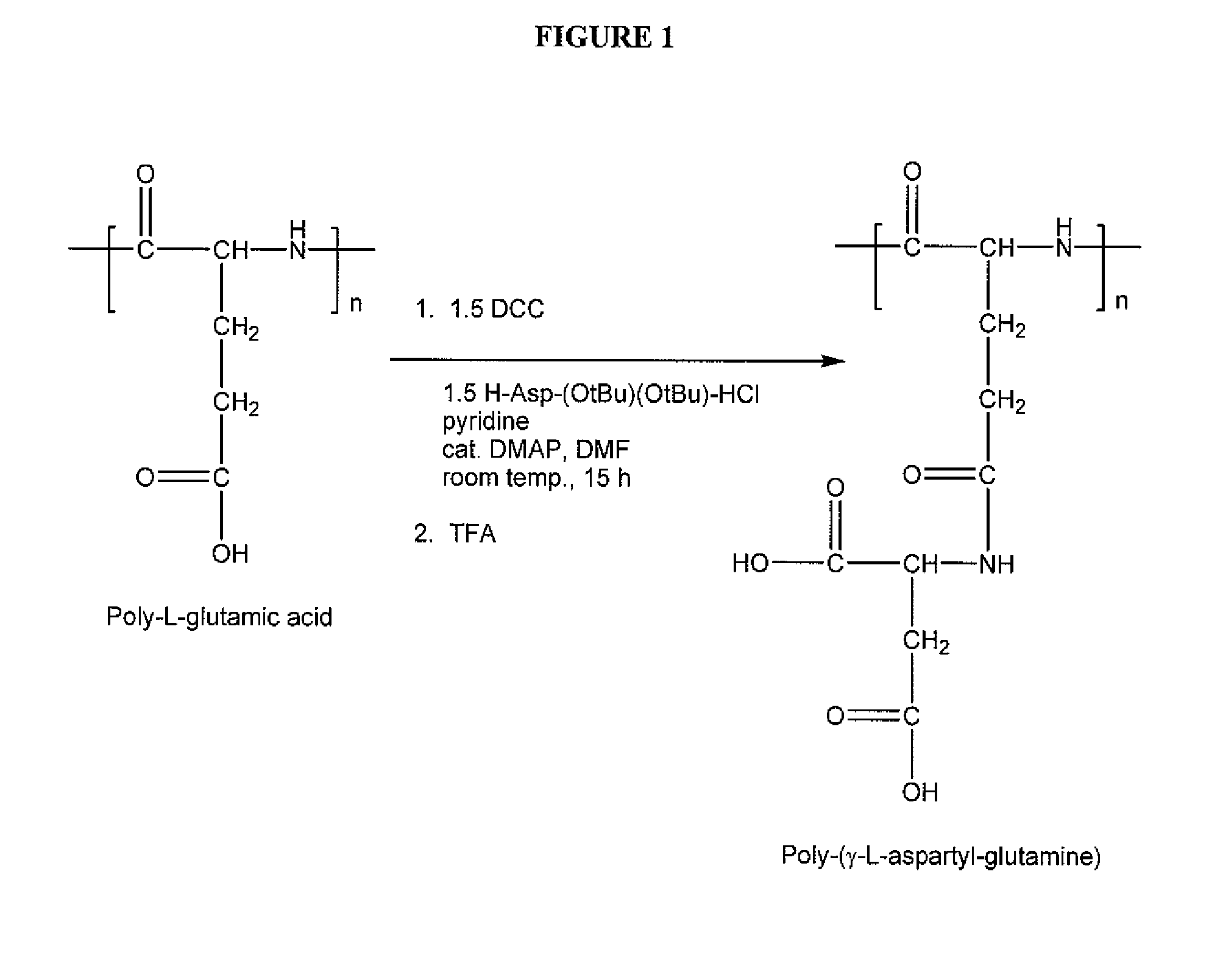
[0167] A poly-(γ-L-aspartyl-glutamine) was prepared according to the general scheme illustrated in FIG. 1 as follows:
[0168] Polyglutamic acid (0.75 g), average molecular weight of 49,000 daltons based on the Heleos system with MALS detector, was partially added into 100 mL dichloromethane (DCM). DCC (8.7 mL, 1 M in DCM) was added and stirred for 20 minutes. DCM was then removed by rotary evaporation, and the residue was dissolved with DMF (80 mL). H-asp(OtBu)-(OtBu) (2.44 g), pyridine (4 mL), and DMAP (0.1 g) were added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15-24 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered into an acidic water solution (500 mL, pH1H-NMR by the presence of the peak for the O-tBu group at 1.4 ppm.
[0169] The intermediate polymer was treated with 95% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in DCM for 5-8 hours. DCM was then added until a precipitate formed. The solvent was removed, and the residue was washed with more DCM. The residue was placed under vacuum to...
example 2
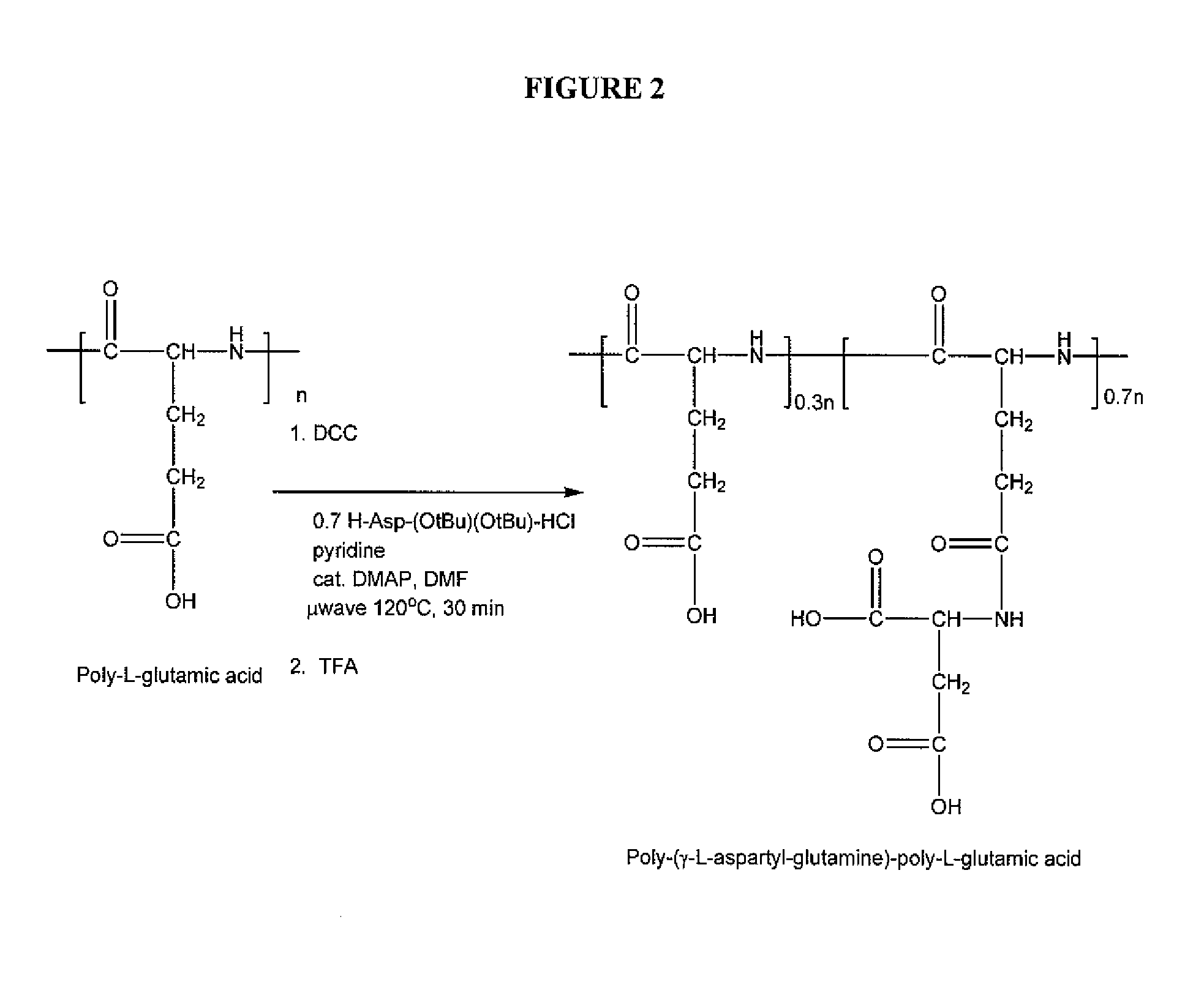
[0170] A poly-(γ-L-aspartyl-glutamine)-poly-L-glutamic acid was prepared according to the general scheme illustrated in FIG. 2 as follows:
[0171] Polyglutamic acid with an average molecular weight of 49,000 daltons based on the Heleos system with MALS detector (0.075 g) was partially dissolved in DMF (3 mL). DCC (130 mg), H-asp(OtBu)-(OtBu) (0.11 g), pyridine (200 μL), and DMAP (0.010 g) were then added. The reaction was carried out using a microwave method at 120° C. for 30 minutes. The reaction was then cooled to room temperature. Completion of reaction was followed by monitoring the complete disappearance of H-asp(OtBu)-(OtBu) using thin-layer-column (TLC, Rf in ethylacetate=0.4). Upon completion, the reaction mixture was filtered into an acidic water solution (150 mL, pH1H-NMR by the presence of a peak for the O-tBu group at 1.4 ppm.
[0172] The intermediate polymer was then treated with 95% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in DCM for 5 hours. DCM was added until a precipitate formed. ...
example 3
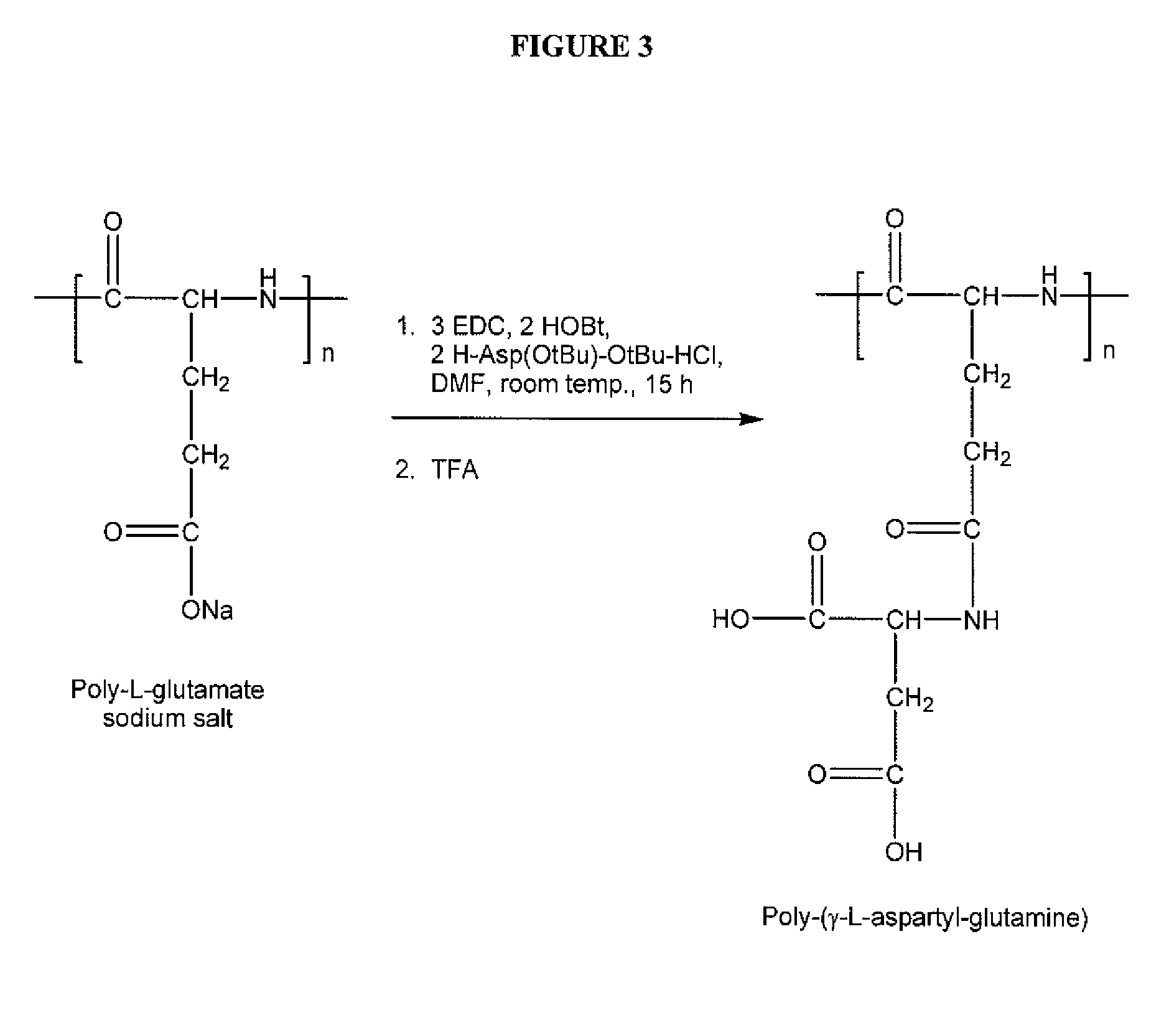
[0173] A poly-(γ-L-aspartyl-glutamine) was prepared according to the general scheme illustrated in FIG. 3 as follows:
[0174] Polyglutamate sodium salt (10.0 g) with an average molecular weight of 49,000 daltons based on the Heleos system with MALS detector, EDC (33.8 g), HOBt (15.9 g), and H-asp(OtBu)-(OtBu)-HCl (32.0 g) were mixed in DMF (700 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15-24 hours, and then poured into a water solution (3 L). A white precipitate formed, and was filtered and washed with water. The intermediate polymer was then freeze-dried. The structure of the intermediate polymer was confirmed via 1H-NMR by the presence of a peak for the O-tBu group at 1.4 ppm.
[0175] The intermediate polymer was treated with TFA (200 mL) for 5 hours. Then, the TFA was partially removed by rotary evaporation. Water was added to the residue and the residue was dialyzed using semi-membrane cellulose (molecular weight cut-off 10,000 daltons) in reverse-osmosis water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com