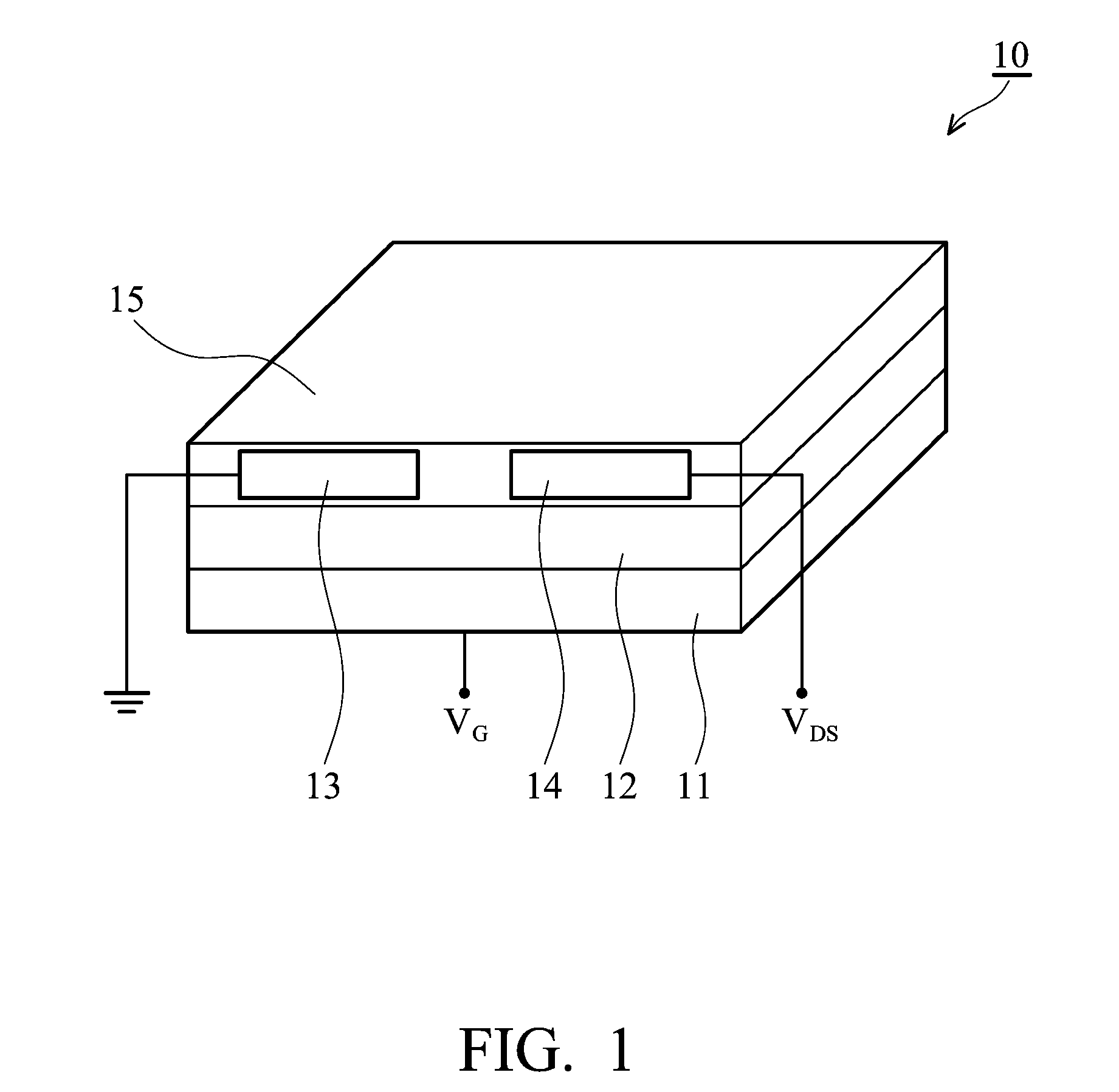
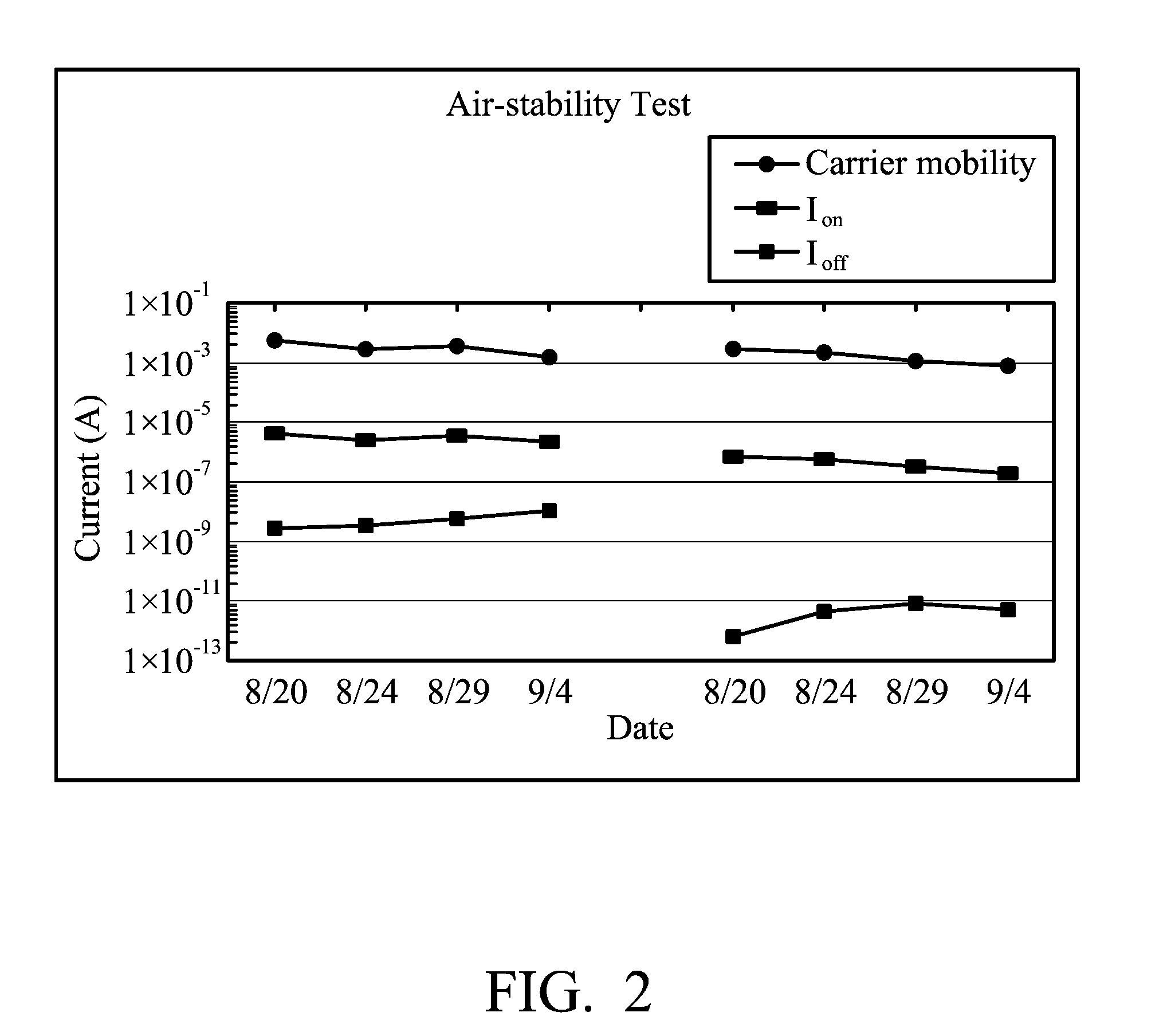
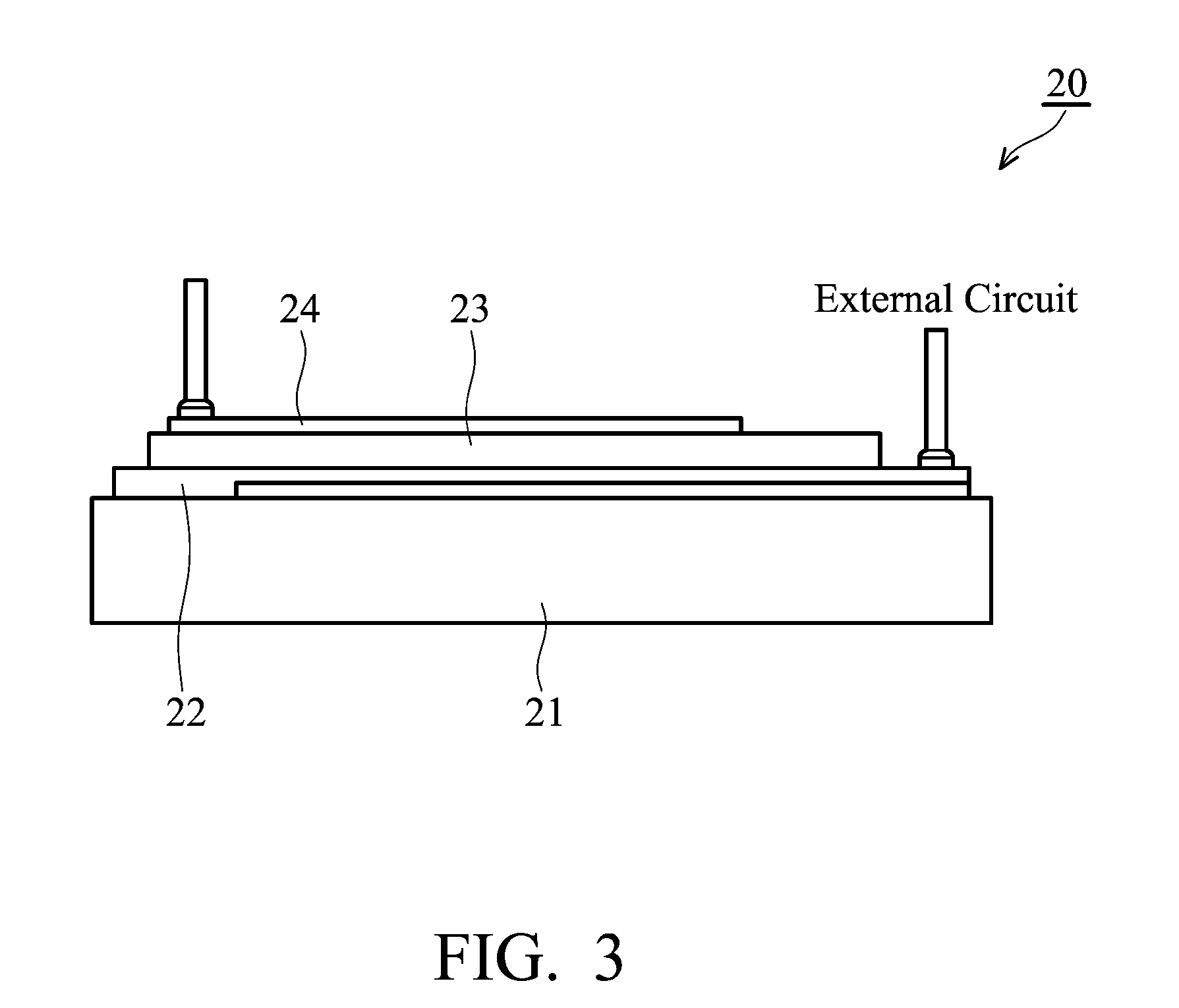
Soluble polythiophene derivatives
a technology of polythiophene and derivatives, which is applied in the field of soluble polythiophene derivatives, can solve the problems of limiting the practicability of optoelectronic devices made of polymer semiconducting materials and reducing the power conversion efficiency of oscs, and achieves the effects of improving the degree of intramolecular conjugation and intermolecular - interaction, and increasing carrier mobility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparative Example 1
Synthesis of p-thiophene-phenylene-thiophene (S2)
[0042]
[0043]Scheme1 depicts the synthesis of compound S2 (p-TPT). Compound 8 was prepared by the synthetic method described in Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5033-5036. 626 mg (1 mmol) of Compound 8 and 392 mg (2.2 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) were dissolved in 20 mL of chloroform in a 100 mL two-necked bottle. The bottle was wrapped by Al foil and kept under N2 atmosphere overnight. The organic phase was extracted by a chloroform and saturated sodium chloride solution. Next, the organic phase was dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated on a rotary evaporator. A pale yellow solid S2 was obtained after precipitation by methanol.
[0044]NMR data of the compound S2 was as follows.
[0045]1H NMR (CDCl3, 200 MHz) δ 2.29 (s, 12H), 6.94 (s, 2H), 7.05˜7.12 (m, 16H), 7.29 (s, 2H).
Preparative Example 2
Synthesis of m-thiophene-phenylene-thiophene (S3)
[0046]
[0047]Scheme 2 depicts the synthesis of compoun...
example
Example 1
Synthesis of Polymer P6
[0067]
[0068]Scheme 7 depicts the synthesis of compound P6. 0.3 mmol of p-TPT, 5.5 mg (2 mol %) of 5,5′-bis-trimethylstanny 4,4′-bis(dodecyl)-2,2′-bithiophene, 14.6 mg (16 mol %) of tri(o-tolyl)phosphine and 5 mL of chlorobenzene were placed in a glass flask. After deoxygenation, the flask was placed in a microwave reactor (640 W, 30 min) for polymerization. After cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was added to methanol for precipitation. The polymer was filtered out and cleaned by using MeOH, acetone and hexane soxhelt extraction and chloroform was used to dissolve the polymer. Removal of the chloroform resulted in the polymer P6 (molecular weight: 25200 g / mol, λmax=490 (film)).
example 2
Synthesis of Polymer P8
[0069]
[0070]Scheme 8 depicts the synthesis of compound P8. 0.3 mmol of m-TPT, 5.5 mg (2 mol %) of 5,5′-bis-trimethylstannyl-4,4′-bis(dodecyl)-2,2′-bithiophene, 14.6 mg (16 mol %) of tri(o-tolyl)phosphine and 5 mL of chlorobenzene were placed in a glass flask. After deoxygenation, the flask was placed in a microwave reactor (640 W, 30 min) for polymerization. After cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was added to methanol for precipitation. The polymer was cleaned by using MeOH, acetone and hexane soxhelt extraction and chloroform was used to dissolve the polymer. Removal of the chloroform resulted in the polymer P8 (molecular weight: 16900 g / mol, λmax=442 (film)).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Short-circuit current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Short-circuit current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com