Oil emulsion
a technology of oil emulsion and oil, applied in the petroleum industry, fuels, liquid carbonaceous fuels, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable practical application, unresolved problems, and unresolved problems such as the inability to completely overcome the drawback of an emulsion fuel unlikely to igni
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
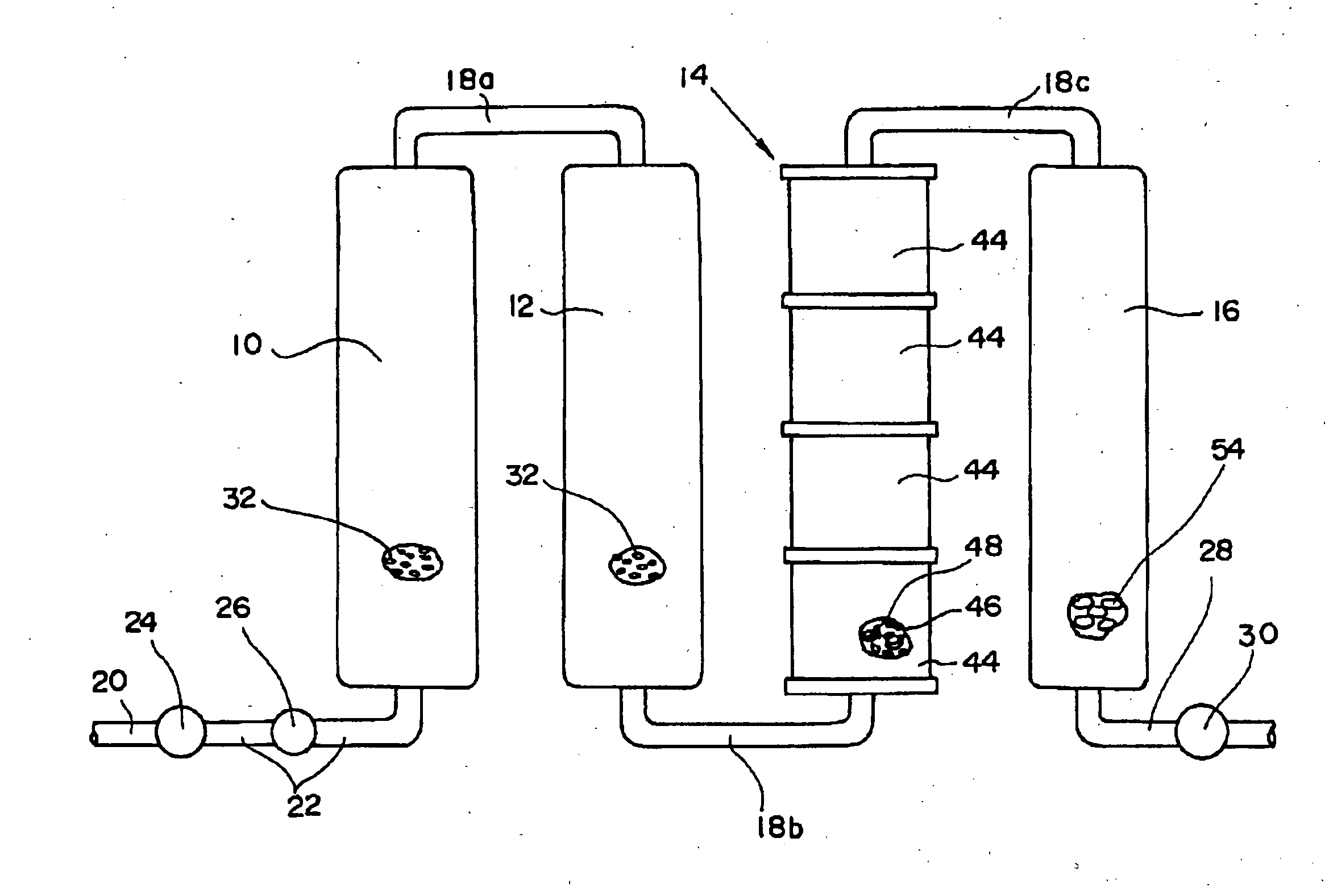
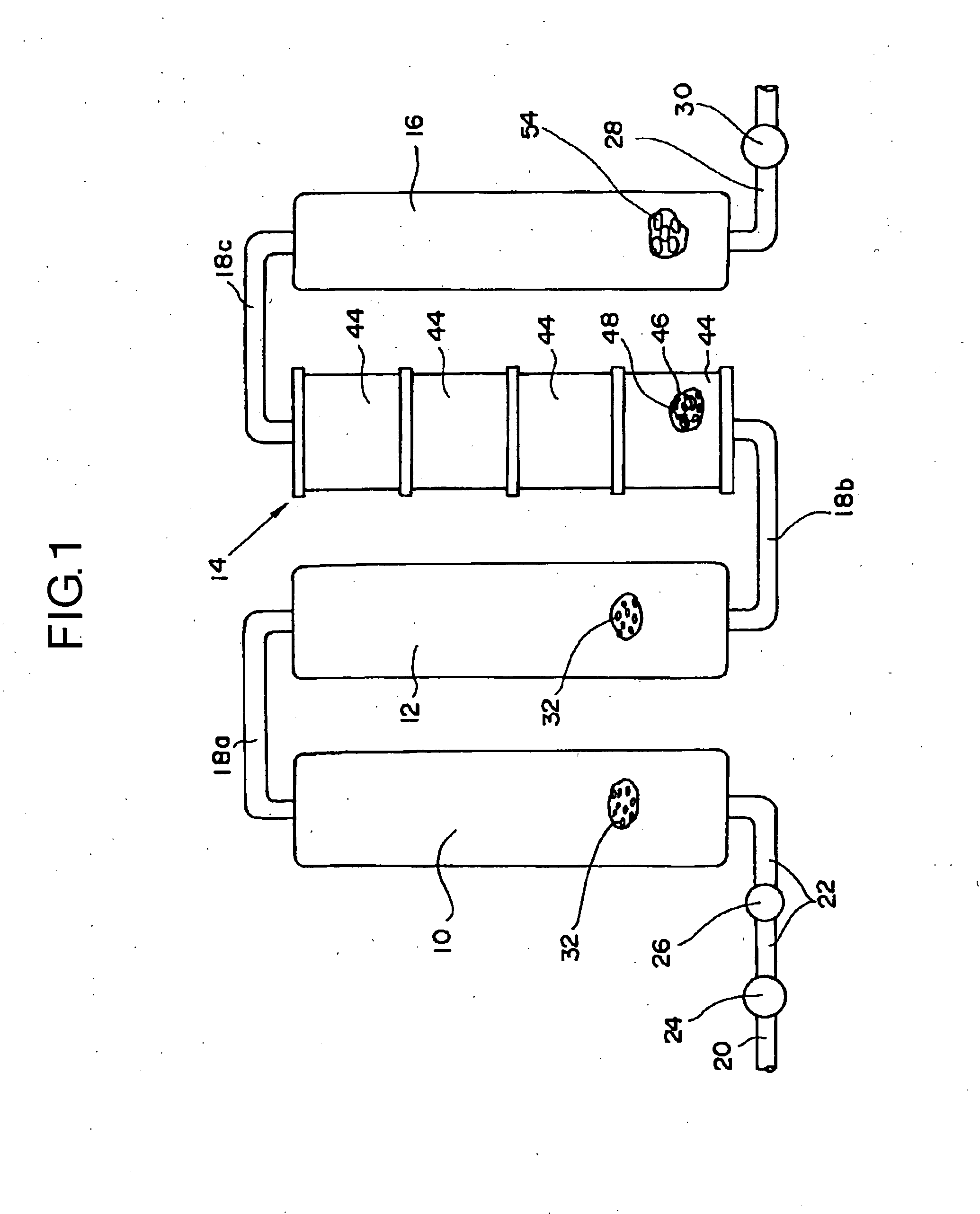
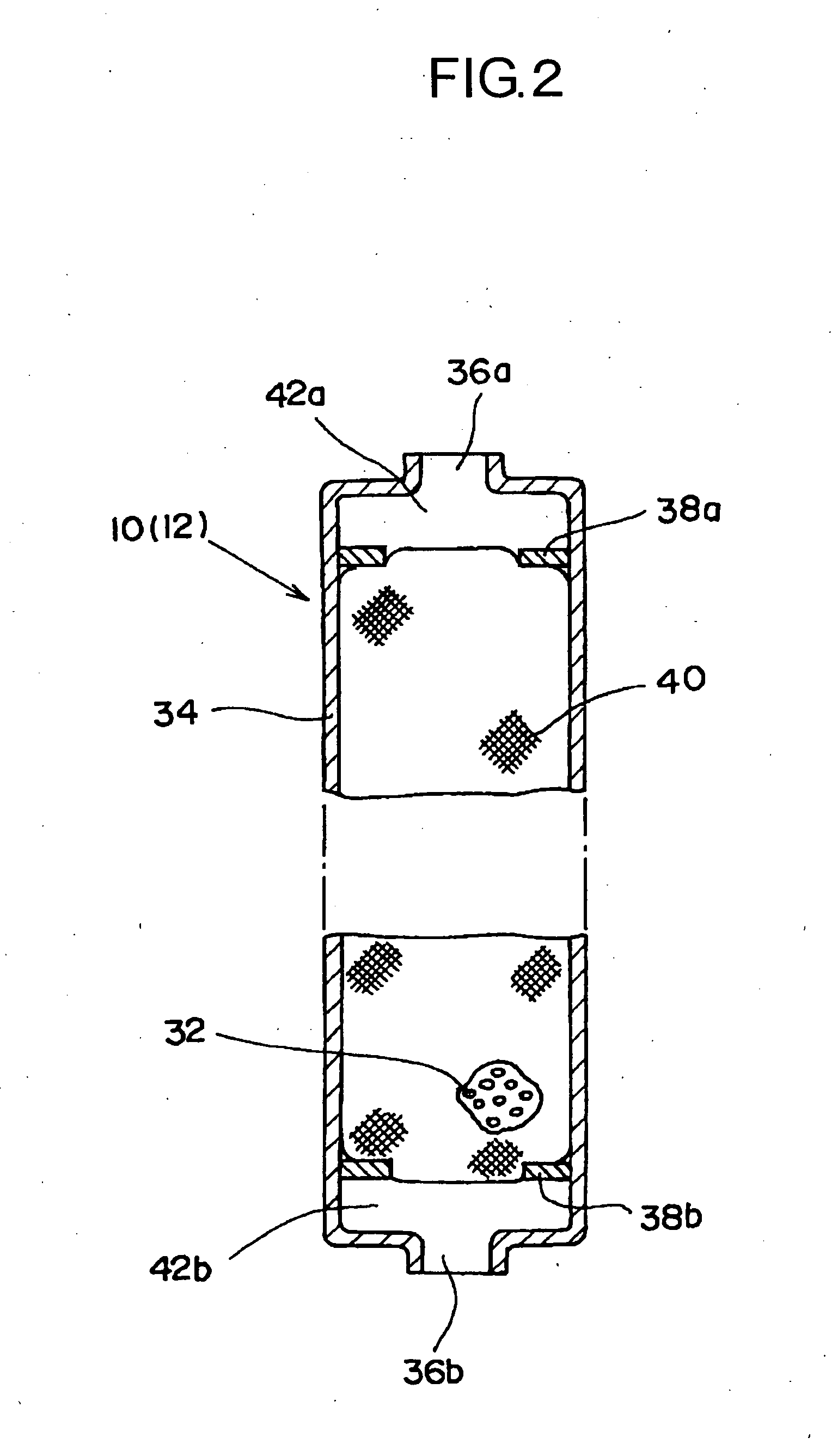
[0028]The specific type of water used in the invention has a minus oxidation-reduction potential and contains a hydrogen ion (H+), hydrogen (H2), a hydroxyl group (OH−), active hydrogen and dissolved oxygen. The emulsion fuel using this specific type of water facilitates combustion by the action of the hydrogen ion (H+), hydrogen (H2), hydroxyl group (OH−), active hydrogen, dissolved oxygen and the like, and is able to ignite by means of a commercially available burner. Accordingly, it is not necessary to use a specific type of expensive burner or a specific combustion method as conventionally employed, thus being very economical. The oil emulsion of the invention can readily ignite by means of a commercially available burner, so that combustion close to complete combustion becomes possible, and emissions of CO2 and NOx generated by incomplete combustion of a conventional emulsion fuel that is unlikely to ignite can be significantly reduced. In the practice of the invention, the oil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| combustion efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com