Methods and means for treating DNA repeat instability associated genetic disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0065]Immortomyoblast cell lines were derived from DM500 or CTG110 mice using standard techniques known to the skilled person. DM500 mice were derived from mice obtained from de Gourdon group in Paris. CTG110 mice are described below and present at the group of Wiering a and Wansink in Nijmegen. Immortomyoblast cell lines DM500 or CTG 110 with variable (CTG)n repeat length in the DMPK gene were grown subconfluent and maintained in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 33° C. on 0.1% gelatin coated dishes. Myoblast cells were grown subconfluent in DMEM supplemented with 20% FCS, 50 μg / ml gentamycin and 20 units of γ-interferon / ml. Myotube formation was induced by growing myoblast cells on Matrigel (BD Biosciences) coated dishes and placing a confluent myoblast culture at 37° C. and in DMEM supplemented with 5% horse serum and 50 μg / ml gentamycin. After five days on this low serum media contracting myotubes arose in culture and were transfected with the desired oligonucleotides. For transfection NaC...
example 2
FIG. 4
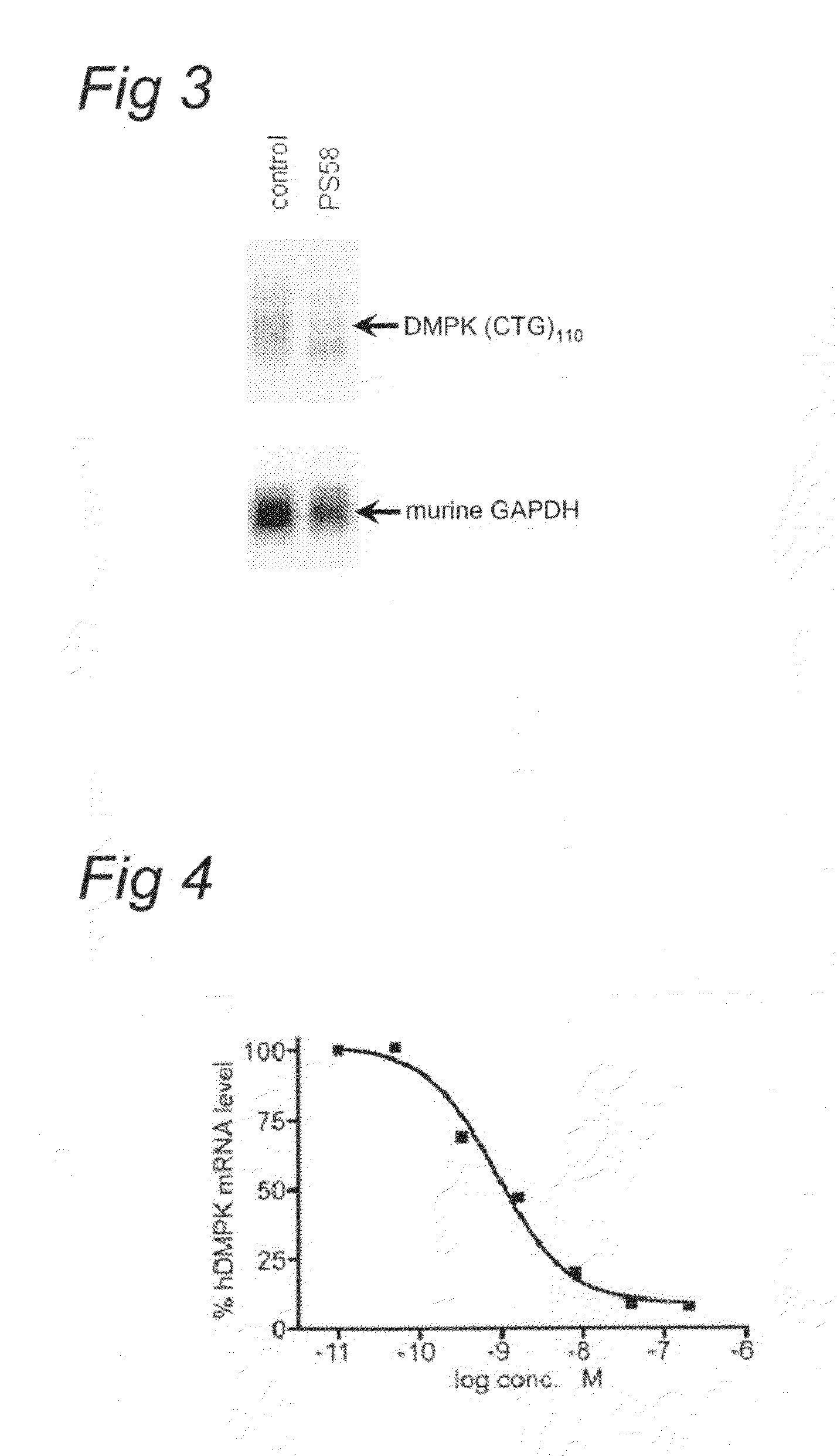
[0070]The DM500 immortomyoblast cell line carrying a human DMPK gene with an approximate (CTG)500 repeat expansion was cultured, prepared and transfected as described above (see example 1). In this example, the transfection was carried out with PS58 at different concentrations. Eighty four hours after start of treatment, the myotubes were harvested and Northern blot analysis was performed on isolated RNA as described above (see example 1).
[0071]FIG. 4 shows the quantification of the hDMPK mRNA signal preformed by phosphoimager analysis and normalized to the GAPDH signal at different concentrations. Under these conditions, a half maximal effect was observed at around 1 nM.
example 3
FIGS. 5 and 6
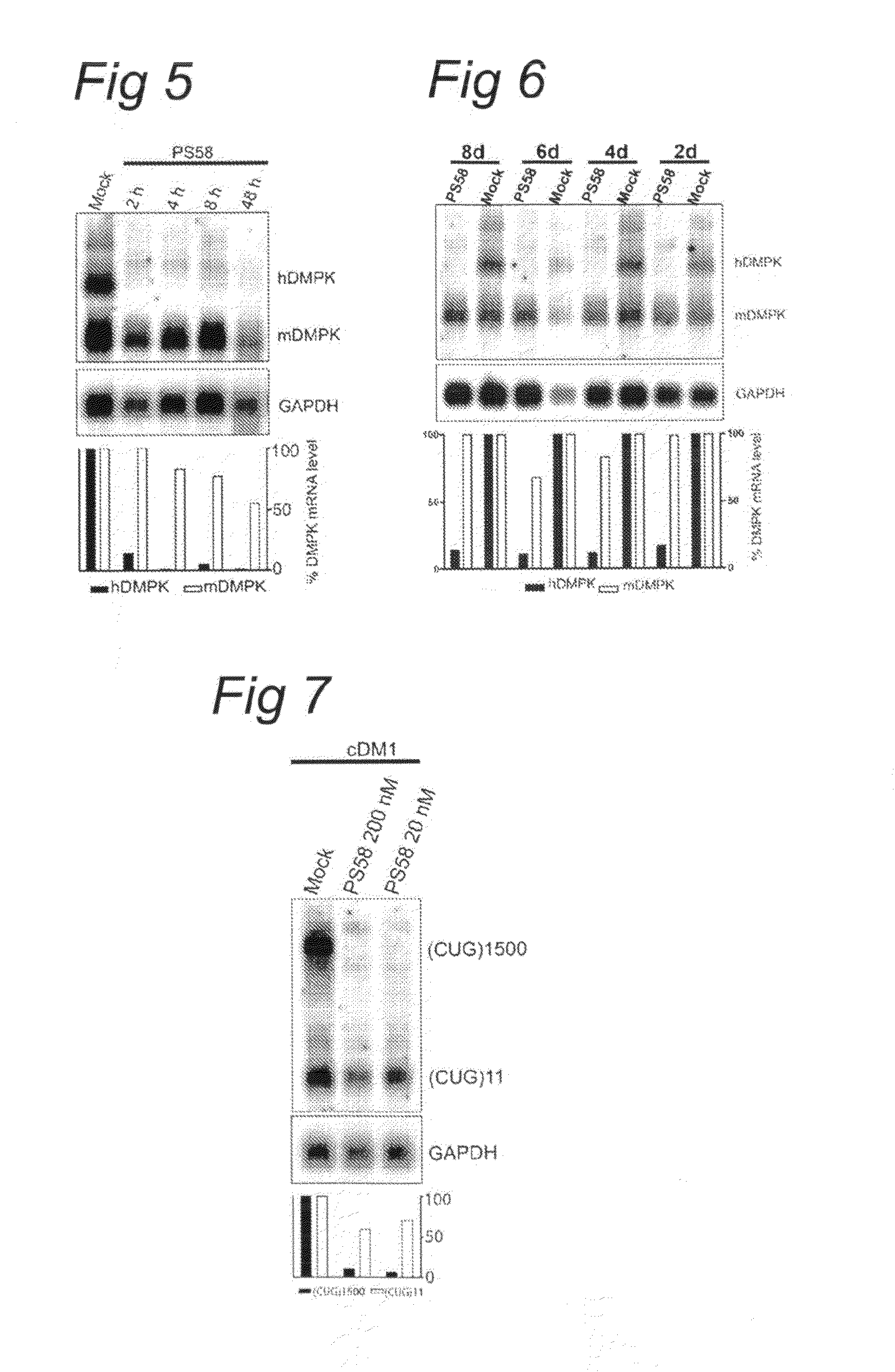
[0072]The DM500 immortomyoblast cell line carrying a human DMPK gene with an approximate (CTG)500 repeat expansion was cultured, prepared and transfected as described above (see example 1). However, in this example the transfection with 200 nM PS58 was carried out at different time points. Usually DM500 myotubes were harvested seven days after switching to low serum conditions to induce myotube formation. The standard procedure (as in example 1 and 2) was to start treatment (transfection) 48 h (two days) before harvesting. Now, treatment with PS58 was started 2 h-48 h (FIG. 5) or 2 d-8 d (FIG. 6) before harvesting. Northern blot analysis and quantification was performed as before.
[0073]FIG. 5 shows that expanded hDMPK mRNA in DM500 myotubes was decreased rapidly within 2 h of treatment with oligonucleotide PS58 compared to mock control treatment.
[0074]FIG. 6 shows a persistent decrease in expanded hDMPK mRNA in DM500 myotubes for at least 8 days. Please note that in the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Radioactivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com