Polymer based radionuclide containing particulate material
a radionuclide and polymer technology, applied in the field of polymer and radionuclide, can solve the problems of slow and continuous radiation delivery, excessive radiation in the focal area, and uneven distribution of radiation in the target organ
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Yttrium (90Y) labelled microspheres are made in the form of a sterile, pyrogen free suspension of resin beads labelled with yttrium (90Y) phosphate. The resin beads consist of sulphuric acid groups attached to a styrene divinylbenzene copolymer lattice. Yttrium oxide is irradiated to produce yttrium-90 from the nuclear reaction Y-89 (n, γ) Y-90. Yttrium-90 has a half life of 64 hours. The yttrium (90Y) oxide is then dissolved in 0.1M sulphuric acid with gentle heating and stirring to form a clear, colourless solution of yttrium (90Y) sulphate.
[0040] Symmetrical microspheres of ion exchange resin (Aminex 50W-X4 cation exchange resin; supplied by Bio-Rad Cat #1474313′) with a diameter of approximately 30 to 35 microns are added to water (Water for Injections BP) to form a slurry that is then transferred into a reaction vessel. Yttrium (90Y) sulphate solution is added to the reaction vessel and the mixture stirred at a speed sufficient to ensure homogeneity to absorb the yttriu...
example 2
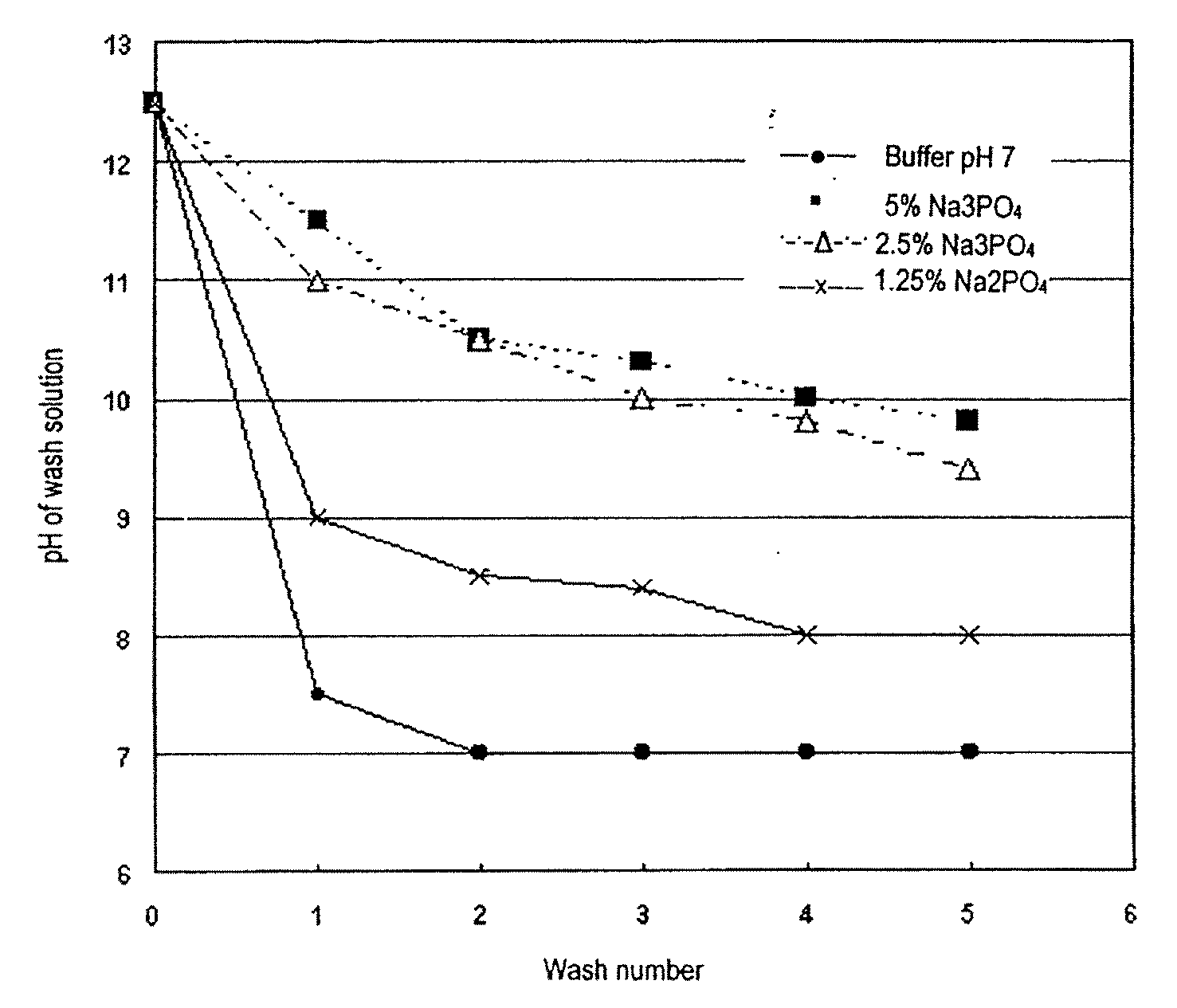
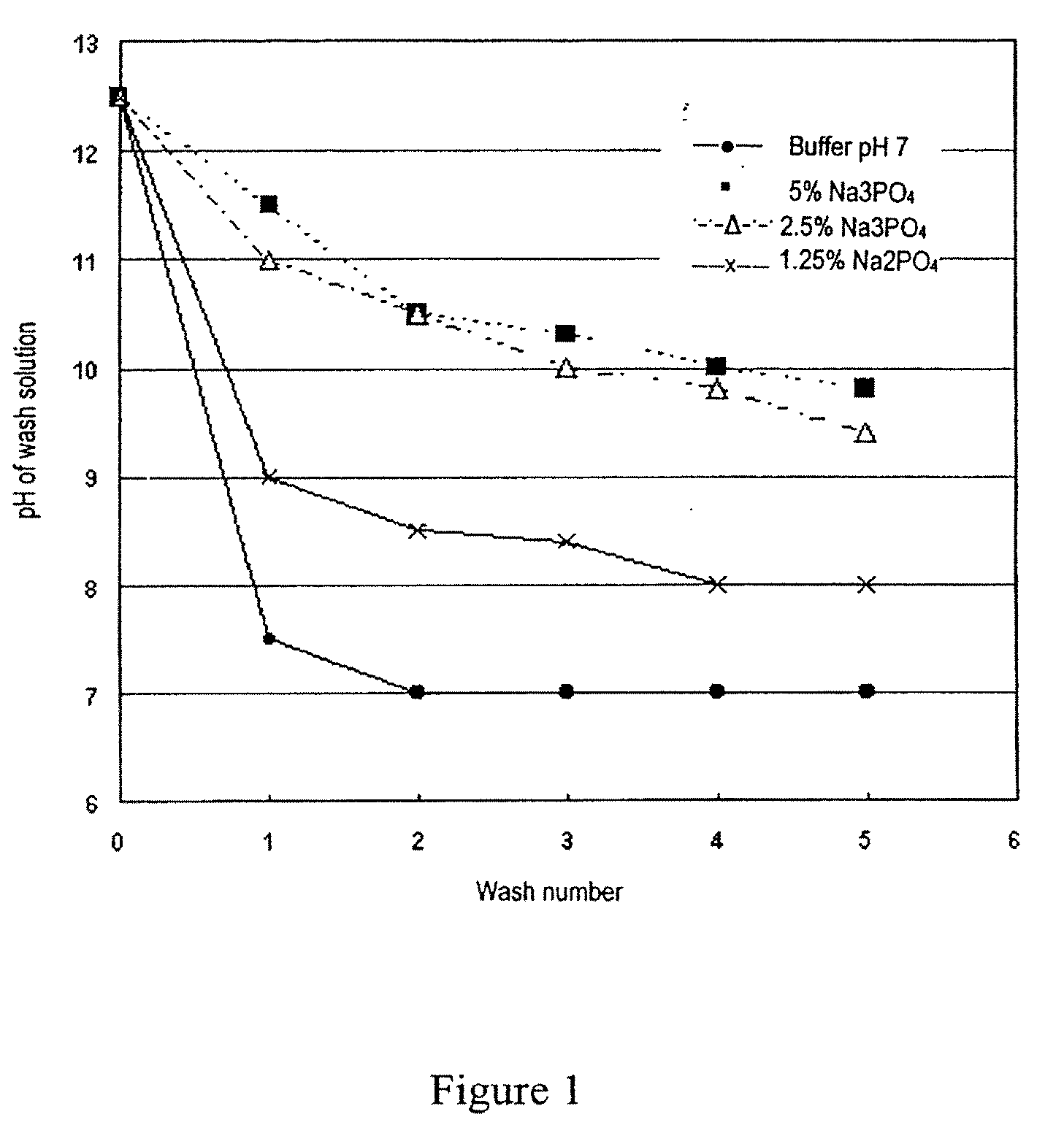
[0044] The effect of phosphate concentration in the precipitation solution, and the effects of washing with phosphate buffer on the pH of a microsphere suspension are shown in the attached FIG. 1 which sets out the results of a number of experiments.
example 3
[0045] The technique of Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) has been described above. It involves either a laparotomy to expose the hepatic arterial circulation or the insertion of a catheter into the hepatic artery via the femoral, brachial or other suitable artery. This may be followed by the infusion of Angiotensin-2 into the hepatic artery to redirect arterial blood to flow into the metastatic tumour component of the liver and away from the normal parenchyma. This is followed by embolisation of resin based yttrium-90 containing microspheres (produced in accordance with Example 1) into the arterial circulation so that they become lodged in the microcirculation of the tumour. Repeated injections of microspheres are made until the desired radiation level in the normal liver parenchyma is reached. By way of example, an amount of yttrium-90 activity that will result in an inferred radiation dose to the normal liver of approximately 80 Gy may be delivered. Because the radiatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com