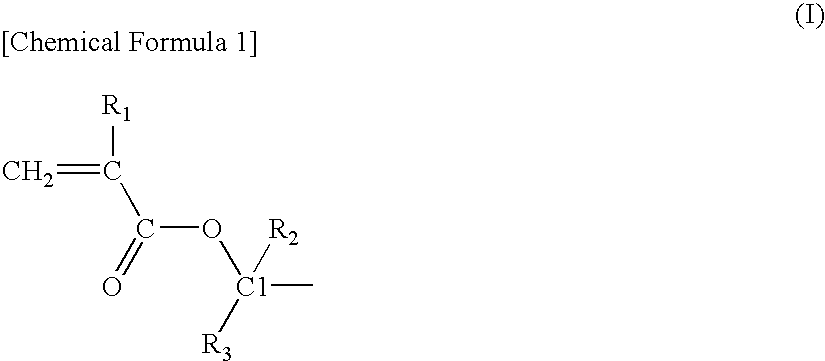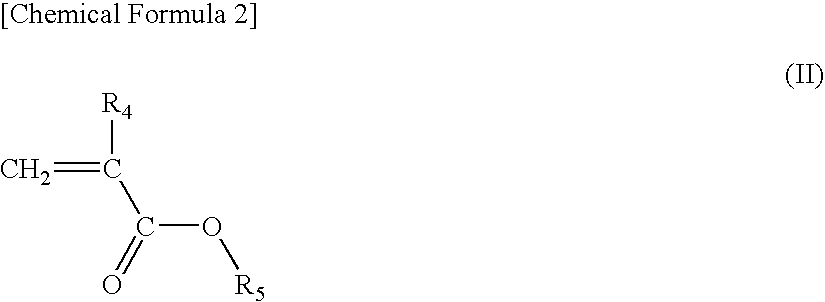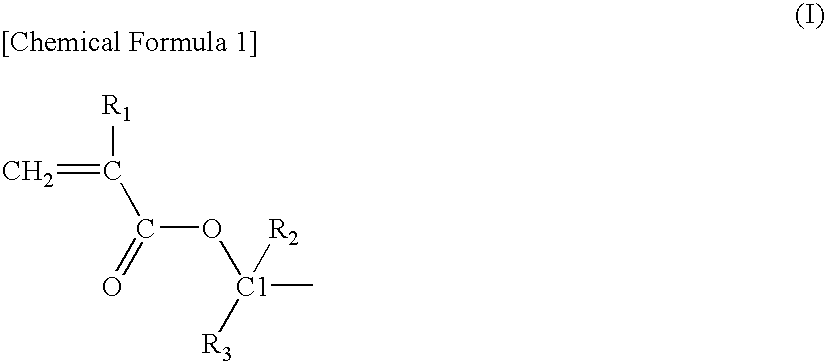Acrylic star polymer
a star polymer and acrylic acid technology, applied in the field of acrylic acid-based star polymer, can solve the problems of not being able to achieve satisfactory properties and cannot be said to control molecular weight, and achieve the effect of excellent acid decomposability and great industrial utility valu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0051]Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 331 g of tetrahydrofuran (THF) containing 13 mmol of lithium chloride was maintained at −40° C. and 26 mmol of sec-butyllithium (SBL) was added while stirring, and then 88 g of a THF solution containing 97 mmol of 2-methyl-2-adamanthyl methacrylate (2MAdMA), 78 mmol of a mixture (TLMA) of (±)-octahydro-3-oxo-4,7-methanoisobenzofuran-5-ylmethacrylate and a (±)-octahydro-1-oxo-4,7-methanoisobenzofuran-5-ylmethacrylate as a positional isomer and 19 mmol of tert-butyl methacrylate (tBMA) was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and gas chromatography (hereinafter, abbreviated as GC) analysis revealed that the monomer was completely consumed.
[0052]Then, 12 g of a THF solution containing 22 mmol of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol dimethacrylate (MDMA) was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution ...
example 2
[0053]Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 233 g of THF containing 15 mmol of lithium chloride was maintained at −40° C. and 31 mmol of SBL was added while stirring, and then 171 g of a THF solution containing 88 mmol of 2MAdMA, 88 mmol of methacrylic acid-5-oxo-4-oxatricyclo[4.2.1.03,7]nonan-2-yl (NLMA) and 19 mmol of tBMA was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and GC analysis revealed that the monomer was completely consumed.
[0054]Then, 12 g of a THF solution containing 22 mmol of MDMA was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and GC analysis revealed that the MDMA monomer was completely consumed, and then the reaction was terminated by the THF solution containing hydrochloric acid. The reaction-terminated solution was poured into a large amount of water thereby to precipitate a poly...
example 3
[0055]Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 341 g of THF containing 7 mmol of lithium chloride was maintained at −40° C. and 14 mmol of SBL was added while stirring, and then 10 g of a THF solution containing 22 mmol of 2MAdMA was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and GC analysis revealed that the 2MAdMA monomer was completely consumed. Then, 78 g of a THF solution containing 66 mmol of 2MAdMA, 88 mmol of TLMA and 19 mmol of tBMA was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and GC analysis revealed that the monomer was completely consumed.
[0056]Then, 12 g of a THF solution containing 22 mmol of MDMA was added dropwise and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. A small amount of the reaction solution was taken out from the reaction system and GC analysis revealed that the MDMA monomer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com