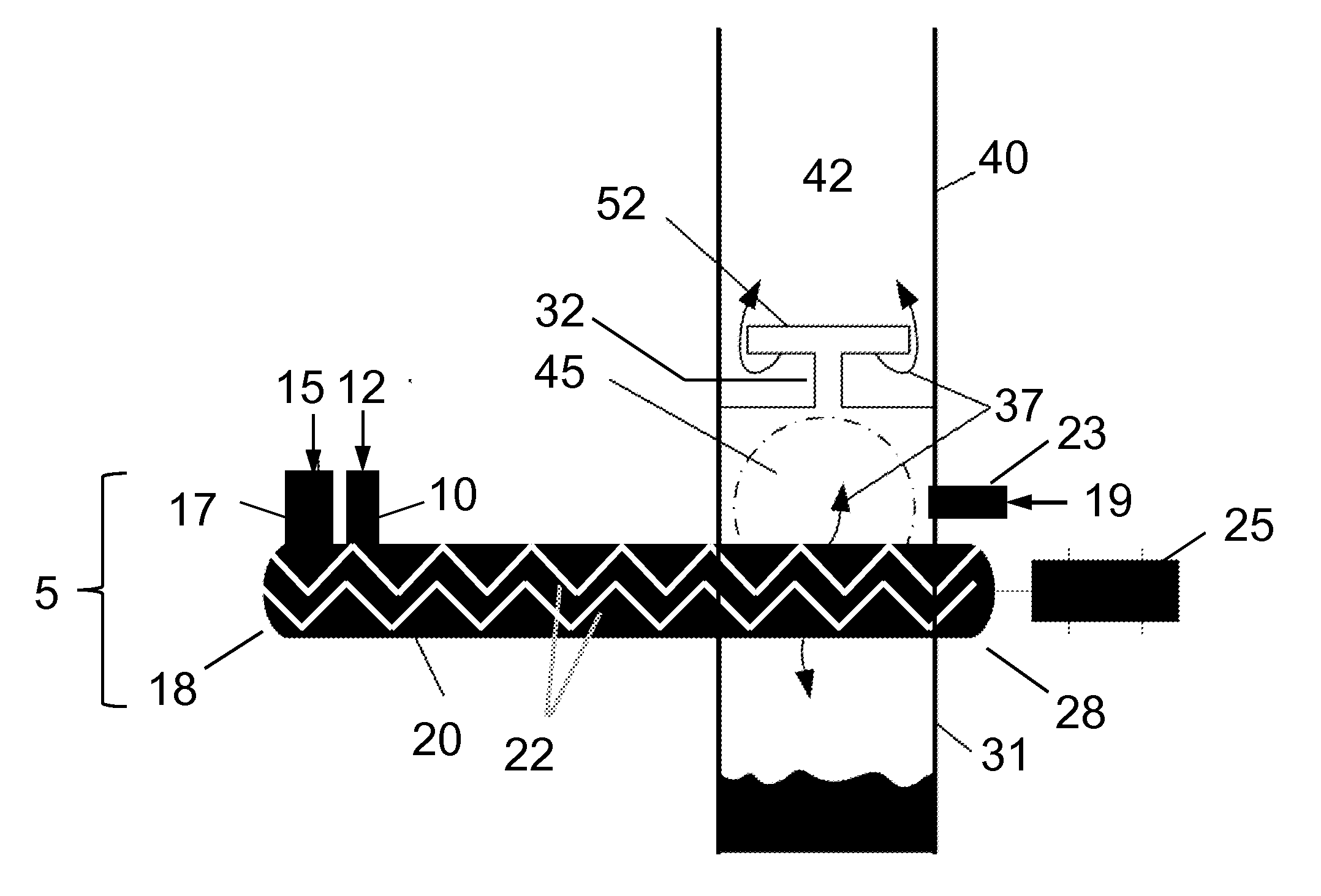
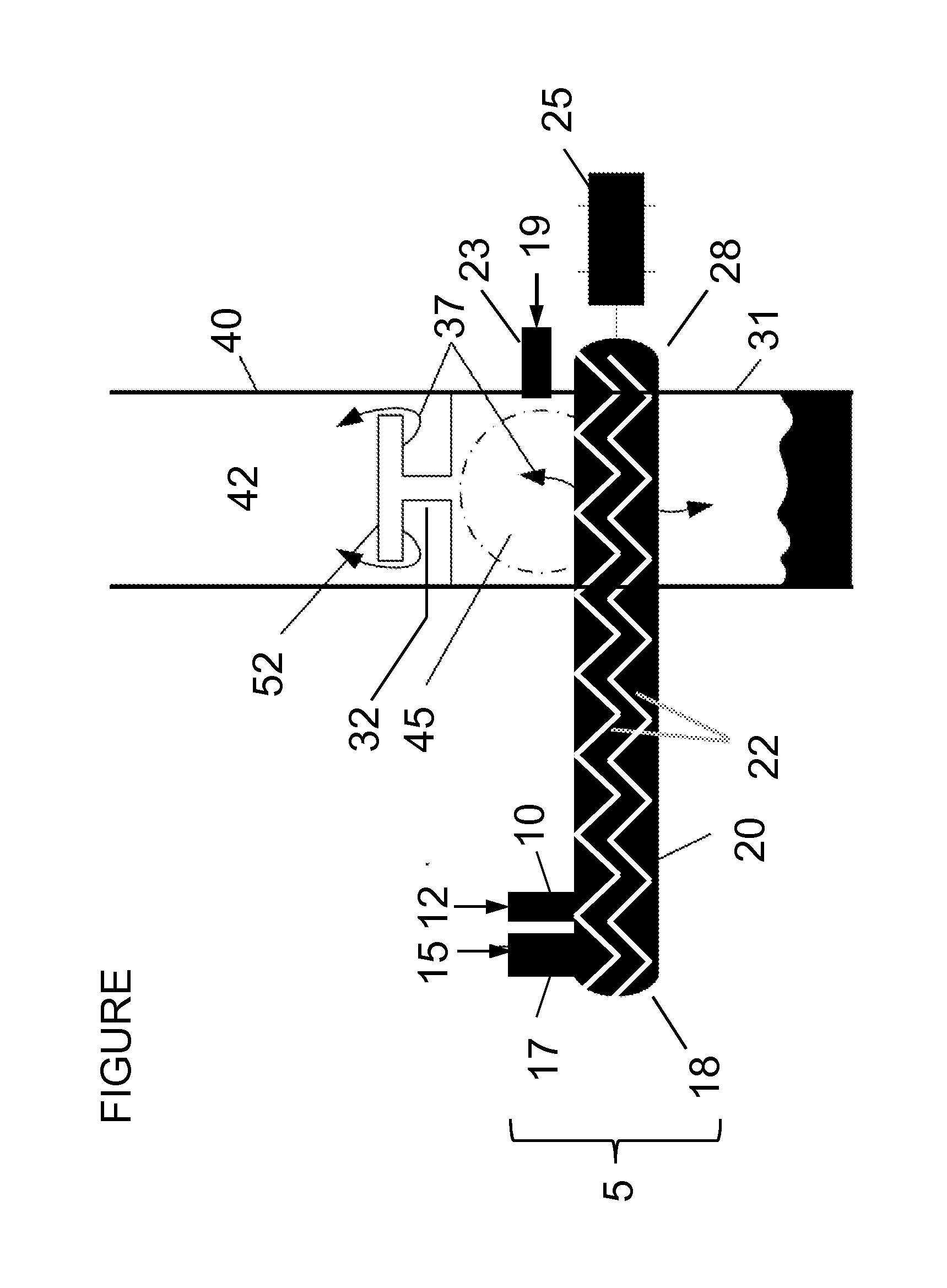
Systems for decreasing char entrainment during pyrolysis
a pyrolysis and char technology, applied in the field of organic matter pyrolysis, can solve the problems of high-oxygenated pyrolysis oil (or pyoil) that is not practical for upgrading, catalysts tend to rapidly deactivate, and condensed liquid product containing solids and metals that can negatively impact downstream processes, so as to reduce the rate of mechanical attrition and increase the average diameter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0061]Kiln-dried Red Oak was ground and the particles were subjected to pyrolysis (“Raw Biomass” in Table 1) or pre-sized into two fractions with a particle diameter ranging from of 300 to 500 microns or a particle size ranging from 750 to 1250 microns (see Table 1).
[0062]Biomass was added to a pyrolysis reactor with a heat carrier heated to a temperature greater than about 1200° F. to thermally decompose solid biomass to condensable pyrolysis vapors, char, and non-condensable gases. The pyrolysis vapors passed out of the pyrolysis reactor and were cooled and collected in a collection system comprised of electrostatic precipitators (ESPs). These ESP collected vapors that condensed at greater than about 180° F., while water-cooled condensers collected vapors that condense at a temperature of less than 180° F.
[0063]In the experiment, solids remained in the pyrolysis reactor (Table 1) and two fractions were collected (refer to Tables 2 and 3, respectively: 1). The vapor-gas stream was ...
example 2
[0066]One example of a compound that can be used as an additive in the inventive processes and systems described herein is magnesium chloride. We performed pyrolysis of red oak impregnated at 1:10 ratio of magnesium chloride to biomass and dried at 70° C. Pyrolysis was performed at 475° C. in a non-reactive helium atmosphere. Production of furfural (and other C5+ oxygenates) and anhydrosugar were enhanced as compared to conventional pyrolysis. Lower yields of phenolics and oxygenated aromatics were also observed. Catalytic pyrolysis of the same feedstock with ZSM-5 catalyst in a 5:1 ratio resulted in a decreased yield of oxygenates and higher yield of hydrocarbons compared to non-impregnated biomass (see Table 4; numbers represent percent of total carbon yield as determined by Gas Chromatography / Mass Spectrometry). The yield of char decreased marginally for pyrolysis of impregnated biomass, improving overall liquid yield.
TABLE 4Pyrolysis Product Distribution Following Impregnation w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com