Compositions and methods for cardiovascular disease
a cardiovascular disease and composition technology, applied in the field of cardiovascular disease compositions and methods, can solve the problems of ineffective and practical methods of inhibiting bmp signals via soluble receptors, endogenous inhibitors such as noggin and follistatin, and limited specificity of endogenous inhibitors such as follistatin for ligand subclasses, so as to reduce the circulating levels of apob-100 and/or ldl and/or total cholesterol,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
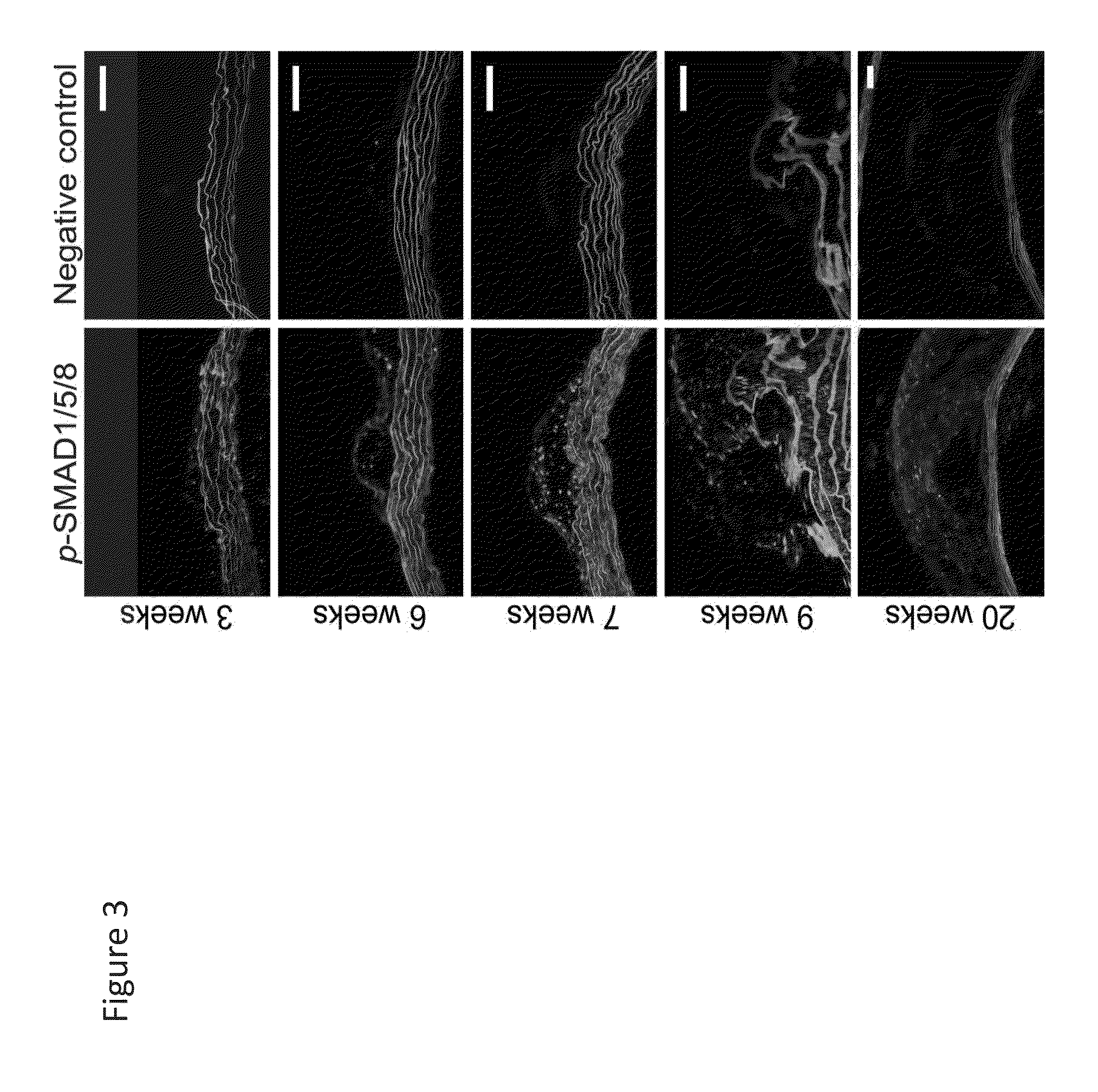
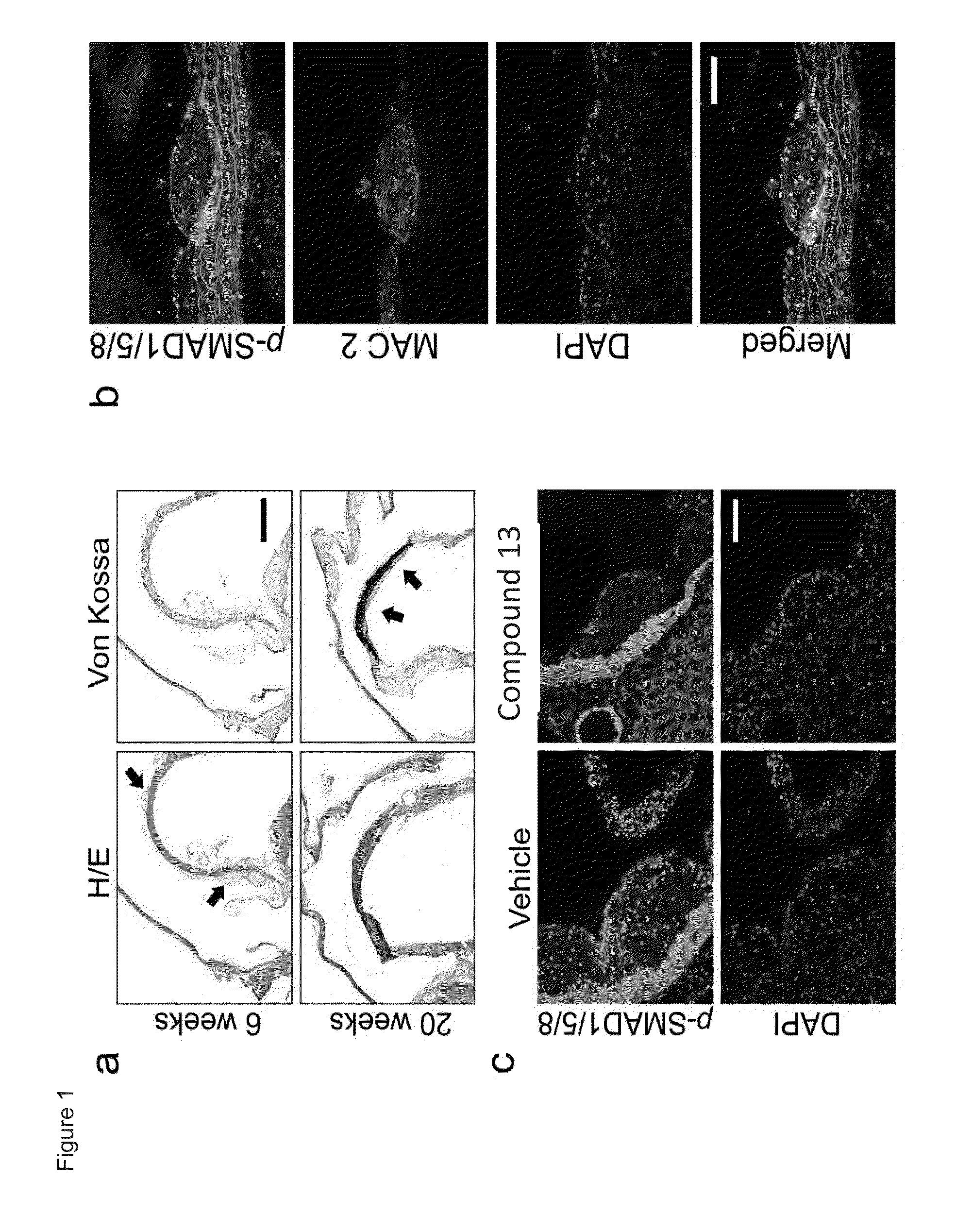
[0287]To elucidate the role of BMP signaling in vascular calcification and atherogenesis, BMP signaling was inhibited in vivo using small molecule and recombinant protein approaches. Mice deficient in the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR− / −) fed a high fat diet (HFD) were studied. (Ishibashi, S., Goldstein, J. L., Brown, M. S., Herz, J. & Burns, D. K. Massive xanthomatosis and atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed low density lipoprotein receptor-negative mice. J Clin Invest 93, 1885-1893 (1994).) These mice developed atheroma within 4-6 weeks followed by intimal and medial calcification by 16-20 weeks (FIG. 1a). At 20 weeks, there was extensive vascular calcification (as reflected by fluorescence labeled bisphosphonate uptake, Alizarin red staining and Von Kossa staining), inflammation (as reflected by cathepsin mediated cleavage of a near infrared imaging probe) and abundant lipid accumulation (as reflected by Oil Red O) in the aorta and large-vessel branches. (FIG. 2a-d)
[0288]...
example 2
Establishment of a Mouse Model of Atheromatous and Vascular Calcific Disease
[0316]The inventors' objectives are to demonstrate the effect of pharmacologic BMP inhibition upon the development of (i) atheromatous disease burden, and (ii) vascular calcification in an accepted animal model of atherosclerosis, in order to provide potential proof-of-concept that BMP inhibition can be an effective strategy for preventing atherosclerosis or limiting its progression.
[0317]BMPs are multifunctional protein ligands which form a subset of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) family of signaling proteins (Feng, X. H. & Derynck, R., Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21, 659-693 (2005)). BMPs, originally identified by their ability to induce ectopic bone formation, serve broad roles in gastrulation, developmental patterning, and organ formation. In the adult organism, BMP signals serve principally to mediate injury repair and inflammation. Aberrant BMP signaling may contribute to a number of acquired dise...
example 3
A BMP Inhibitor can Inhibit the Development of Vascular Calcification and Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation Associated with Atheromatous Disease
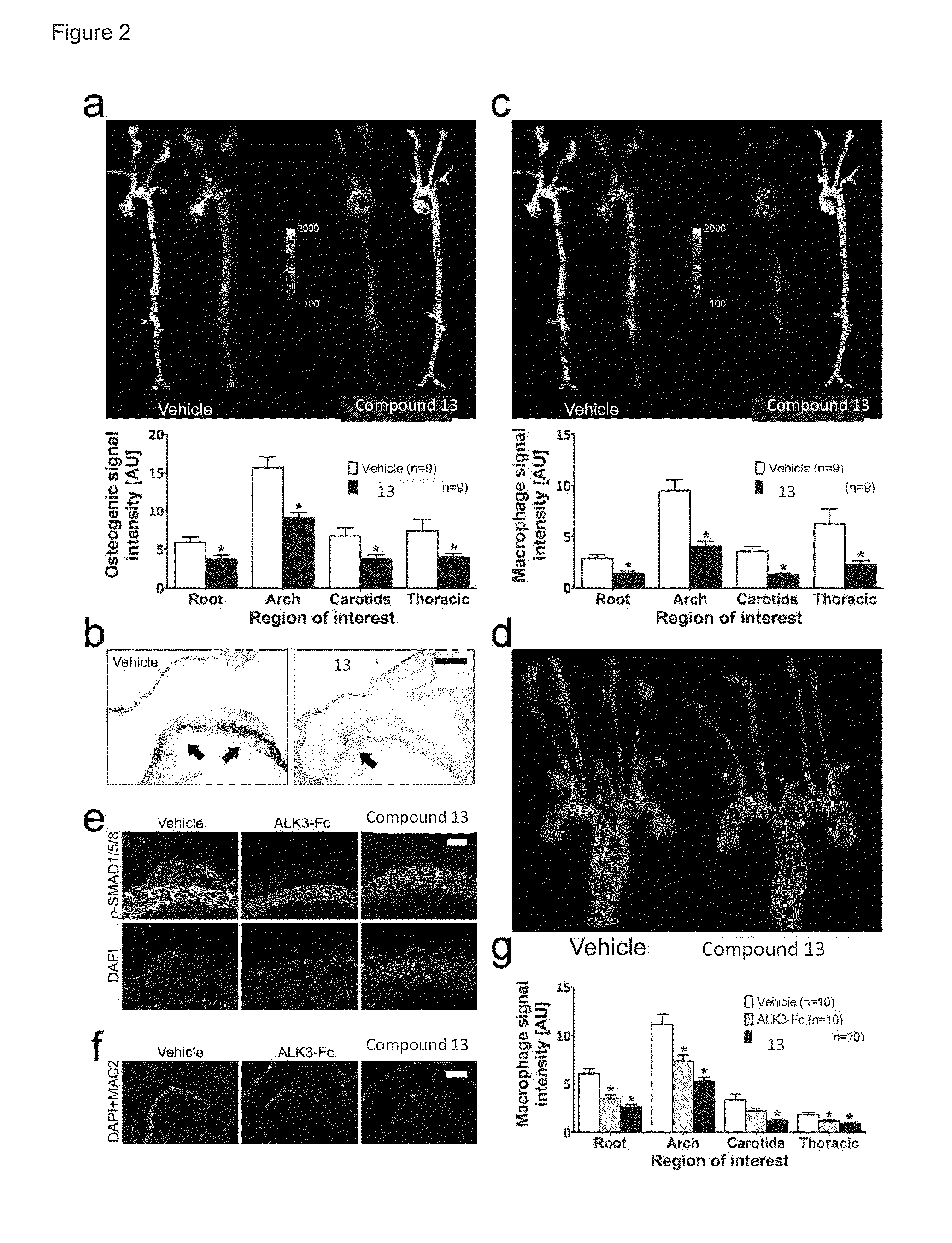
[0320]LDLr− / − mice were treated with a BMP inhibitor positive control compound (compound 13, 2.5 mg / kg / d intraperitoneally) or vehicle (saline) for 20 weeks following the initiation of a high fat diet. Mice were injected with Osteosense (to label sites of bone-forming activity via osteoblast binding of this probe) and Prosense (to label sites of macrophage-mediated inflammation). Aortae were explanted and subjected to fluorescence reflectance imaging (LICOR Odyssey imager). Fluorescence in the 700 nm channel (Osteosense) revealed diminished fluorescence in the aortae of the BMP inhibitor positive control compound-treated as compared to vehicle-treated mice (data not shown). Significant differences in macrophage and osteoblast staining were observed throughout the vascular tree in a cohort of treated and control mice (n=10 each). In examining ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pKa | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com