Composition and dressing with nitric oxide
a technology of nitric oxide and composition, applied in the field of composition and dressing with nitric oxide, can solve the problems of short half-life, inability to target or selectivity, and inability to achieve high concentrations of toxic substances,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A zinc ion-exchanged zeolite was prepared by slurrying 40 g of a commercial sodium zeolite A (zeolite Doucil 4A from PQ Silicas UK Ltd.—mean particle diameter typically 3 to 5 μm) in 4 litres of 0.05 molar zinc acetate solution for 24 hours. The resulting ion exchanged zeolite was filtered, washed with water and dried at 300° C. under vacuum for 3 hours.
Referring to formula IV, corresponding to formula III above but with M′=Zn and hence g=2, M=Na, and with x=2 for zeolite 4A, y=0.
w(ZnO).z(Na2O).Al2O3.xSiO2 IV
the resulting zeolite as measured by XRF had w 0.65 and z=0.58.
The dry zeolite was loaded with nitric oxide by exposure to dry NO gas at a pressure of 2 bar at 25° C. Excess NO was allowed to escape and the NO loaded zeolite was flushed with a flow of dry nitrogen gas to remove any NO which was physisorbed rather than adsorbed.
NO levels were measure using a Sievers NOA 280i chemiluminescence NO analyser. The NO was released by passing nitrogen gas of known humidity over the loa...
example 2
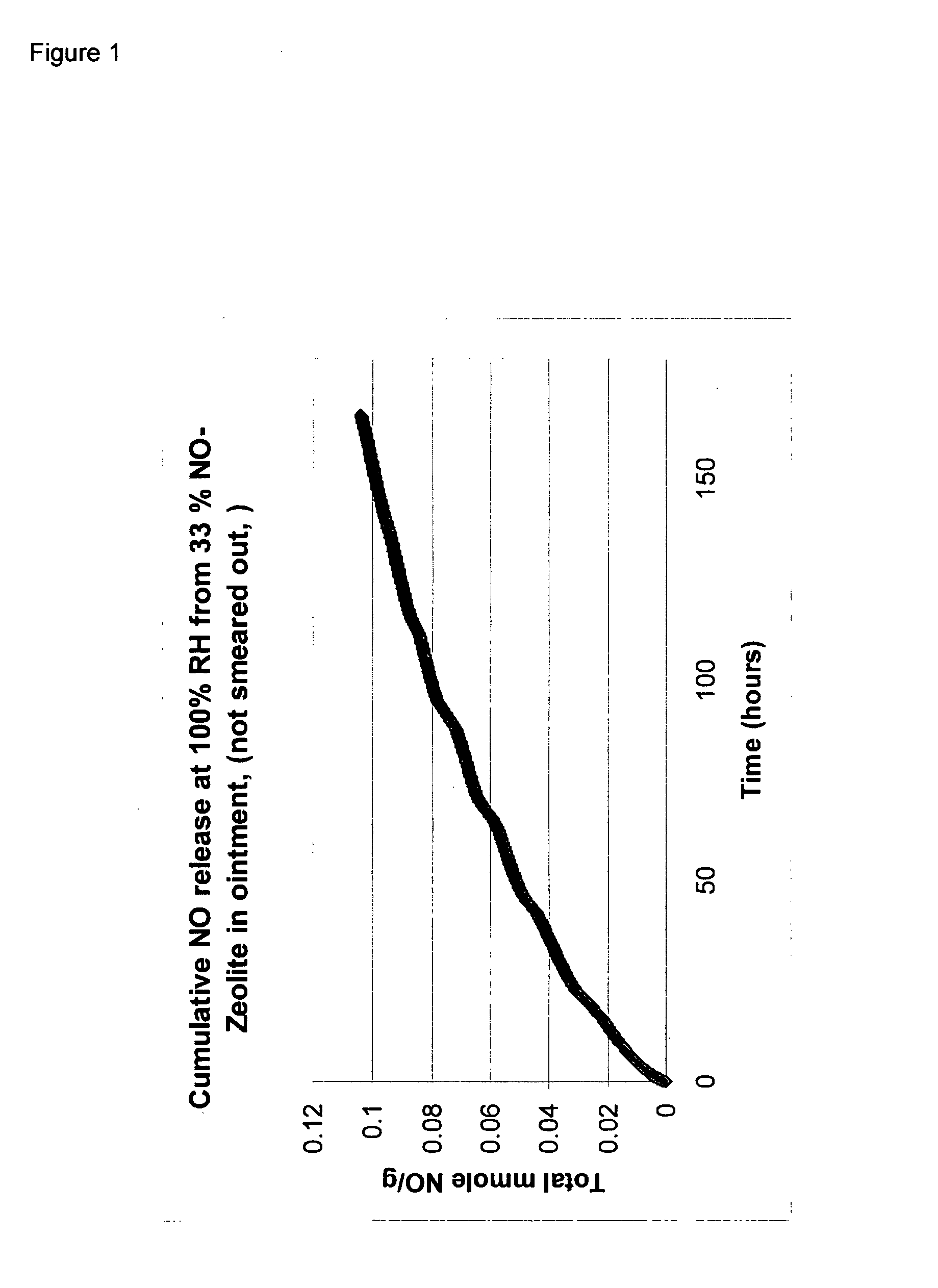
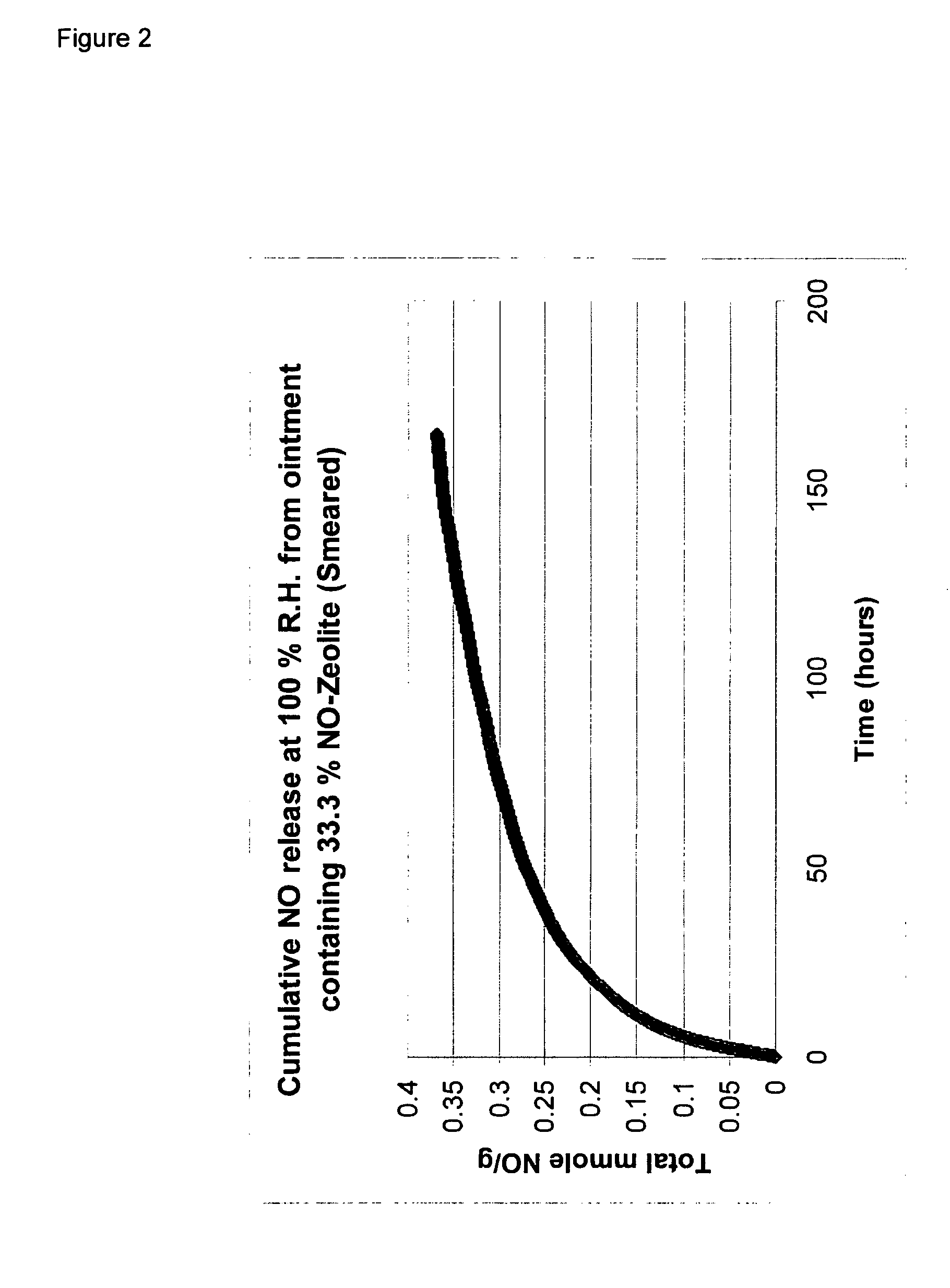
A homogeneous ointment was prepared from 6.6 grams of Zeolite-NO prepared as for Example 1 and 13.4 grams of Emulsifying Ointment (BP) supplied by Boots Company PLC (50% by weight white soft paraffin BP and 20% by weight liquid paraffin BP with 30% by weight emulsifying wax). The resulting ointment is referred to below as “Ointment A”.
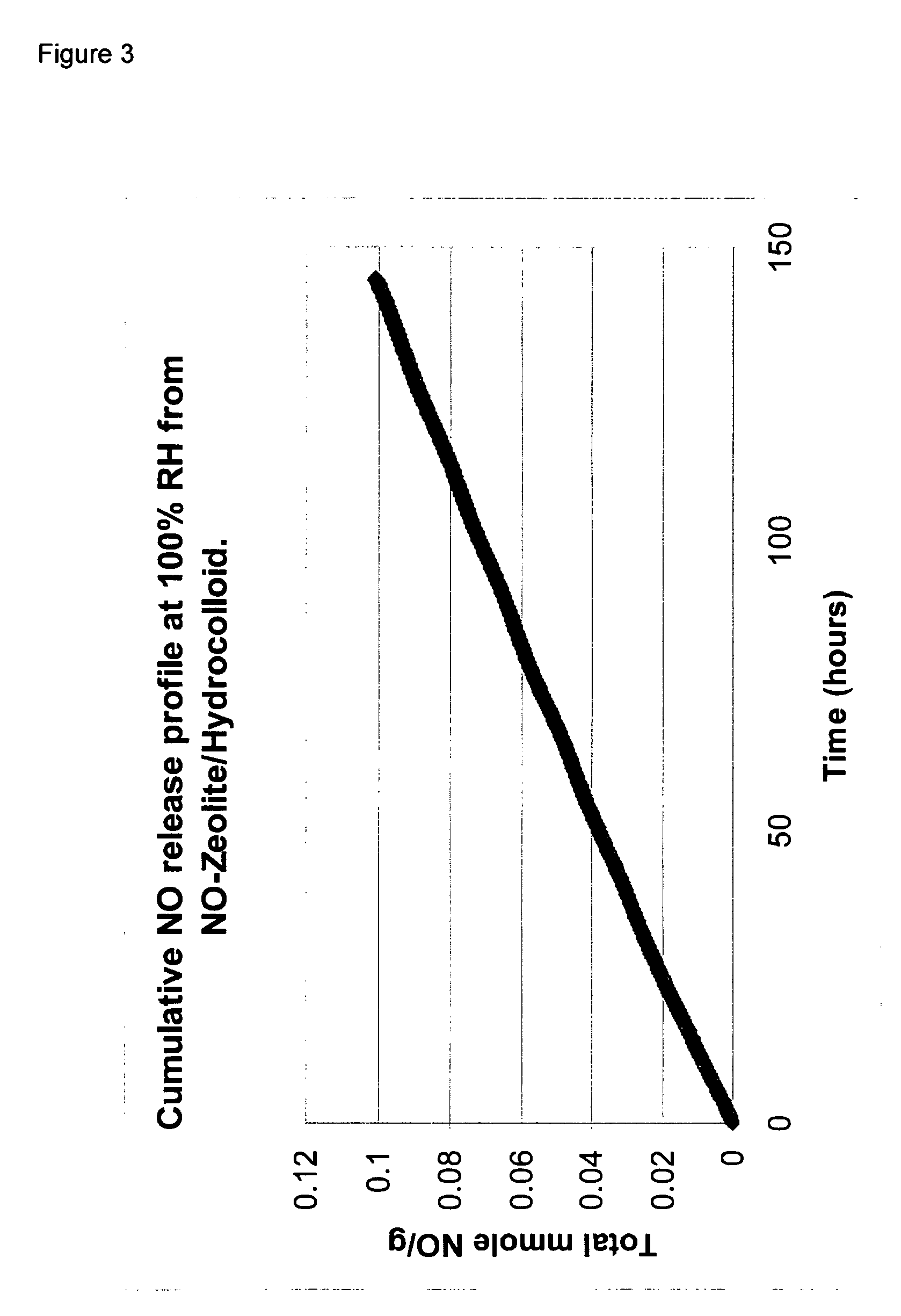
A hydrocolloid preparation was prepared from 5 grams of Blanose 7H4FX (Polyisobuthylene) and 1 gram of SCMC blended with 4 grams of the Zeolite-NO of Example 1 in a dry nitrogen atmosphere. The hydrocolloid preparation is referred to below as “Hydrocolloid B”
The rate of release of NO from samples of Ointment A and Hydrocolloid B levels were measured using a Sievers NOA 280i chemiluminescence NO analyser. In each case, a sample of either 0.4 grams of Ointment A or 0.3 grams of Hydrocolloid B was placed in a sealed glass vial (internal volume 4.55 mls), so that in each case the amount of NO initially in the vial was approximately the same for Hydrocolloi...
example 3
Zeolite 1
4 grams of zeolite 4A (Doucil 4A from PQ Silicas UK Ltd.—mean particle diameter 3 to 5 μm) was slurried in 400 mls of 0.05M zinc acetate solution for 24 hours. The slurry was then filtered, washed and dried. The resultant product was analysed by XRF (x-ray fluorescence) analysis.
Zeolite 2
This example is as for Example A 1 but zinc sulphate was used as the soluble salt and a more concentrated solution and shorter exchange time were used. 22.5 grams of zinc sulphate heptahydrate was dissolved in 60 grams of deionised water. 13 grams of zeolite 4A was first slurried in 22.5 grams of deionised water. The pH of the slurry was 11.4. The zeolite slurry was then added to the zinc sulphate solution. The mixture was slurried for 30 minutes washed and dried. The product was analysed by XRF.
Zeolite 3 (According to the First Method)
The procedure of example B was repeated, except that prior to adding the zeolite slurry to the zinc sulphate solution, the pH of the zeolite slurry was reduc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume mean particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume mean particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com