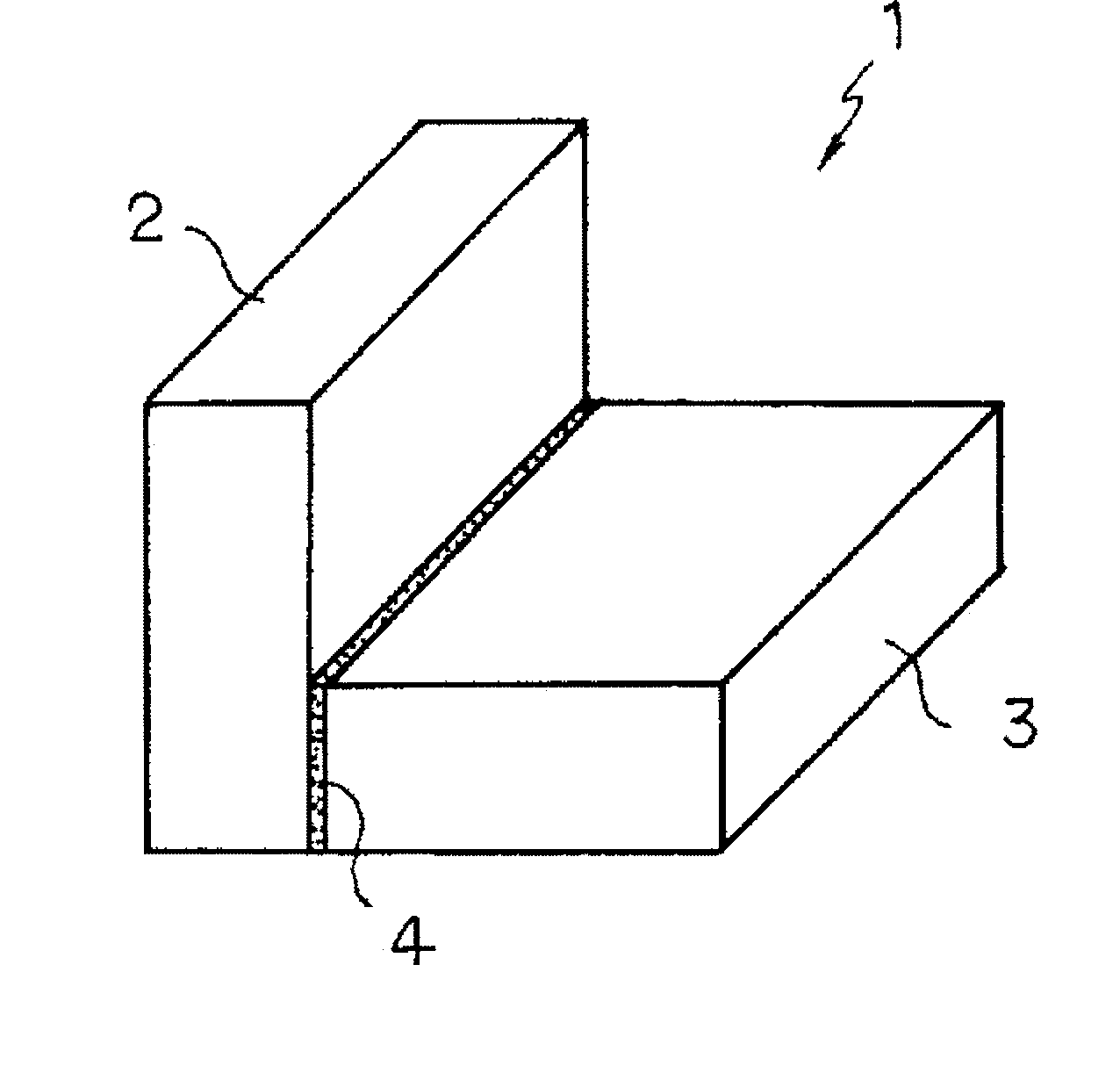
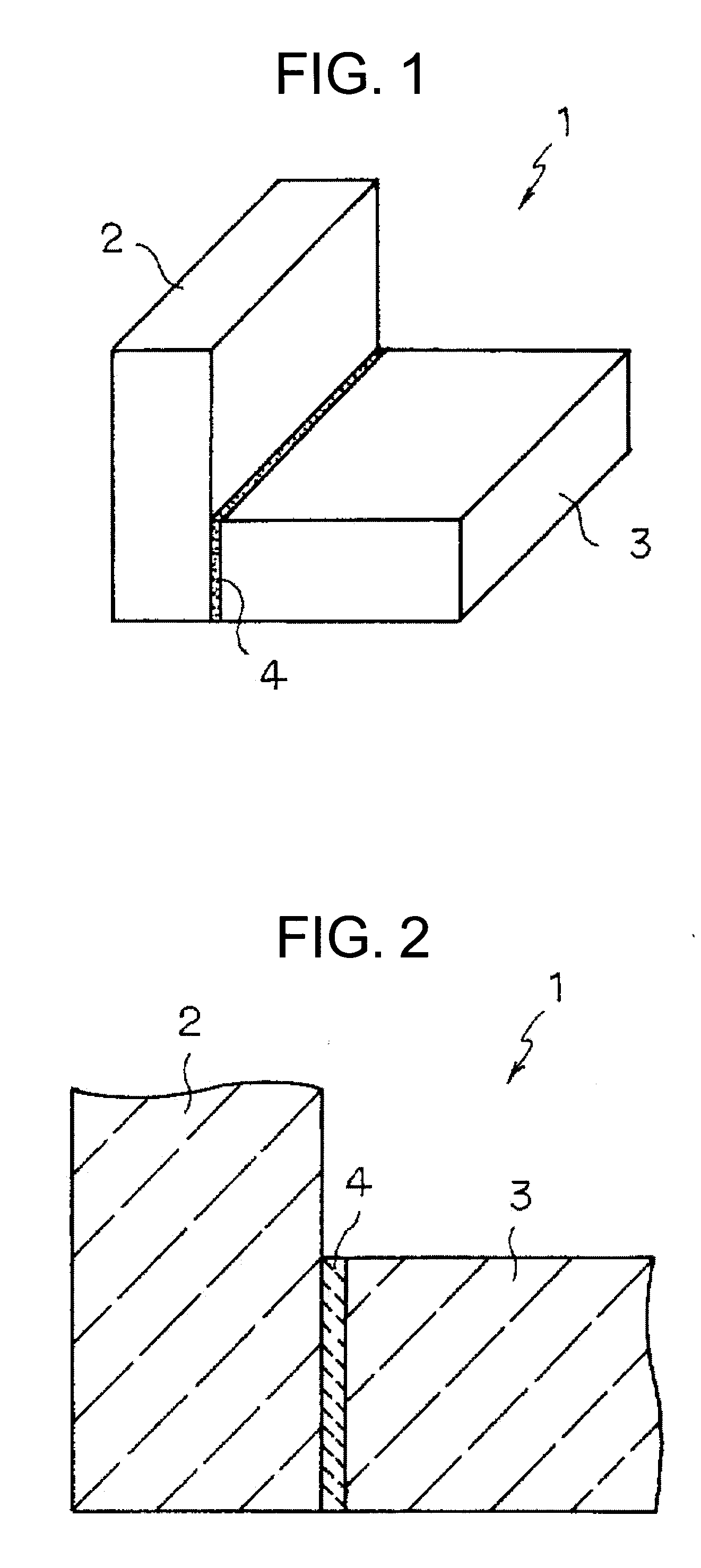
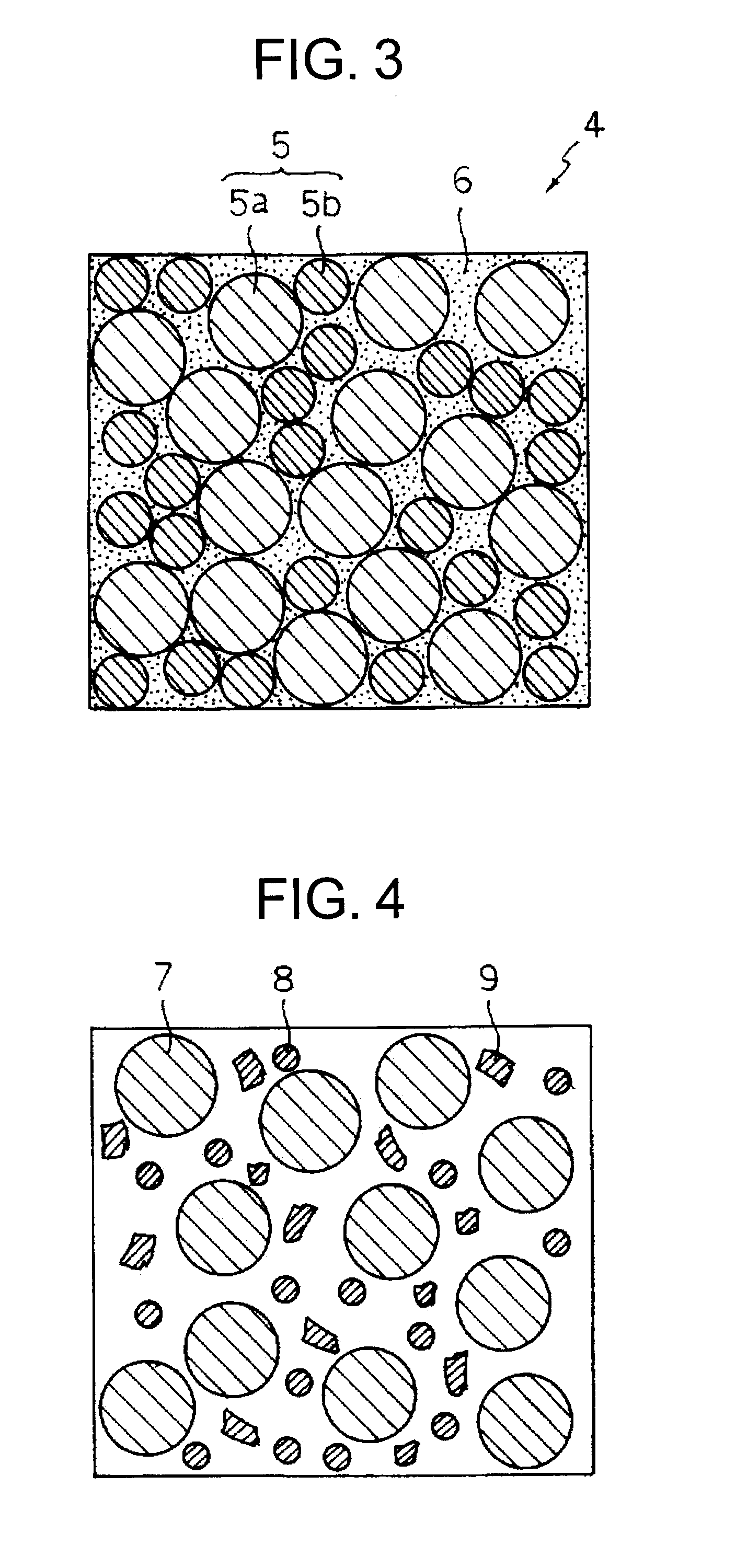
Ceramics composite member and method of producing the same
a composite member and ceramic technology, applied in the field of ceramic composite members, can solve the problems of limited heat resistance and strength of parts, limited application shape of components, limited sintering of silicon carbide, etc., and achieve the effects of good reproducibility, enhanced strength, and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069]Silicon carbide powder having an average particle diameter of 0.5 μm and carbon powder (carbon black) having an average particle diameter of 0.01 μm were mixed at a mass ratio of 10:3 (=SiC:C). The mixture powder was mixed with an appropriate amount of an organic binder, and the mixture was dispersed into a solvent to prepare a slurry. The slurry was charged into a forming die under a pressure of 1 MPa by a pressure casting machine. Thus, two plate-like shaped bodies having a prescribed shaped body density were produced.
[0070]Then, the two plate-like shaped bodies were air dried and adhered with an adhesive. As the adhesive, a mixture of a phenol resin with silicon carbide powder having an average particle diameter of 0.1 μm and carbon powder (carbon black) having an average particle diameter of 0.08 μm was used. The ratio between the silicon carbide powder and the carbon component derived from the carbon powder and the phenol resin was determined to be SiC:C=25:75. The adhere...
example 2
[0072]Two shaped bodies produced in the same manner as in Example 1 described above were heated and kept at a temperature of 600° C. in an inert gas atmosphere to remove (degrease) the organic binder. The degreased shaped bodies were heated to a temperature of 1400° C. or more under reduced pressure or in an inert gas atmosphere, and the shaped bodies kept in the heated state were impregnated with melted silicon. In the melted silicon impregnation step, the shaped bodies were subjected to reaction-sintering to obtain two Si—SiC composite sintered bodies.
[0073]Then, the adhered surfaces of the two SiC radical reaction sintered bodies were subjected to a blast treatment and adhered with an adhesive. As the adhesive, a mixture of a phenol resin with silicon carbide powder having an average particle diameter of 1 μm and carbon powder (carbon black) having an average particle diameter of 0.8 μm was used. The ratio between the silicon carbide powder and the carbon component derived from t...
examples 3 to 10
[0075]As to-be-bonded members, an Si—SiC composite sintered body, shaped bodies for Si—SiC composite body, an ordinary SiC sintered body, an Si3N4 sintered body, a ZrO2 sintered body and an SiC-continuous fiber composite material were prepared. They were coupled according to the combinations shown in Table 1 to produce ceramics composite members. The coupling step was performed in the same manner as in Examples 1 and 2. The adhesives used for coupling had the compositions as shown in Table 1. Table 1 also shows the properties of the joint portions. The joint portions of the ceramics composite members had the texture in which the free Si phase is continuously provided in the network form in the interstices of the SiC particles, and also had the single layer structure. The individual ceramics composite members were subjected to the characteristic evaluation to be described later.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com