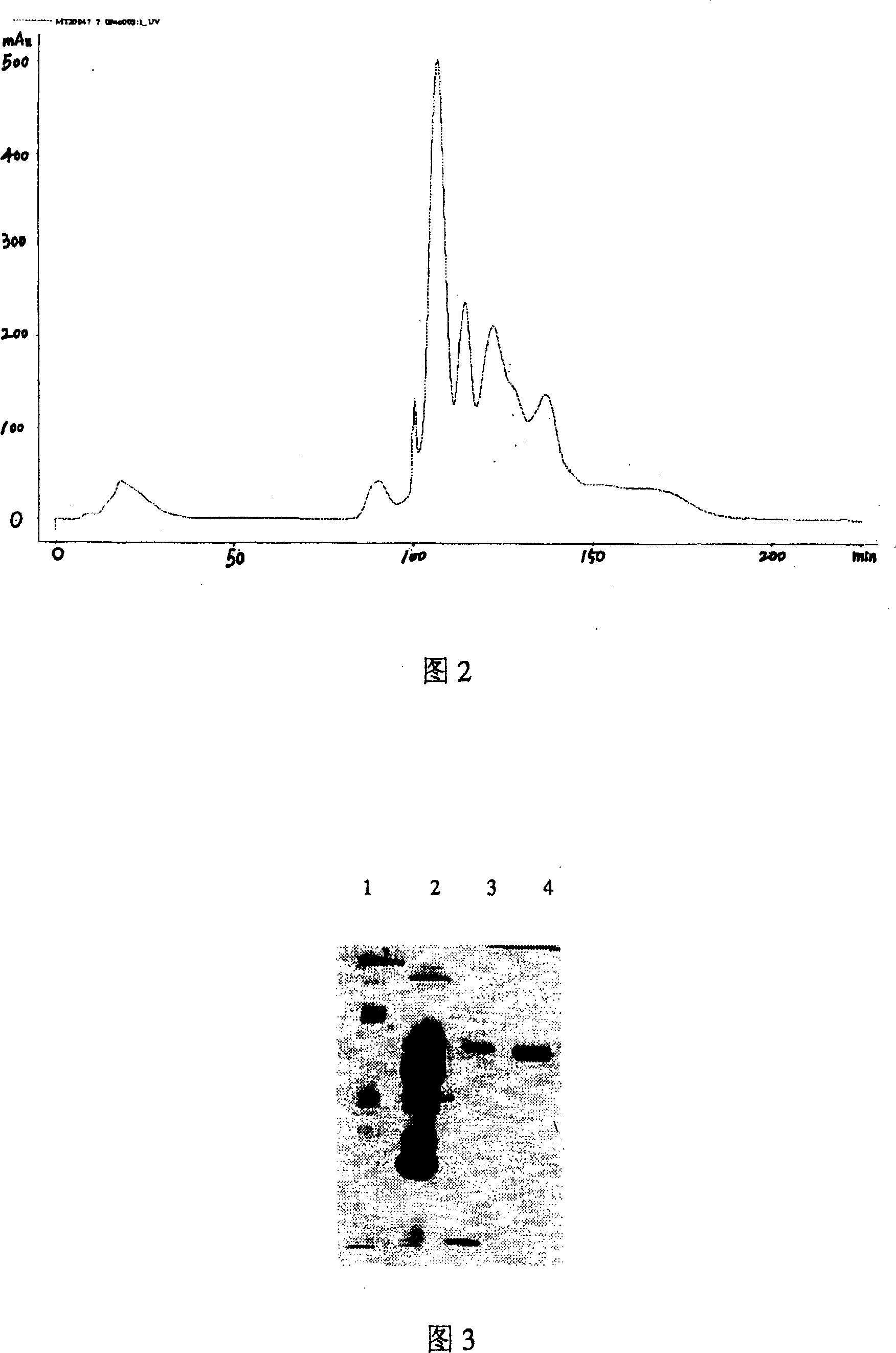
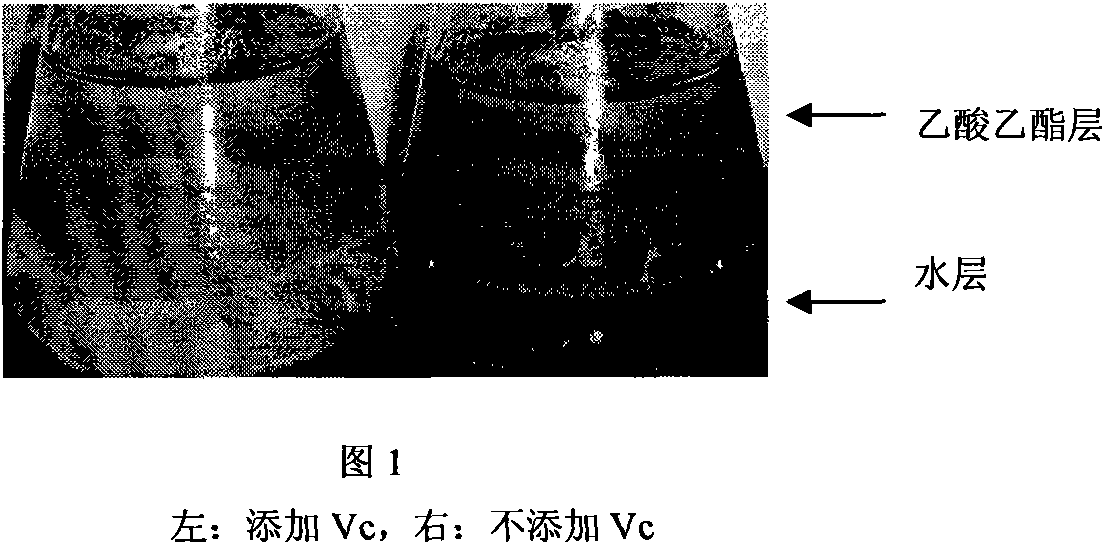
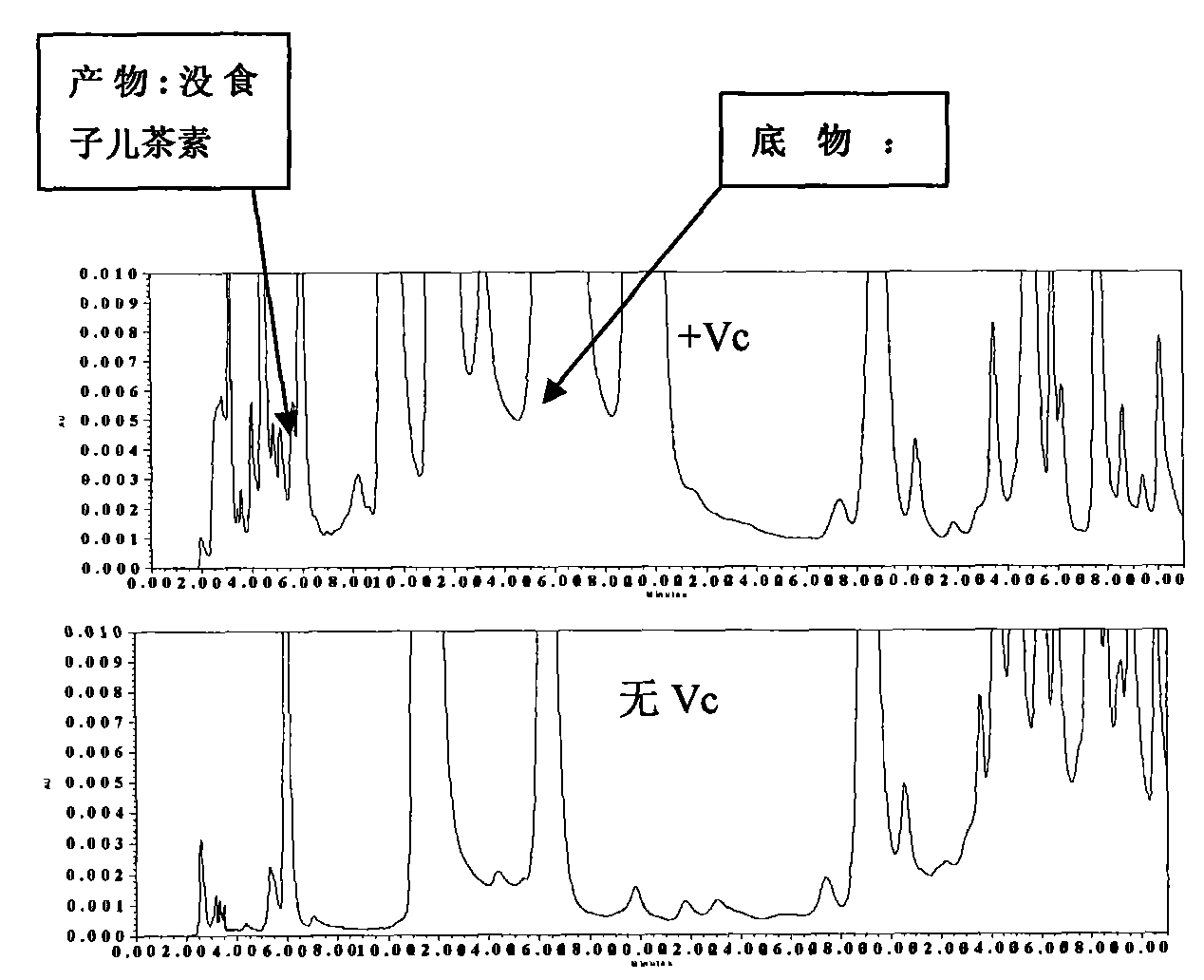
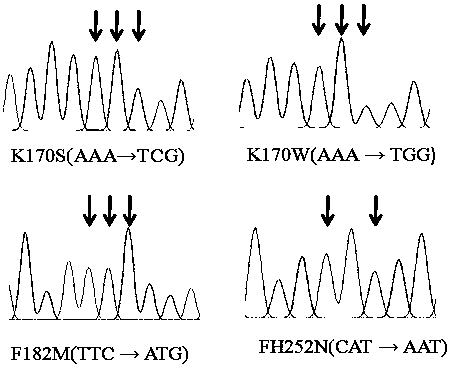
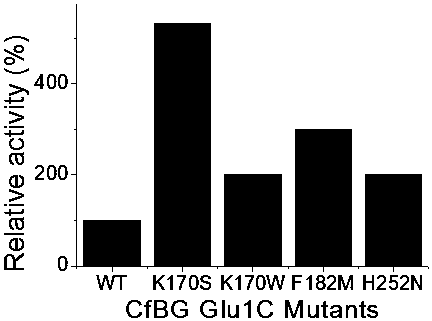
Patents
Literature
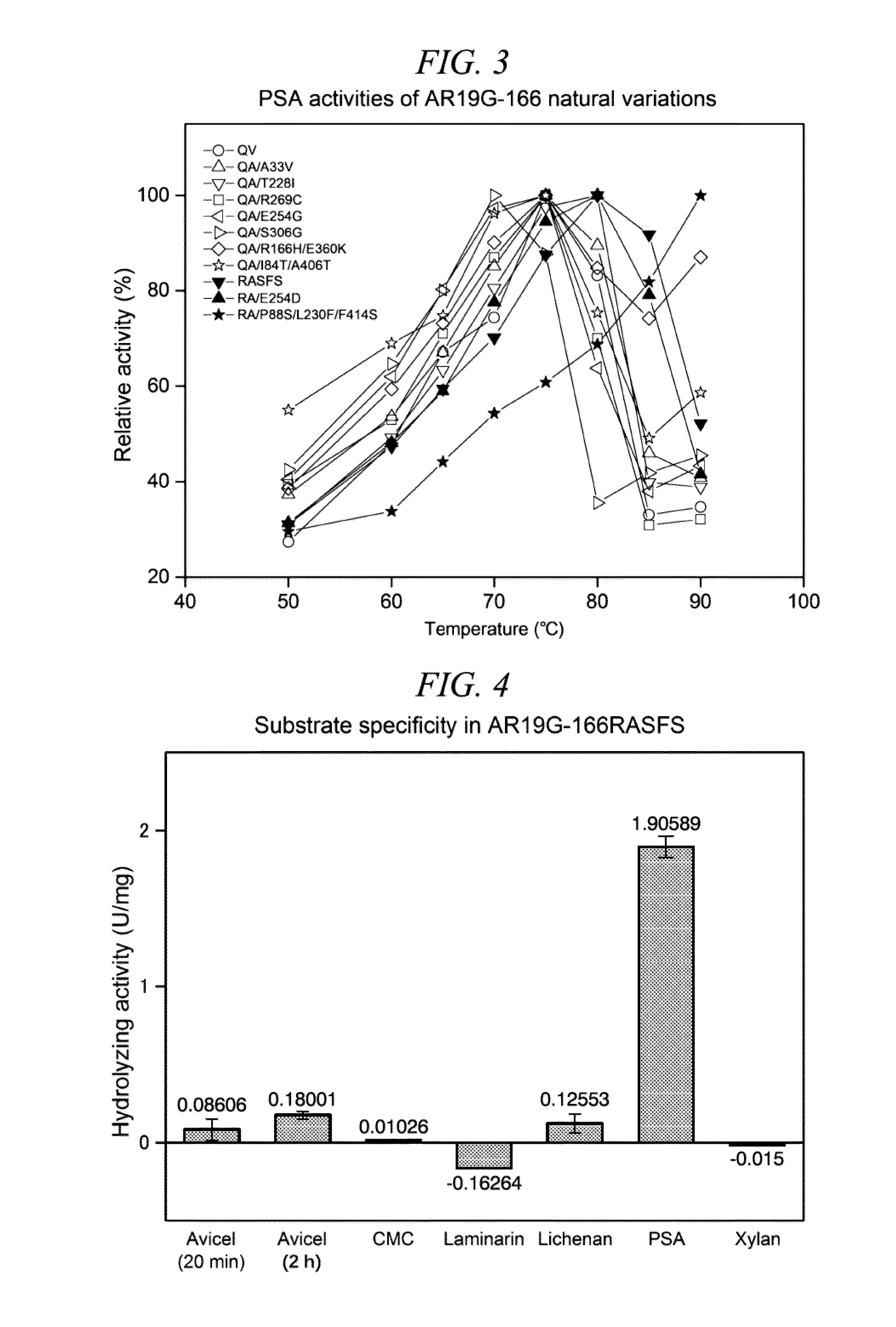
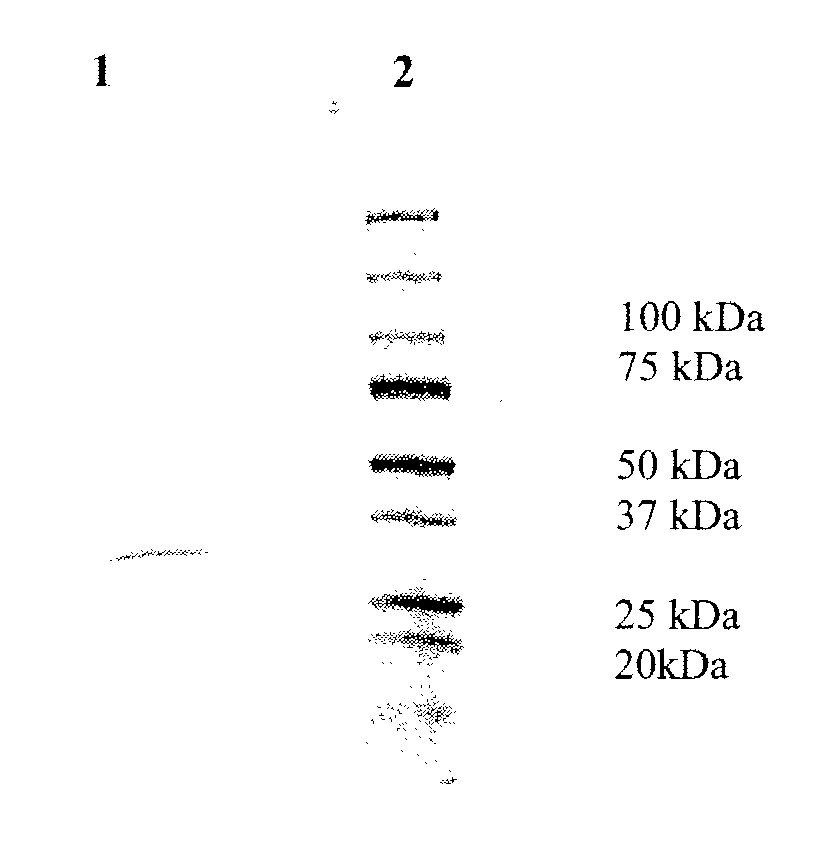
30 results about "Levanase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the random hydrolysis of 2,6-beta-D-fructofuranosidic linkages in 2,6-beta-D-fructans (levans) containing more than 3 fructose units. [EC:3.2.1.65, GOC:mlg]
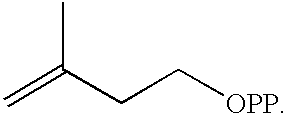
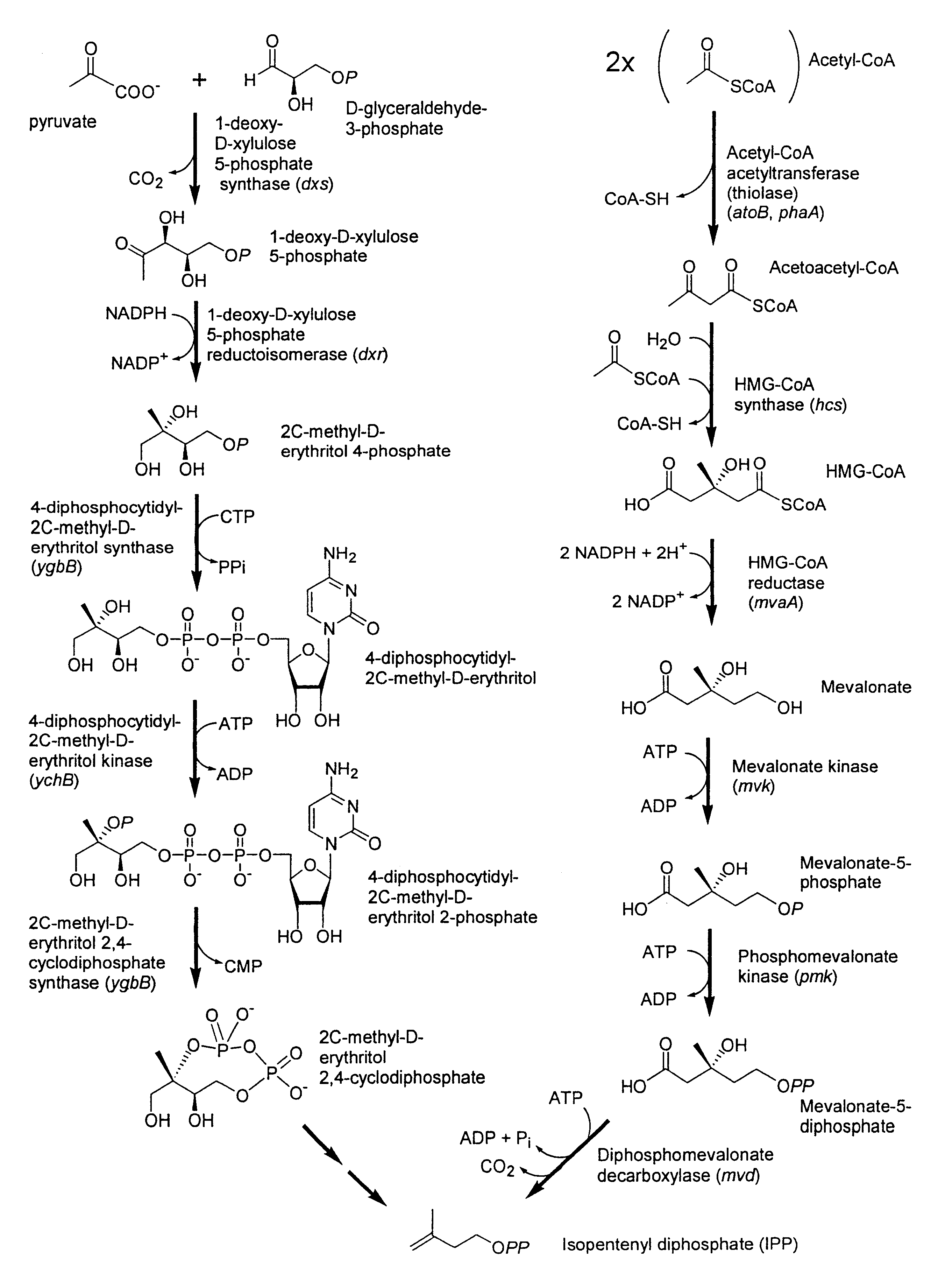
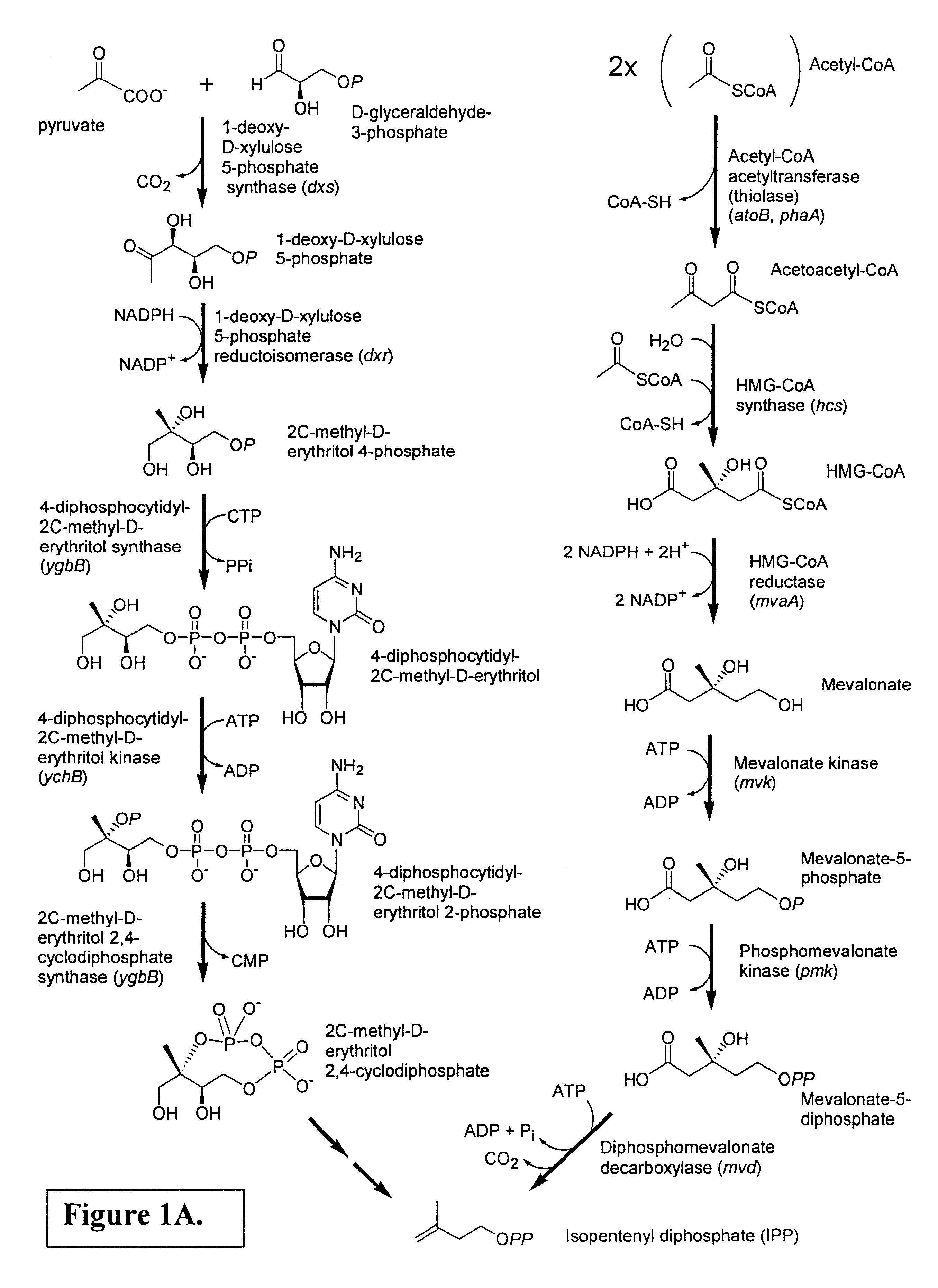
Isoprenoid production
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD +1
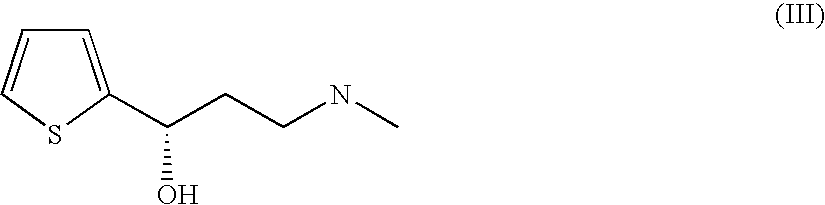
L-carnitin dehydrogenases, their derivatives and method for producing substituted (s) alkanols
The present invention relates to proteins having an enzymatic activity of reducing substituted alkanones such as 3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-propan-1-one. The invention furthermore relates to nucleic acids coding for said proteins, nucleic acid constructs, vectors, genetically modified microorganisms and to methods for preparing substituted (S)-alkanols, such as, for example, (S)-3-methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-(S)-propanol.
Owner:BASF AG
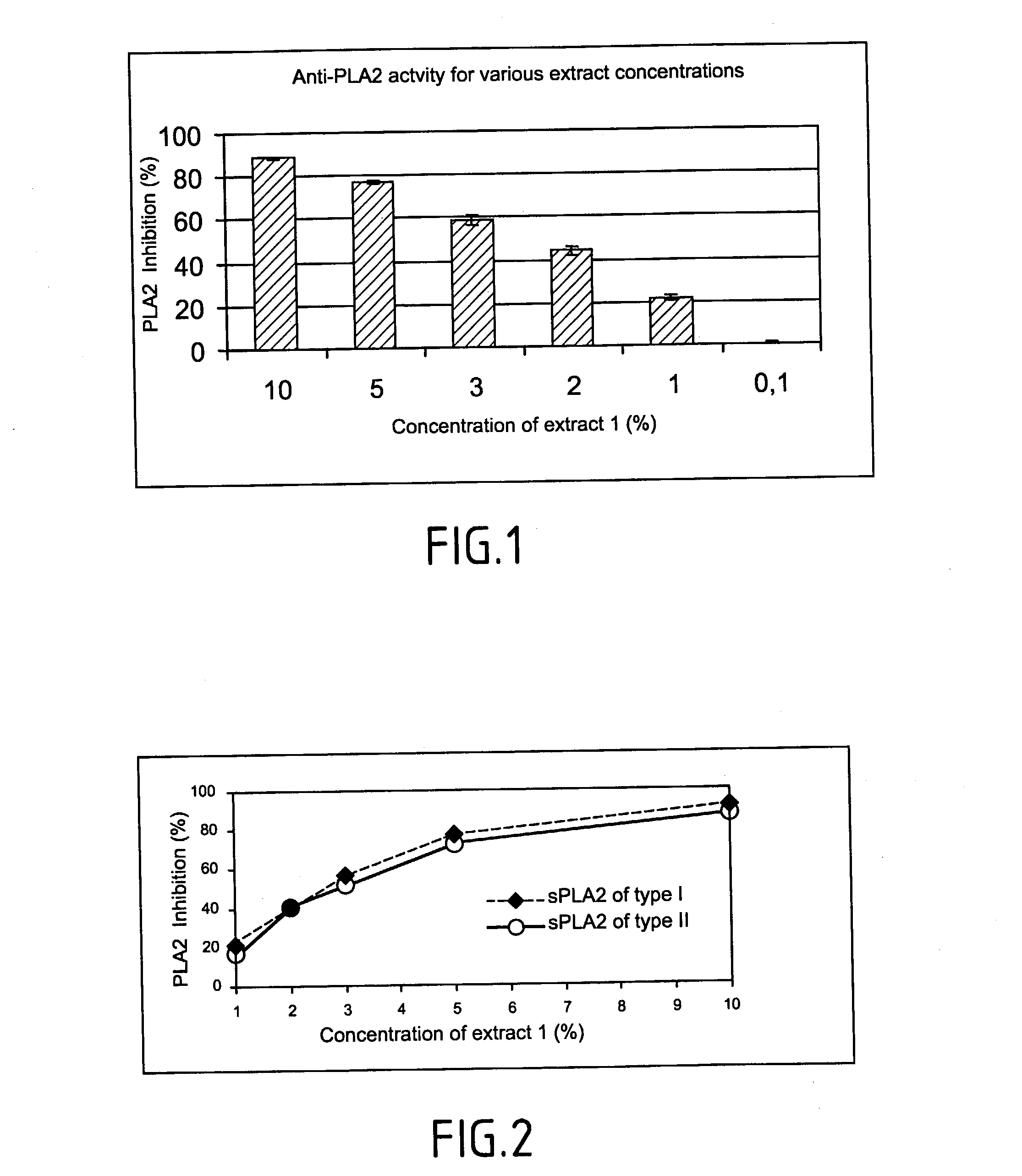
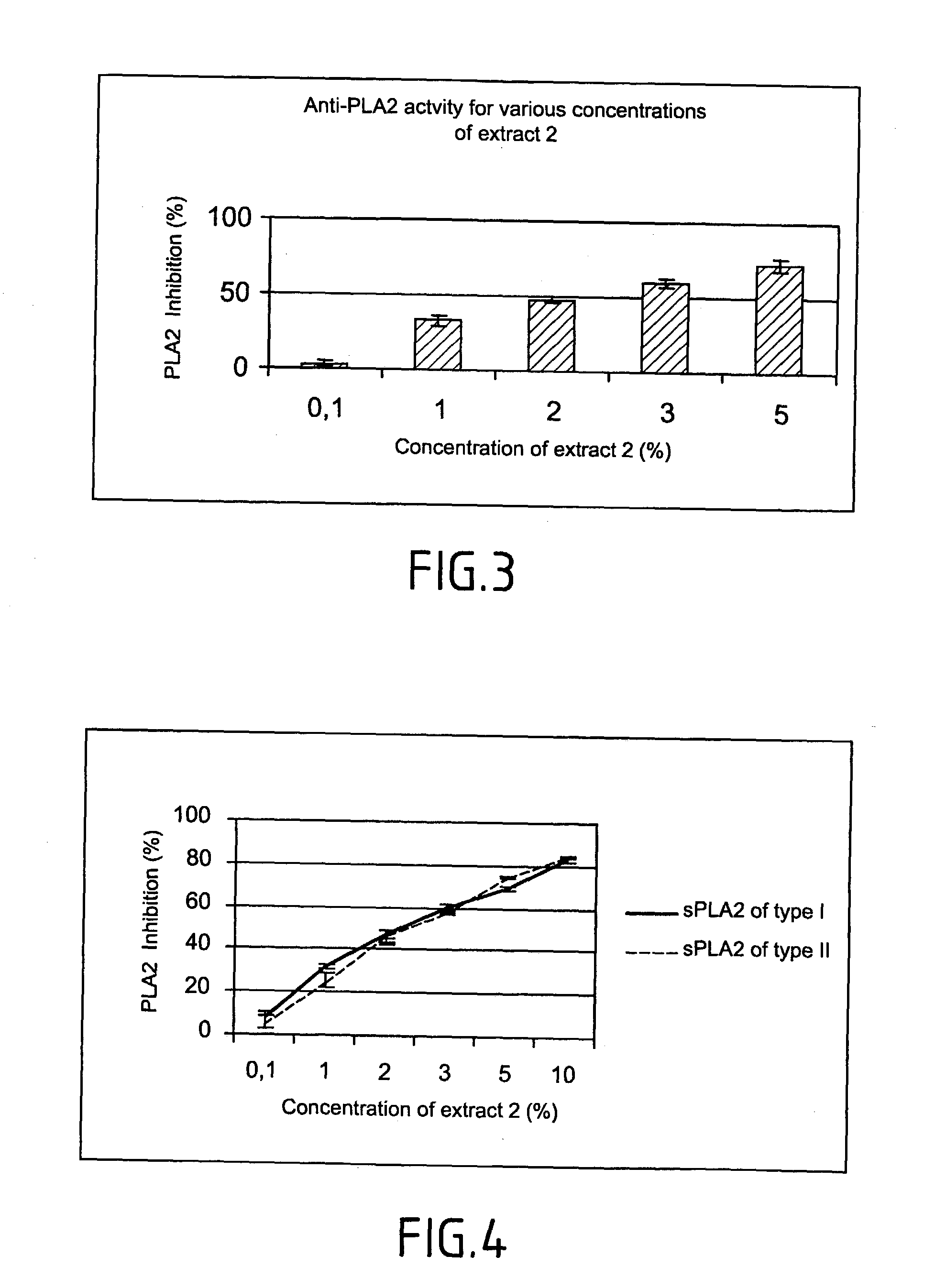
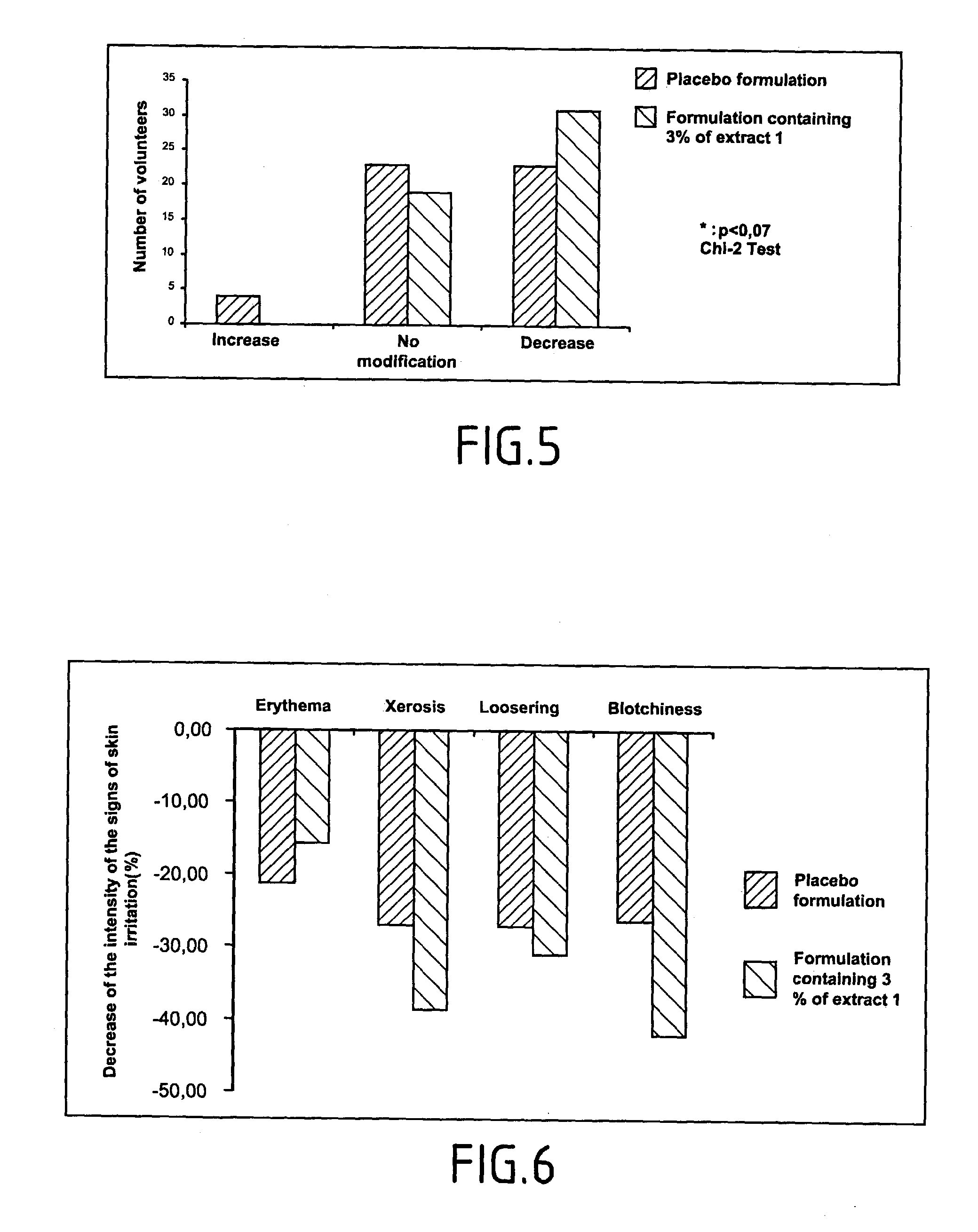
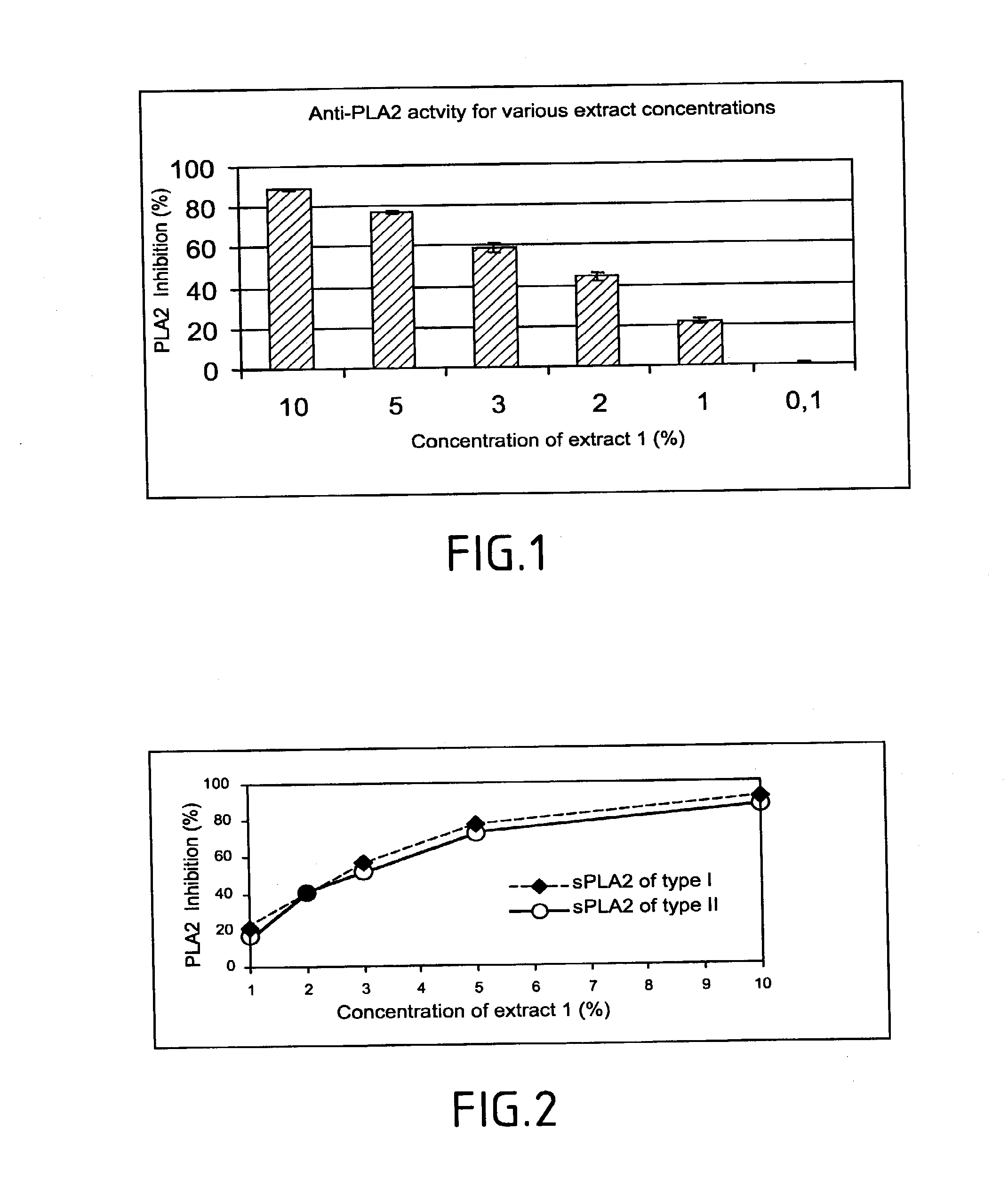
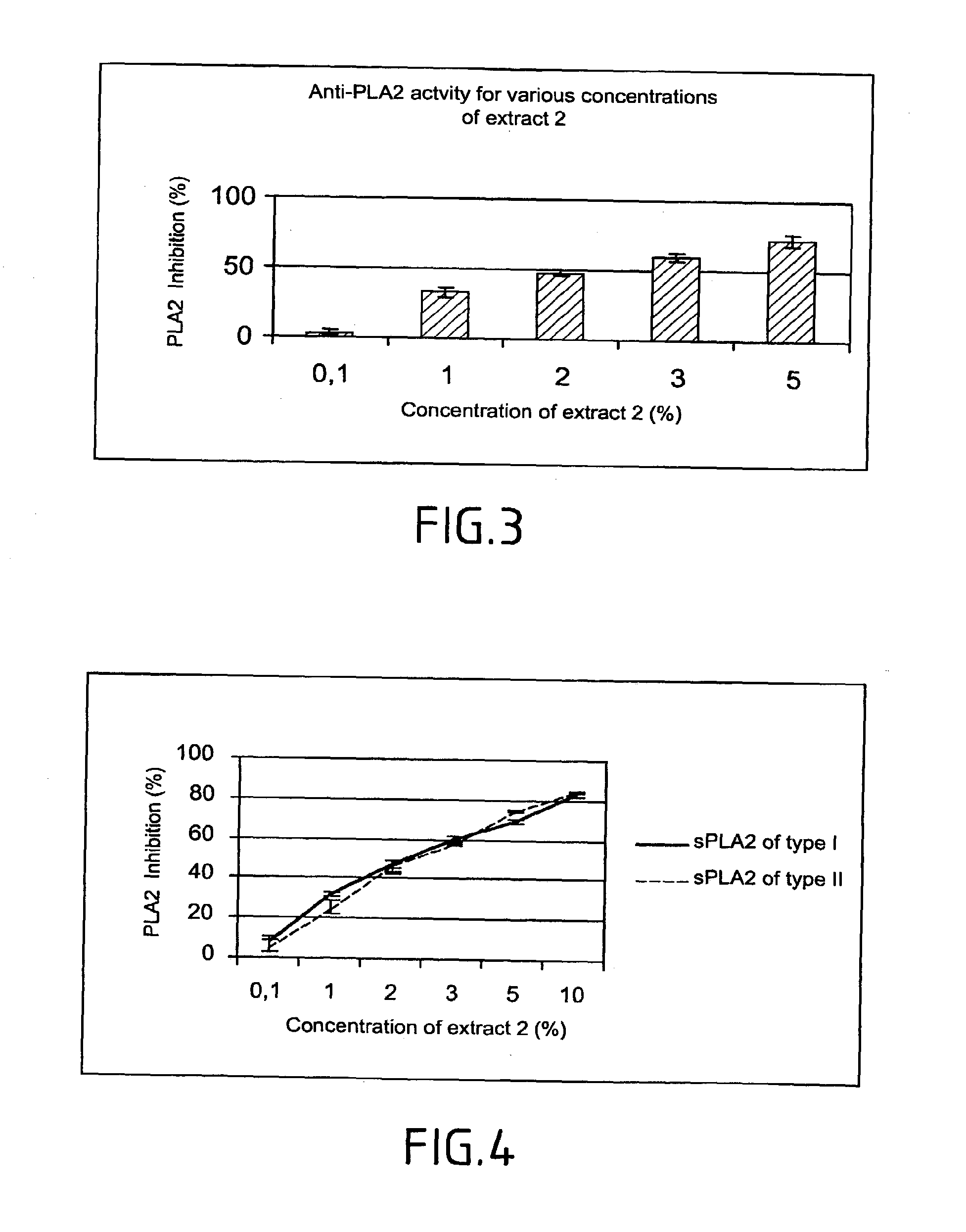
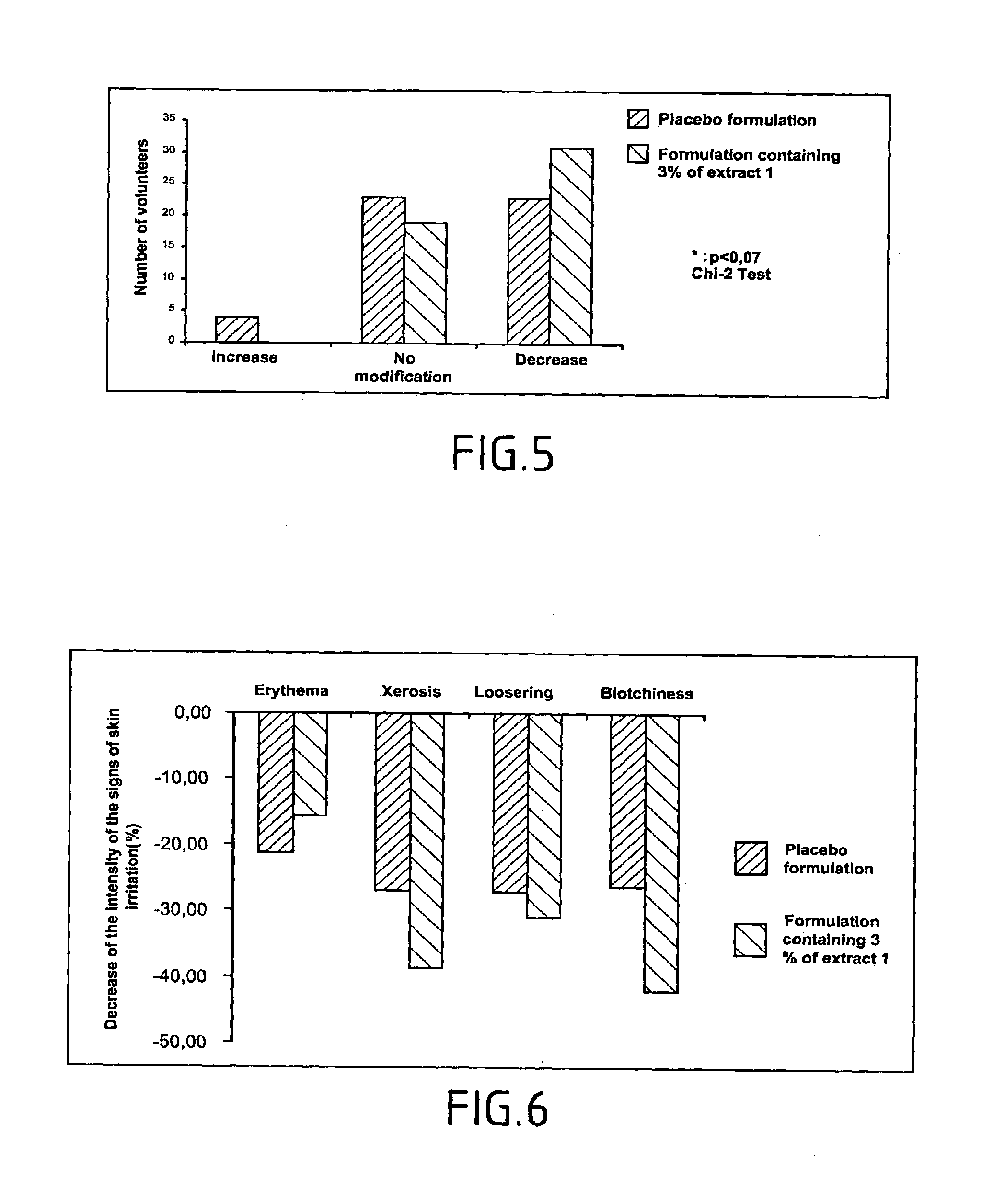
Method of testing the activity of a potentially active substance to inhibit the enzymatic activity of phospholipase A2
InactiveUS20040096925A1Organic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsQuantitative determinationPhospholipase A2
The invention relates mainly to a method of testing the activity of a potentially active substance to inhibit the enzymatic activity of phospholipase A2. The invention relates notably to a method wherein it comprises a) placing said potentially active substance in the presence with the phospholipase A2; a substrate which is a phospholipid, comprising at least one fatty acid in the form of an ester, the fatty acid is preferably a long chain having between 15 and 22 carbon atoms, this fatty acid preferably being unsaturated or poly-unsaturated, said substrate being capable of releasing at least one fatty acid during its hydrolysis; b) measuring the enzymatic activity of the phospholipase A2, notably comprising detecting the presence of said fatty acid and eventually its quantitative determination. The use of this test method notably enables identifying and selecting an active principle capable of inhibiting the enzymatic activity of phospholipase A2.
Owner:BASF BEAUTY CARE SOLUTIONS FRANCE SAS
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
InactiveUS20150259659A1Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganismsLibrary screeningGenome databaseEnzyme
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Polypeptide having glyoxalase iii activity, polynucleotide encoding the same and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a novel polypeptide having the enzymatic activity of conversion of methylglyoxal to lactic acid in a single step (known as glyoxalase III activity), a polynucleotide having a nucleotide sequence encoding such polypeptide and uses thereof.The invention relates to the modulation of the glyoxalase III activity in a microorganism by varying the expression level of the polynucleotide coding for such polypeptide.The invention also relates to the production of commodity chemicals, especially 1,2-propanediol, acetol, and lactic acid by fermenting microorganisms wherein their glyoxalase III activity is modulated.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Preparation method conducive to enhancing enzymatic activity of cellulase
ActiveUS20150118717A1Improve enzymatic activityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesAdditive ingredientLactose
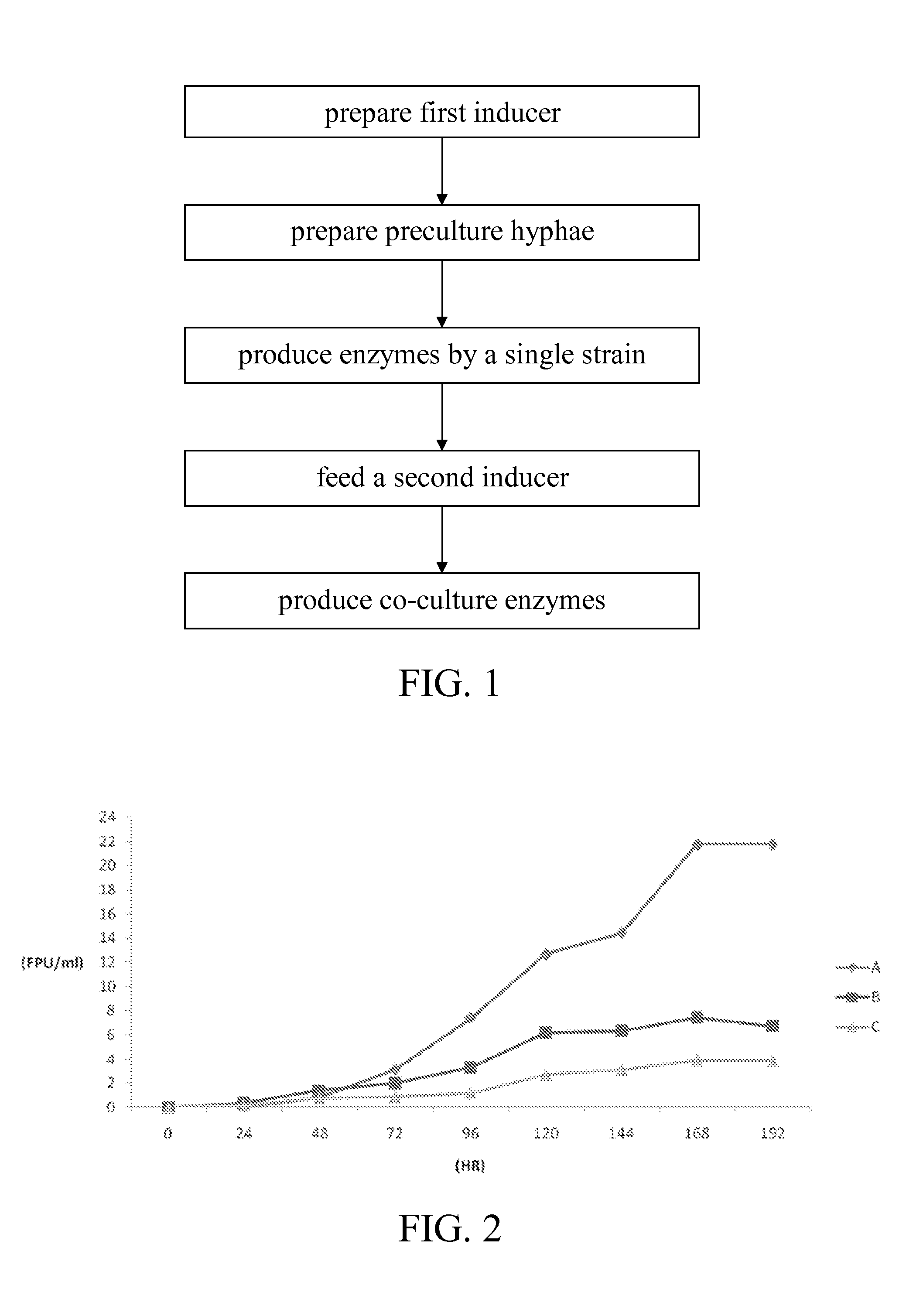
A preparation method conducive to enhancing enzymatic activity of cellulase includes the steps of preparing a first inducer, preparing preculture hyphae, producing enzymes by a single strain, feeding a second inducer, and producing enzymes by co-culture strains. Main ingredients of the first inducer and the second inducer are cellulose and lactose, respectively. The enzymatic activity of the cellulase produced is enhanced by induction of cellulose and lactose and co-culture of Trichoderma and Aspergillus.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Method of enhancing enzyme activity and enzyme solution having enhanced activity
InactiveUS7892805B2Easy to useHigh activityEnzyme stabilisationOn/in organic carrierActivated carbonXylanase Y
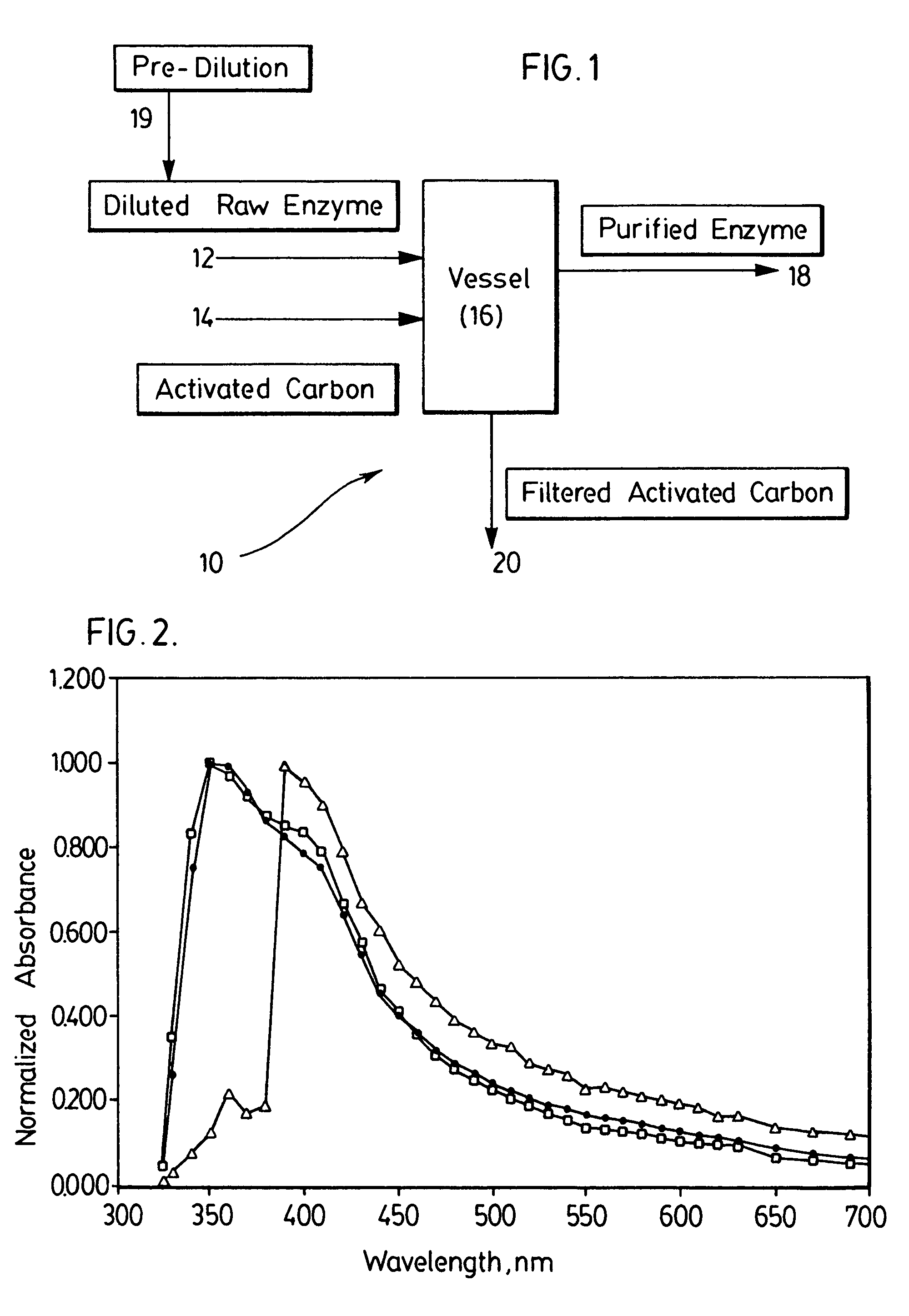
A method of enhancing the intrinsic activity of an enzyme in a raw enzyme solution, the method comprising treating the raw enzyme solution with an effective amount of a purifying agent, most preferably, activated carbon, to effect the enhancement and provide an enzyme solution of enhanced activity. Preferred enzymes are amylase, glucoamylase, cellulase, xylanase, and all other group 3 hydrolases.
Owner:IMMORTAZYME
Novel glucose oxidase variants
InactiveUS20160068824A1Many applicationsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFuel cellsGlucose oxidase activity
The technology provided herein relates to novel variants of microbial glucose oxidase with improved properties, more specifically to polypeptides having glucose oxidase activity as their major enzymatic activity; to nucleic acid molecules encoding said glucose oxidases; vectors and host cells containing the nucleic acids and methods for producing the glucose oxidase; compositions comprising said glucose oxidase; methods for the preparation and production of such enzymes; and to methods for using such enzymes for food and feed processing, for the measurement of free glucose in clinical samples and bioreactors, and the development of miniature biofuel cells.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Process for double-enzyme coupling-chemical synthesis of epsilon-caprolactone
InactiveCN106701859AHigh activityHigh selectivityImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesHigh concentrationChemical synthesis
The invention relates to a process for double-enzyme coupling-chemical synthesis of epsilon-caprolactone; hydrogen peroxide generated in situ from GOD oxidation of glucose by a GOD / CALB or GOD / ROL double-enzyme cross-linked enzyme aggregate is used as an oxidant, at the same time, peroxy acid is generated in situ through catalyzing oxidation of an acyl donor by CALB or ROL in the cross-linked enzyme aggregate, and then epsilon-caprolactone (epsilon-CL) is generated through oxidation of cyclohexanone by peroxy acid. The yield of the epsilon-caprolactone reaches 97% or more, and the selectivity of the epsilon-caprolactone is 100%. The process reduces enzyme inactivation caused by too high concentration of hydrogen peroxide, avoids an easily explosiveness risk possibly caused by direct addition of peroxy acid, reduces the influence of decrease of enzyme micro-environment pH on the enzyme activity, and can reduce the inhibition of a substrate on an enzyme.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
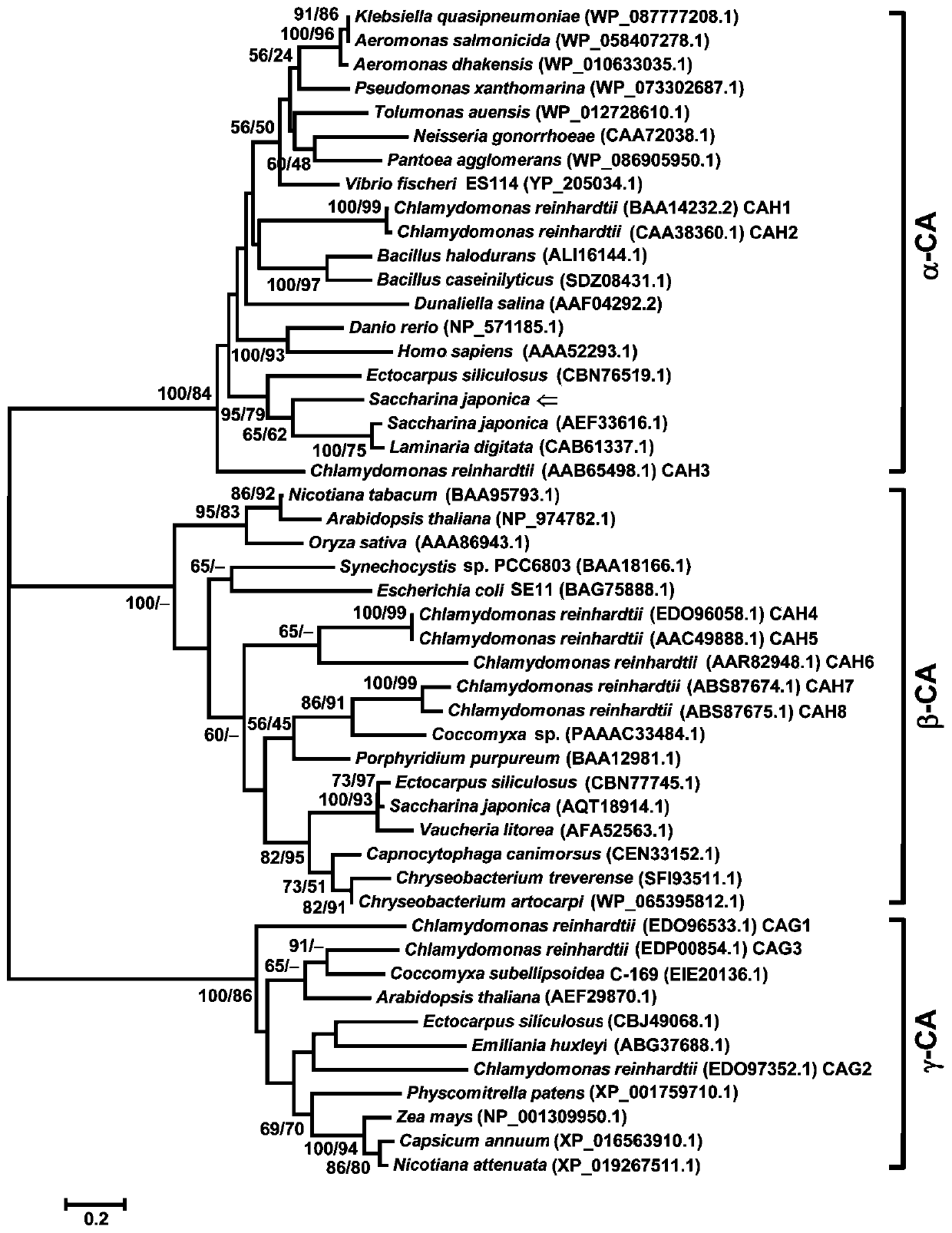
Kelp alpha type carbonic anhydrase gene Sjalpha-CA2 and encoding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN110066817AIncrease productionIncrease gene expressionClimate change adaptationFermentationDNAGene
The invention discloses a kelp alpha type carbonic anhydrase gene Sjalpha-CA2 and an encoding protein and application thereof. The cDNA sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the DNA sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the amino acid sequence of the encoding protein of the gene Sjalpha-CA2 is shown in SEQ ID NO:3, by constructing an expression vector of the gene Sjalpha-CA2, the amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein rSjalpha-CA2 is shown in SEQ ID NO:4, and the recombinant protein rSjalpha-CA2 has the enzyme activity of a CO2 hydration reaction and the esterase activity for esterifying nitrophenyl acetate into p-nitrophenol; the gene Sjalpha-CA2, the encoding gene thereof and the recombinant protein rSjalpha-CA2 can be used for high-yield transgenic kelp cultivation.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
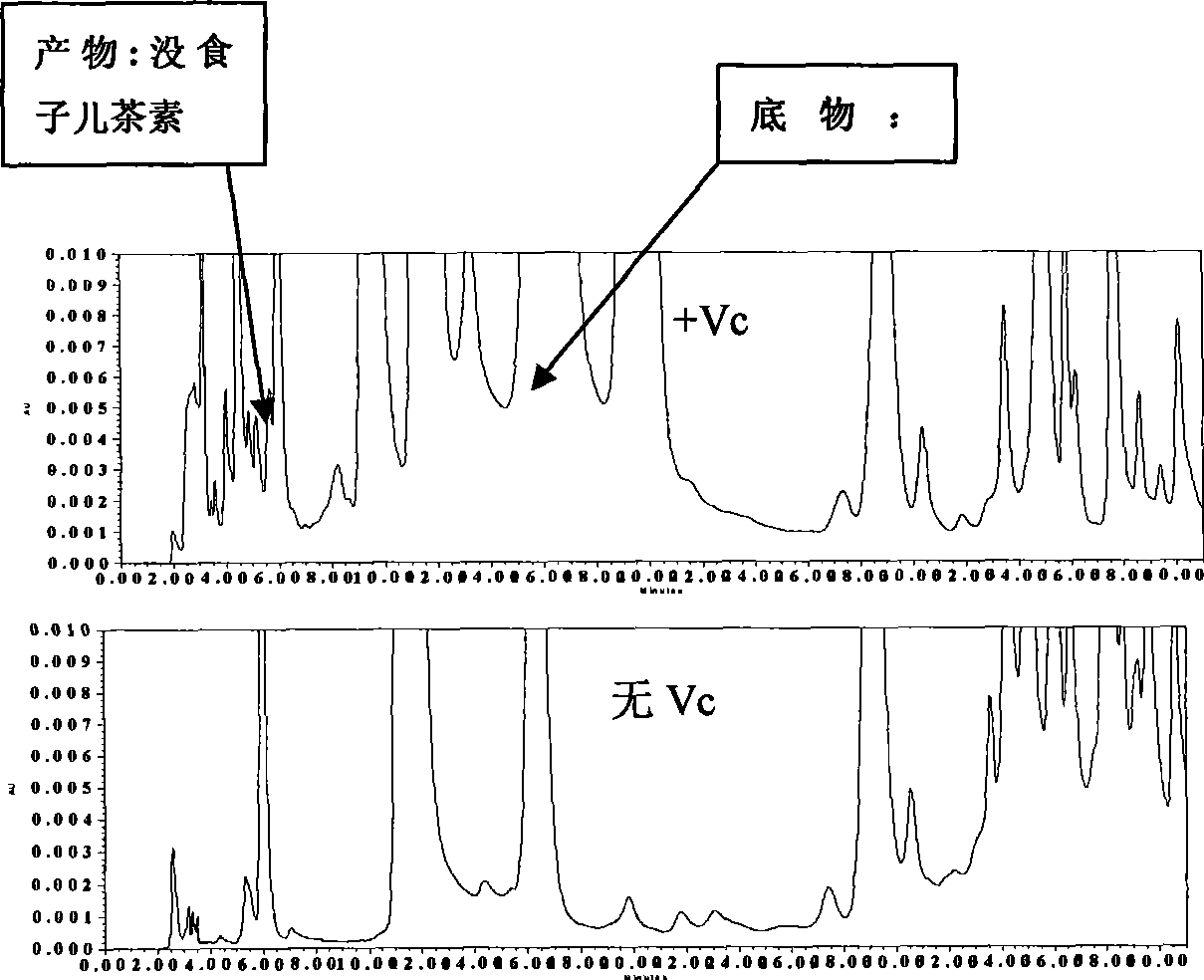
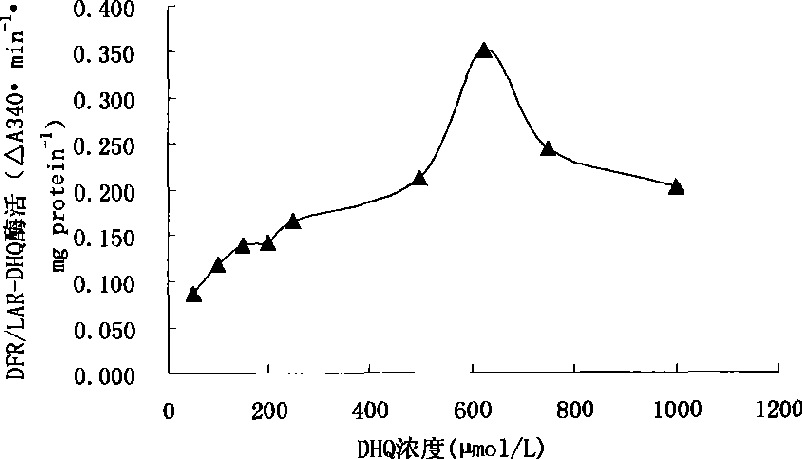
Fast detection method for dihydro flavanol 4-reductase/leucocyanidin reductase in tree plant
InactiveCN101482500ASimple methodDoes not require extraction and concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsVitamin CProtein insertion
The invention relates to a quick detection method of dihydrogen-flavanol4-reductase / leucocyanidin reductase and anthocyanin reductase in tea tree, which can solve the problems of the prior technique of complicated operation in enzymatic activity detection method, high cost, long detection time. The quick detection method comprises: preparing an enzyme extracting-solution, measuring the protein content in enzyme extracting-solution and enzymatic activity, wherein the enzymatic activity is detected by detecting the consumption of the reduction type nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate solution (NADPH) and the vitamine C is added into the reaction system to reduce the interference of the substrate DHM and CYA on enzymatic activity detection. The quick detection method using ultraviolet spectrophotometer has features of simple method, low cost, short detection time of 15-25 minutes; environmental protection, safety, no need of noxious organic solvent, higher detection accuracy due to continuous detection of the changed enzymatic activity.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separating L-amino-acid oxidase from venin
InactiveCN1614012AAvoid influenceSimple methodOxidoreductasesL-amino-acid oxidaseGloydius ussuriensis
It was involved in separating L-amino acid oxidase from the snake venom of Agkistrodonhalysussuriensis. Through two steps of colum chromatography (i.e. heparin fast flow and qsepherose fast flow) L-amino acid oxidase was separated and purified from the snake toxin of Gloydius ussuriensis. Not including transfer between concentrating and buffer system. It could avoid the influence of freezing and the pH value change to enzyme activity. The method was found to be simple, rapid and convenient. The ratio of recovery was high.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Process for producing gene engineering immobilized enzyme N-glycoamidase
InactiveCN1740324AImprove stabilityReduce spendingFungiOther foreign material introduction processesYeastAgglutination
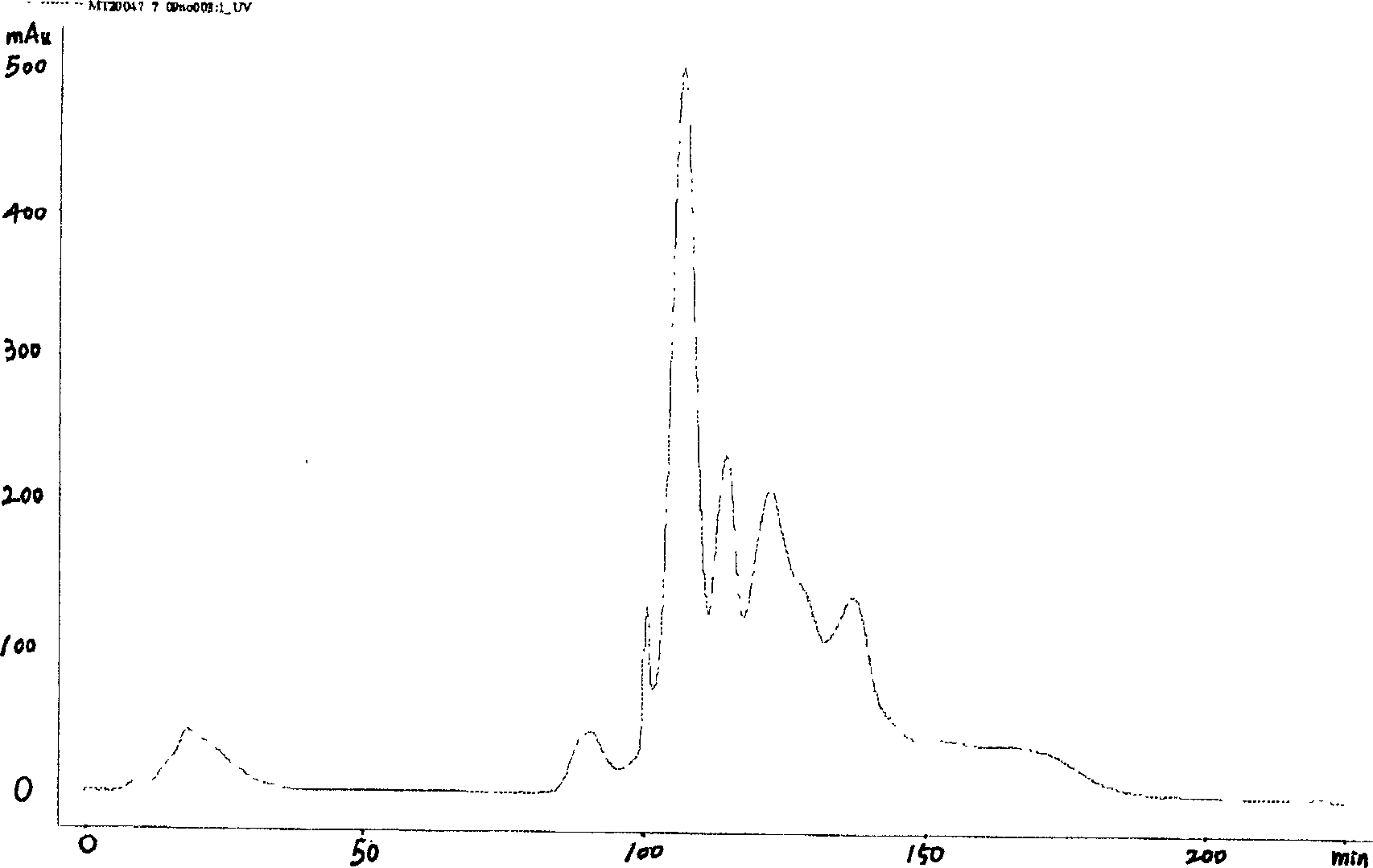
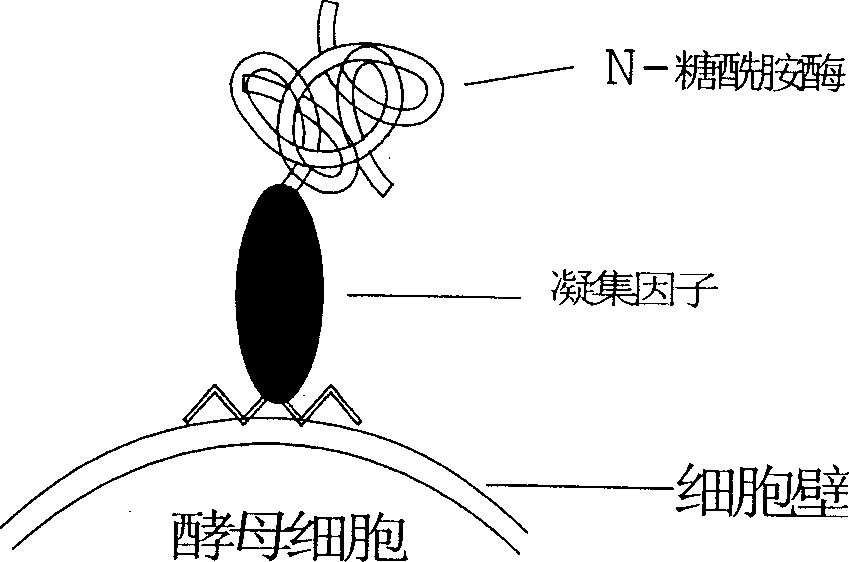
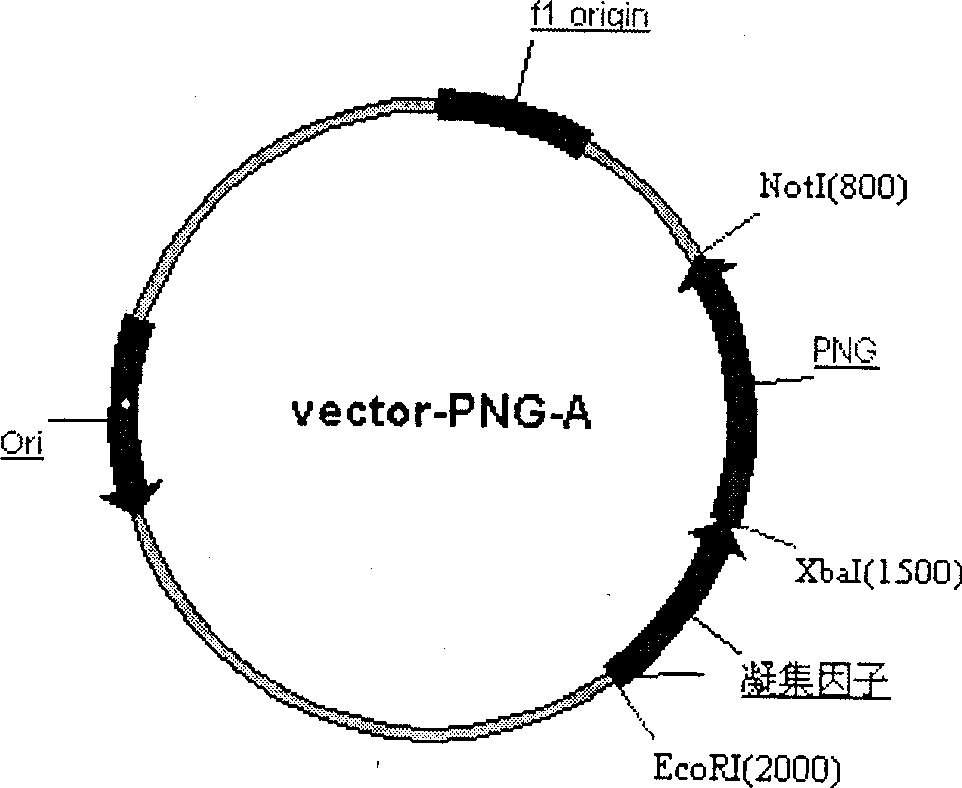
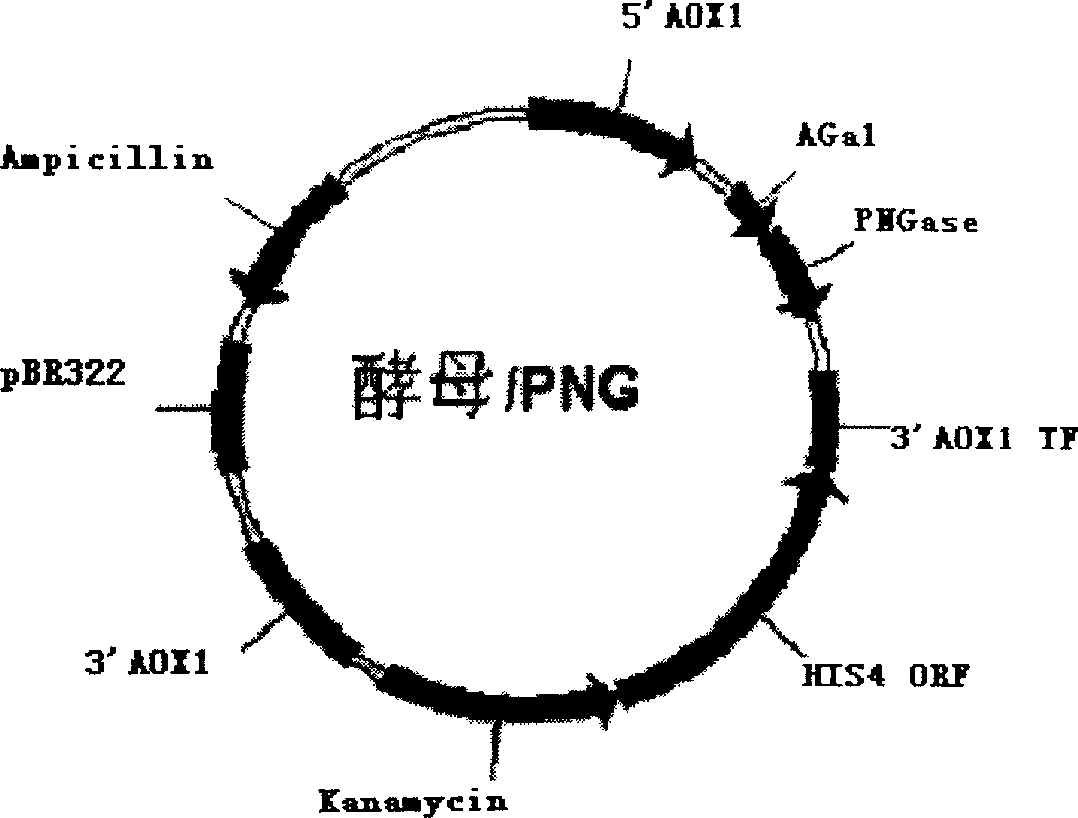
This invention discloses a kind of method of producing genetic engineering immobilized enzyme N-glycoamidase (PNGase). The N-glycoamidase is fused with yeast agglutination factor by the genetic engineering technique, Anchor it to the surface of methanol nutrition type yeast cell and get a kind of immobilized N-glycoamidase using cells as carrier. In this method, the activity of the enzyme during immobilizing process will not decrease. The produced immobilized enzymes have high stability and can use repeatedly. The method also leaves out purification and reduces the cost. The N-glycoamidase can be widely used in extracting oligosaccharide chain which has biological function from farm product remains (egg yolk powder, milk)
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Application of novel fructosidase coding gene
InactiveCN105349508AThe probiotic effect is fully exertedIncrease metabolic functionalityGlycosylasesHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses an application of a novel fructosidase coding gene. Fructosidase has the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ.ID NO:1 in a sequence table. The coding gene has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ.ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The fructosidase originates from Lactobacillus plantarum, compared with fructosidase originating from other sources, the enzyme has the enzymatic activity of decomposing FOS (fructooligosaccharides) and freeing fructose radicals from the FOS as well as the inulinase activity and levanase activity; lactic acid bacteria without the capability of utilizing the FOS can have the capability of utilizing the FOS when the enzyme is heterogeneously expressed in the other lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD CO LTD
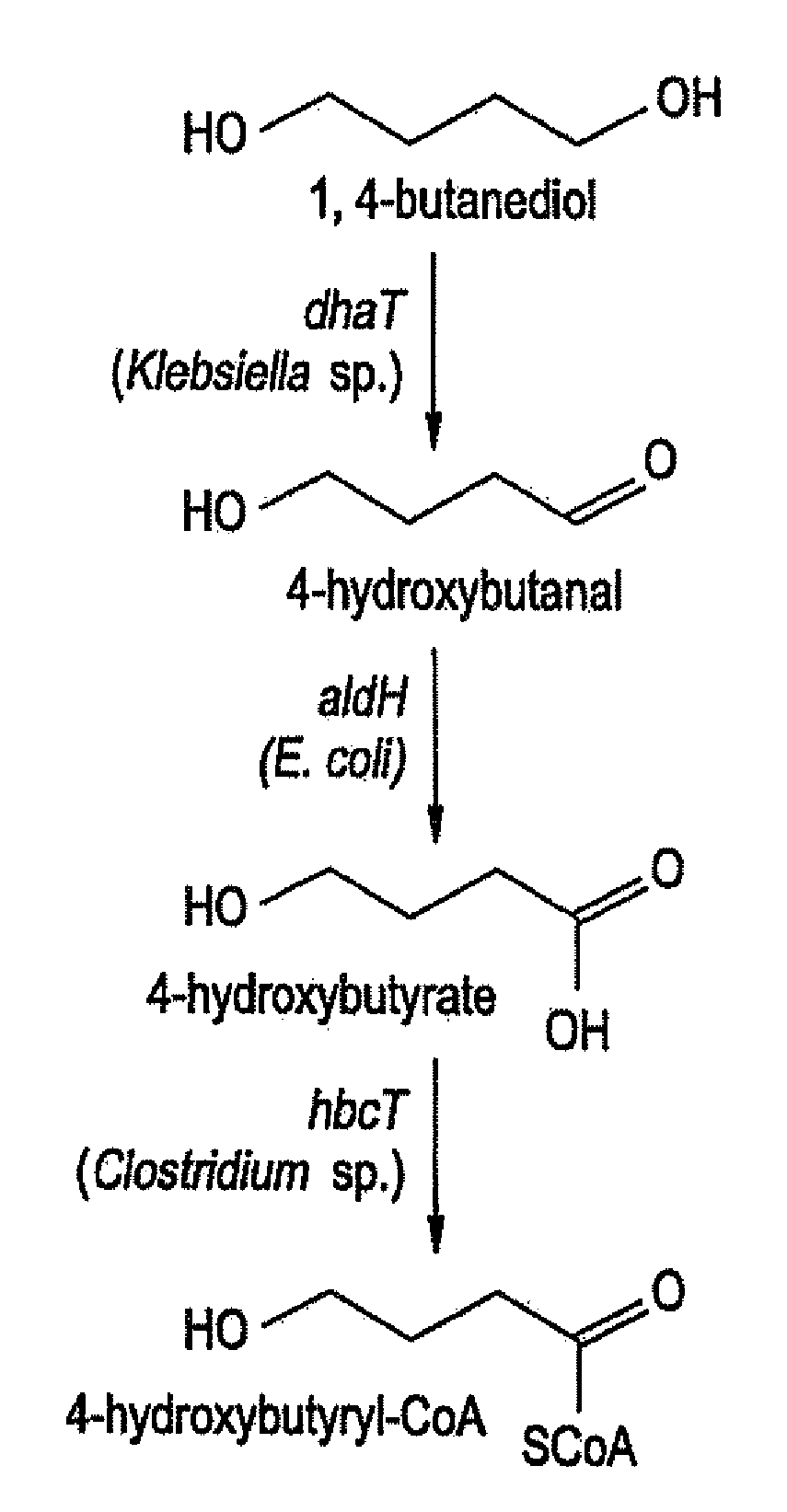
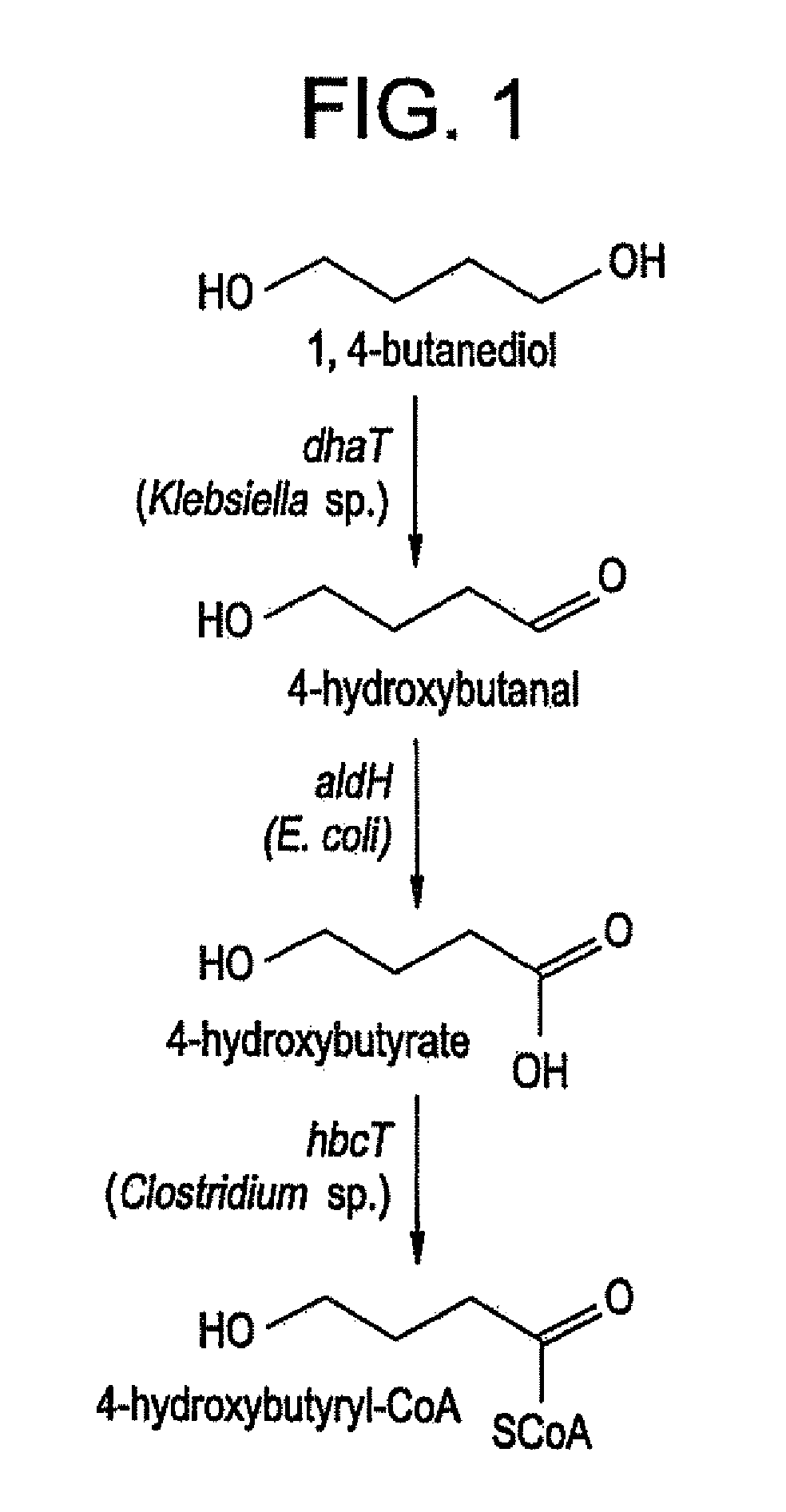
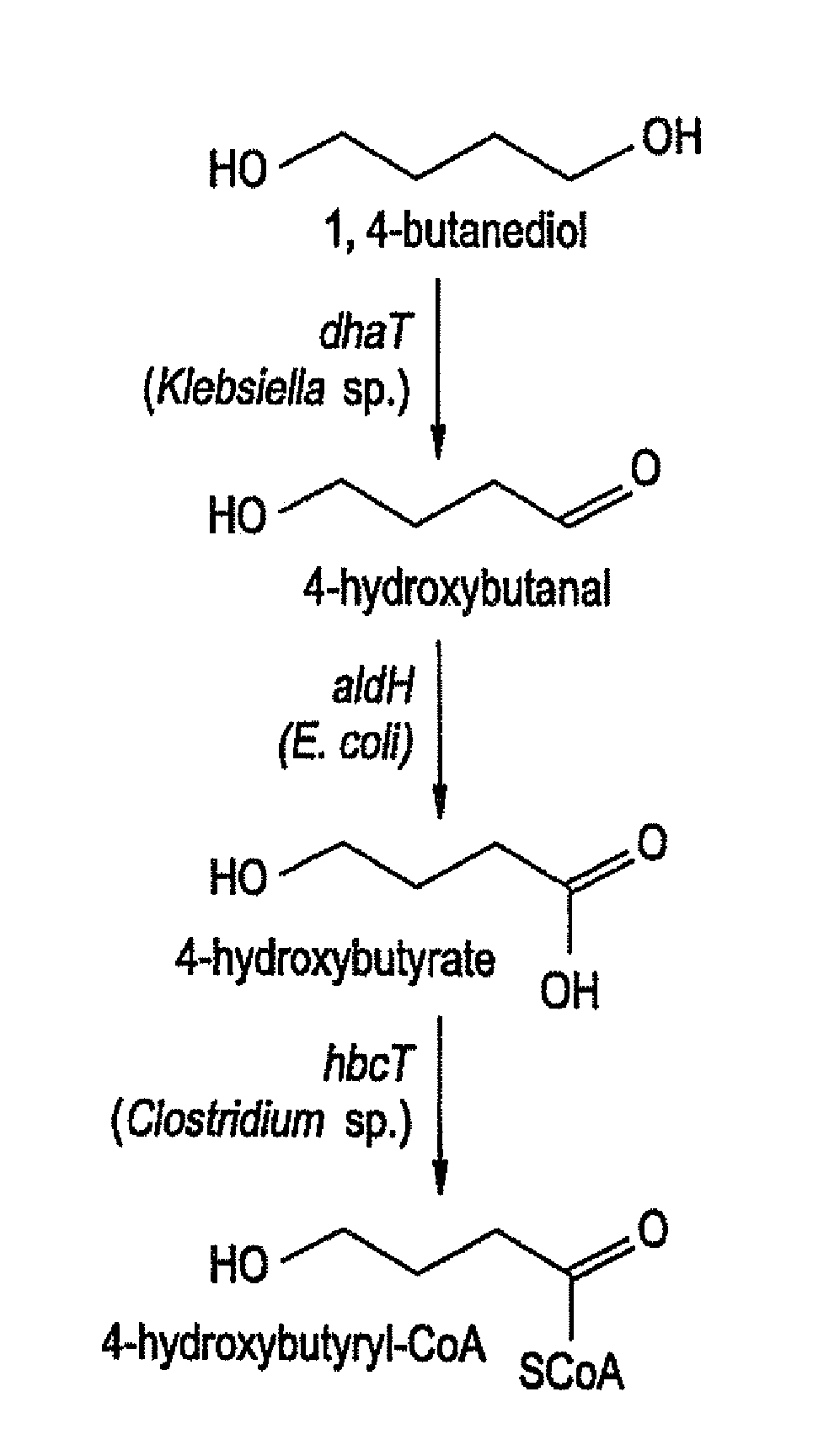
Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates From Polyols
InactiveUS20100021919A1Increase productionPromote recoveryBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Recombinant processes are provided whereby additional genes are introduced into E. coli which have been genetically engineered to produce PHA so that the improved strains produce PHA homopolymers and copolymers directly from diols. In preferred embodiments, PHAs containing 4-hydroxybutyrate monomers are produced directly from 1,4-butanediol; PHAs containing 5-hydroxyvalerate are produced from 1,5-pentanediol; PHAs containing 6-hydroxyhexanoate (6HH) are produced from 1,6-hexanediol; PHAs containing 3-hydroxypropionate are produced from 1,3-propanediol; PHAs containing 2-hydroxypropionate (lactate) are produced from 1,2-propanediol (propylene glycol); PHAs containing 2-hydroxyethanoate (glycolate) are produced from 1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol). Genes encoding these same enzyme activities can be introduced or their expression amplified in wild type PHA producers to improve the production of PHA homopolymers and copolymers directly from diol and other alcohol feedstocks. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Sequence of Thermotolerant L-Rhamnose Isomerase Gene and Use of the Same
InactiveUS20090004694A1Reduce pollutionIncrease working temperatureSugar derivativesMicroorganismsIsomerizationHeat stability
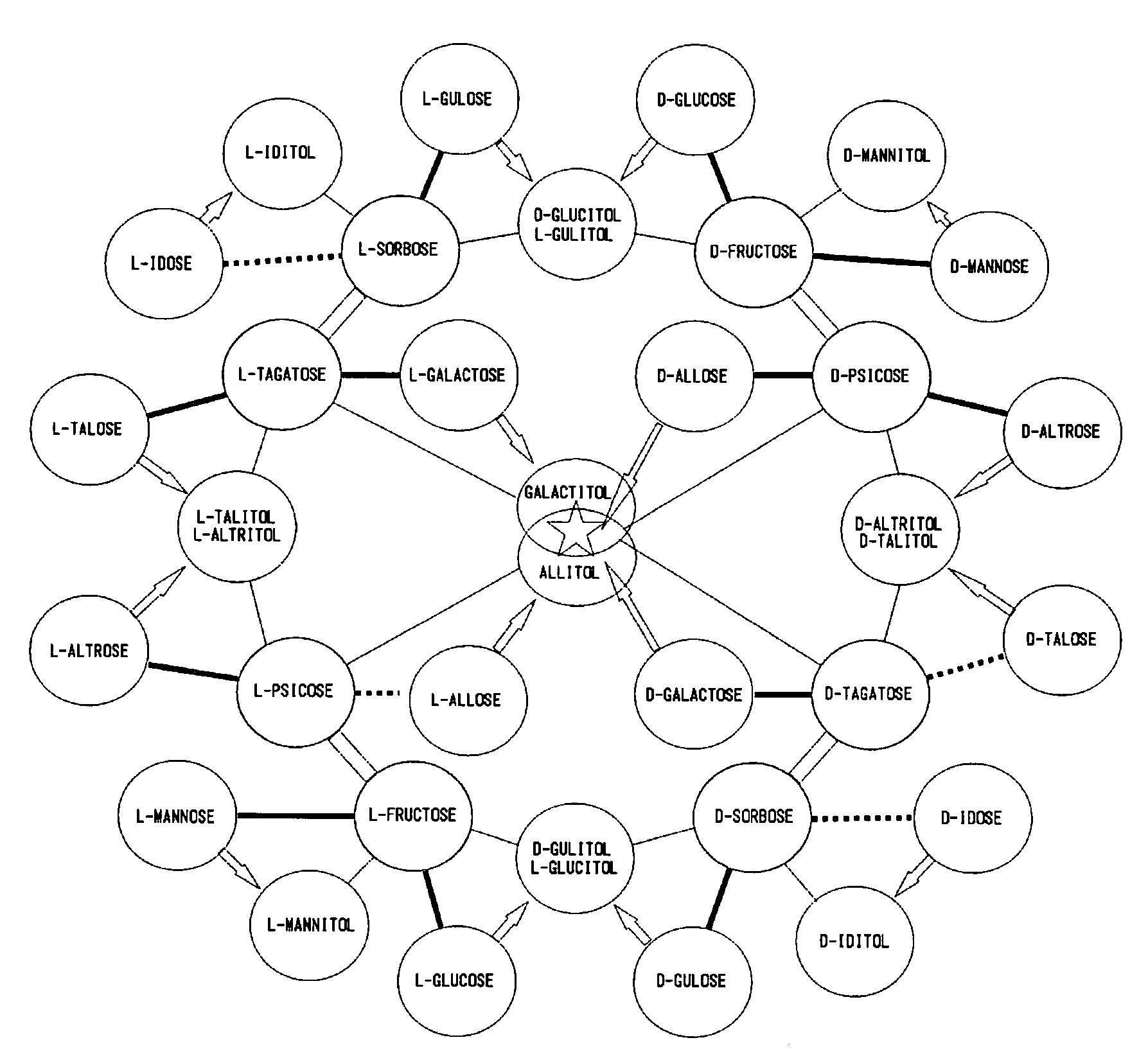
[PROBLEMS] To provide the sequence of a thermotolerant L-rhamnose isomerase gene. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A DNA comprising the base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1. A protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. A protein originating in Bacillus pallidus strain 14a (FERM AP-20172) and having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity. A protein having an L-rhamnose isomerase activity which is specified as having the following characteristics: optimum temperature and working temperature: showing the maximum enzymatic activity at 80° C. (the optimum temperature) and working temperature ranging from 30 to 80° C.; heat stability: concerning the effect of temperature on the enzymatic activity, being stable at up to 50° C. in the case of heating for 1 hour; and catalyzing the isomerization from D-psicose to D-allose. A method of producing D-allose which comprises treating a solution containing D-psicose with the above protein having the L-rhamnose isomerase activity as a catalyst at 35 to 80° C. to thereby convert D-psicose into D-allose.
Owner:IZUMORING +1
Preparation method of immobilized glucose oxidase
InactiveCN107502598AEasy accessReduce breakage rateOxidoreductasesOn/in organic carrierPolyvinyl alcoholBreakage rate
The invention belongs to the field of a food preservation additive, and specifically relates to a preparation method of immobilized glucose oxidase. A fungi strain is separated and screened from soil and is used for fermenting glucose oxidase. The fungi strain is simple in acquiring approach, is green and eco-friendly, and is super easy to obtain. Through co-action of an entrapping method and a crosslinking method, polyvinyl alcohol is taken as a carrier, and bis-diazotized benzidine with the concentration being 10% is added to immobilize glucose oxidase. The immobilized glucose oxidase can be repeatedly used. The method is saved in cost and reduced in breakage rate of glucose oxidase cells. The immobilized glucose oxidase is improved in mechanical strength and enzyme activity and prolonged in enzyme activity maintaining time.
Owner:蒋文明
Esterase free enzymes
InactiveCN1174096CDecreased esterase activityHigh activityHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierAcylamidase activityCarboxylic acid
A process for decreasing esterase activity present in the presence of D-amino acid oxidase activity or in the presence of glutarylacylase activity in a mixture having esterase activity and D-amino acid oxidase activity and / or having esterase activity and glutarylacylase activity by treatment with phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride; immobilized biocatalysts in spherical particle form obtainable by treating microorganism cells having enzyme activity with a primary or secondary amine containing polymer, an organic solvent which is able to form a two-phase system with water and a bifunctional agent; and the use of that process and biocatalysts in the production of 7-aminocephalo-sporanic acid, 7-amino-3-hydroxymethyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid and cephalosporin antibiotics.
Owner:SANDOZ AG
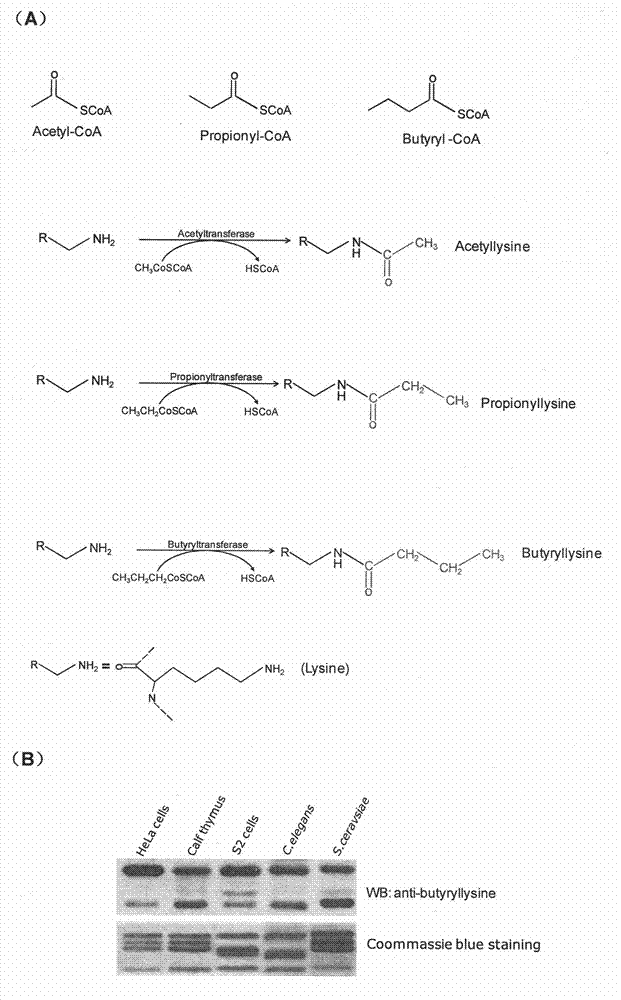
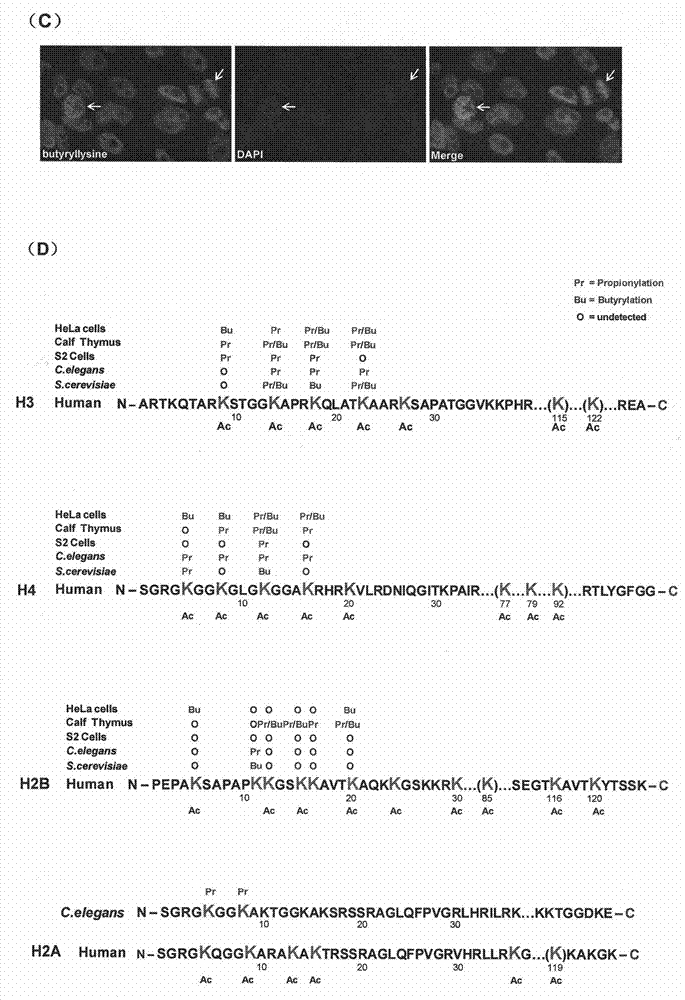
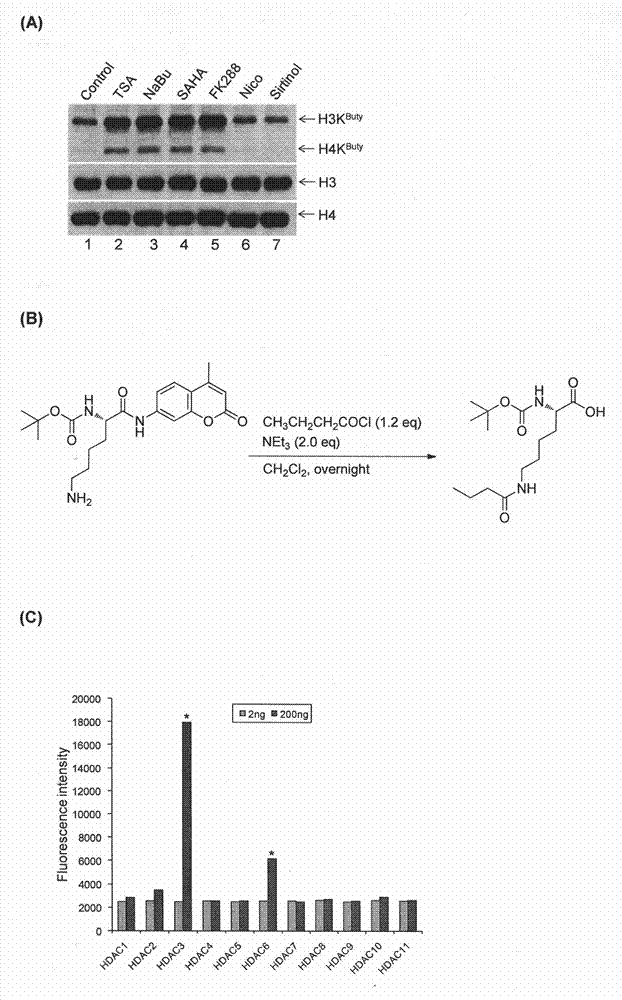
Method for screening and testing activity of lysine propionylation removal enzyme and butyrylation removal enzyme
Owner:JINGJIE PTM BIOLAB HANGZHOU CO LTD
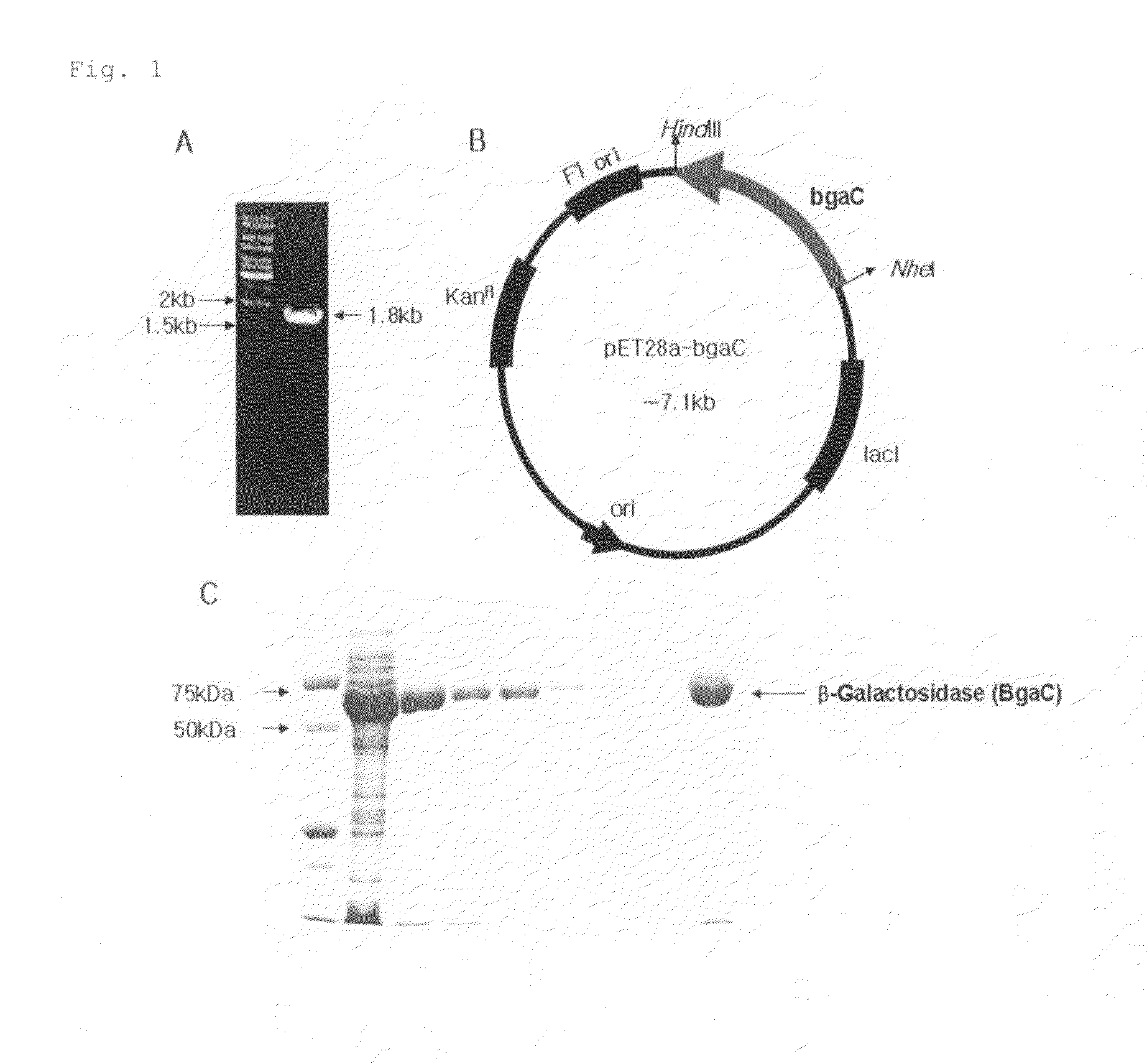
Recombinant beta-galactosidase derived from Streptococcus pneumaniae
InactiveUS20080248019A1Inhibit cancer cell growthSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaeBeta-Galactosidases
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
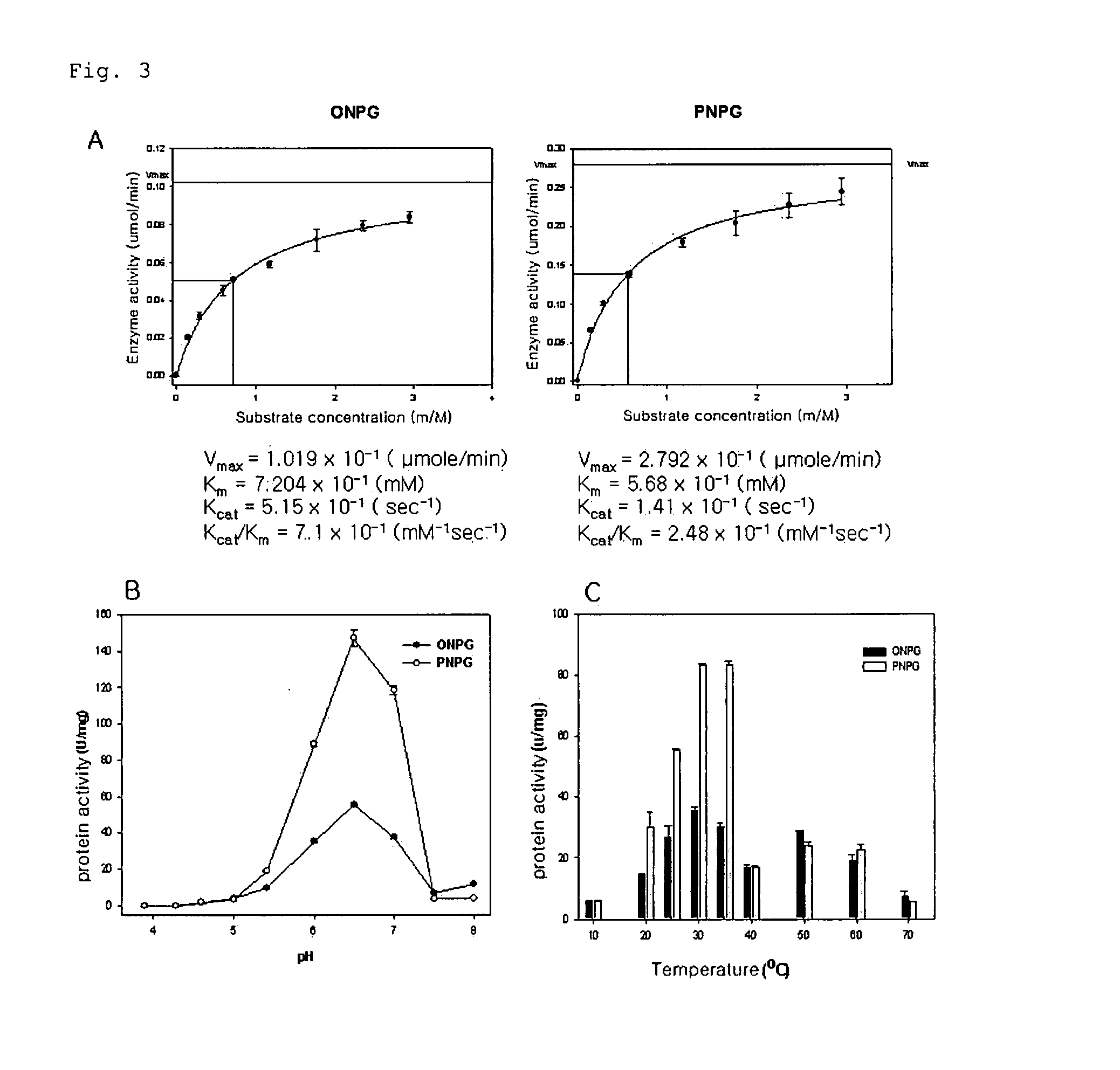
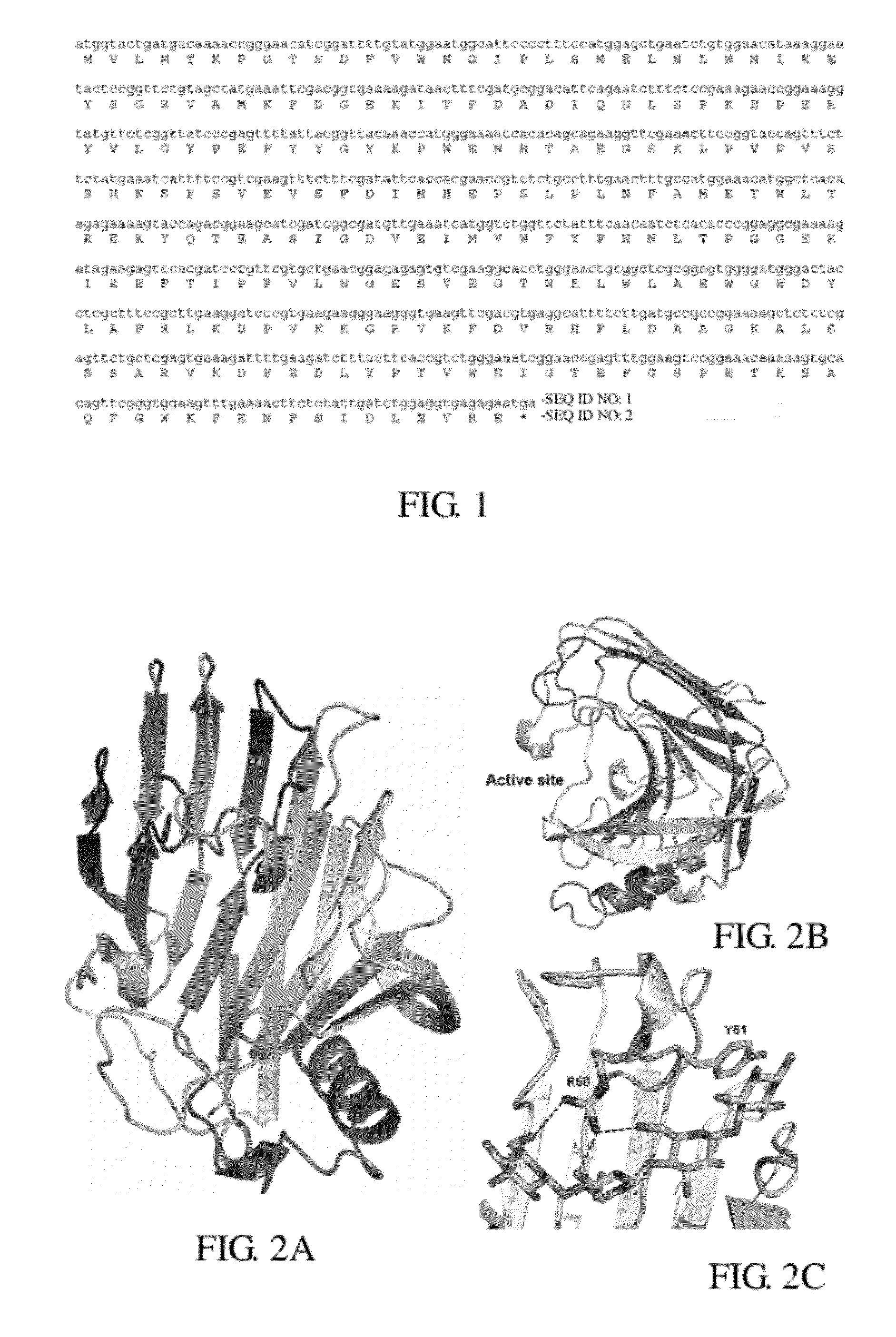
Thermostable cellulase having increased enzyme activity
ActiveUS8137945B1Increase enzyme activityHigh industrial valueGlycosylasesGlycineAmino acid substitution
A thermostable cellulase having increased enzyme activity is disclosed. The cellulase comprises a modified amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, wherein the tyrosine at position 61 is substituted with an amino acid selected from the group consisting of phenylalanine, alanine and glycine.
Owner:GENOZYME BIOTECH
Thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase and crystal structure thereof
ActiveCN102676464BThermally stableImprove thermal stabilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention relates to thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase in an n-alkane end degradation process of thermophilic denitrified bacillus and a crystal structure thereof. A molecular clone method is utilized, so that a target gene is cloned into escherichia coli (E. coli) so as to be heterologously expressed. A purified product of aldehyde dehydrogenase is obtained through a protein purification method. A crystal of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, which is suitable for diffraction, is obtained through a hanging droplet crystallization method. The crystal structure of the aldehyde dehydrogenase is analyzed by utilizing an X-ray diffraction method. The results show that the aldehyde dehydrogenase contains a characteristic ALDH fold which is formed by three structural domains. Site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on conserved residues on an enzyme activity part, and the influence of the conserved residues on enzyme activity is proved through wild type of the enzyme and enzyme activity experiment of the mutant thereof. The results can comprehensively reflect space conformation of the enzyme, and provide theoretical guidance for further researching relation between structures and functions of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, and improving the degradation activity of the enzyme.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
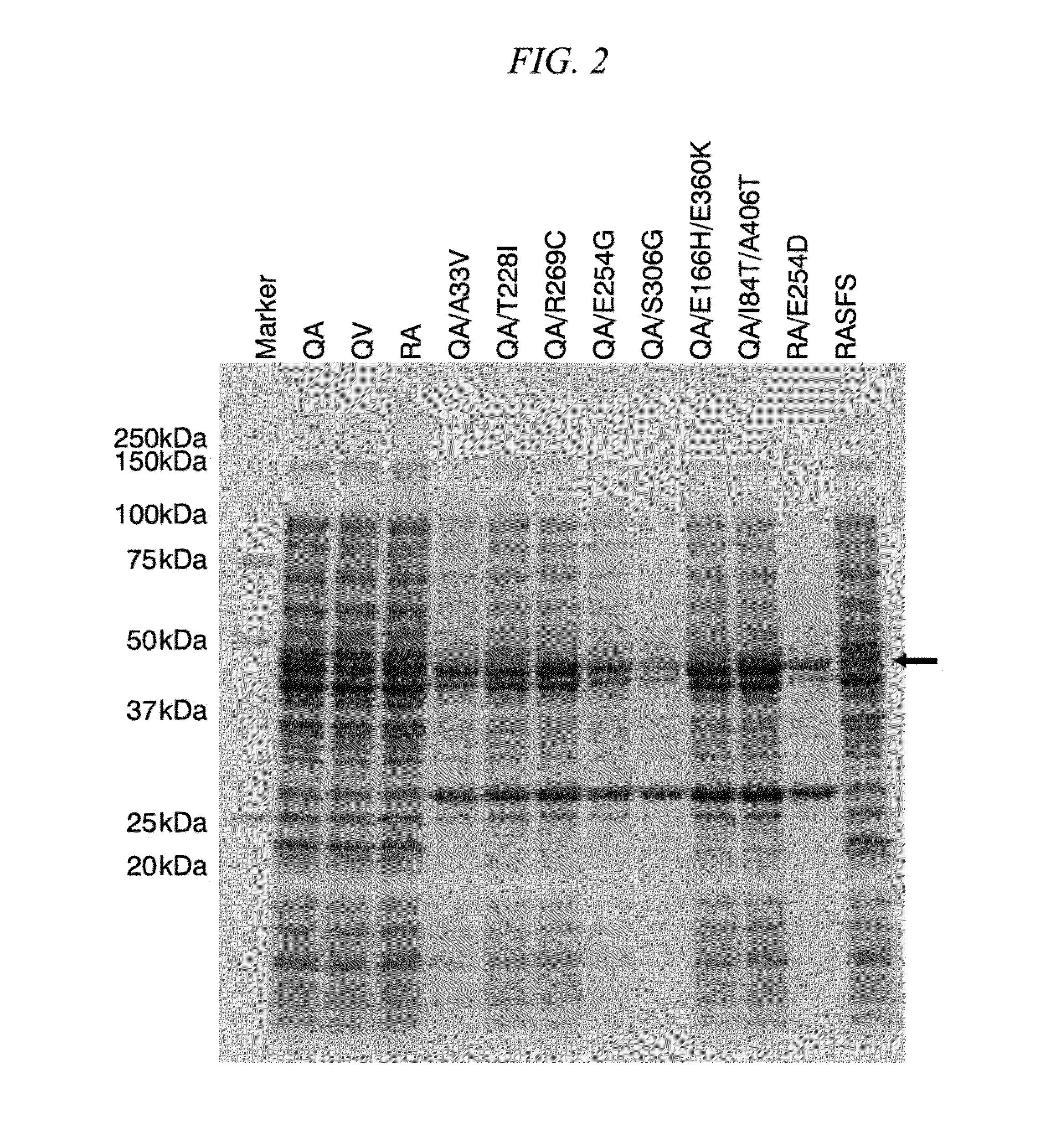
Method of testing the activity of a potentially active substance to inhibit the enzymatic activity of phospholipase a2
InactiveUS20150110907A1Use minimizedReduce stimulationOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsPhospholipase A2Quantitative determination
The invention relates to a method of testing the activity of a potentially active substance to inhibit the enzymatic activity of phospholipase A2. The invention relates notably to a method wherein it comprises a) placing the potentially active substance in the presence with the phospholipase A2; a substrate which is a phospholipid, comprising at least one fatty acid in the form of an ester, the fatty acid is preferably a long chain having between 15 and 22 carbon atoms, this fatty acid preferably being unsaturated or poly-unsaturated, the substrate being capable of releasing at least one fatty acid during its hydrolysis; b) measuring the enzymatic activity of the phospholipase A2, notably comprising detecting the presence of the fatty acid and eventually its quantitative determination. The use of this test method notably enables identifying and selecting an active principle capable of inhibiting the enzymatic activity of phospholipase A2.
Owner:BASF BEAUTY CARE SOLUTIONS FRANCE SAS
Gene encoding alkaline beta-glucosidase and application thereof
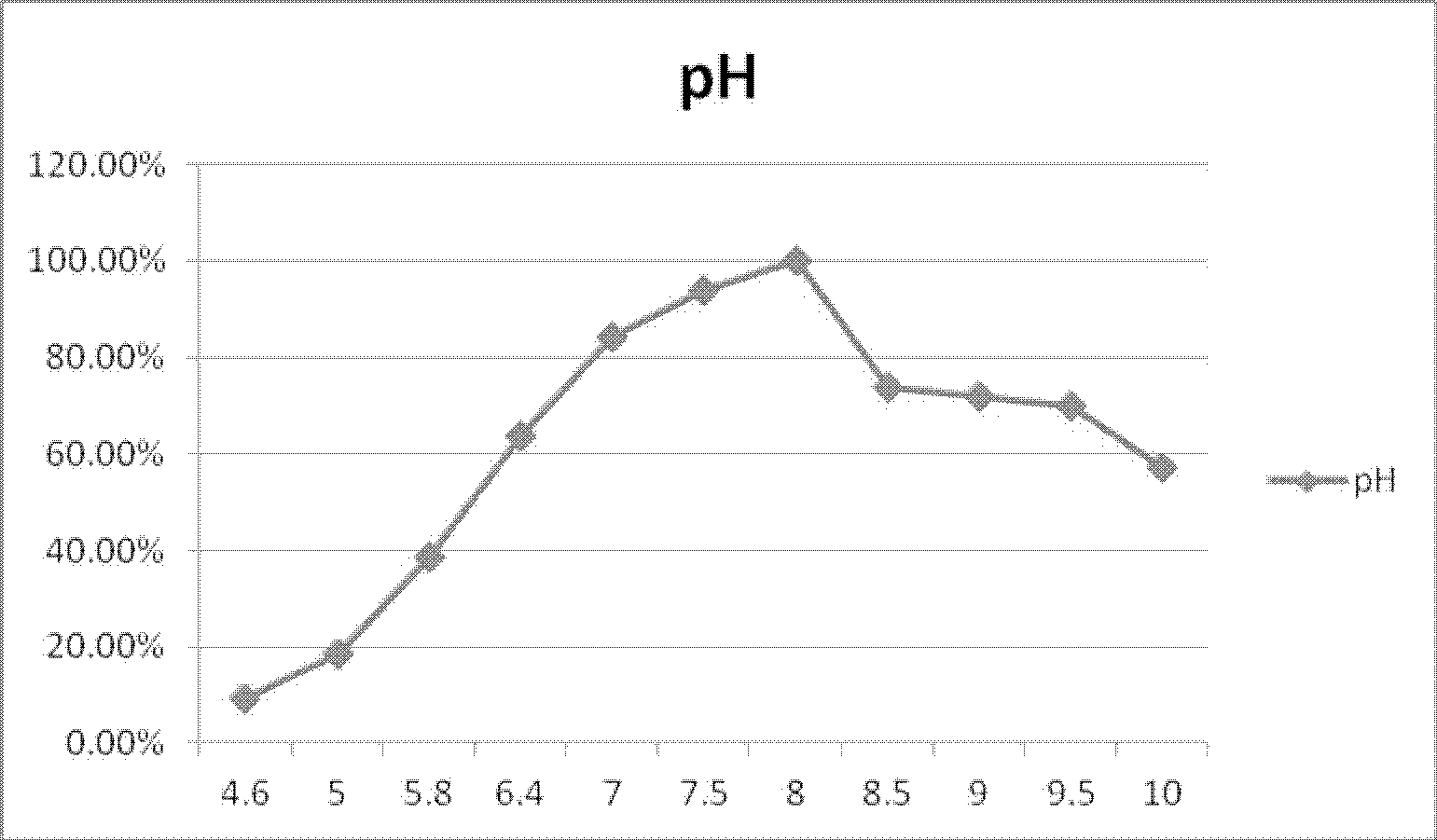
The present invention discloses a gene encoding alkaline beta-glucosidase and application thereof. A gene Pbgl of the alkaline beta-glucosidase contains a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1; and an amino acid sequence of the said gene encoding the alkaline beta-glucosidase is provided, and shown as a SEQ ID NO. 2. Activity of the alkaline beta-glucosidase adapts a pH range of 5-10, and an optimum pH is 8.0. When pH is 10, enzymatic activity still retains at 58% of the highest activity, and is superior to the activity of an existing alkaline beta-glucosidase. Therefore, the alkaline beta-glucosidase has improved application value, and is suitable for application to the decomposition of cellooligosaccharide.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
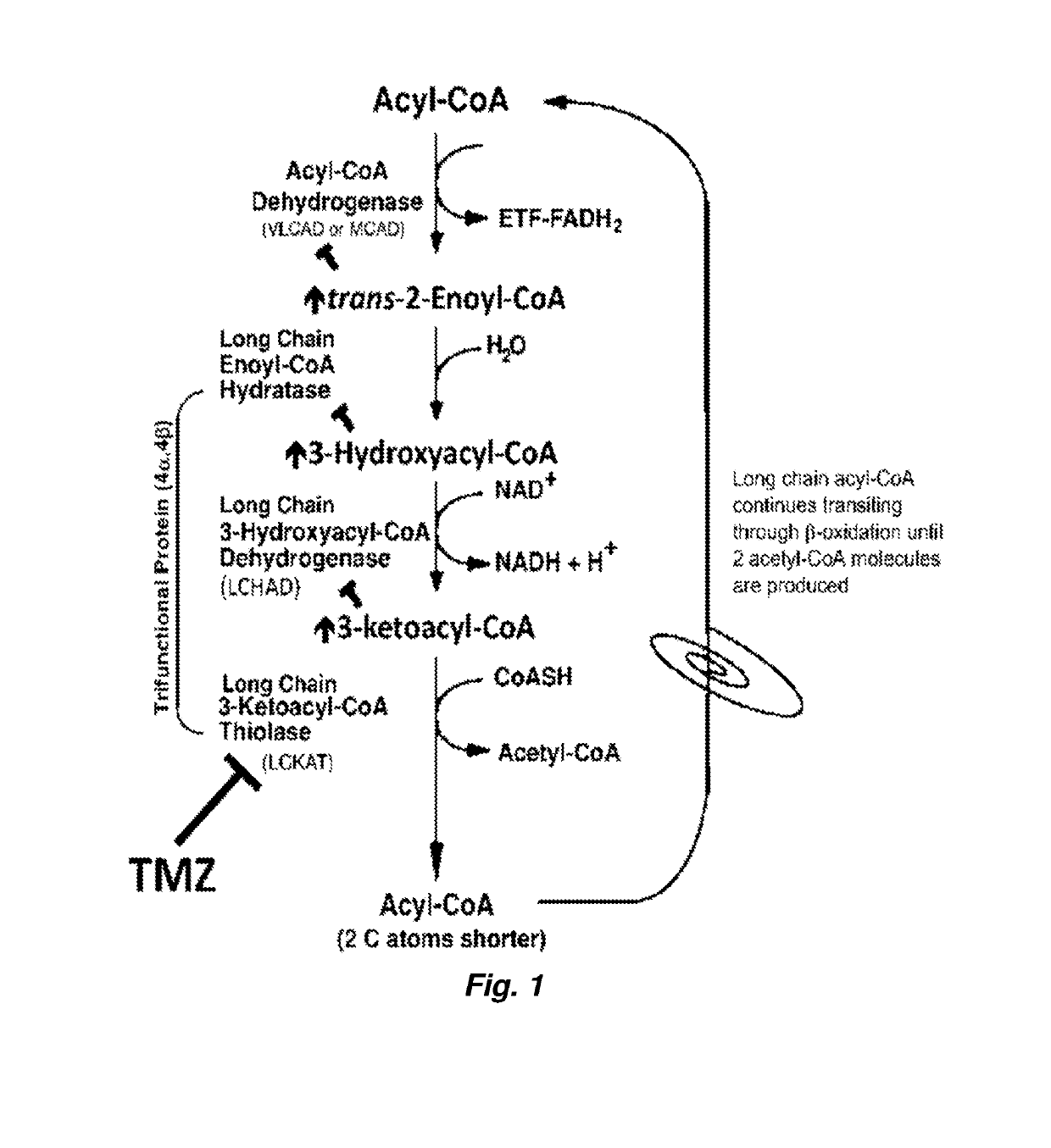
Therapy for Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation and Transport Disorders
ActiveUS20190290642A1High activityLoss of activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinTrimetazidine
Methods of treating mitochondrial fatty acid b-oxidation and / or transport disorders arising from mutant proteins in the mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation and transport metabolic pathways in patients are provided. The methods modulate the mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation pathway at the last step so that the product of the mutant protein accumulates and stabilizes the mutant protein and / or the substrate(s) / product(s) of the down stream reactions accumulate and possibly bind to allosteric sites on the mutant protein to stabilize it. Trimetazidine pharmacodynamics function as such in the β-oxidation pathway. Further, a synergistic effect is observed where trimetazidine and PPARδ agonist combination enhanced enzyme activity and presence significantly more than either alone.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from polyols
InactiveUS8741624B2Increase productionPromote recoverySugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Recombinant processes are provided whereby additional genes are introduced into E. coli which have been genetically engineered to produce PHA so that the improved strains produce PHA homopolymers and copolymers directly from diols. In preferred embodiments, PHAs containing 4-hydroxybutyrate monomers are produced directly from 1,4-butanediol; PHAs containing 5-hydroxyvalerate are produced from 1,5-pentanediol; PHAs containing 6-hydroxyhexanoate (6HH) are produced from 1,6-hexanediol; PHAs containing 3-hydroxypropionate are produced from 1,3-propanediol; PHAs containing 2-hydroxypropionate (lactate) are produced from 1,2-propanediol (propylene glycol); PHAs containing 2-hydroxyethanoate (glycolate) are produced from 1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol). Genes encoding these same enzyme activities can be introduced or their expression amplified in wild type PHA producers to improve the production of PHA homopolymers and copolymers directly from diol and other alcohol feedstocks. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for separating L-amino-acid oxidase from venin
It was involved in separating L-amino acid oxidase from the snake venom of Agkistrodonhalysussuriensis. Through two steps of colum chromatography (i.e. heparin fast flow and qsepherose fast flow) L-amino acid oxidase was separated and purified from the snake toxin of Gloydius ussuriensis. Not including transfer between concentrating and buffer system. It could avoid the influence of freezing and the pH value change to enzyme activity. The method was found to be simple, rapid and convenient. The ratio of recovery was high.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Fast detection method for dihydro flavanol 4-reductase/leucocyanidin reductase in tree plant
InactiveCN101482500BSimple methodDoes not require extraction and concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsVitamin CLeucocyanidin
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
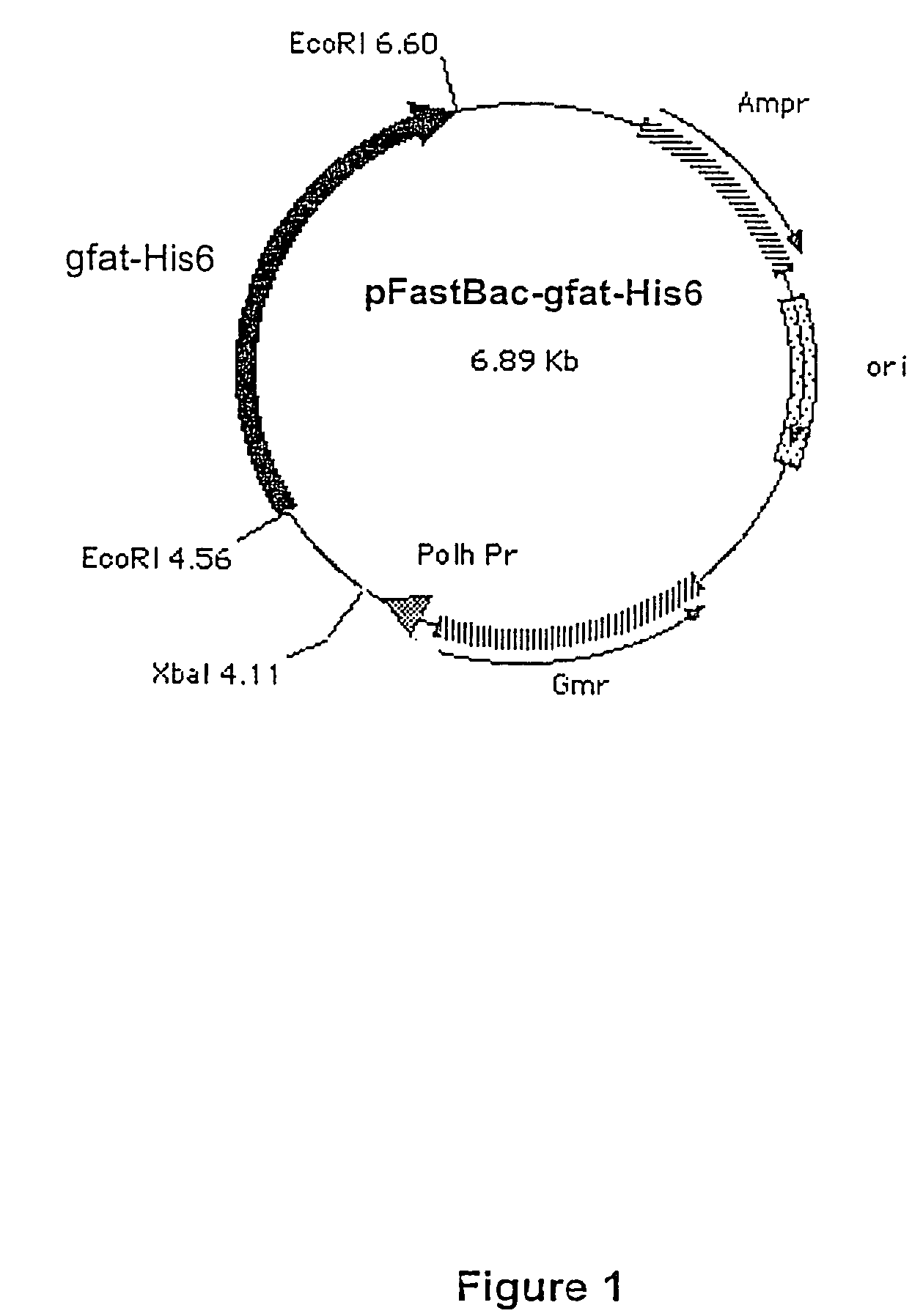
Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) comprising an internal purification marker and use thereof for the screening of compounds
InactiveUS7625734B2High level of of activityHigh level of purityBacteriaSugar derivativesBiologyFructose 6-phosphate
The invention relates to a protein with enzymatic activity, comprising a GFAT sequence and at least one sequence of a purification marker, the sequence for the purification marker being inserted between two consecutive amino acids of the GFAT sequence.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
A kind of c-type β-glucosidase mutant and its expression plasmid and recombinant bacteria
InactiveCN104531743BIncrease enzyme activityAchieve efficient optimizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTryptophanMutant
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com