Recombinant beta-galactosidase derived from Streptococcus pneumaniae
a technology of streptococcus pneumaniae and beta-galactosidase, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, enzymology, etc., can solve the problems of inability to commercialize drugs able to inhibit the metastasis of cancer cells, problems that may still exist, and the effect of preventing cancer cell growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Amplification of bgaC Gene from Streptococcus pneumoniae
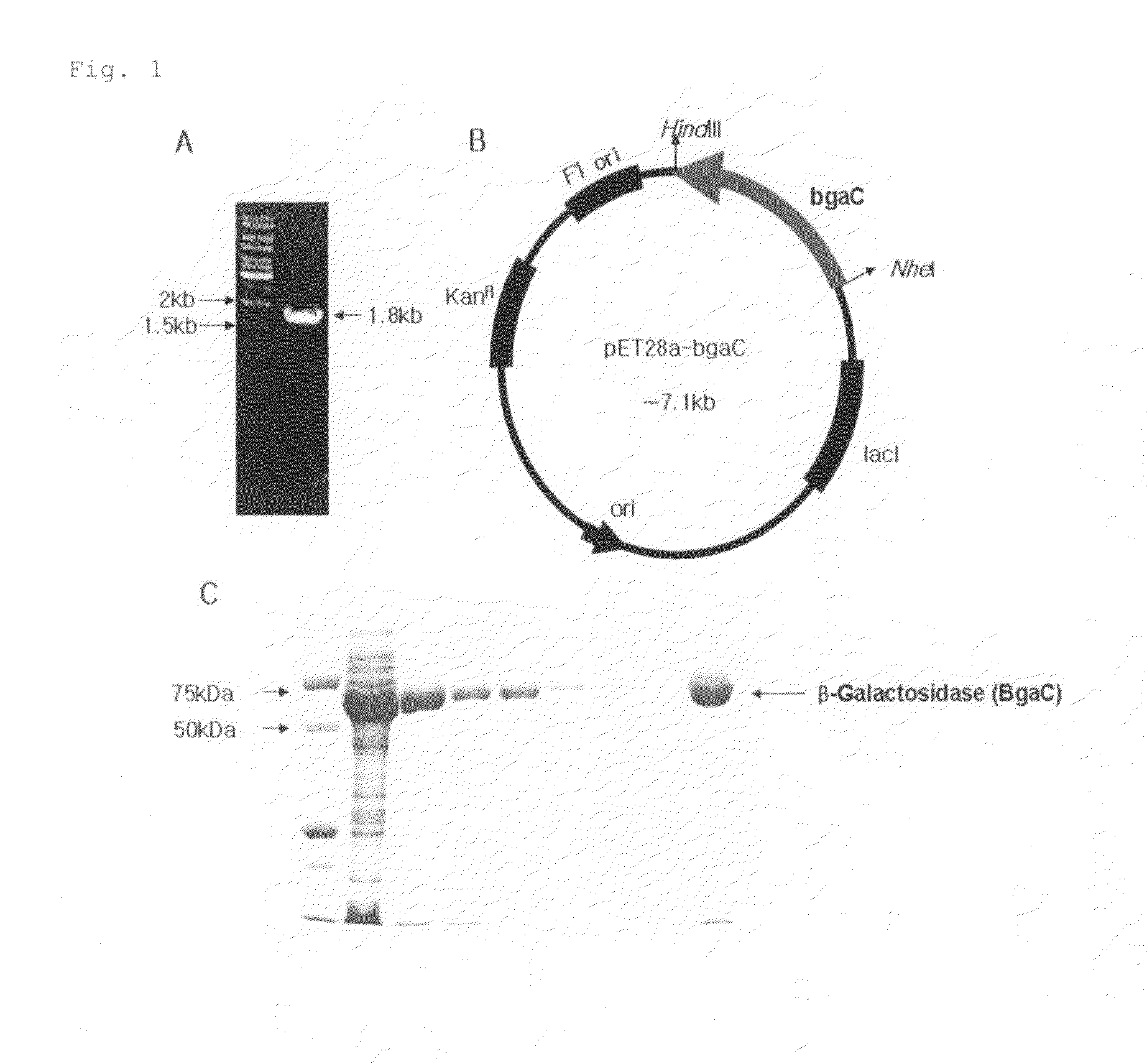
[0054]A Streptococcus pneumoniae chromosome was isolated from Streptococcus pneumoniae (ATCC BBA-255D) using a known phenol extraction (Ushiro et al., J Dent Res 70: 1422-1426, 1991). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed using the extracted chromosomal DNA as a template, and a pair of primer, bgaC-N(cgctagCATGACACGATTTGAGATACGAG) and bgaC-C(ggaagcttTCATAAGTTTTCCCCCTTTATATG), at which NheI and HindIII enzyme restriction sites were artificially inserted, so as to prepare a DNA fragment containing bgaC with a size of 1.8 kb (see FIG. 1A).
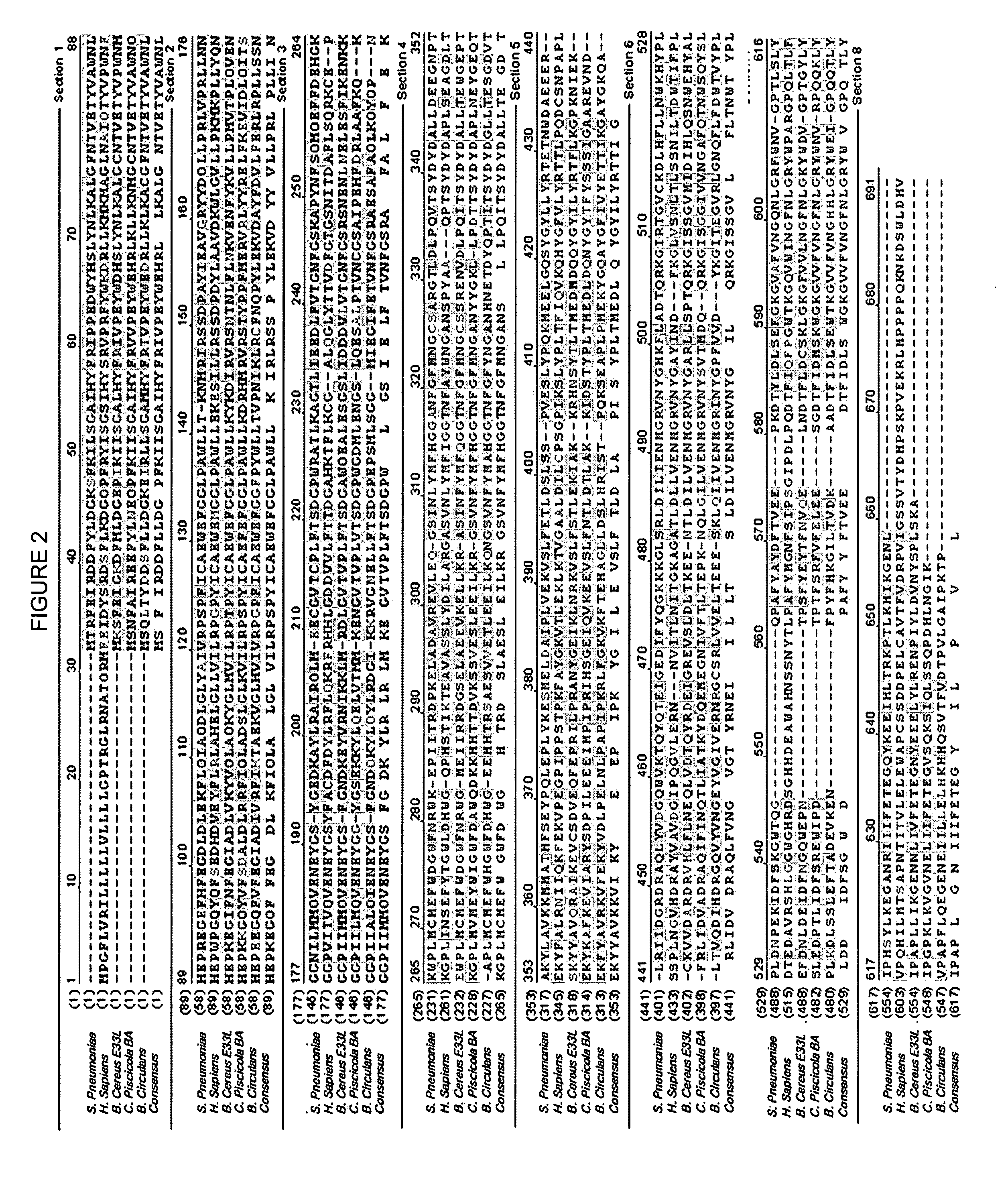
[0055]The base sequence of the prepared DNA fragment was translated. As a result, it was found that the Streptococcus pneumoniae bgaC gene encodes an intracellular protein consisting of 595 amino acids. From the result of translating into the amino acid sequence, it was found that the Streptococcus pneumoniae BgaC protein has 29.8%, 54.3%, 65.4%, and 46.7% homologies and 40.8%, 58.1%, 41...
example 2
Large-scale Expression, Isolation, and Purification of BgaC Protein
[0056]A recombinant vector pET28a (Novagen) was cleaved with NheI and HindIII restriction enzymes, and the PCR product, which is treated with the same enzymes and amplified in Example 1, was introduced into the vector (FIG. 1B). The prepared recombinant vector was transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) strain. The transformed E. coli was precultured in 5 ml of LB liquid medium (1% Bacto Tripton, 1% Sodium chloride, 0.5% Yeast extract) at 37° C. for 16 hours. The precultured medium was inoculated into fresh LB medium at a dilution of 1:100, and cultured at 37° C. When the absorbance of the medium was 0.4 to 0.6 at 600 nm, IPTG (isopropyl thiogalactoside) was added thereto to be a final concentration of 1 mM. Thus, the BgaC protein expression was induced and the medium was cultured at 18° C. for 24 hours. The cultured E. coli cells were centrifuged, recovered, and then disrupted by sonication. The disrupted cells were cen...
example 3
Galactosidase Activity Test for BgaC Protein
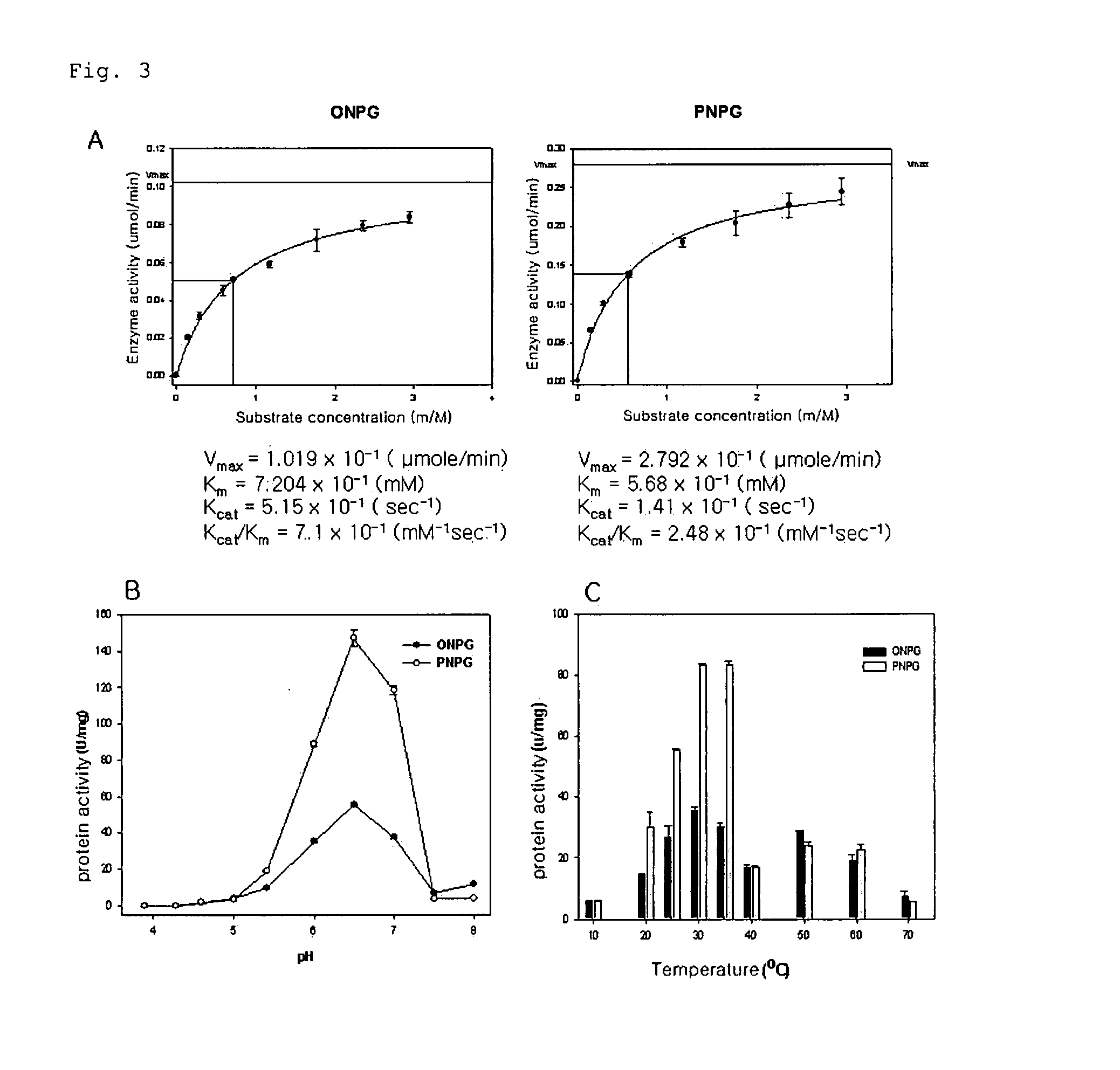
[0057]The basic activity of the BgaC protein was confirmed using ONPG (o-nitrophenyl-D-galactopyranoside) and PNPG (p-nitrophenyl-D-galactopyranoside) as a substrate. 2.2 mg of BgaC protein was mixed with a reaction mixture [90 mM sodium phosphate (NaPO4) (pH 6.5), 10 mM magnesium chloride (MgCl2), 45 mM beta-mercaptoethanol, 0.3 mM ONPG or PNPG] to be 300 μl, and reacted at 30° C. for 30 minutes. Then, its absorbance was measured at 420 nm to determine the amount of ONP (o-nitrophenol) or PNP (p-nitrophenol) produced. The activity of BgaC protein (Unit) was defined as ability to convert 1 nmole of ONPG or PNPG into ONP or PNP at 30° C. for 1 minute. The maximum reaction rate of the enzyme is 2.6 times higher in the case of using PNPG than in the case of using ONPG as the substrate. Further, the substrate affinity of the enzyme is 3.5 times stronger for PNPG than for ONPG (see FIG. 3A). In accordance with the Example, it was found that the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com