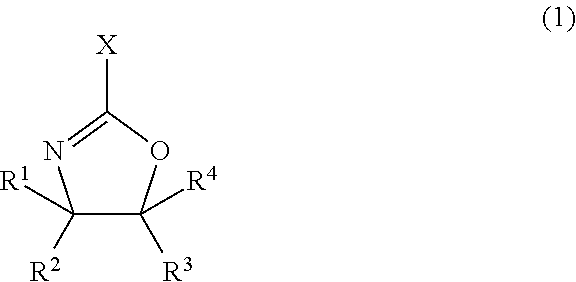
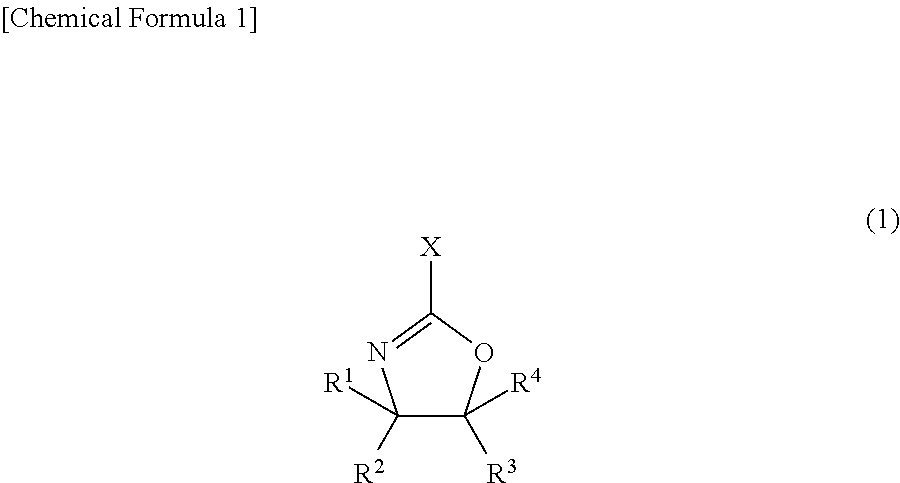
Agent for dispersing electrically conductive carbon material, and dispersion of electrically conductive carbon material
a technology of electrically conductive carbon and agent, which is applied in the direction of non-conductive materials with dispersed conductive materials, film/foil adhesives, and final product manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of battery capacity, shortening and variability of battery capacity, and poor adhesion of above-mentioned binders to current collectors, etc. , to achieve excellent adhesion to current-collecting substrates, excellent ability to dispers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
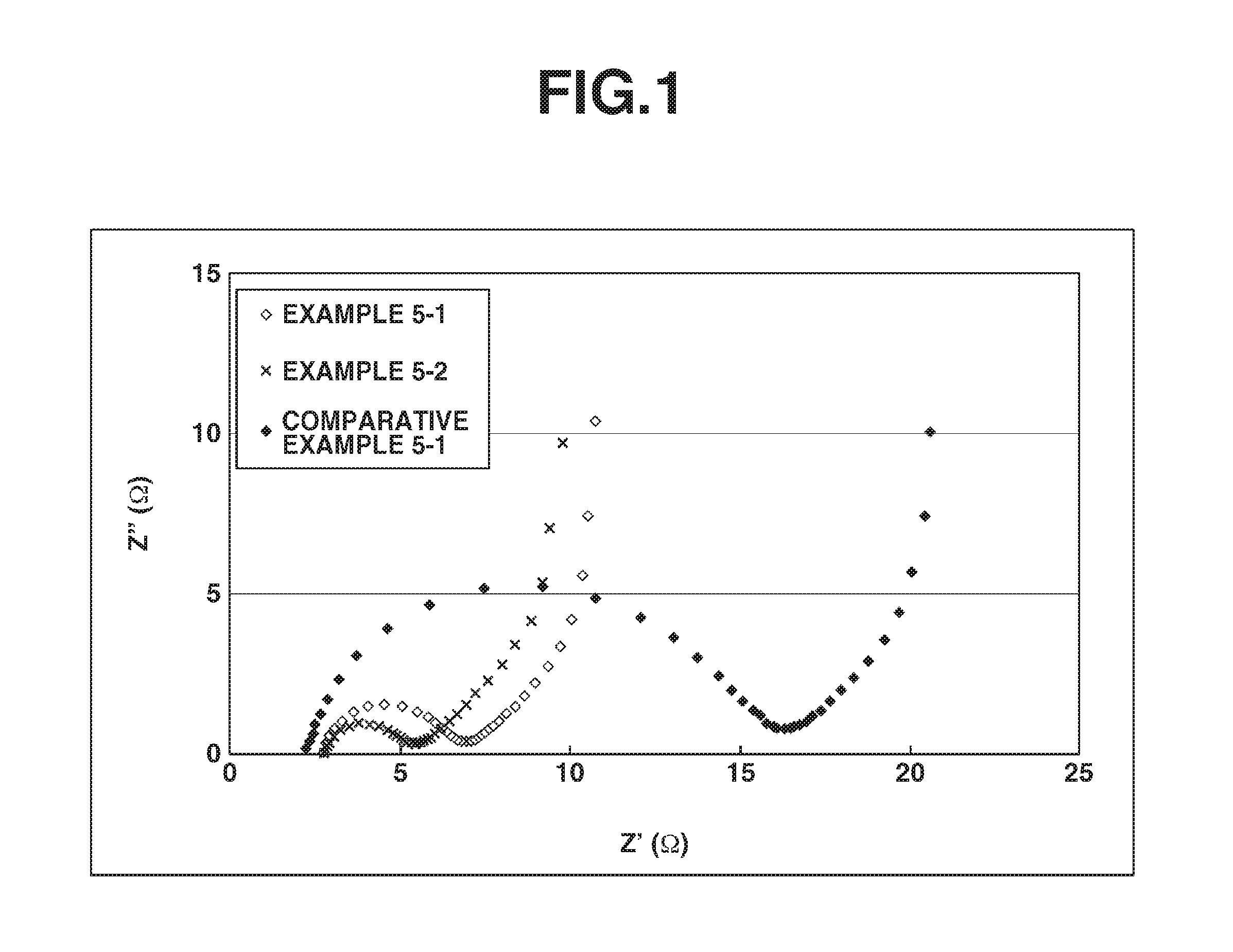
Examples
example 1-1
[0154]The oxazoline polymer-containing aqueous solution Epocros WS-300 (from Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.; solids concentration, 10 wt %; weight-average molecular weight, 1.2×105; oxazoline group content, 7.7 mmol / g), 4.9 g, was mixed together with 44.6 g of distilled water, after which 0.5 g of multi-walled CNTs (“NC7000”, from Nanocyl) was mixed therein. The resulting mixture was ultrasonically treated for 30 minutes at room temperature using a probe-type ultrasonicator, thereby preparing Conductive Carbon Material Dispersion A.
example 1-2
[0155]The oxazoline polymer-containing aqueous solution Epocros WS-700 (Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.; solids concentration, 25 wt %; weight-average molecular weight, 4×104; oxazoline group content, 4.5 mmol / g), 2.0 g, was mixed together with 47.5 g of distilled water, after which 0.5 g of multi-walled CNTs (“NC7000”, from Nanocyl) was mixed therein. The resulting mixture was ultrasonically treated for 30 minutes at room temperature using a probe-type ultrasonicator, thereby preparing Conductive Carbon Material Dispersion B.
example 1-3
[0156]Sodium polyacrylate (PAA-Na) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Co., Ltd.; degree of polymerization, 2,700 to 7,500), 0.36 g, was dissolved in 49.64 g of distilled water. The resulting solution was mixed with 50 g of Conductive Carbon Material Dispersion A prepared in Example 1-1, thereby preparing Conductive Carbon Material Dispersion C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com