Modulators of p-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1
a technology of pselectin and glycoprotein, which is applied in the direction of immunological disorders, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the therapeutic application of these two antibodies, hampered attempts to use fas and tnfr2 molecules to control unwanted t cells, etc., to prevent immune activation, induce t cell depletion, and/or apoptosis in
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of an Anti-T Cell Apoptosis Inducing Protein (“TAIP”) Monoclonal Antibody
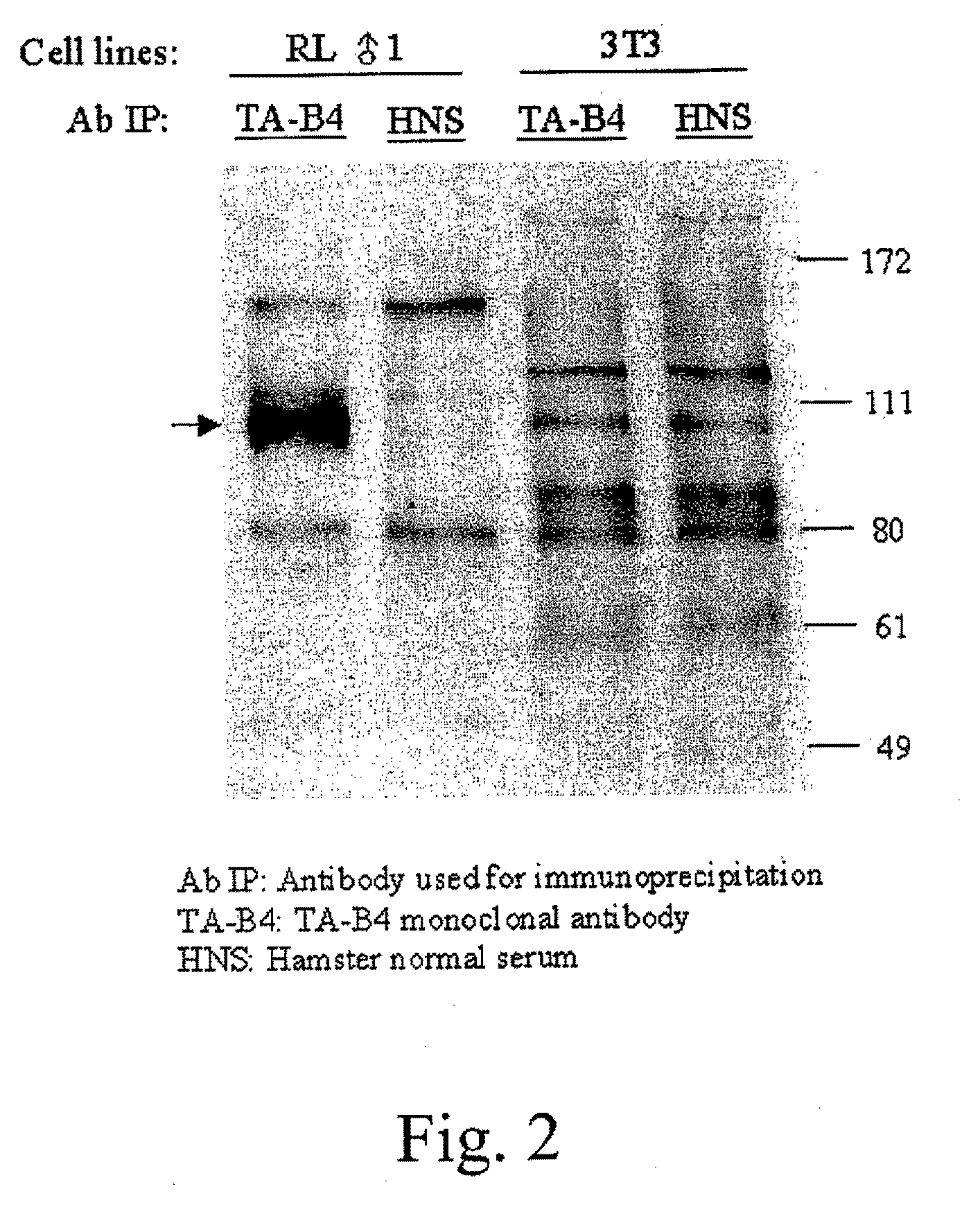
[0107]A TAIP-specific monoclonal antibody was generated by applying the well known cell fusion methods of Kohler and Milstein ((1976) European Journal of Immunology 6:511-519) to produce a hybridoma secreting desired antibodies. Antibody-producing cells from a hamster injected with Concanavalin A (Con A)-activated Balb / c spleen T cells were fused with a myeloma cell line to form an antibody secreting hybridoma. The two populations of cells were fused with polyethylene glycol, and the resulting antibody producing cells were cloned and propagated by standard tissue culture methods. One hybridoma generated according to these methods secreted a monoclonal antibody, designated TAB4, that was able to induce T cell apoptosis in vitro and deplete T cells in vivo. The protein recognized by TAB4 was designated T cell apoptosis inducing protein (TAIP).
[0108]C57BL / 6J (B6) and BALB / c mice were purchased from the...
example 2
Preparation of a Mouse Spleen Cell Suspension and the Activation and Enrichment of T cells
[0110]Mouse spleen was immersed in 8 ml of Hank's balanced salt solution (HBSS), gently minced with a sterile cover slip, transferred to a 15 ml centrifuge tube (Costar), and spun at 200×g for 5 minutes. The supernatant was discarded and the cell pellet was resuspended in the residual buffer by gently tapping the wall. The contaminating red blood cells (RBC) were lysed by the addition of 1 ml of RBC lysis buffer (0.6 M NH4Cl, 0.17 M Tris-base, pH 7.65), followed by a 2 min incubation at room temperature and rapid quenching with 9 ml of HBSS. The cells were pelleted at 200×g for 5 minutes, washed twice and resuspended in RPMI medium. The concentration and viability of cells in the mixture were determined with a hemocytometer (Cambridge Scientific Inc.) and Trypan blue exclusion.
[0111]The spleen cells were adjusted to a final concentration of 3×106 / ml with RPMI medium and Concanavalin A was added...
example 3
Apoptosis of Activated T cells
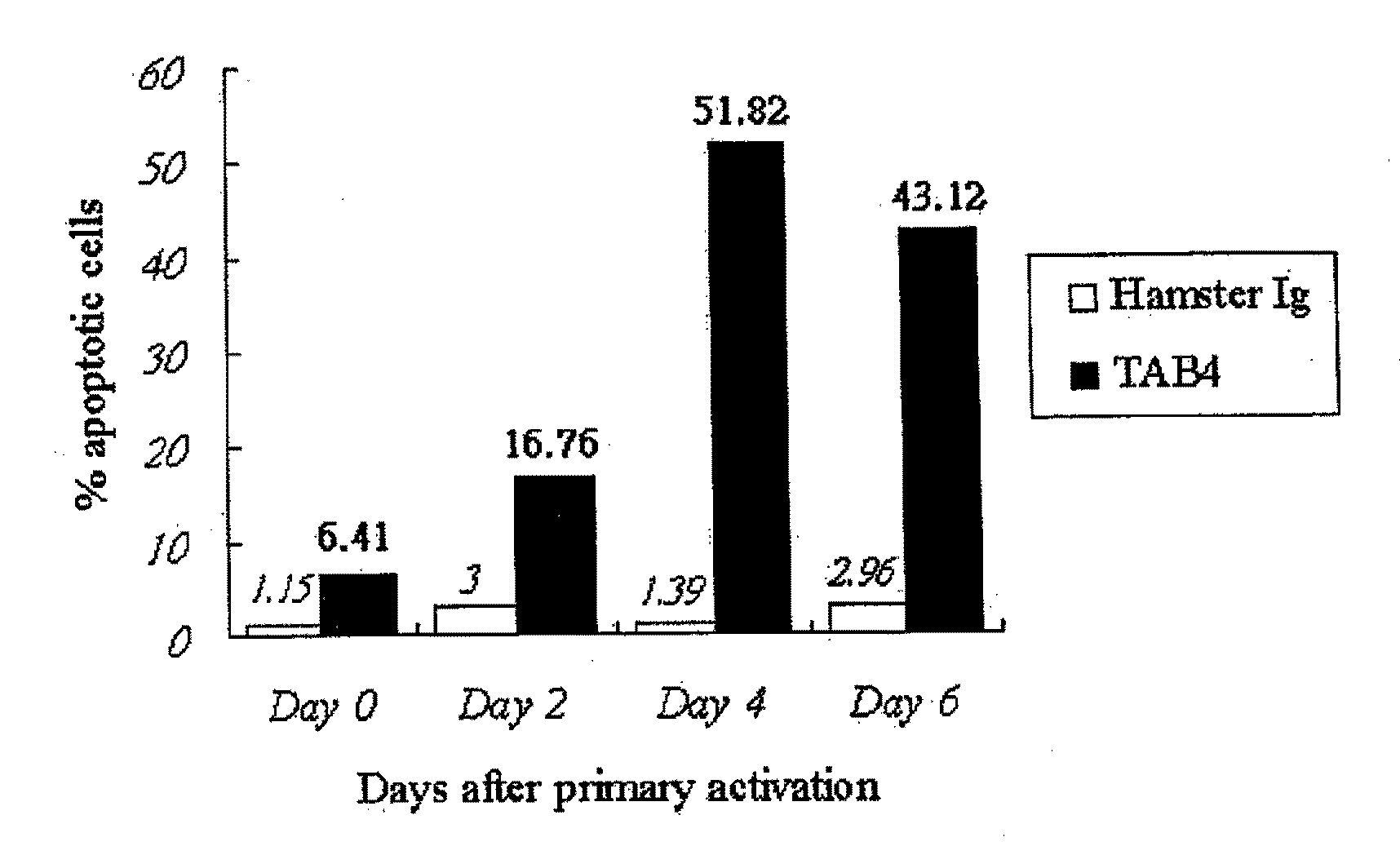
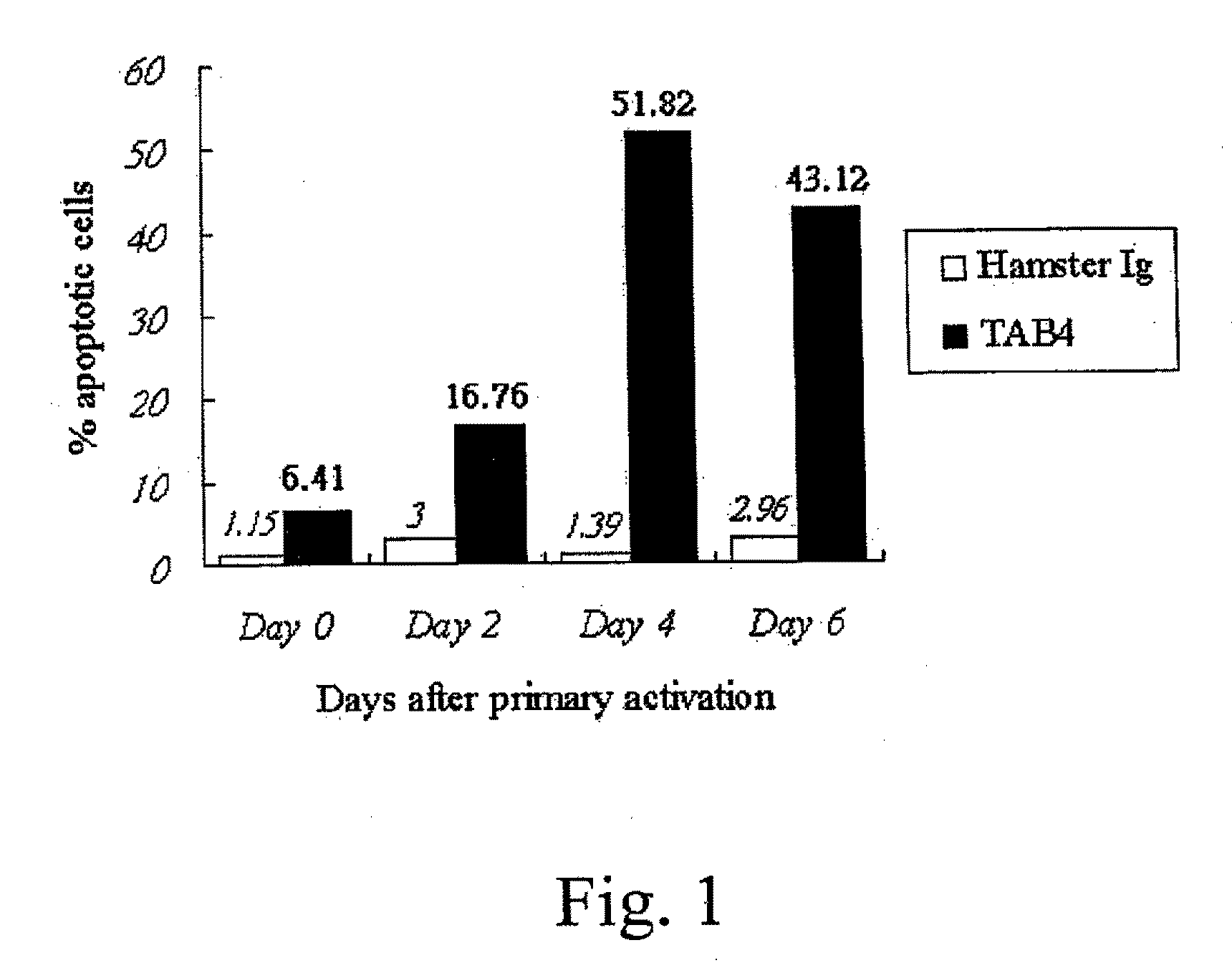
[0112]Activated T cells (see Example 2) were resuspended to a final concentration of 5×105 cells / ml in RPMI medium containing 5 ng / ml of IL-2, and treated with control Ig, TAB4, or anti-CD3 according to the conditions shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Experiment groupsTreatment*Negative control3 ug / ml hamster Ig5 ng / ml IL-23 ug / ml cross-linker antibody (anti-hamster Ig)TAB43 ug / ml TAB4 hamster mAb5 ng / ml IL-23 ug / ml cross-linker antibody (anti-hamster Ig)Positive control1 ug / ml anti-CD3 mAb5 ng / ml IL-21 ug / ml cross-linker antibody (anti-mouse Ig)*Final concentration of the designated reagents in the medium.
[0113]After an incubation period of 18-24 hours, the extent of apoptosis in each culture was determined using the 7-AAD apoptosis assay. The treated cells were transferred to FACS tubes (Falcon), washed twice with ice-cold FACS solution (1% fetal bovine serum, 0.05% sodium azide in PBS), pelleted at 200×g at 4° C. The cells were resuspended in ice-cold FACS sol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Biological properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com