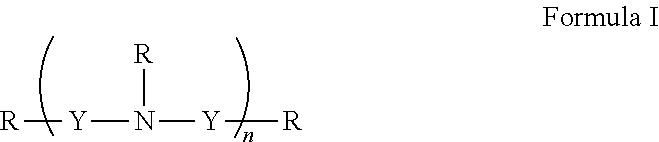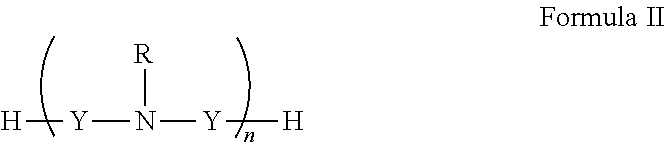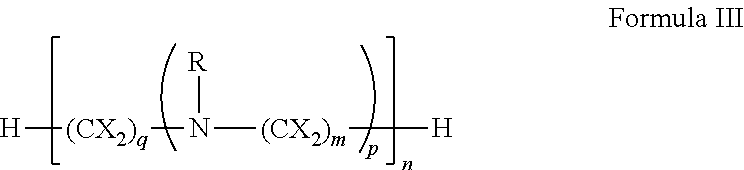Substituted polyamines as inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps
a technology of bacterial efflux pump and substituted polyamine, which is applied in the direction of antibiotics, drug compositions, applications, etc., can solve problems such as therapeutic failures, and achieve the effects of increasing susceptibility to drugs, decreasing the translocation of these agents, and increasing the affinity of nitrogenous substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Substituted Polyamines
[0151]In general, polyamines may be derivatized using by, e.g., reductive amination with aryl aldehydes. Suitable polyamines include spermidine, spermine, norspermidine, spergaulin, 1,3,5-triamimocyclohexane, agrbactin, acyria pigments, and other products possessing 2 or more chemically modifiable amines. The polyamine substitution pattern may reside on one, two or three or more ring systems interconnected and in any pattern in a 3-D array.
[0152]For example, paromomycin derivatives (FIG. 2 and Table 2) are aminoglycosides possessing five primary amino functional groups (FIG. 1 and Table 1) and were produced by 5-N-benzylation using unsubstituted or substituted benzaldehydes under reduction by sodium borohydride. Many of these polysubstituted paromomycins are substrates of the efflux system of Haemophilus influenzae (Table 3) and act in synergy with tetracycline, doxycycline, and gentamicin to increase antibiotic susceptibility in H. influenzae (T...
example 2
Susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae to Various Paromomycin Derivatives
[0155]AcrAB deleted strains of H. influenzae were constructed (see, e.g., Provence, D. L. and R. Curtiss III. (1994) In P. Gerhardt, R. G. E. Murray, W. A. Wood, and N. R. Krieg. (ed.), “Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology,” American Society for Microbiology, Washington. pp. 317-347). Deletion of acrAB was confirmed by the absence of intact target DNA in a PCR assay.
[0156]MICs of selected antimicrobial agents were determined by a standard broth microdilution procedure with cation adjusted Mueller Hinton broth (Becton Dickinson, Cockeysville, Md.) and an inoculum of 5×105 CFU / ml according to NCCLS performance and interpretive guidelines (NCCLS. 1997. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility. Tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, Fourth Edition; Approved Standard. NCCLS document M7 A4 (ISBN 1 56238 309 4). NCCLS, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pa. 19087). Antimicrobial agents t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperature Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com