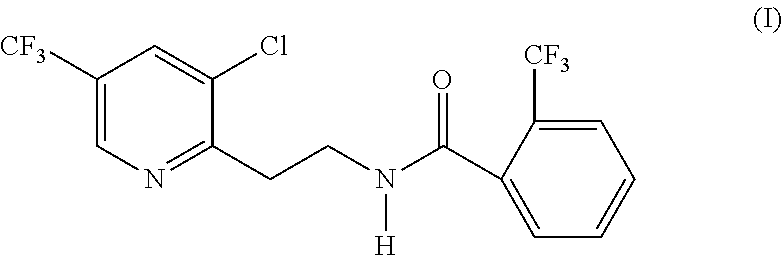
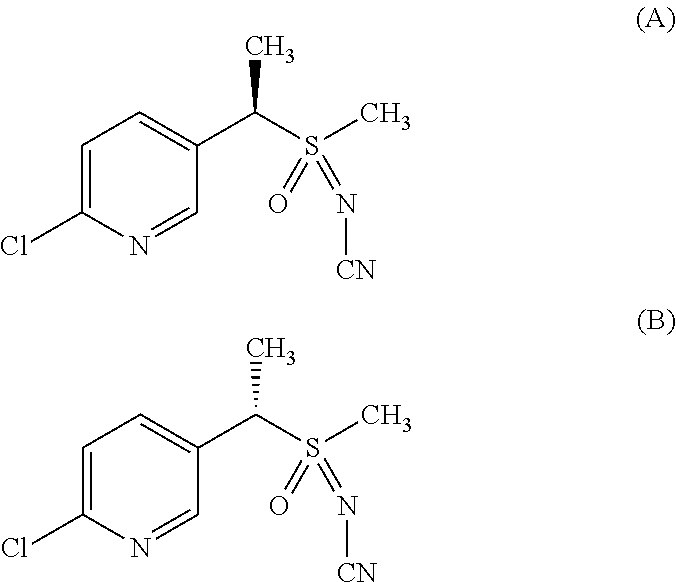
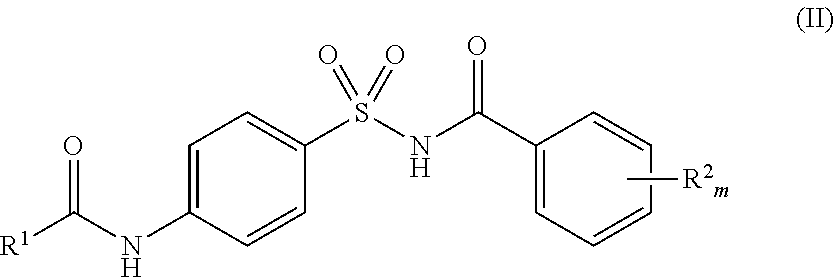
Use of biological or chemical control agents for controlling insects and nematodes in resistant crops
a technology of nematodes and control agents, applied in the field of biological and/or chemical control agents for controlling nematodes or insects in nematodes or insect resistant crops, can solve the problems of reducing the uptake of nutrients and water by plants, killing plants, and reducing the productivity of plants, so as to improve the resistance or tolerance to one, improve the yield or vigor, and improve the effect of resistance or toleran
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experimental examples
Example 1
[0285]Two tests were planted with Jack (an SCN resistant soybean variety with PI 88788 resistance) and two genetically modified Jack varieties (AXN2 and AXMI031) known to produce a nematicidal protein. The seed were treated with a color / coating base or the same base plus one of two different rates of fluopyram (experiment 1 used 0.075 mg fluopyram / seed and experiment 2 used 0.15 mg fluopyram / seed). The SCN used to inoculate both tests were collected from an inbred colony (OP50) with the ability to overcome PI 88788 resistance.
[0286]Tests were conducted as non-randomized blocks with a minimum of 10 replicates. Seed were planted in individual 4″ clay pots with coarse sand and inoculated with approximately 20,000 OP50 juveniles in ten equal inoculations beginning at planting and again approximately every third day. Plants were maintained in a germination chamber. Blocks were rotated approximately every third day to minimize potential influence of environmental variance. Two mo...
example 2
[0292]Glycine max (soybean) seed from an event traited with Axmi031 was selected. Axmi031 historically shows efficacy against species of nematode. Plants that screened negative for the presence of the transgene were used for control comparisons.
[0293]Seed was treated with seed applied pesticides using a hege bowl treater. Metalaxyl (MTL), available as Allegiance through Bayer CropScience, was applied at rates of 2 and 4 g ai / 100 kg seed. Trilex 2000 was also included as a commercial standard package.
[0294]During testing, samples of each plant were submitted for PCR to determine if an individual plant carried the Axmi031 gene (Positive or Negative). Plants for which no PCR results could be obtained were not included in results. There were a disproportionate number of positive plants. As a result, the number of negative plants available in some comparisons was very small.
[0295]Testing was conducted as a randomized complete block with 30 replications. Seed were planted into sand at a r...
example 3
[0299]Zea Mays (Corn) seed from events traited with Axmi205 were selected. Axmi205 historically shows efficacy against Diabrotica virgifera (western corn rootworm). The population of the seed used is not entirely transgenic; plants without the trait in their DNA were used for control comparisons.
[0300]Seed was treated with seed applied pesticides using a hege bowl treater. Applications were made of: Clothianidin; available as Poncho though through Bayer CropScience. Rates were applied as mg ai / seed. The evaluation had non-target variables controlled.
[0301]During testing, samples of each plant were submitted for PCR to determine if an individual plant carried the Axmi205 gene (positive or negative). Plants for which no PCR results could be obtained were not included in the results.
[0302]Seed were planted into germination mix at a rate of one seed per root-trainer. Testing was conducted as a randomized complete block with 30 replications. Plants were maintained in a greenhouse and per...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com