Method of converting feeds from renewable sources in co-processing with a petroleum feed using a catalyst based on nickel and molybdenum
a technology of nickel and molybdenum and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of metal/metal-oxide/metal-hydroxide catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, fuel, etc., can solve the problems of single stage of co-processing vegetable oil, limiting the optimum operation of the above hydrotreatment catalyst, and affecting the activity and stability of the catalyst as used in these patents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 3
According to the Invention
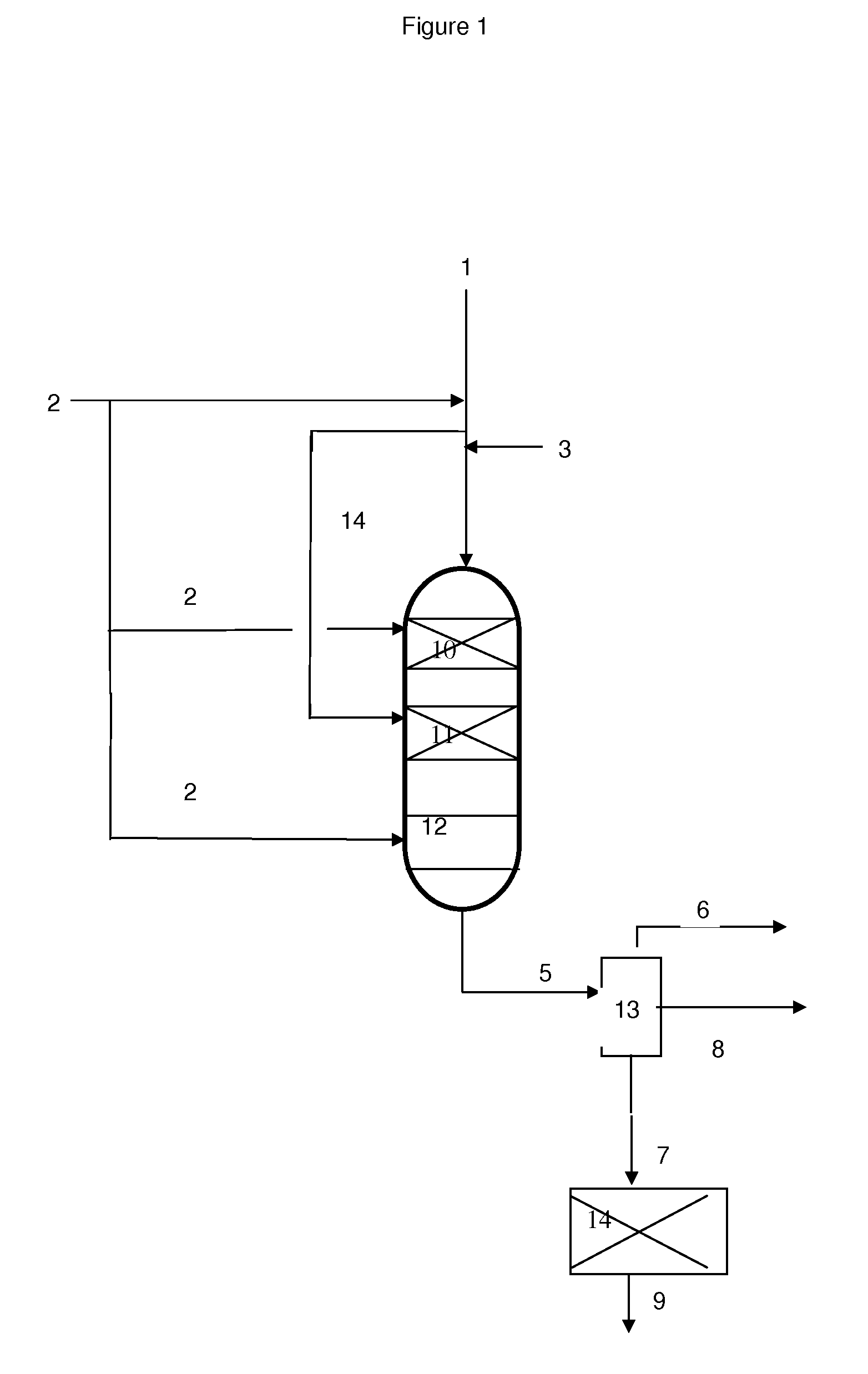
[0182]Method of hydrotreatment of a mixture constituted by a petroleum feed and a vegetable oil using a series of NiMo / alumina catalysts having an Ni / Mo atomic ratio equal to 0.02 +conventional NiMo / alumina having an Ni / Mo atomic ratio equal to 0.4 in both hydrotreatment stages a) and b).
[0183]The petroleum feed and the rapeseed oil feed are strictly identical to those described in Example 2. The mixture processed is also strictly identical to that described in Example 2 and constituted by 70 wt. % of petroleum gas oil and 30 wt. % of DND rapeseed oil.
[0184]The co-processing of this mixture is carried out in a fixed-bed isothermal unit of the descending flow type
[0185]The total feed is subjected to a first hydrotreatment stage a) in which the feed passes through a catalytic zone comprising 50 ml of NiMoP / alumina catalyst having an Ni / Mo atomic ratio equal to 0.02 intended to promote the reactions of HDO of the vegetable oil.
[0186]The effluent from the first...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com