Conformable Microporous Fiber and Woven Fabrics Containing Same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1a
[0145]A fine powder PTFE resin (Teflon 669 X, commercially available from E.I. du Pont de Nemours, Inc., Wilmington, Del.) was obtained. The resin was blended with Isopar® K in the ratio of 0.184 g / g by weight of powder. The lubricated powder was compressed in a cylinder and allowed to dwell at room temperature for 18 hours. The pellet was then ram extruded at a 169 to one reduction ratio to produce a tape of approximately 0.64 mm thick. The extruded tape was subsequently compressed to a thickness of 0.25 mm. The compressed tape was then stretched in the longitudinal direction between two banks of rolls. The speed ratio between the second bank of rolls and the first bank of rolls, hence the stretch ratio was 1.4:1 with a stretch rate of 30% / sec. The stretched tape was then restrained and dried at 200° C. The dry tape was then expanded between banks of heated rolls in a heated chamber at a temperature of 300° C. to a ratio of 1.02:1 at a stretch rate of 0.2% / sec, followed by an addit...
example 1b
[0151]A fluoroacrylate coating was applied to the woven fabric of Example 1a in order to render it oleophobic while preserving the porous and microporous structure.
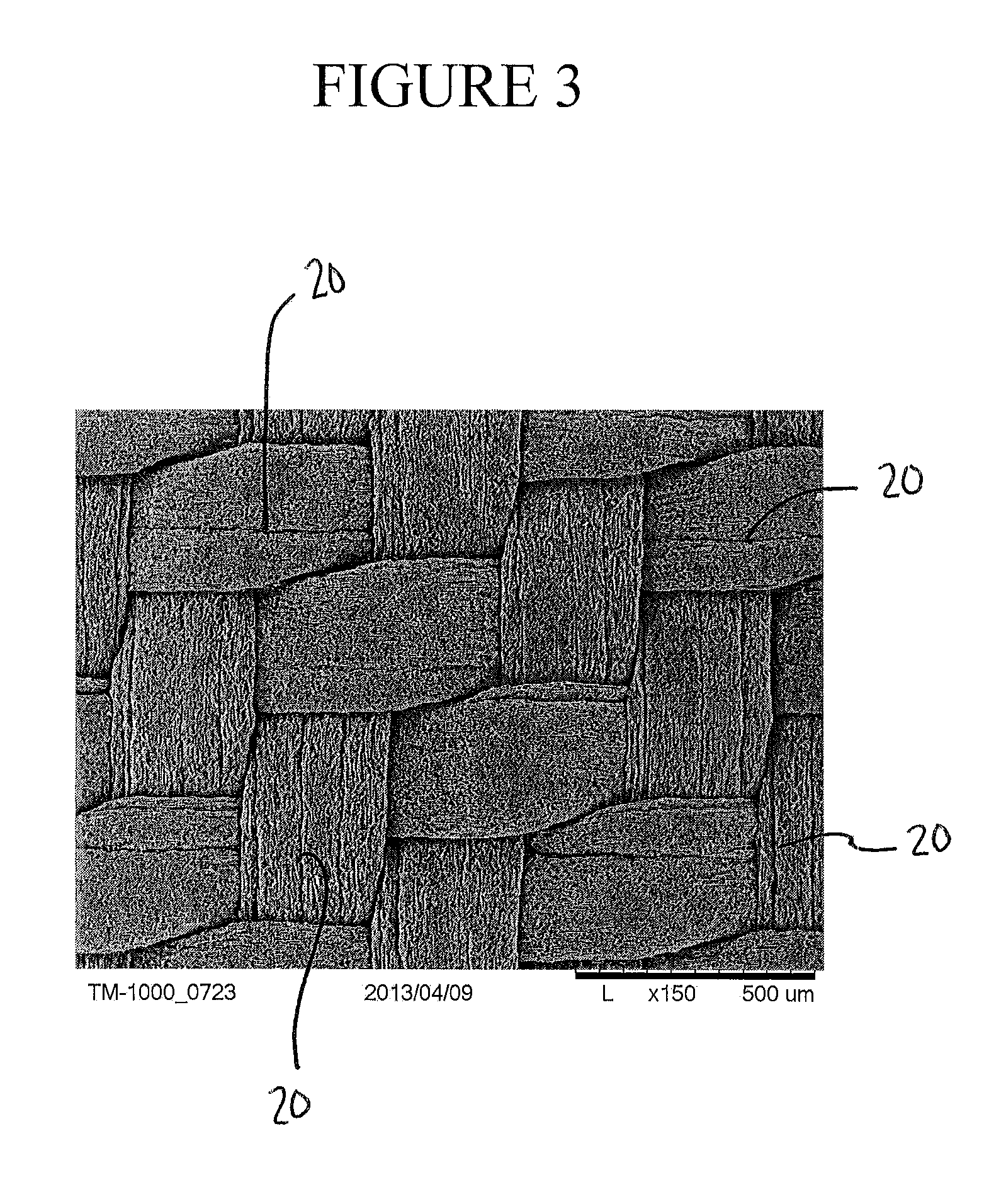
[0152]The resulting oleophobic woven fabric had the following properties: thickness=0.20 mm, MVTR=21206 g / m2 / 24 hours, water pick-up=11 gsm, hand=131 g, tear strength=63.8 N, WEP=6.11 KPa, air permeability=1.72 cfm, and oil rating=6. A scanning electron micrograph of surface of the woven fabric taken at 150× magnification is shown in FIG. 5. A scanning electron micrograph of a side view of the fabric taken at 150× magnification is shown in FIG. 6. The length and width of the gaps between the fibers were less than 0.01 mm. The fabric had a weight of 158 g / m2.
example 1c
[0153]An amorphously locked ePTFE membrane was obtained having the following properties: thickness=0.04 mm, density=0.47 g / cc, matrix tensile strength in the strongest direction=105.8 MPa, matrix tensile strength in the direction orthogonal to the strongest direction=49.9 MPa, Gurley=16.2 s, MVTR=64168 g / m2 / 24 hours.
[0154]The woven fabric of Example 1b was laminated to the ePTFE membrane in the following manner. The fabric and the ePTFE membrane were bonded together by applying a dot pattern of a melted polyurethane adhesive to the membrane. While the polyurethane adhesive dots were molten, the fabric was positioned on top of the adhesive side of the membrane. This construct (article) was allowed to cool.
[0155]The resulting article had the following properties: thickness=0.22 mm, MVTR=12845 g / m2 / 24 hours, water pick-up=12 gsm, hand=196 g, tear strength=46.19 N, and oil rating=6. A scanning electron micrograph of the top surface of the article taken at 150× magnification is presented...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com