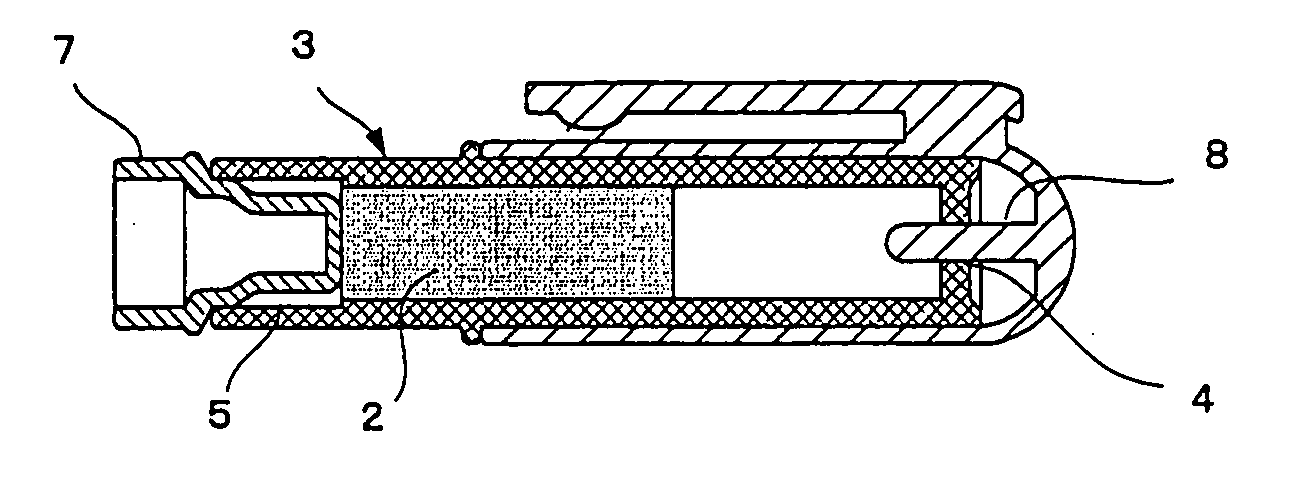
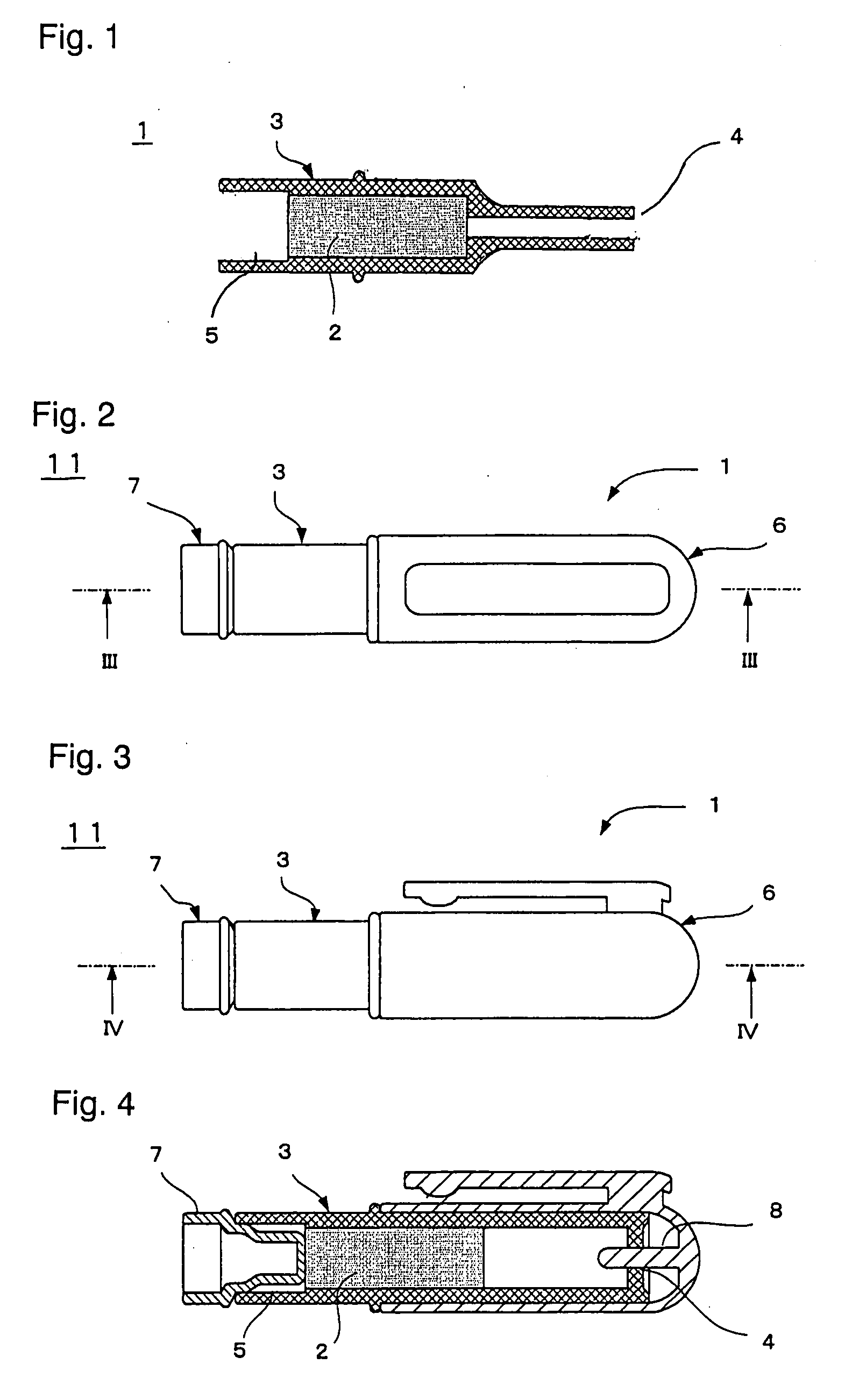
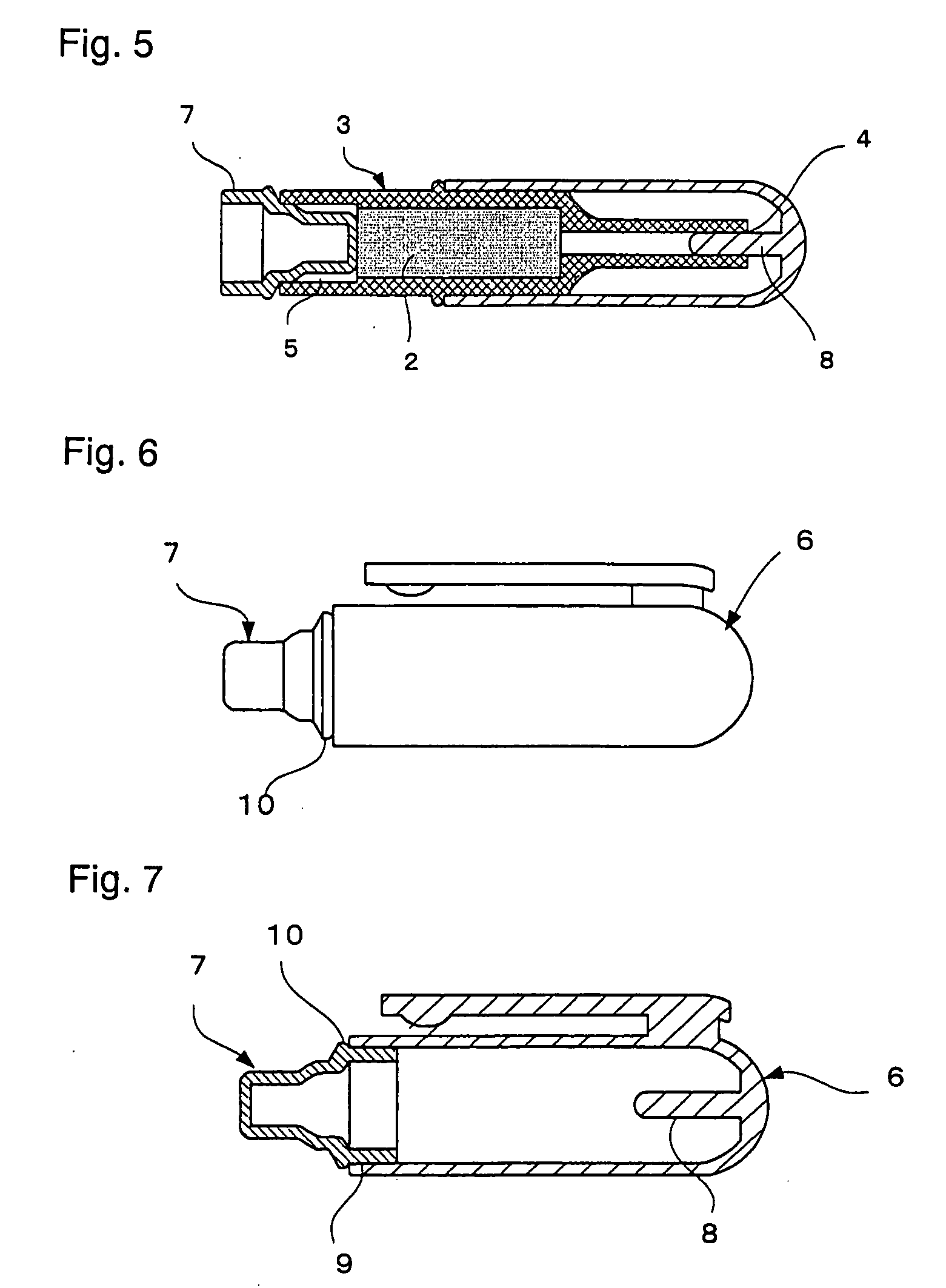
Nicotine-Reducing Agent And Nicotine Reducing Method
a nicotine-reducing agent and nicotine-reducing technology, applied in the direction of tobacco, tobacco treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the resistance of inhalation, difficulty in smoking itself, and water containing harmful nicotine and tar entering the mouth, so as to improve the viscosity and viscosity stability, reduce sugar, and reduce the effect of nicotine and tar reduction percentag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental example 1
(1) Preparation of Aqueous Liquid Composition
[0128]Aqueous liquid compositions (Examples 1-15) were prepared according to the formulations shown in Table 2. More specifically, one or more of the polysaccharides shown in Table 1 (tamarind seed gum, locust bean gum, xanthan gum, tara gum, guar gum, pullulan, psyllium seed gum, HM pectin, LM pectin, λ-carageenan, carboxymethylcellulose) together with trehalose were added to ion-exchanged water, and the mixture was dissolved by stirring while heating at 80° C. for 10 minutes, however methylcellulose (Example 14) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (Example 15) were added together with trehalose to ion-exchanged water, and the mixture was dissolved by stirring at 60° C. for 10 minutes and further stirring at 10° C. for 10 minutes.
[0129]To each solution were added an aqueous solution of sodium benzoate, an aqueous solution of citric acid, an aqueous solution of trisodium citrate, and an aqueous solution of colorant (red No. 2, red No. 40), t...
experimental example 2
(1) Preparation of an Aqueous Liquid Composition
[0134]Aqueous liquid compositions (Examples 16-25) were prepared according to the formulations shown in Table 3. More specifically, tamarind seed gum, xanthan gum and one of the saccharides shown in Table 3 (trehalose, sucrose, glucose, fructose, maltose, sorbitol, maltitol, erythritol, xylitol, dextrin) were added to ion-exchanged water, and each mixture was dissolved by stirring while heating at 80° C. for 10 minutes. To each solution were added an aqueous solution of sodium benzoate, an aqueous solution of citric acid, an aqueous solution of trisodium citrate, and an aqueous solution of colorant (red No. 2, red No. 40), these solutions having been dissolved in ion-exchanged water beforehand, and then mixed. The total amount of each mixture was adjusted with ion-exchanged water to be 100% by weight, preparing aqueous liquid compositions (Examples 16-25).
(2) Property Evaluation of Aqueous Liquid Compositions
[0135]In the same manner as...
experimental example 3
(1) Preparation of an Aqueous Liquid Composition
[0139]Aqueous liquid compositions (Examples 26-29) were prepared by the following procedure according to the formulations shown in Table 4. The viscosity of each aqueous liquid composition obtained above was measured using a B-type rotational viscometer (Rotor No. 3) at 20° C. at 60 rpm for 1 minute.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com