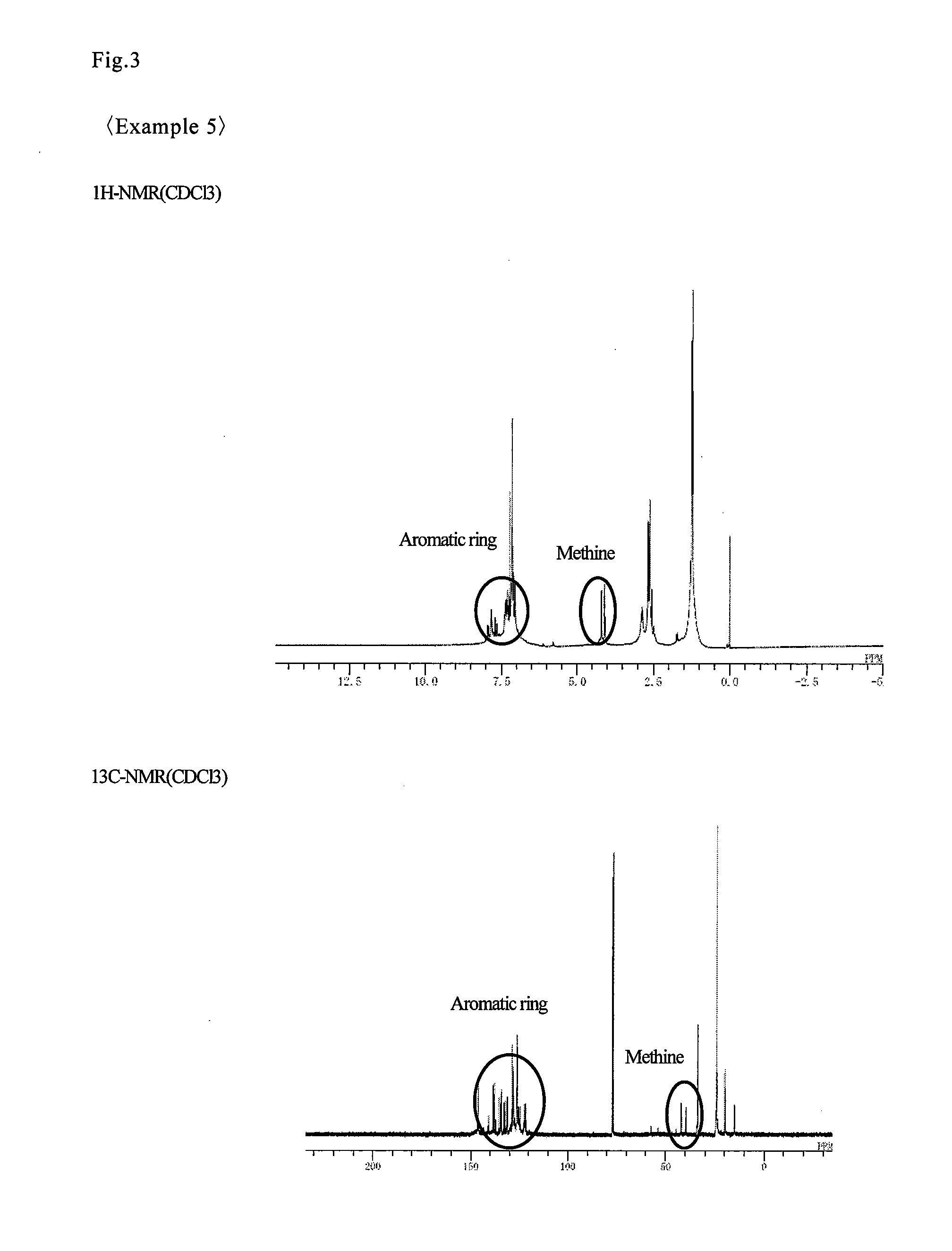
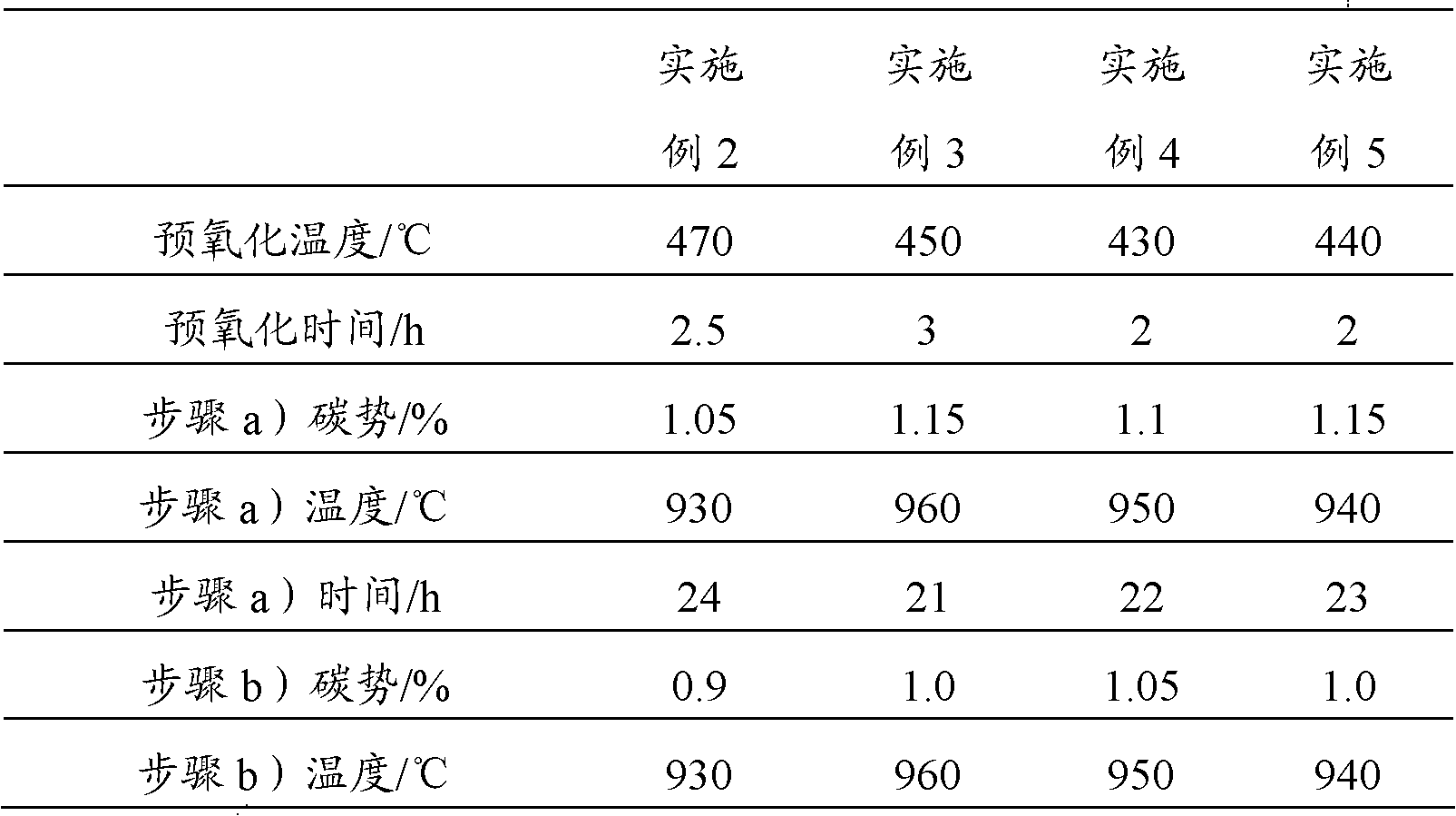
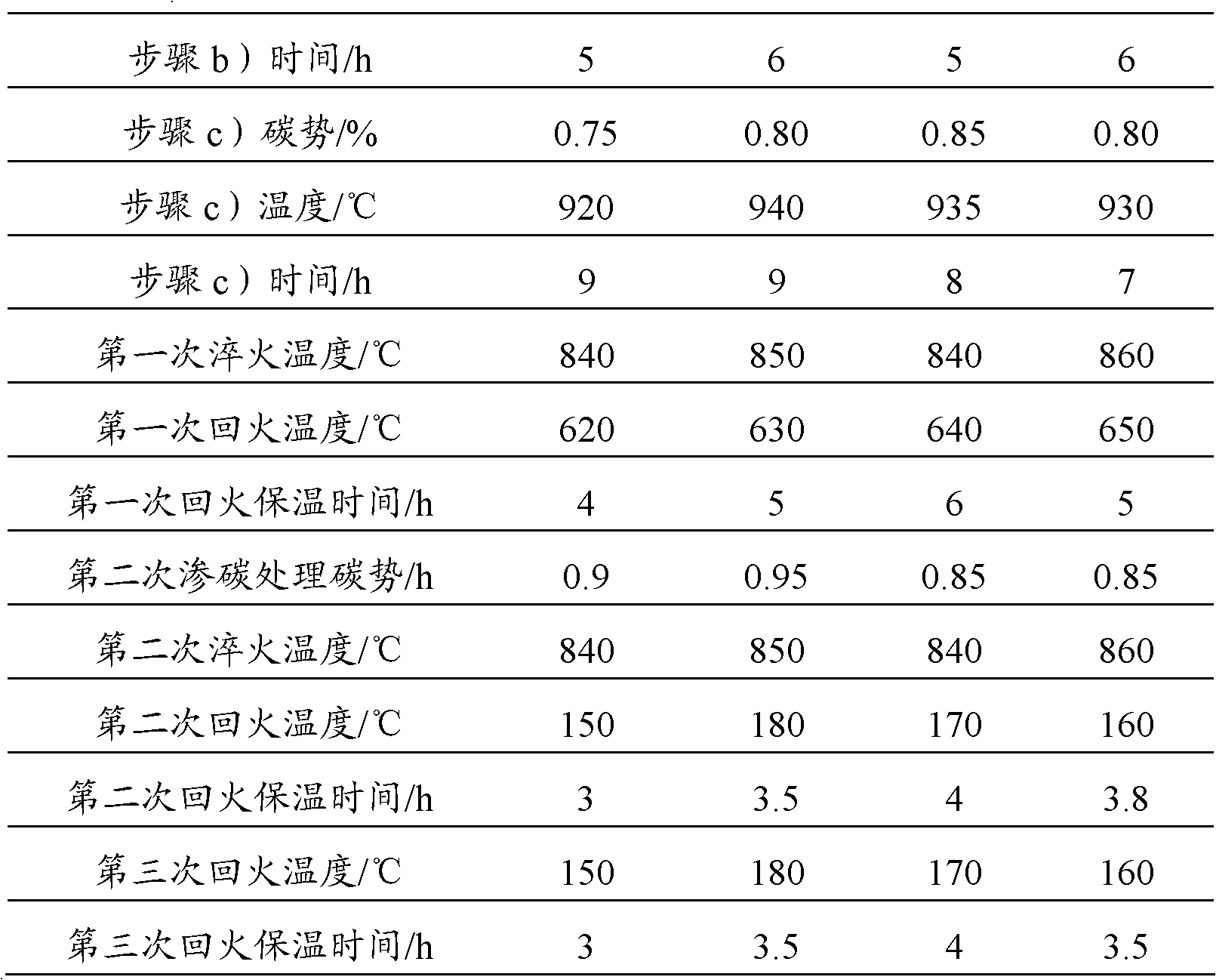
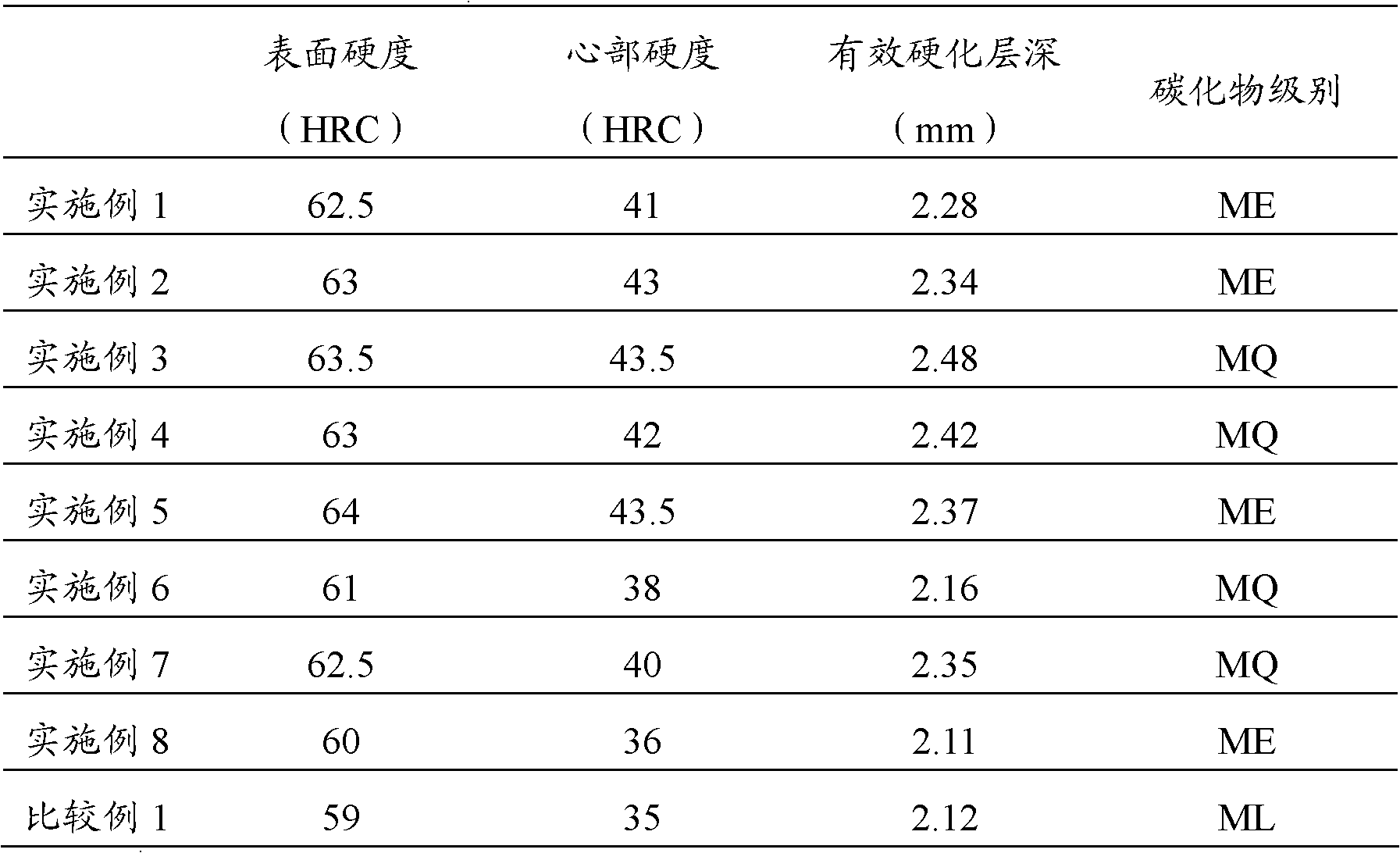
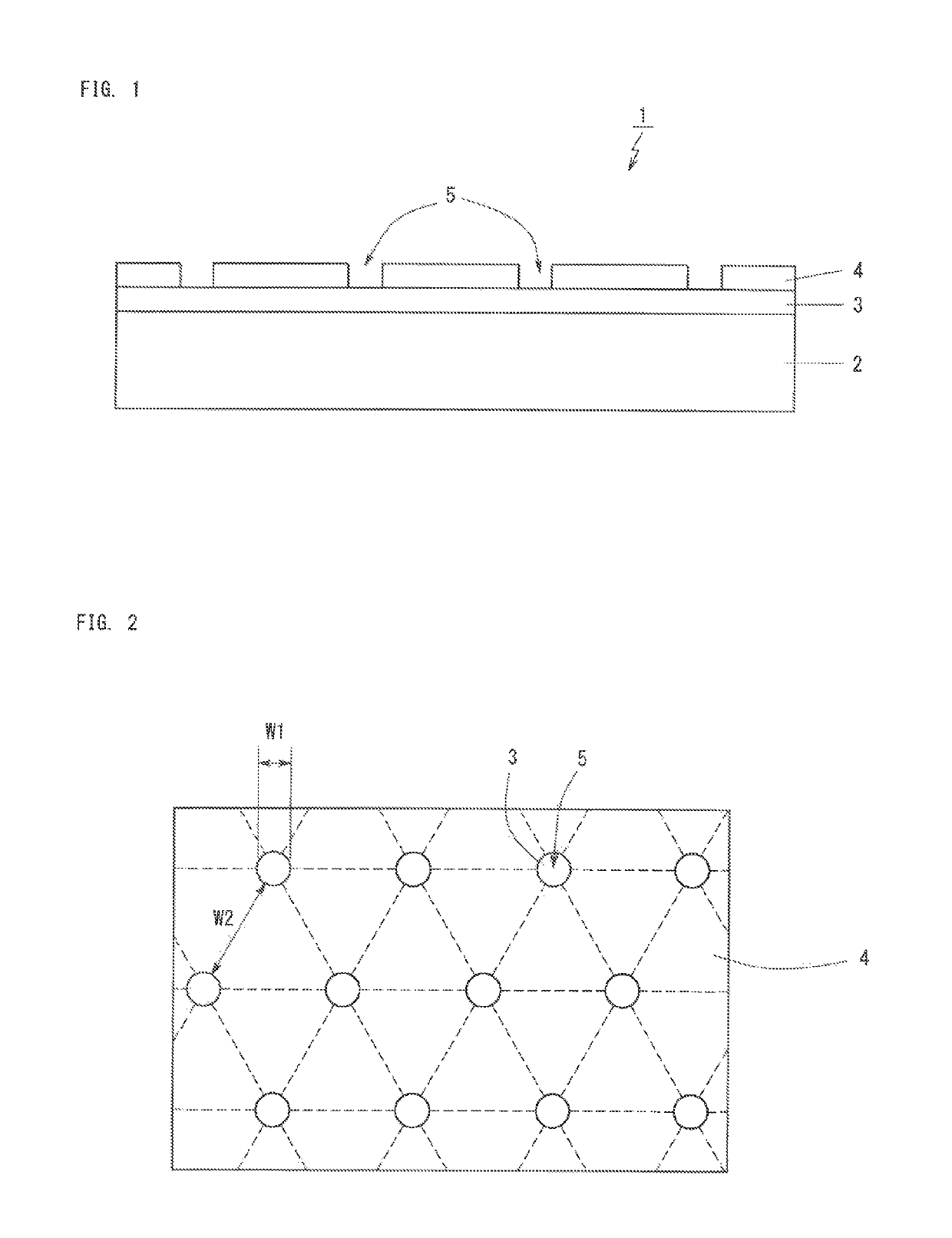
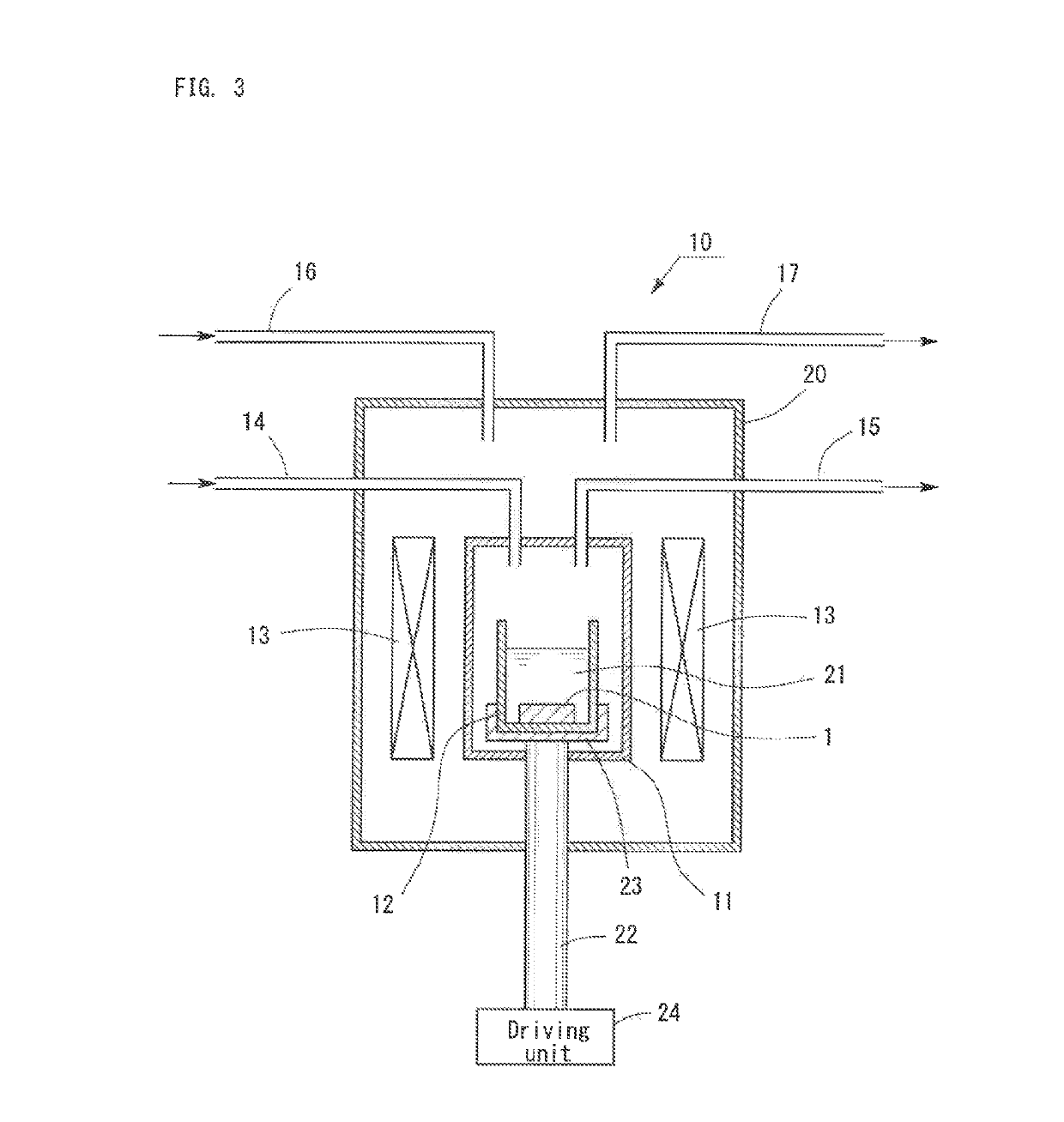
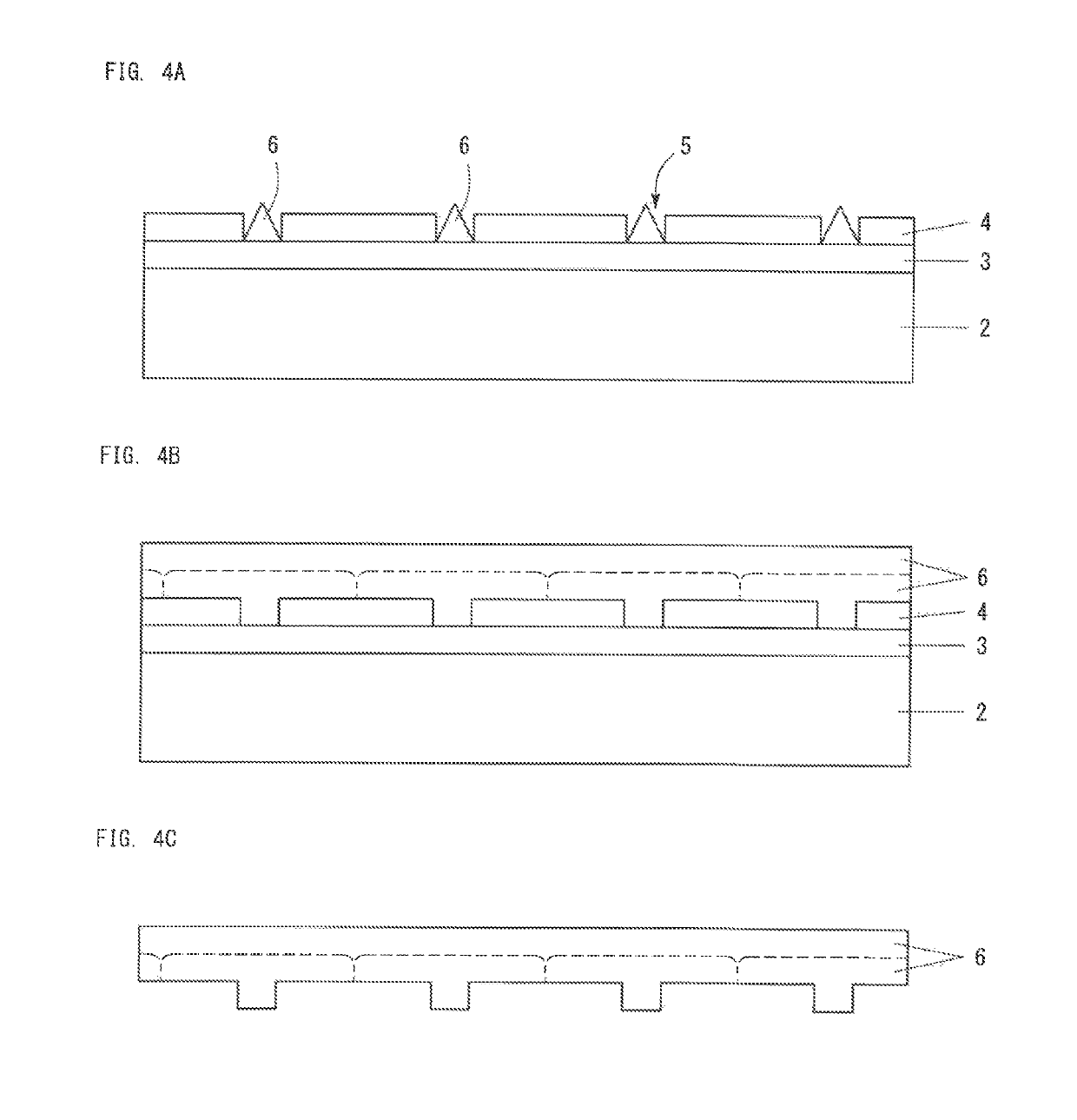
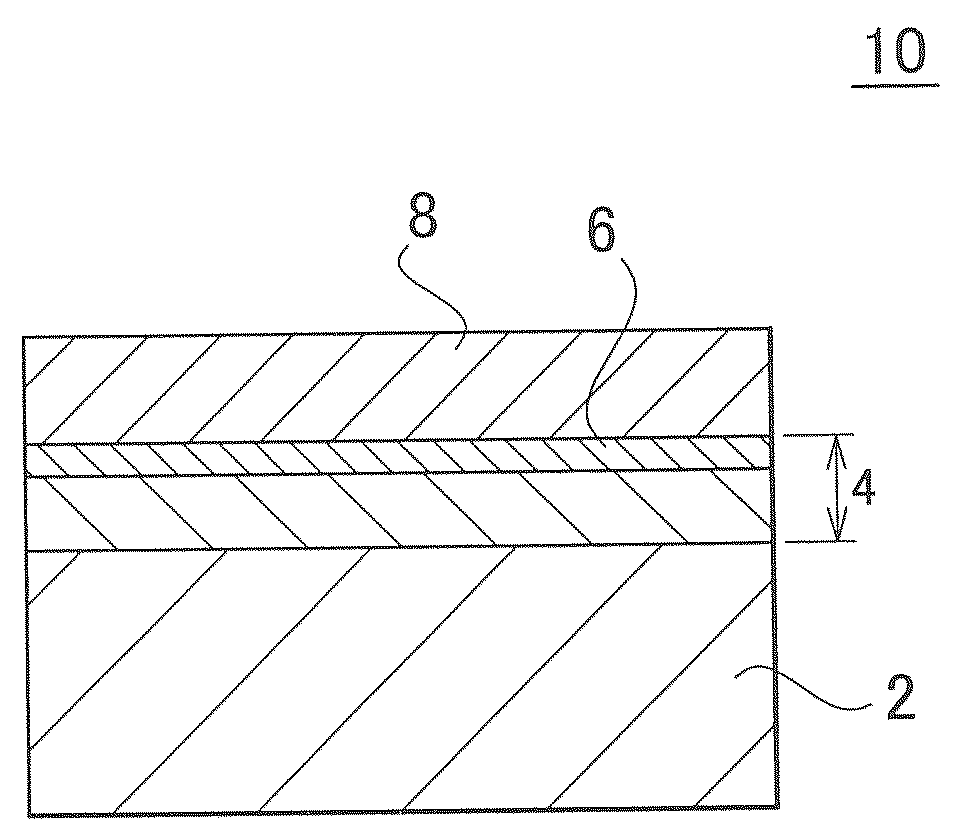
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Increase carbon concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
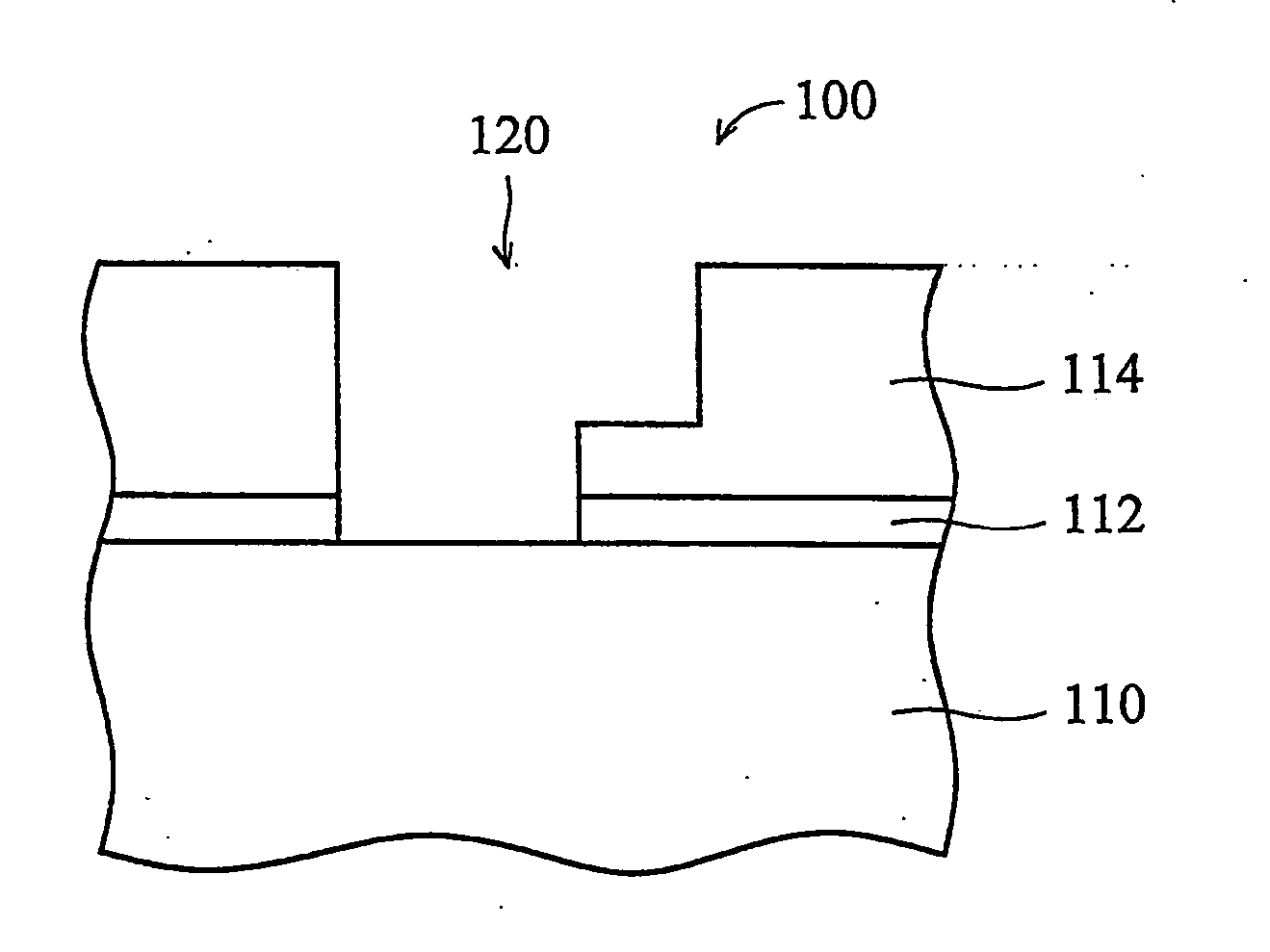
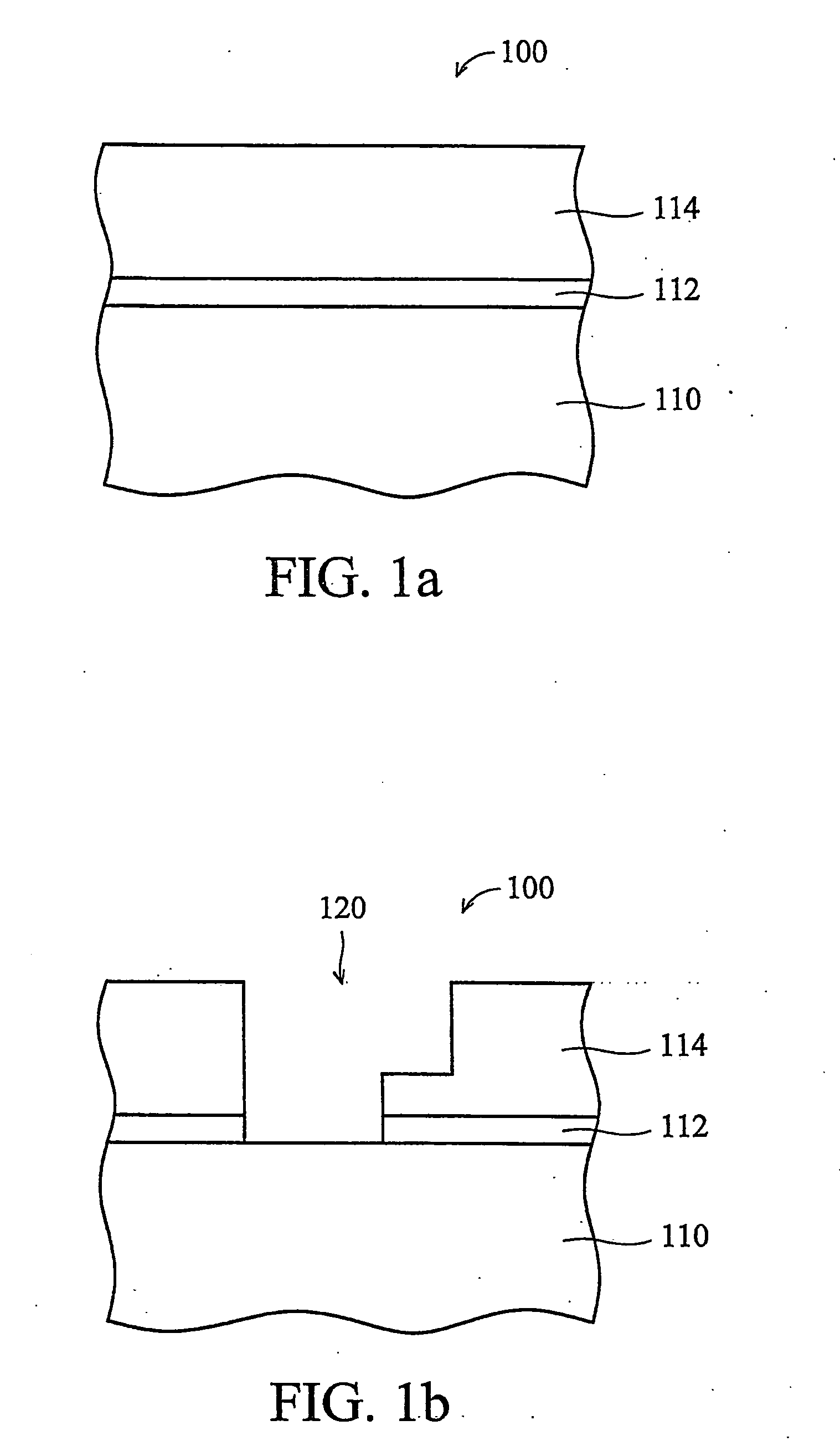
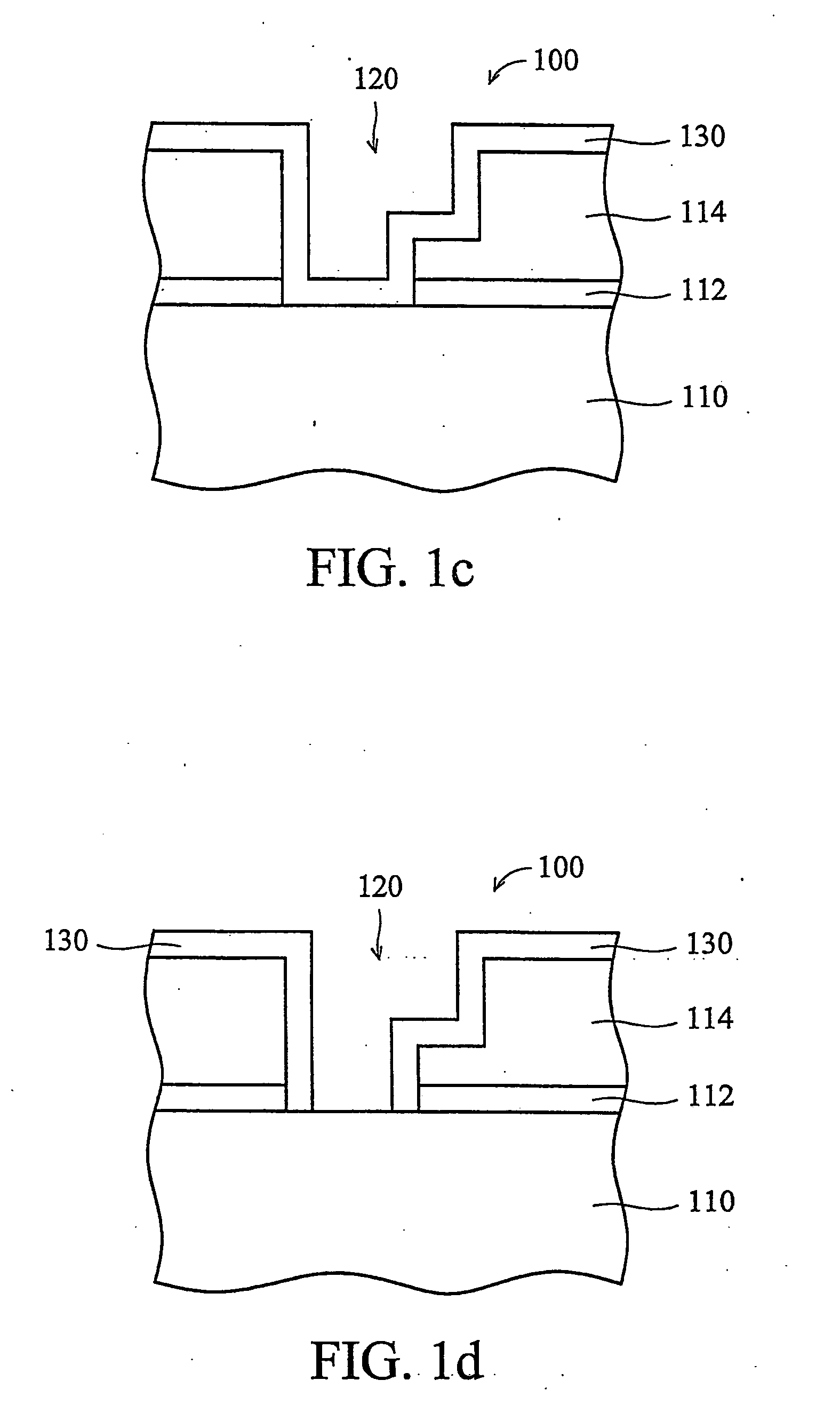
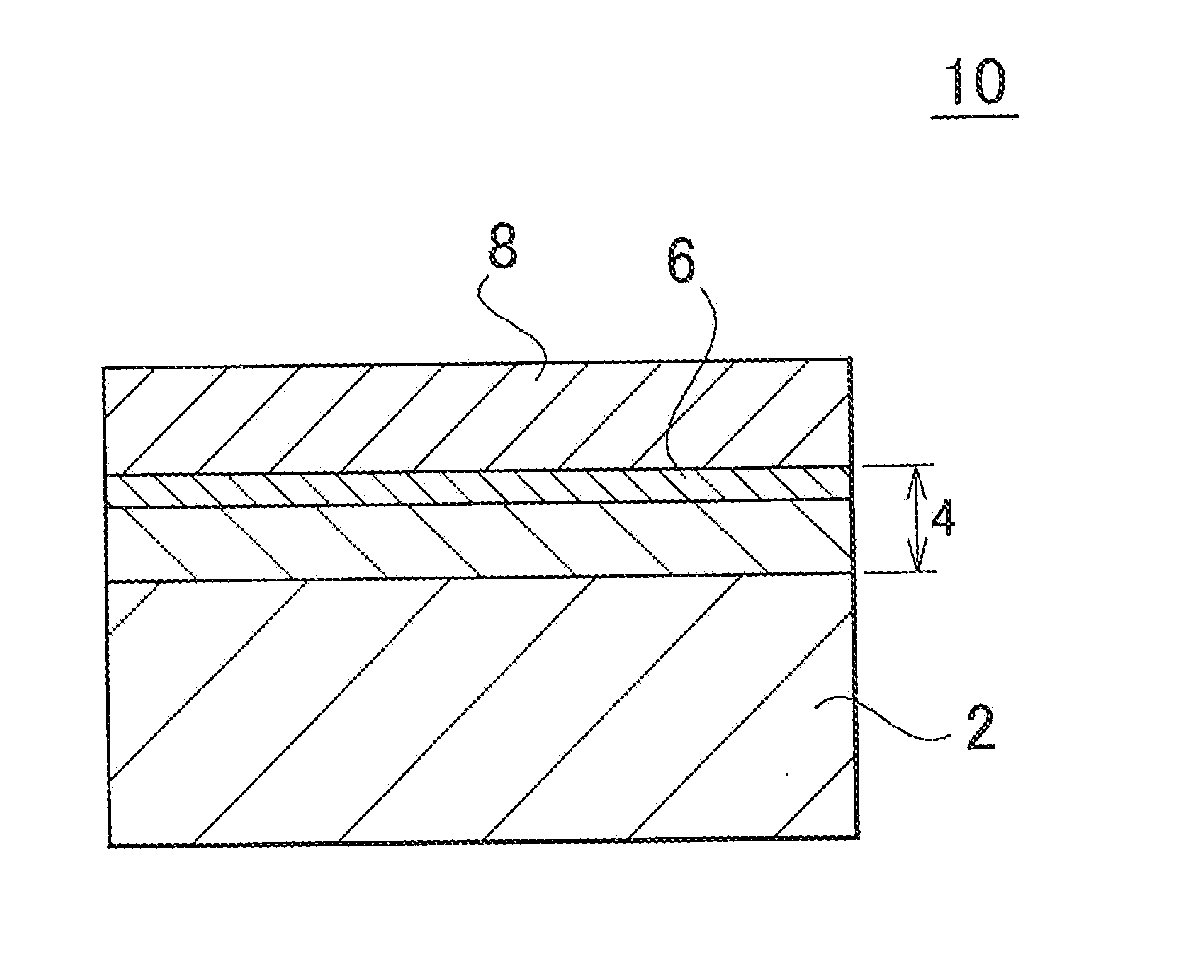
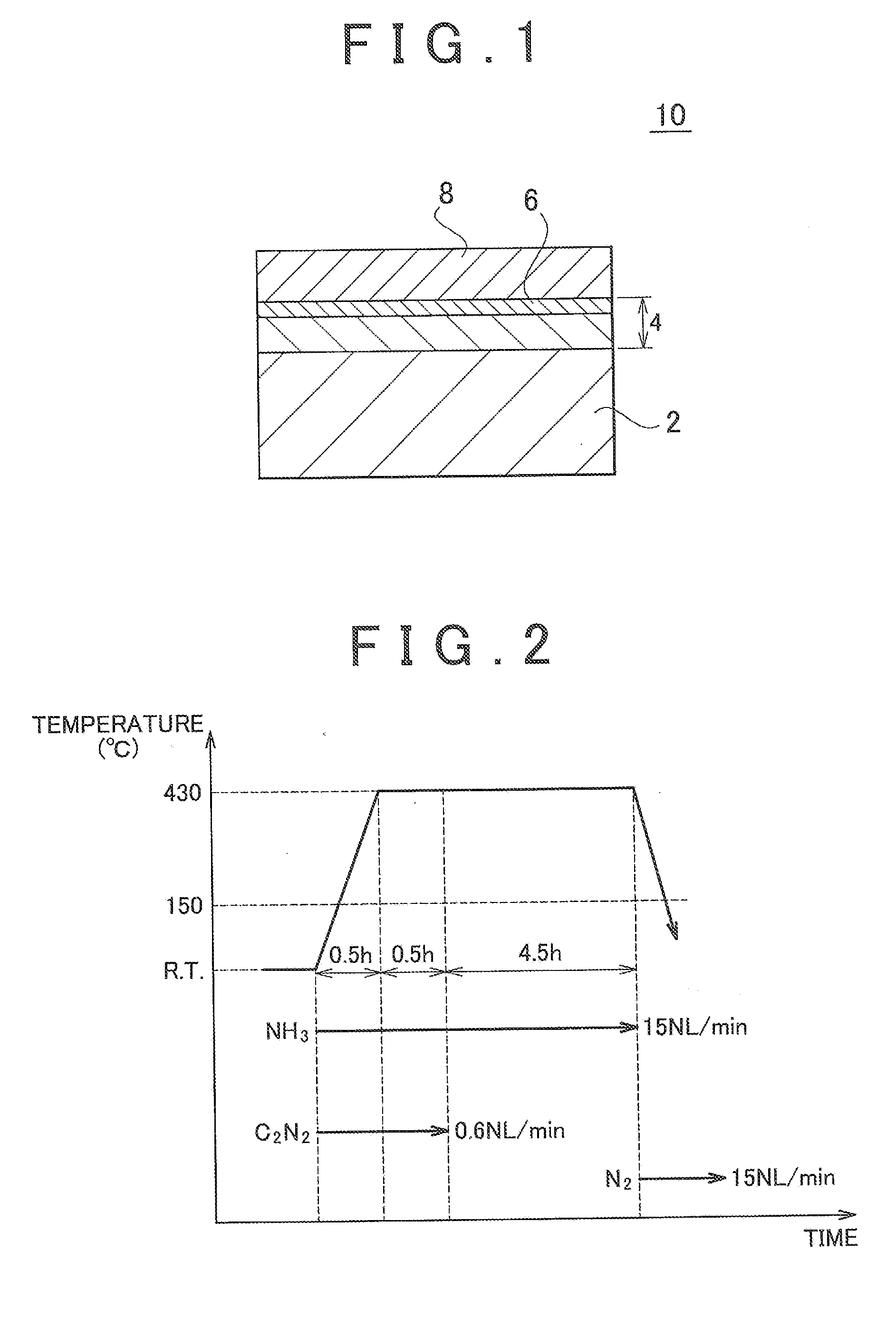
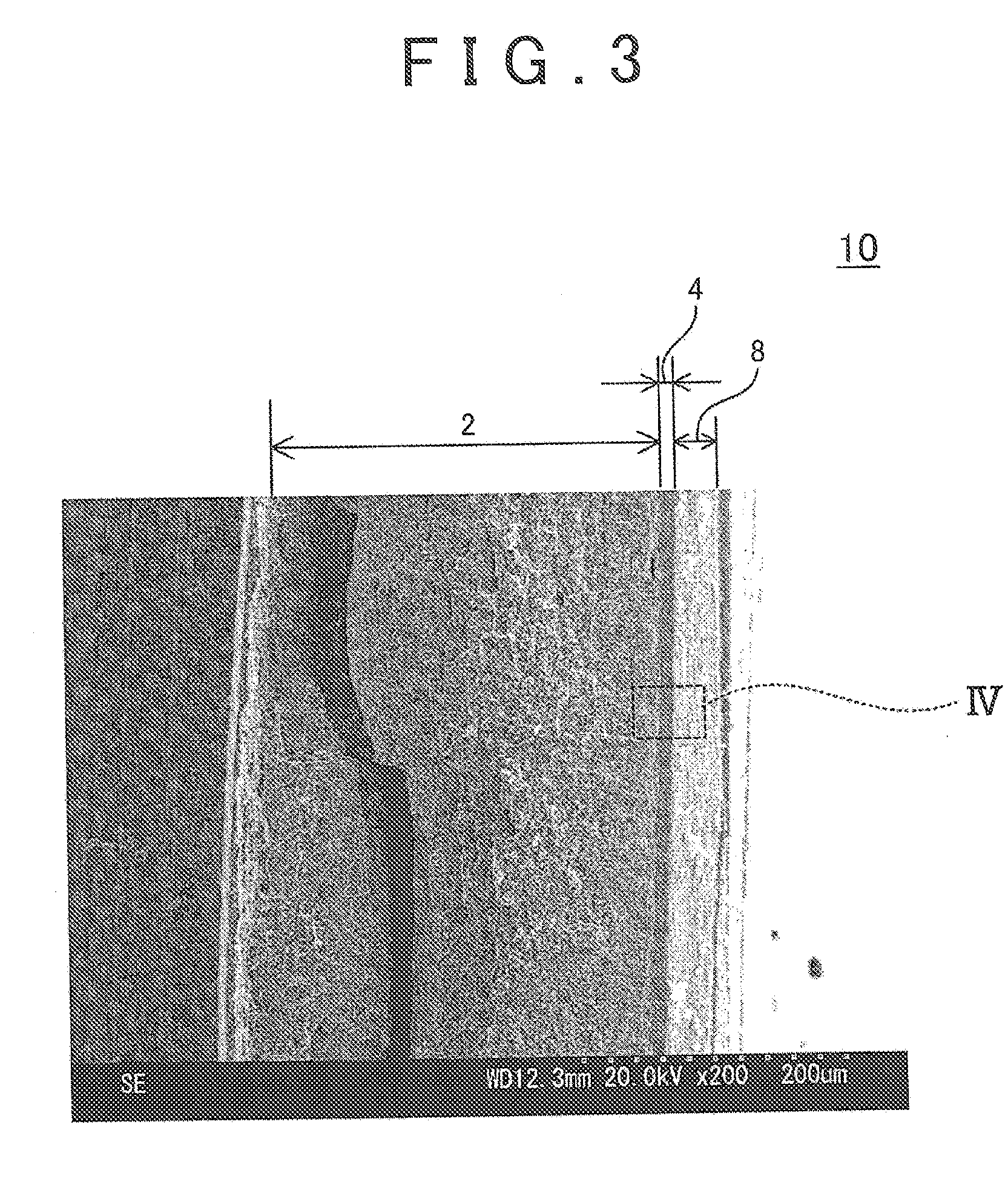
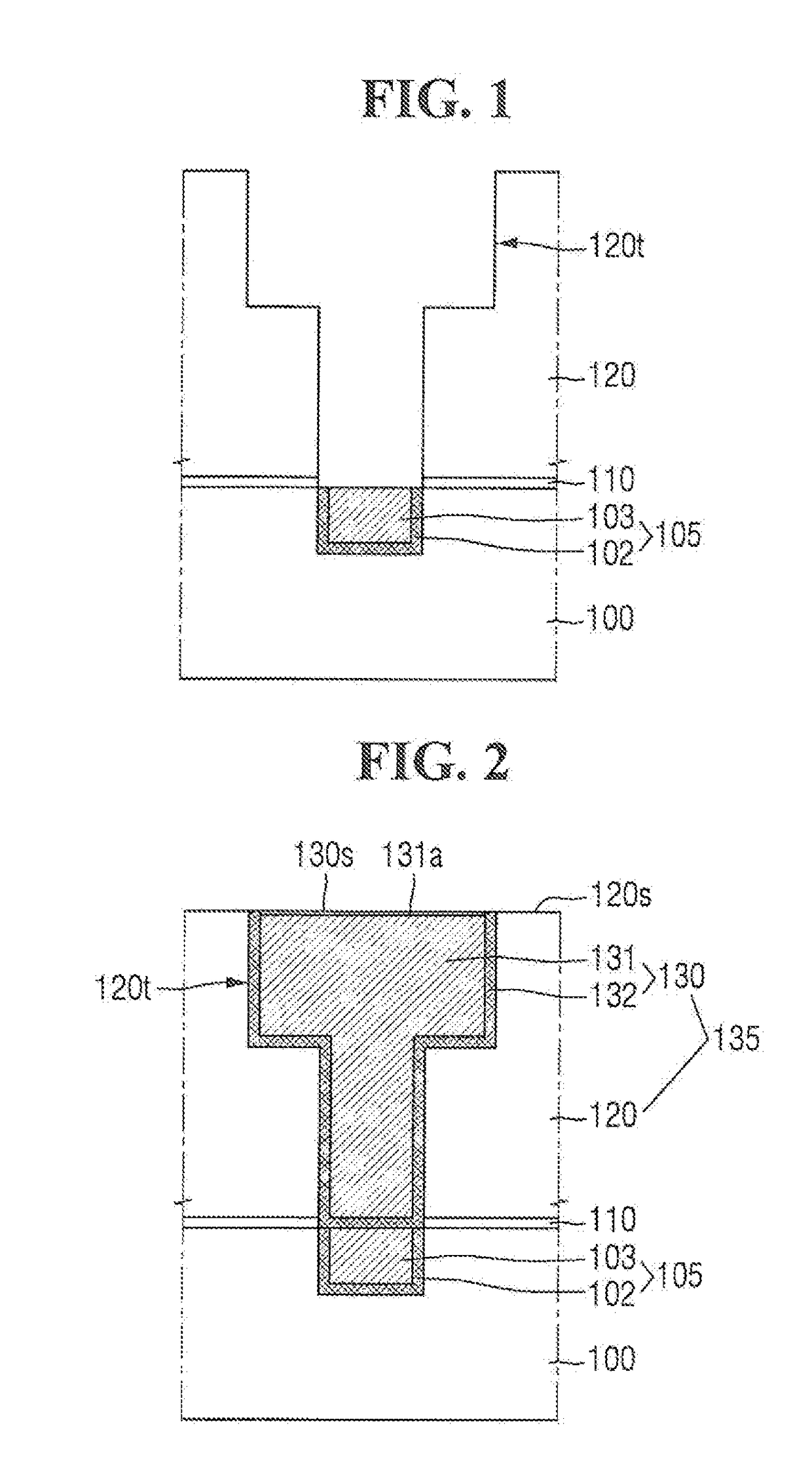
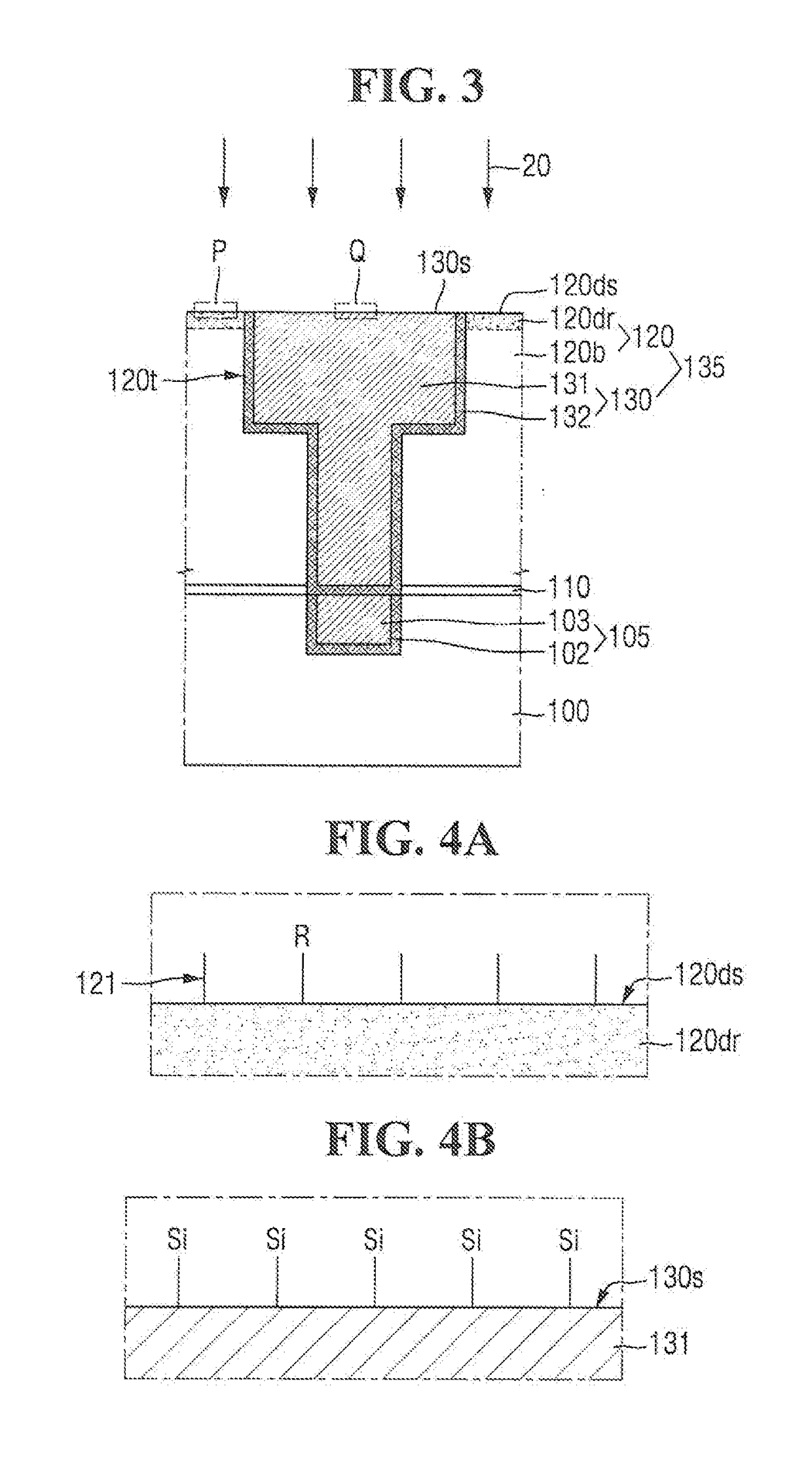
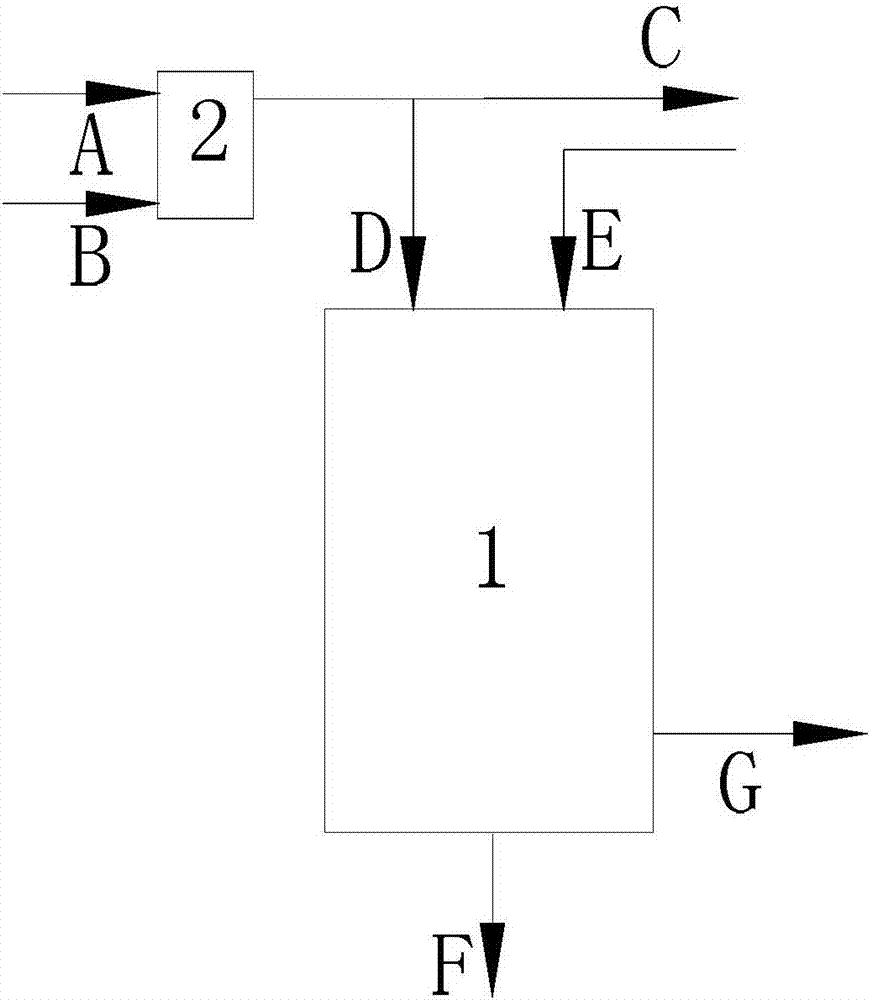
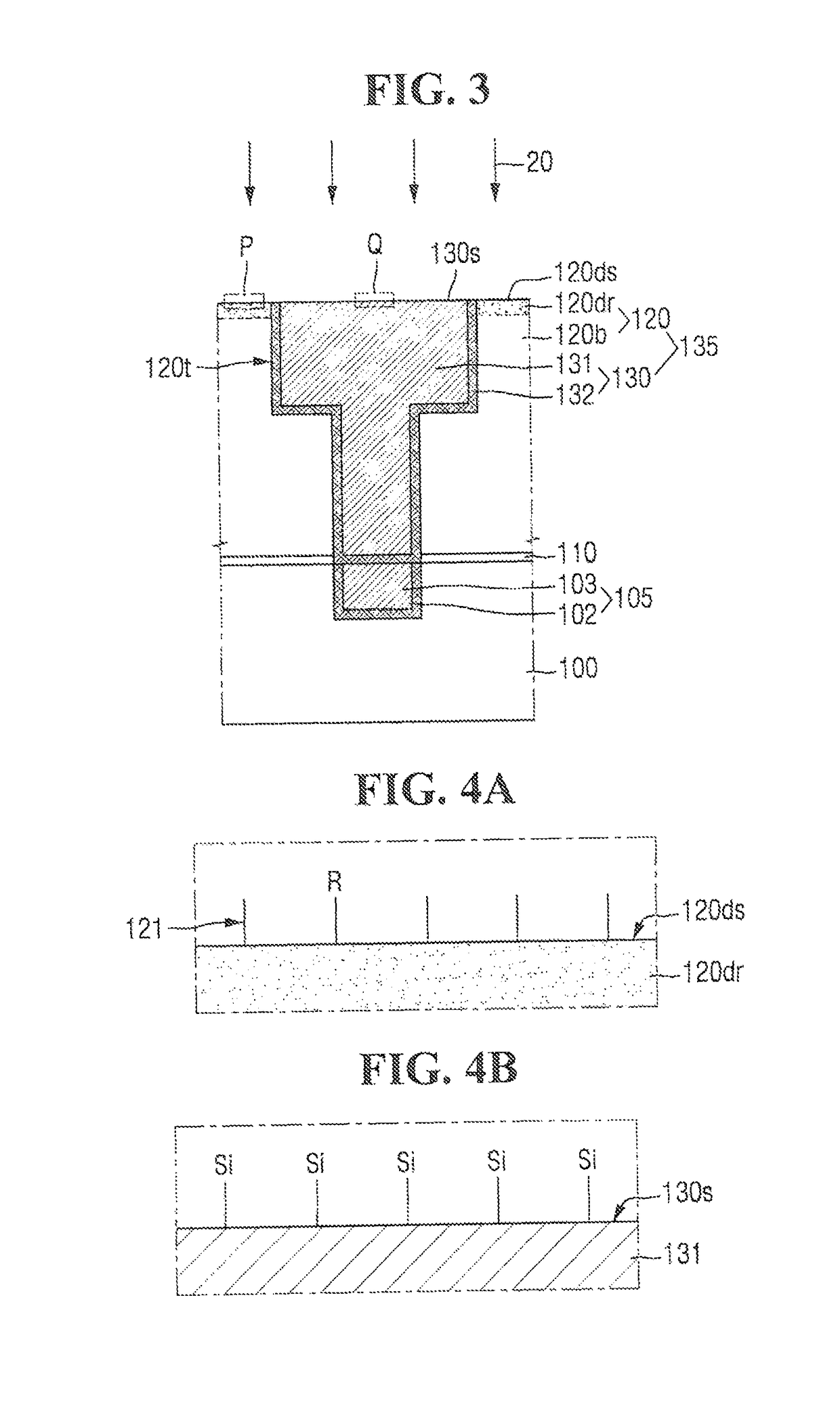
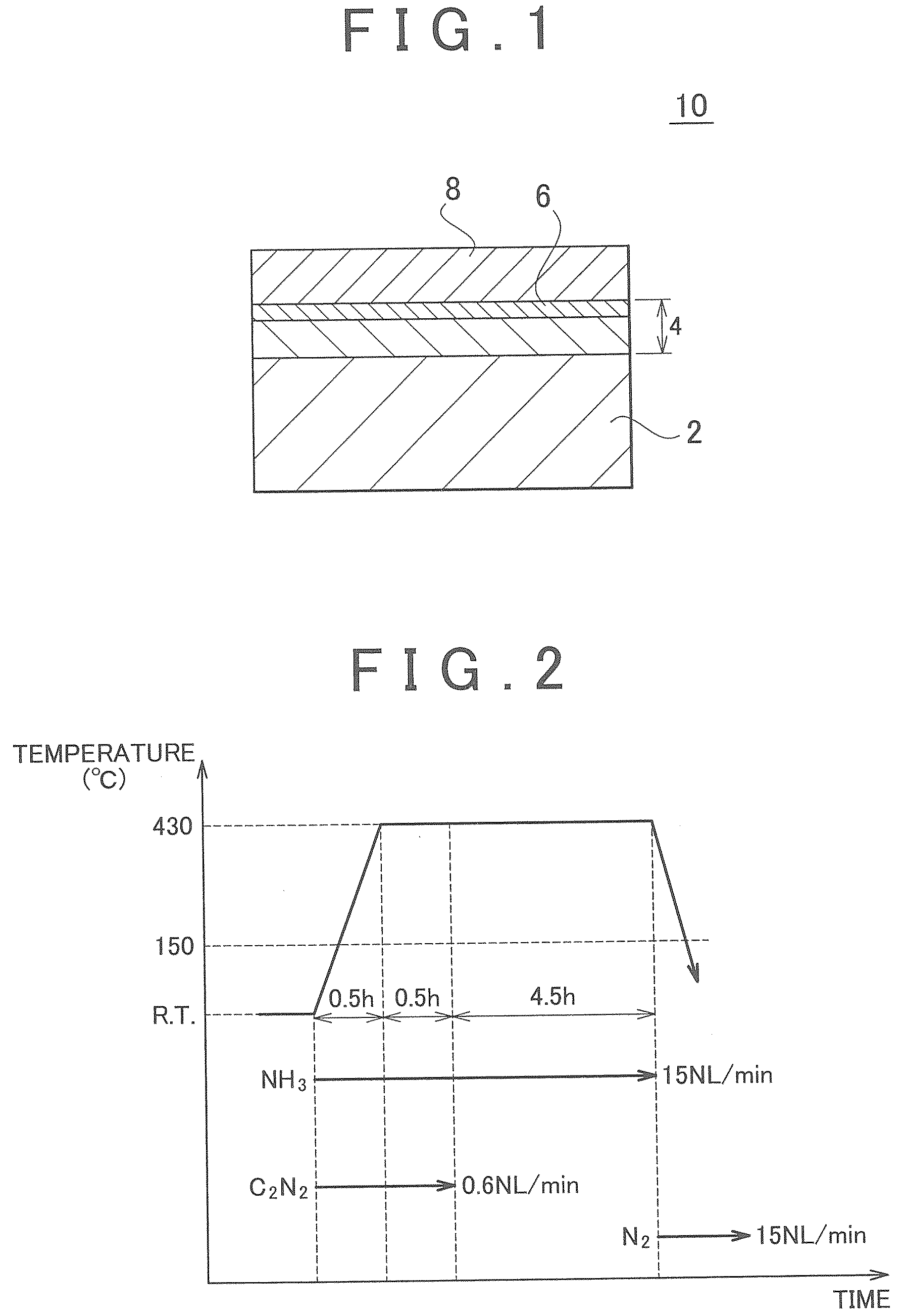
Method of forming conformal dielectric film having Si-N bonds by PECVD
ActiveUS7972980B2Increase deposition rateHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricNoble gas
Owner:ASM JAPAN
METHOD OF FORMING CONFORMAL DIELECTRIC FILM HAVING Si-N BONDS BY PECVD
ActiveUS20100221925A1Reduce the temperatureIncrease deposition rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricHydrocotyle bowlesioides
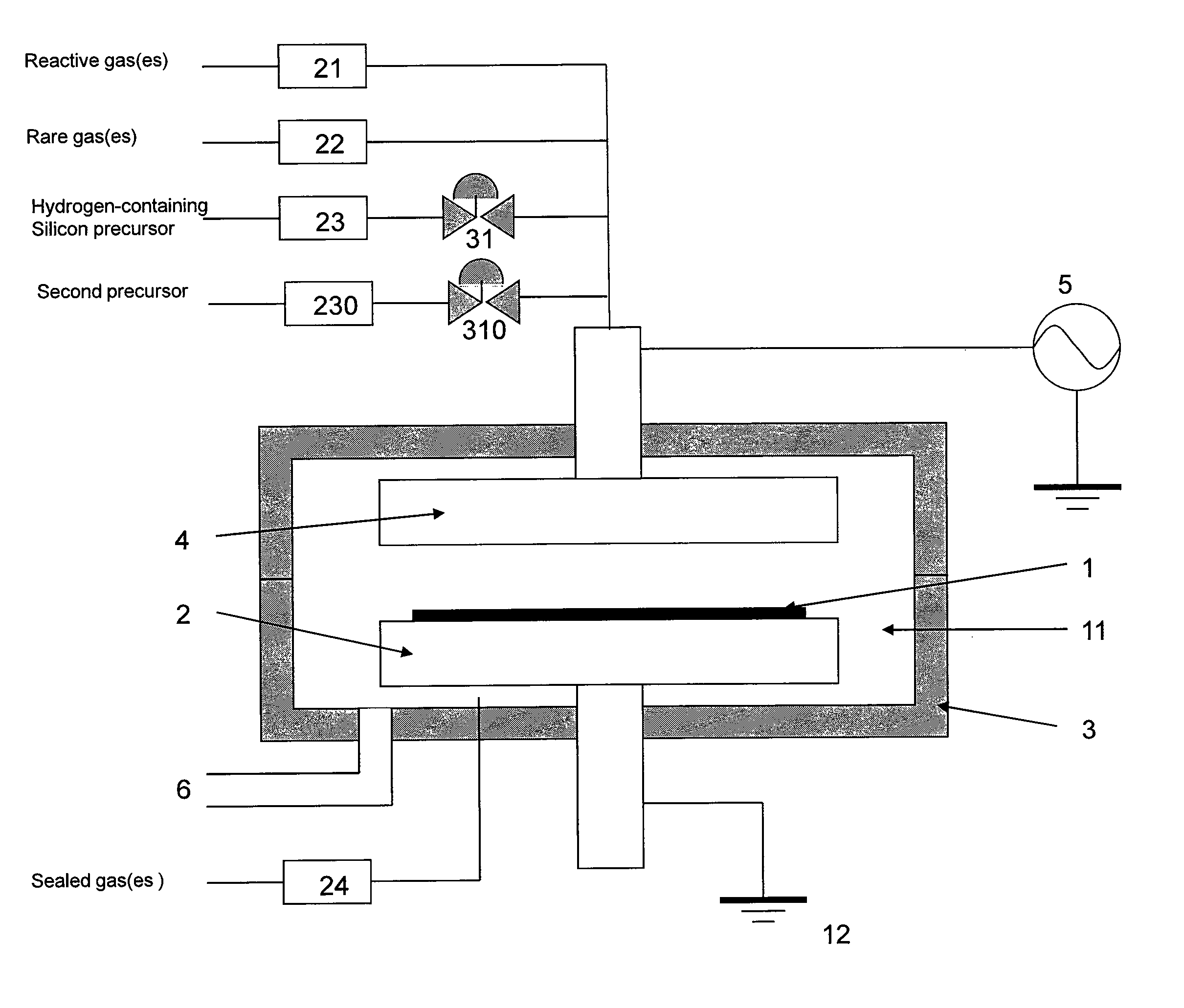
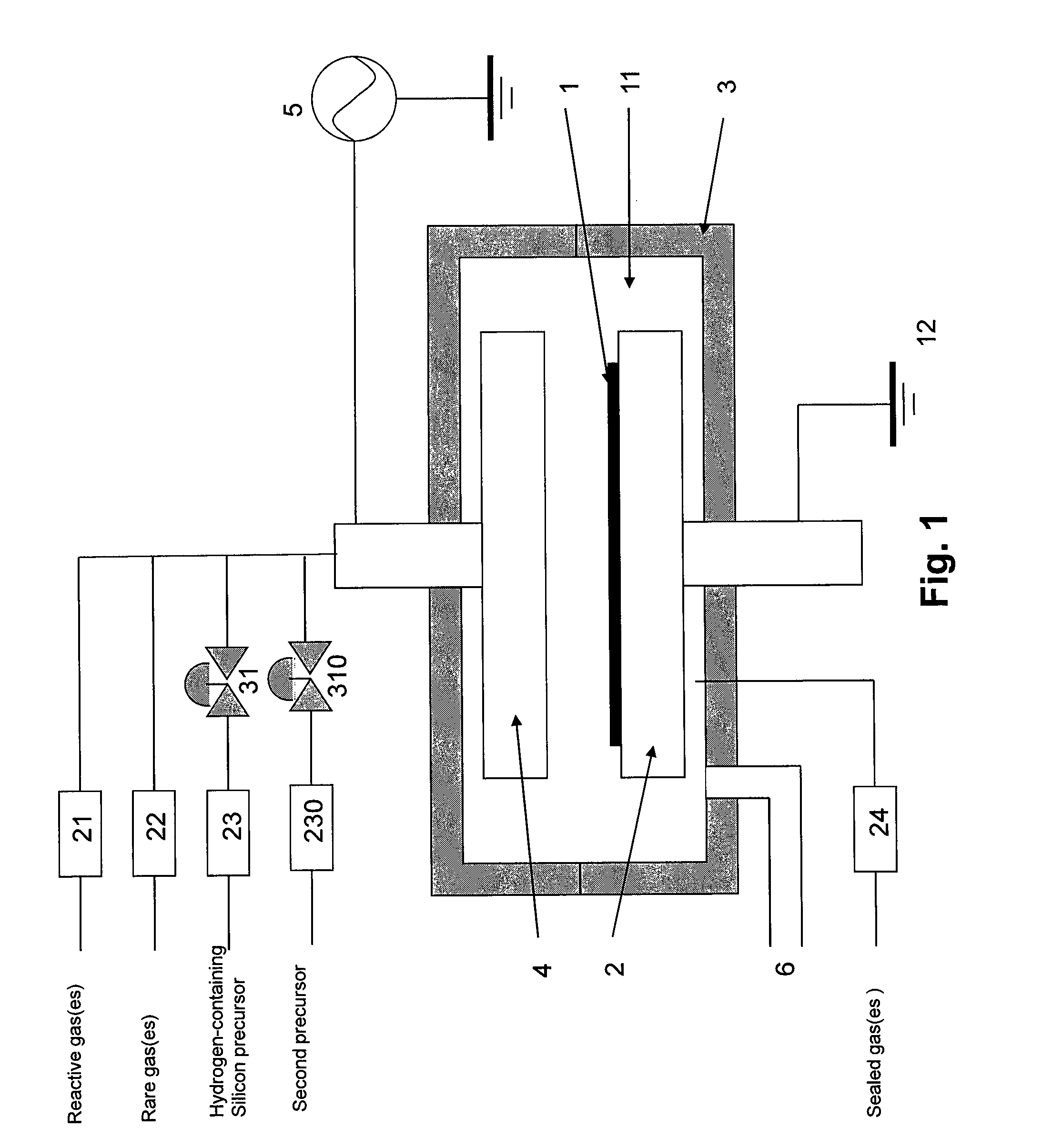
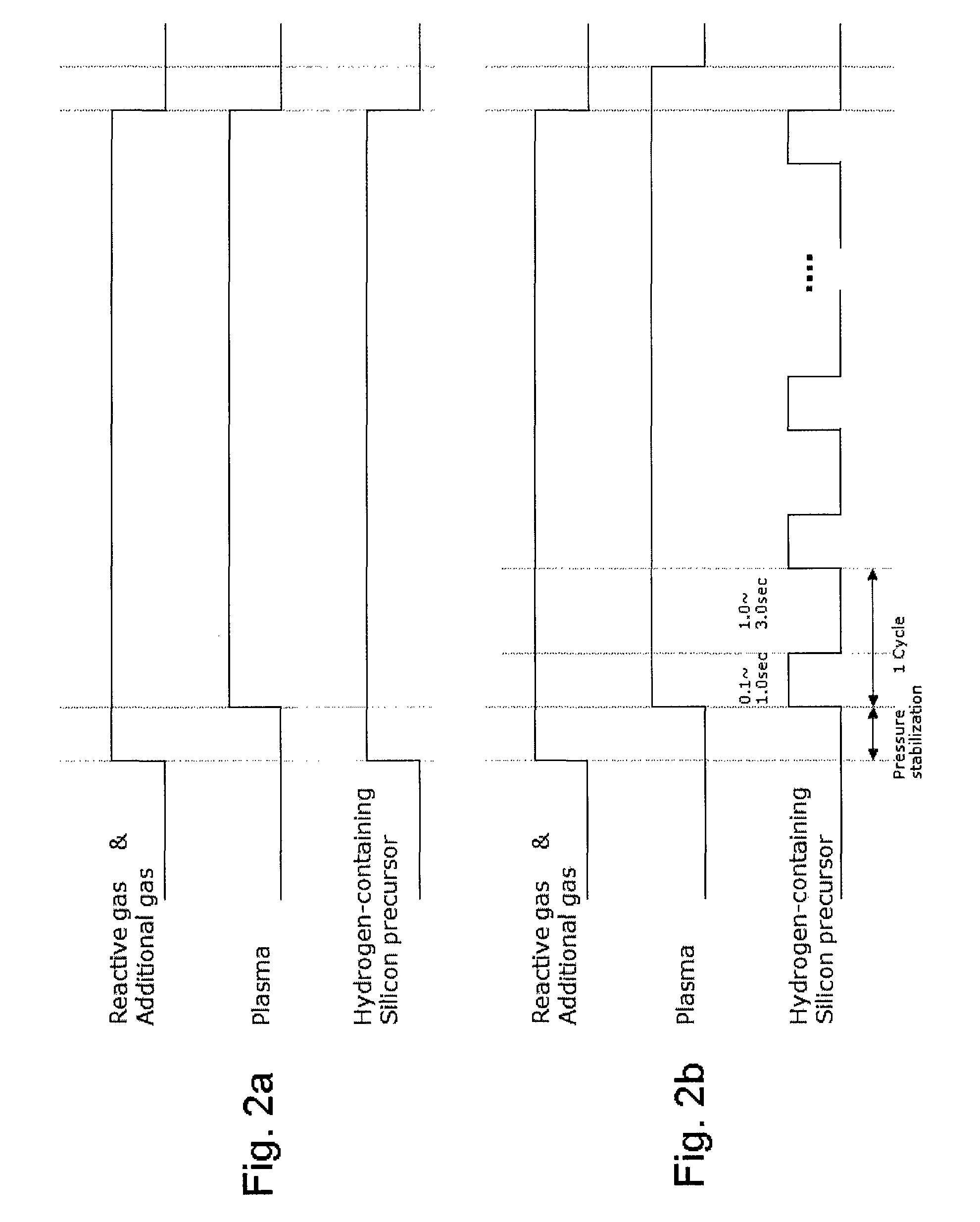
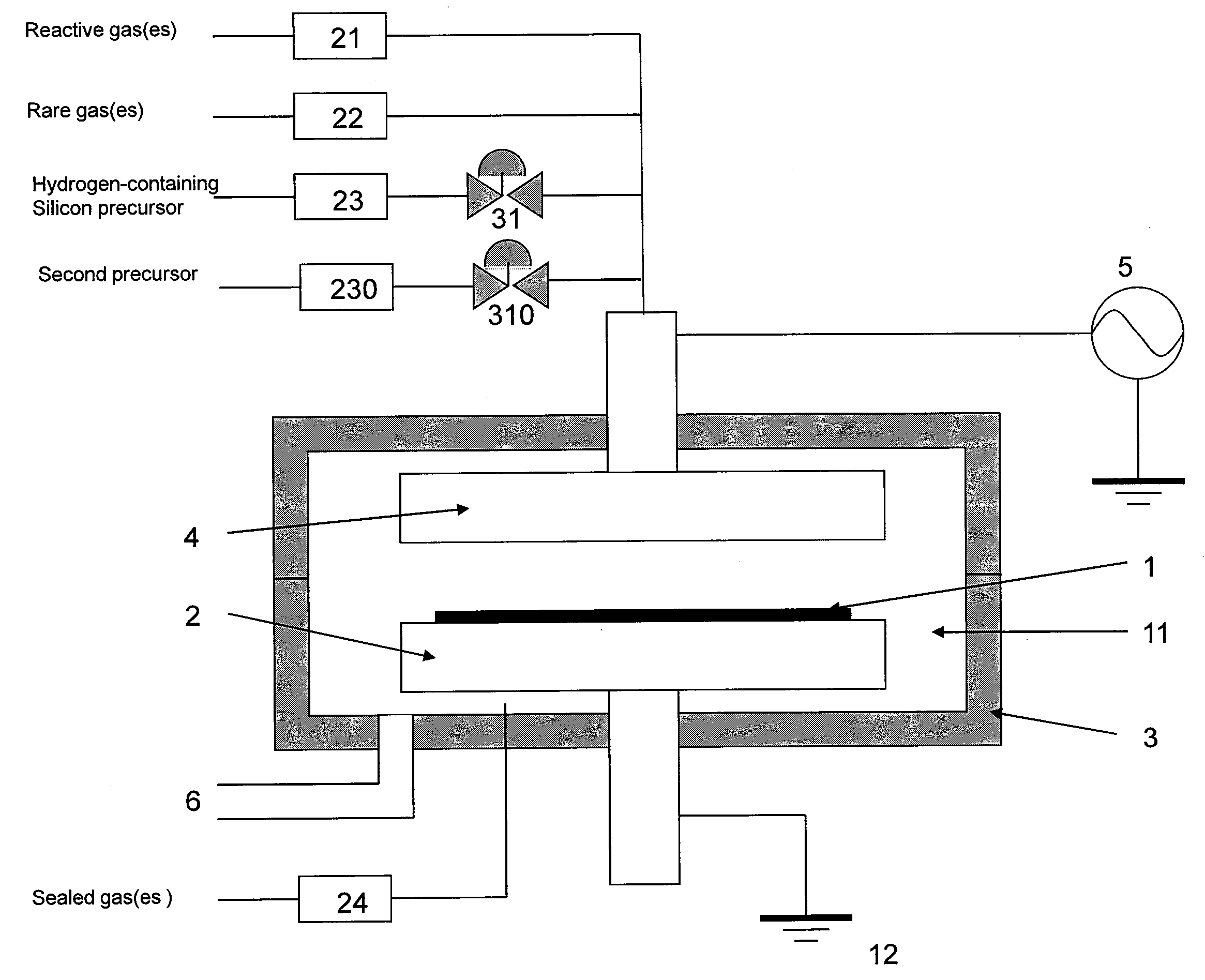
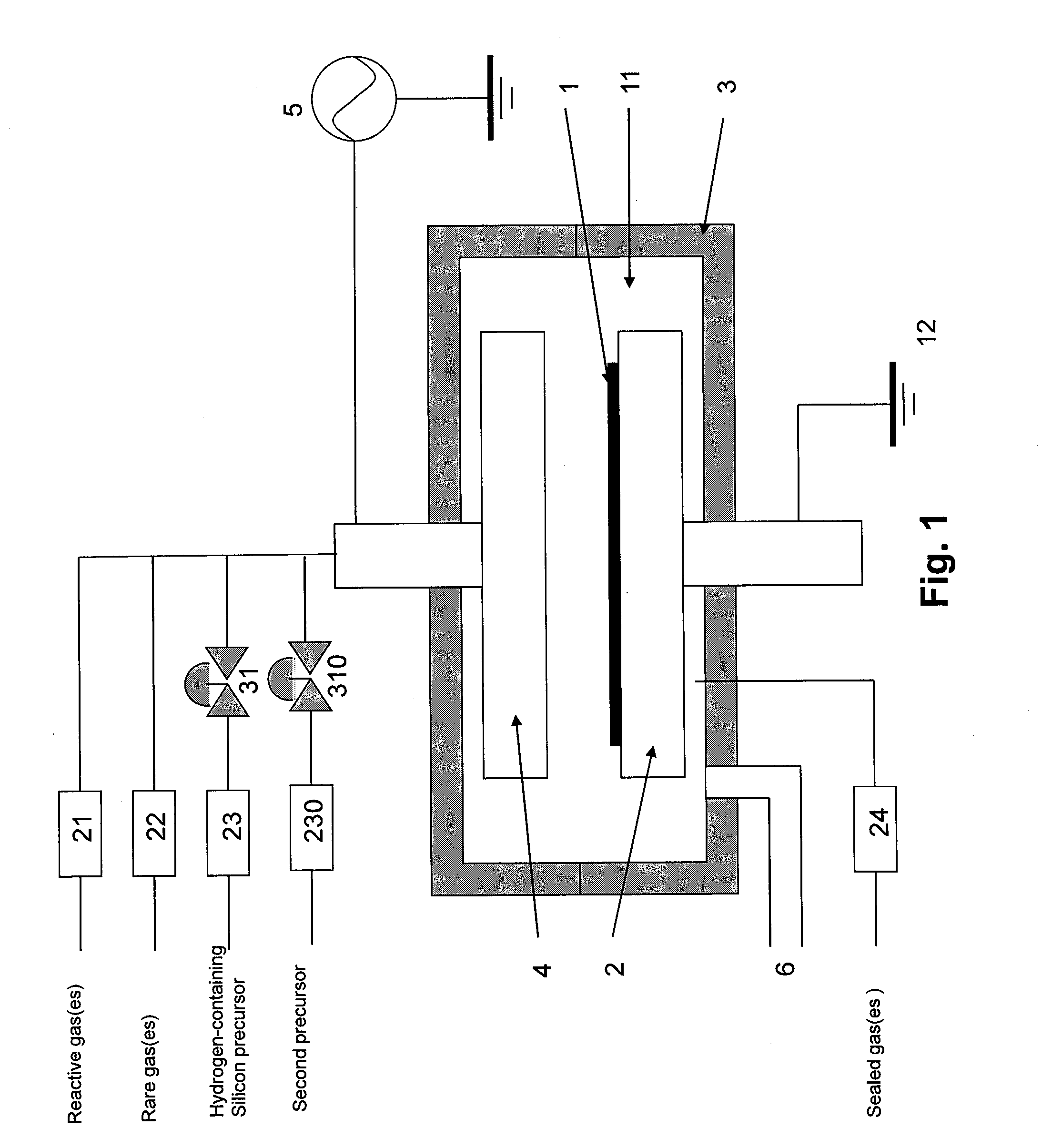
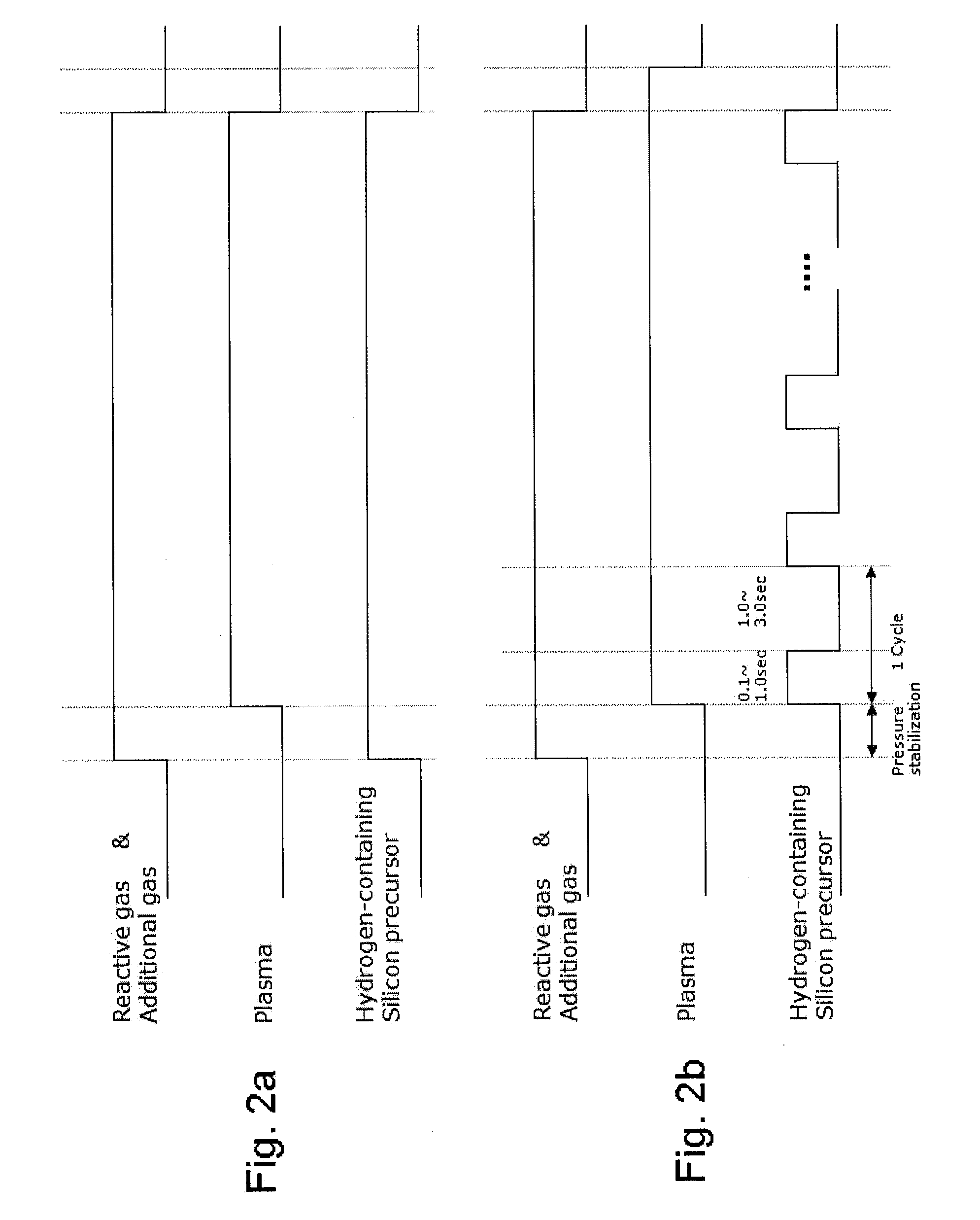
A method of forming a conformal dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which a semiconductor substrate is placed; applying RF power to the reaction space; and introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor as a first precursor and a hydrocarbon gas as a second precursor in pulses into the reaction space wherein a plasma is excited, thereby forming a conformal dielectric film doped with carbon and having Si—N bonds on the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Aromatic hydrocarbon resin and composition for forming underlayer film for lithography
ActiveUS20120171611A1Increase carbon concentrationReduce oxygen concentrationPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The aromatic hydrocarbon resin can be used as a coating material and a resist resin for a semiconductor, and has a high carbon concentration and a low oxygen concentration. A composition for forming an underlayer film for lithography that has excellent etching resistance as an underlayer film for a multilayer resist process, an underlayer film formed with the same, and a pattern forming method using the same are disclosed. An aromatic hydrocarbon is reacted with an aromatic aldehyde in the presence of an acidic catalyst, thereby providing an aromatic hydrocarbon resin that has a high carbon concentration of from 90 to 99.9% by mass and a low oxygen concentration of from 0 to 5% by mass. A composition for forming an underlayer film for lithography contains the resin and an organic solvent, an underlayer film is formed with the same, and a pattern forming method uses the same.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
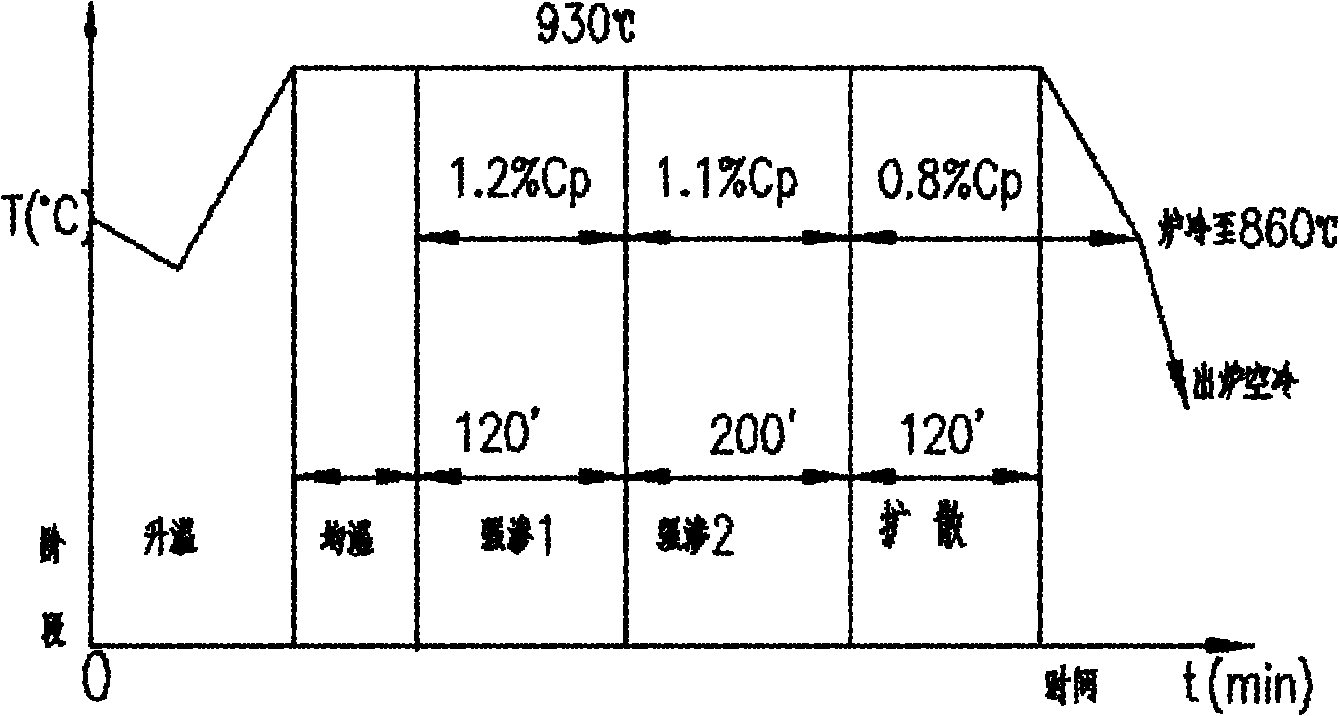
Carburizing method for wind power gear used for wind power generation
ActiveCN101984139AIncrease carbon concentrationImprove surface strengthSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesQuenchingSurface strength
The invention provides a carburizing method for a wind power gear used for wind power generation, which comprises the following steps: carrying out first carburizing treatment on the wind power gear to be treated under the atmosphere with carbon potential of 0.8%-1.1%, then carrying out first quenching treatment, further rising the temperature to 600 DEG C-660 DEG C, and carrying out first tempering treatment; then carrying out second carburizing treatment under the atmosphere with the carbon potential of 0.8%-1.0%, and carrying out second quenching treatment after the second carburizing treatment; and further carrying out second tempering treatment on the wind power gear at 150 DEG C-200 DEG C after the second quenching treatment. Compared with the prior art, the carburizing method is characterized by firstly carburizing the wind power gear for 30-40h under the atmosphere with the carbon potential of 0.8%-1.1%, and then uniformly dissolving and dispersing over-saturated carbon in martensite after the first high-temperature tempering so as to be conductive to the next step of the treatment; and further carburizing the wind power gear for 1-4h under the atmosphere with the carbon potential of 0.8%-1.0% after the first high-temperature tempering treatment, thereby further increasing the carbon concentration on the surface of the wind power gear and improving the surface strength during the second carburizing treatment.
Owner:江苏丰东热技术有限公司
Diffusion barrier for damascene structures
InactiveUS20060099802A1Increase carbon concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureConductive materials
A semiconductor structure having a via formed in a dielectric layer is provided. The exposed pores of the dielectric material along the sidewalls of the via are partially or completely sealed. Thereafter, one or more barrier layers may be formed and the via may be filled with a conductive material. The barrier layers formed over the sealing layer exhibits a more continuous barrier layer. The pores may be partially or completely sealed by performing, for example, a plasma process in an argon environment.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Agent for dispersing electrically conductive carbon material, and dispersion of electrically conductive carbon material
InactiveUS20160200850A1Improve abilitiesImprove adhesionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesElectrolytic capacitorsArylHydrogen atom
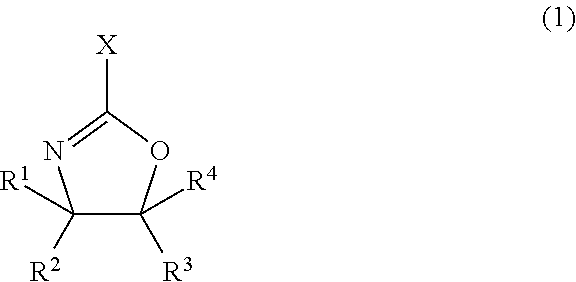
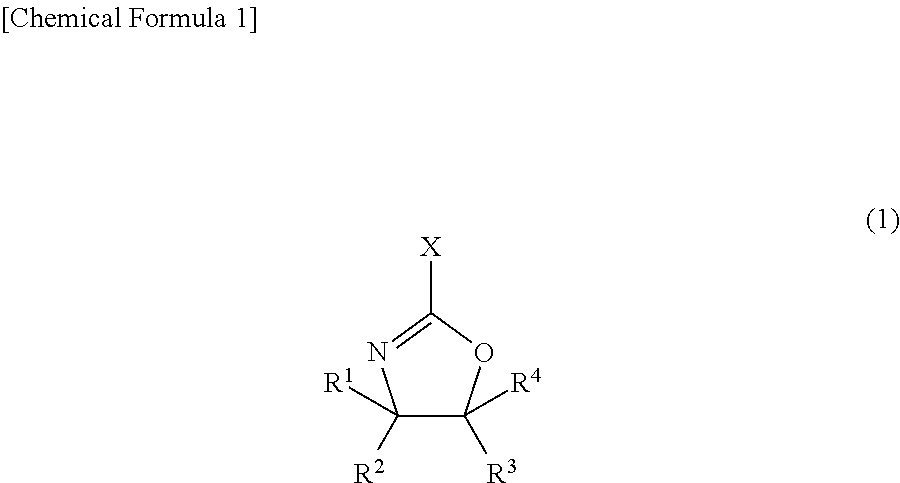
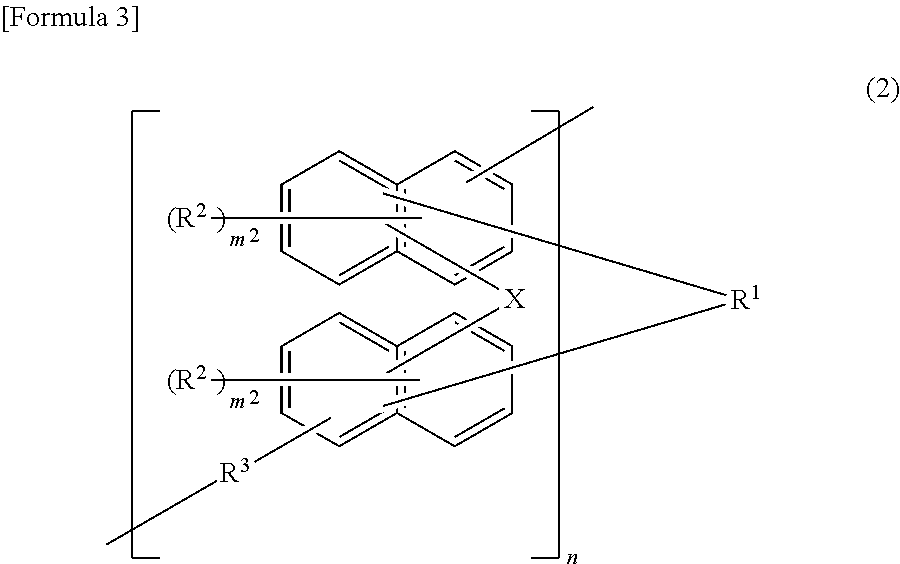
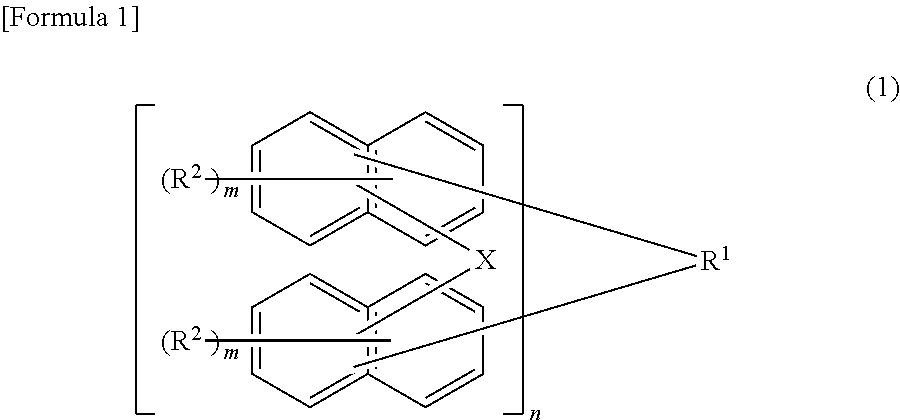
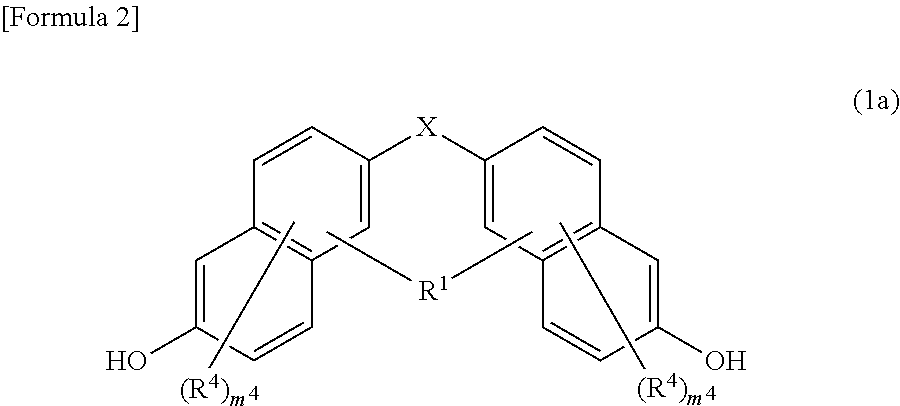
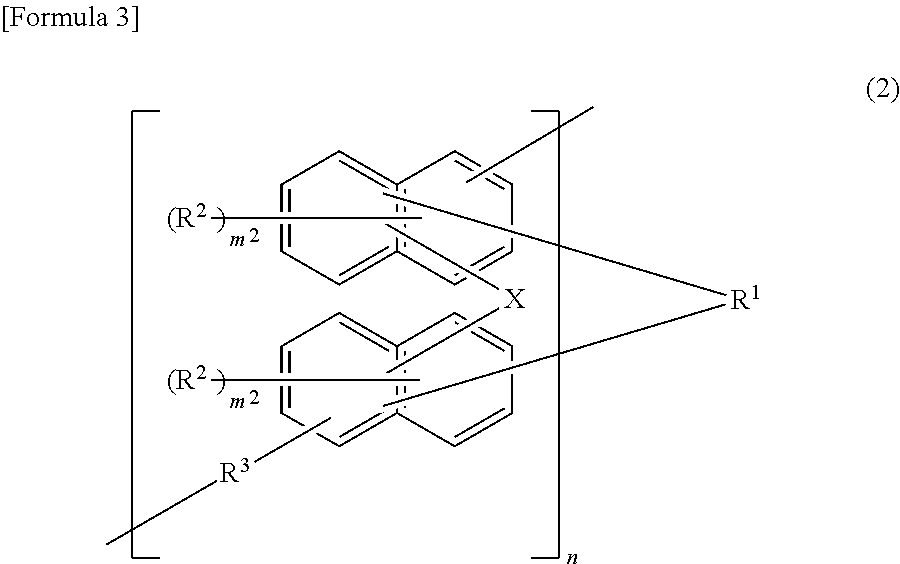
Provided is an agent for dispersing an electrically conductive carbon material, in which the agent consists of a polymer which has an oxazoline group in a side chain and which is obtained by using an oxazoline group-containing monomer such as that represented by formula (1) for example, and in which the agent exhibits excellent dispersion of an electrically conductive carbon material and produces a thin film that exhibits excellent adhesion to a current collection substrate when formed into a thin film together with the electrically conductive carbon material.(In the formula, X denotes a polymerizable carbon-carbon double bond-containing group, and R1-R4 each independently denote a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkyl group optionally having a branched structure having 1-5 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6-20 carbon atoms, or an aralkyl group having 7-20 carbon atoms.)
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Material for forming underlayer film lithography, underlayer film for lithography and pattern forming method
ActiveUS20150090691A1Excellent in heat resistance and etching resistanceImprove the immunityOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesSolubilityHeat resistance
Material for forming an underlayer film for lithography, which has a high carbon concentration, a low oxygen concentration, a relatively high heat resistance and also a relatively high solvent solubility, and which can be applied to a wet process is disclosed. Material for forming an underlayer film for lithography contains a compound represented by general formula (1).
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Carburization processing method
ActiveCN102676983AIncrease carbon concentrationHigh hardnessSolid state diffusion coatingThermal insulationHardness
An embodiment of the invention discloses a carburization processing method. Composite carburization is adopted in the carburization processing method. First a workpiece is placed in a carburization medium of 900-980 DEG C, thermal insulation and cooling are carried out, then the workpiece is continuously placed in the carburization medium of 900-980 DEG C, and thermal insulation is performed. After carburization for the first time, the surface of the workpiece has a certain carbon concentration distribution and macroscopic thickness. Meanwhile, carburization for the second time in the step (b) is utilized to improve carbon concentration of the surface of the workpiece, and accordingly macrohardness and surface hardness of the surface of the workpiece are improved. Experimental results show that the macroscopic thickness of the workpiece processed by the method is 0.78-1mm, and the hardness at the position of 0.15mm is larger than 700HV.
Owner:青岛德盛机械制造有限公司
Underlayer film-forming material for lithography, underlayer film for lithography, and pattern formation method
ActiveUS9316913B2Excellent in heat resistance and etching resistanceImprove the immunityOrganic chemistrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityLithographic artist
Material for forming an underlayer film for lithography, which has a high carbon concentration, a low oxygen concentration, a relatively high heat resistance and also a relatively high solvent solubility, and which can be applied to a wet process is disclosed. Material for forming an underlayer film for lithography contains a compound represented by general formula (1).
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
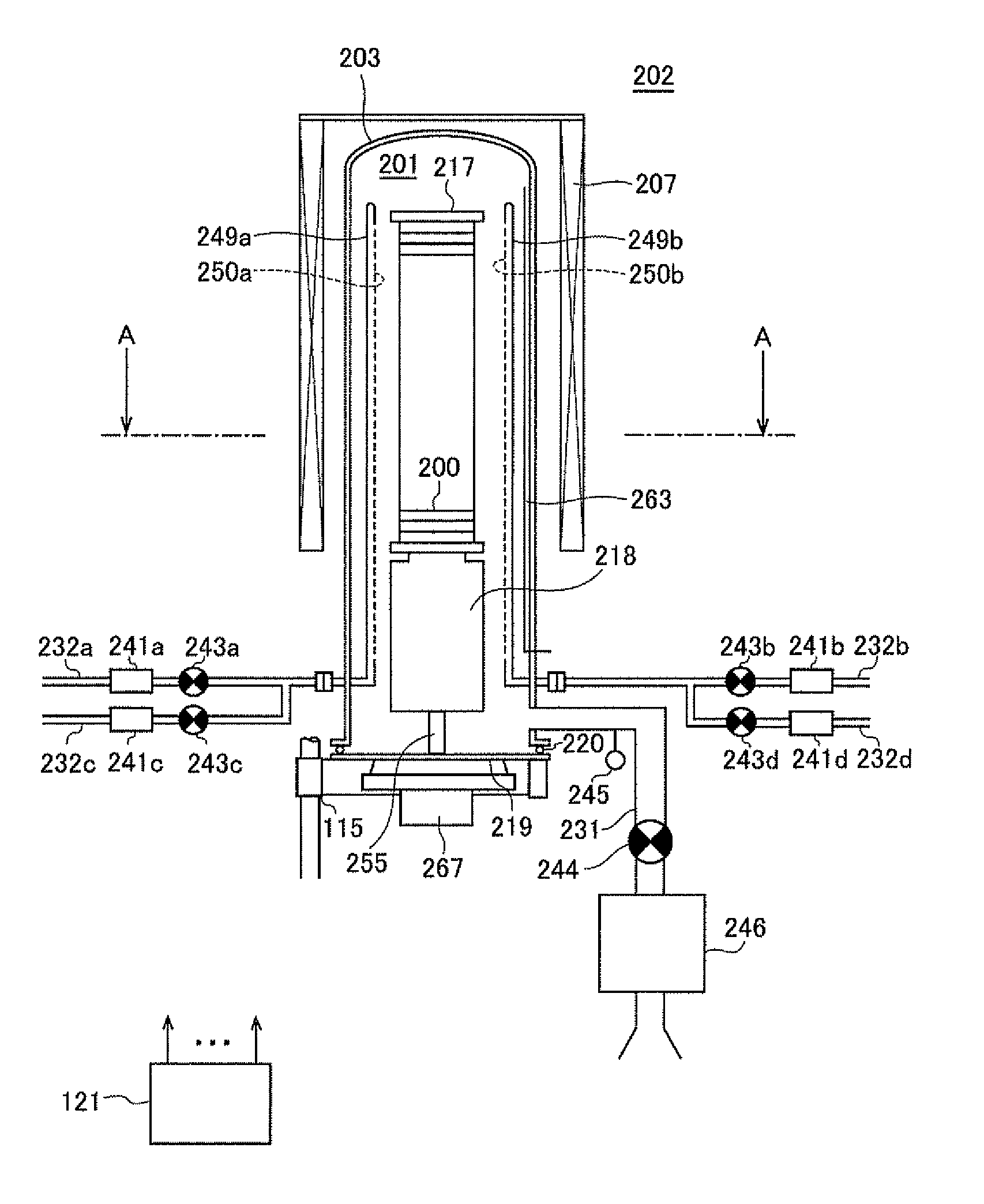
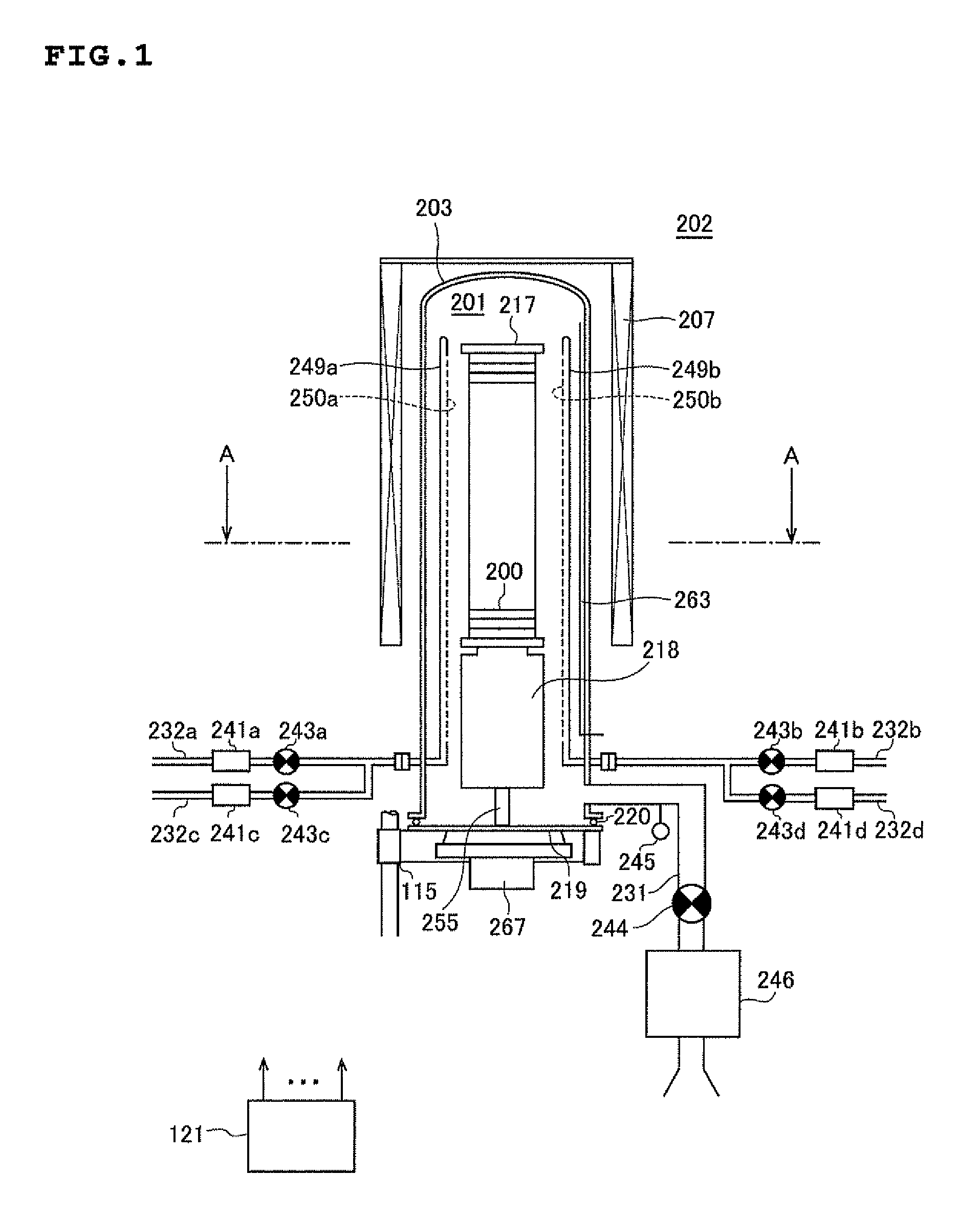
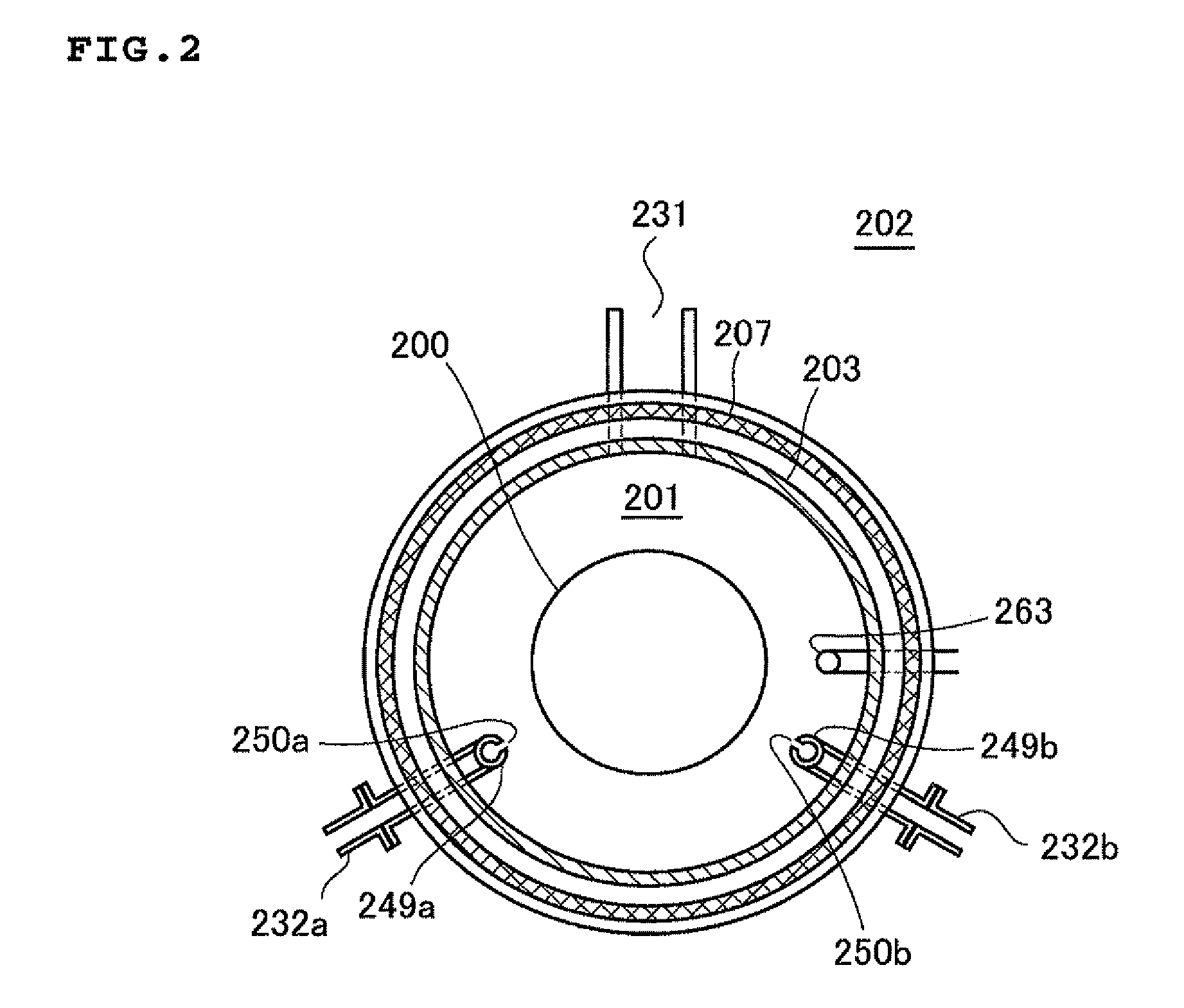
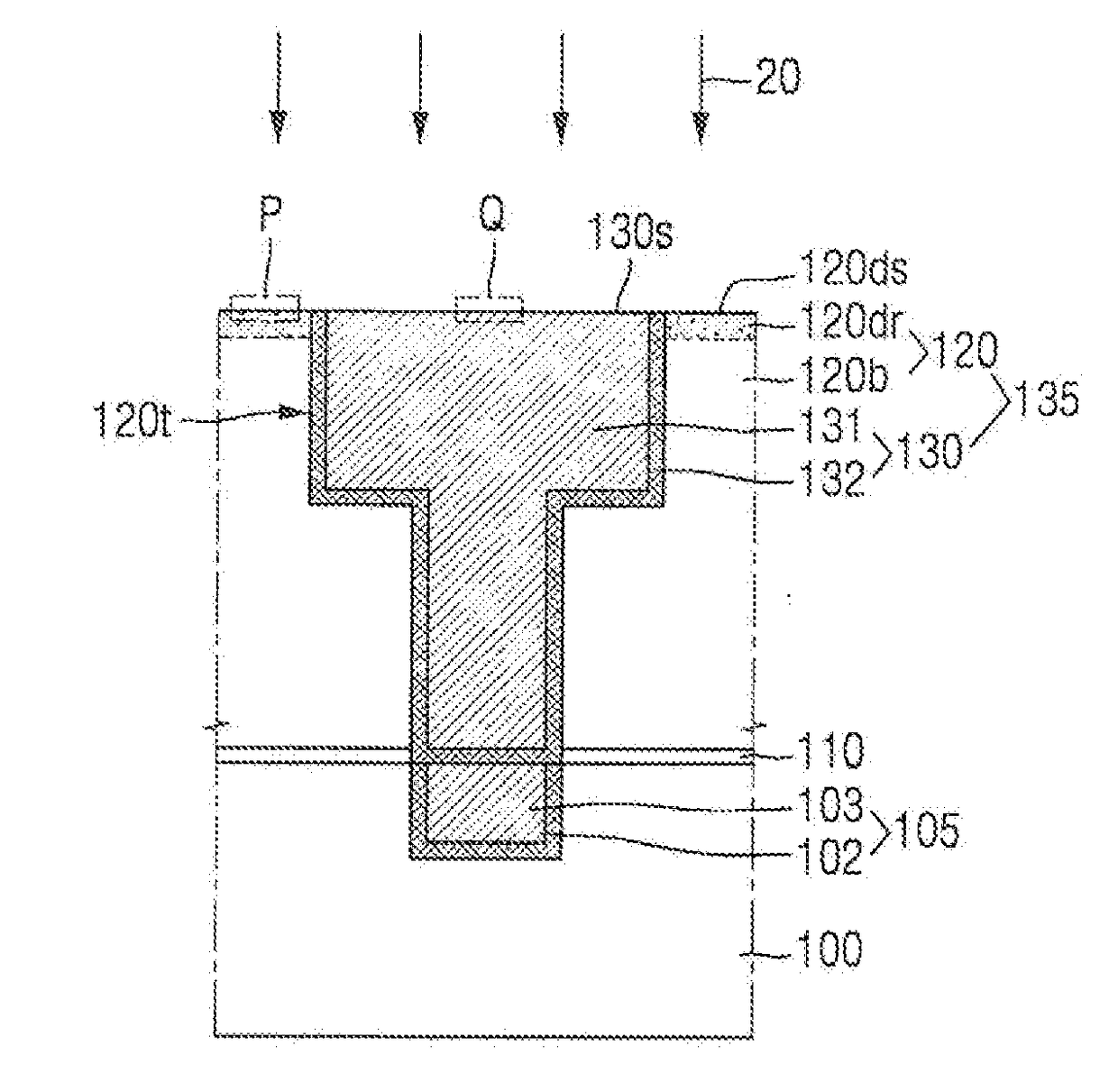
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, method of processing substrate, substrate processing apparatus and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS20130149872A1Improve productivityIncrease carbon concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenHalogen
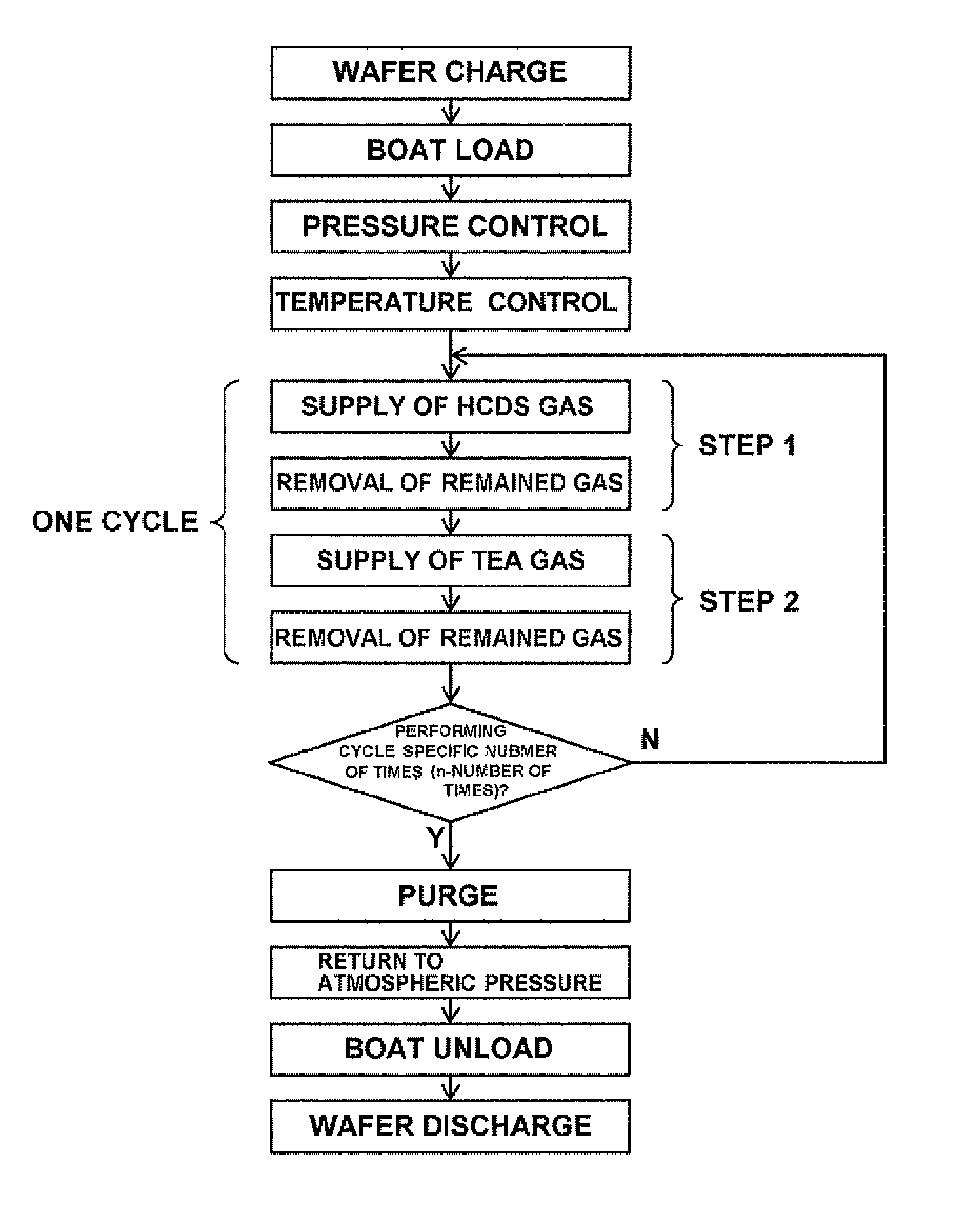
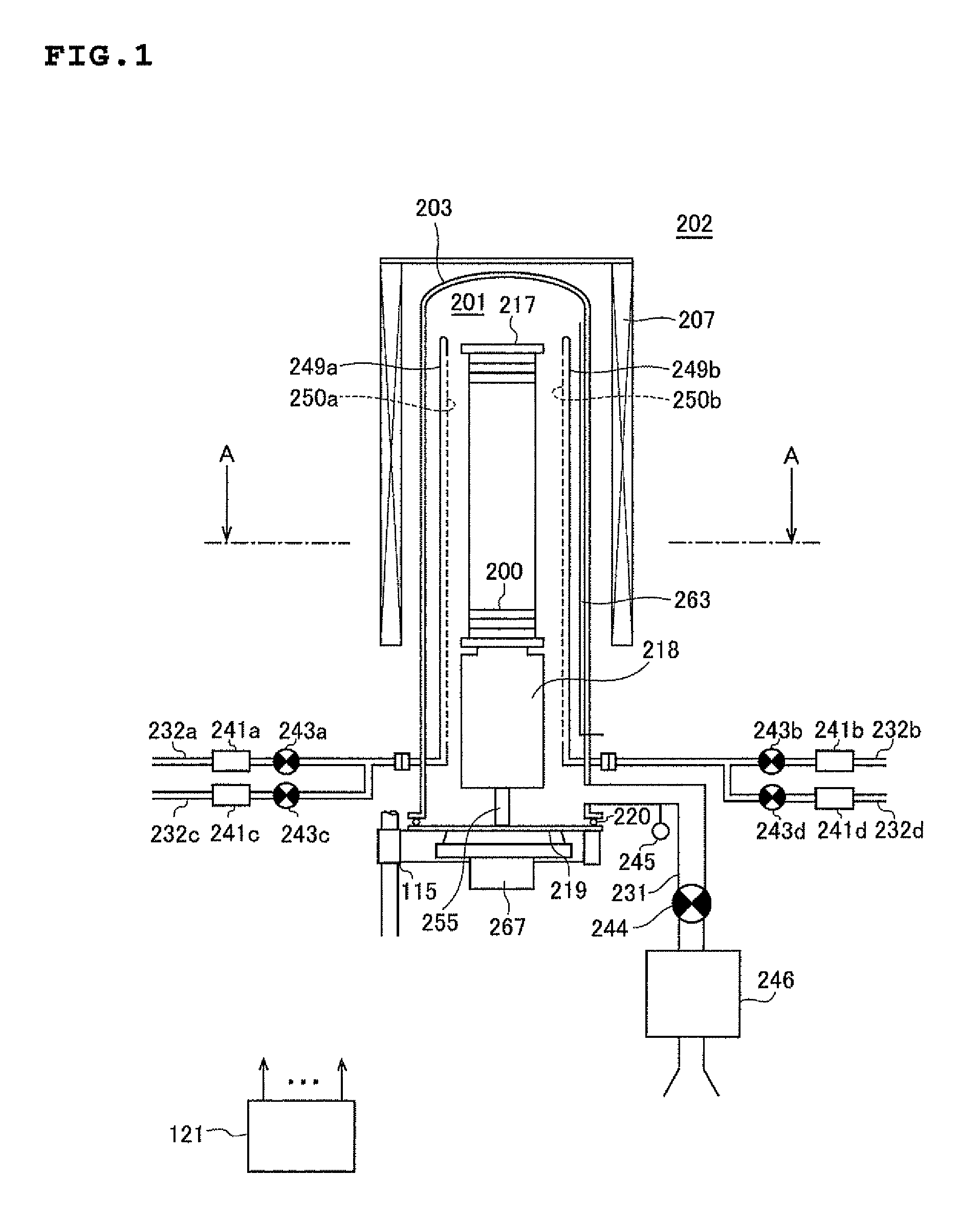
There is provided a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, including: forming a film containing a specific element, nitrogen, and carbon on a substrate, by alternately performing the following steps a specific number of times: a step of supplying a source gas containing the specific element and a halogen element, to the substrate; and a step of supplying a reactive gas composed of three elements of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen and having more number of a carbon atom than the number of a nitrogen atom in a composition formula thereof, to the substrate.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
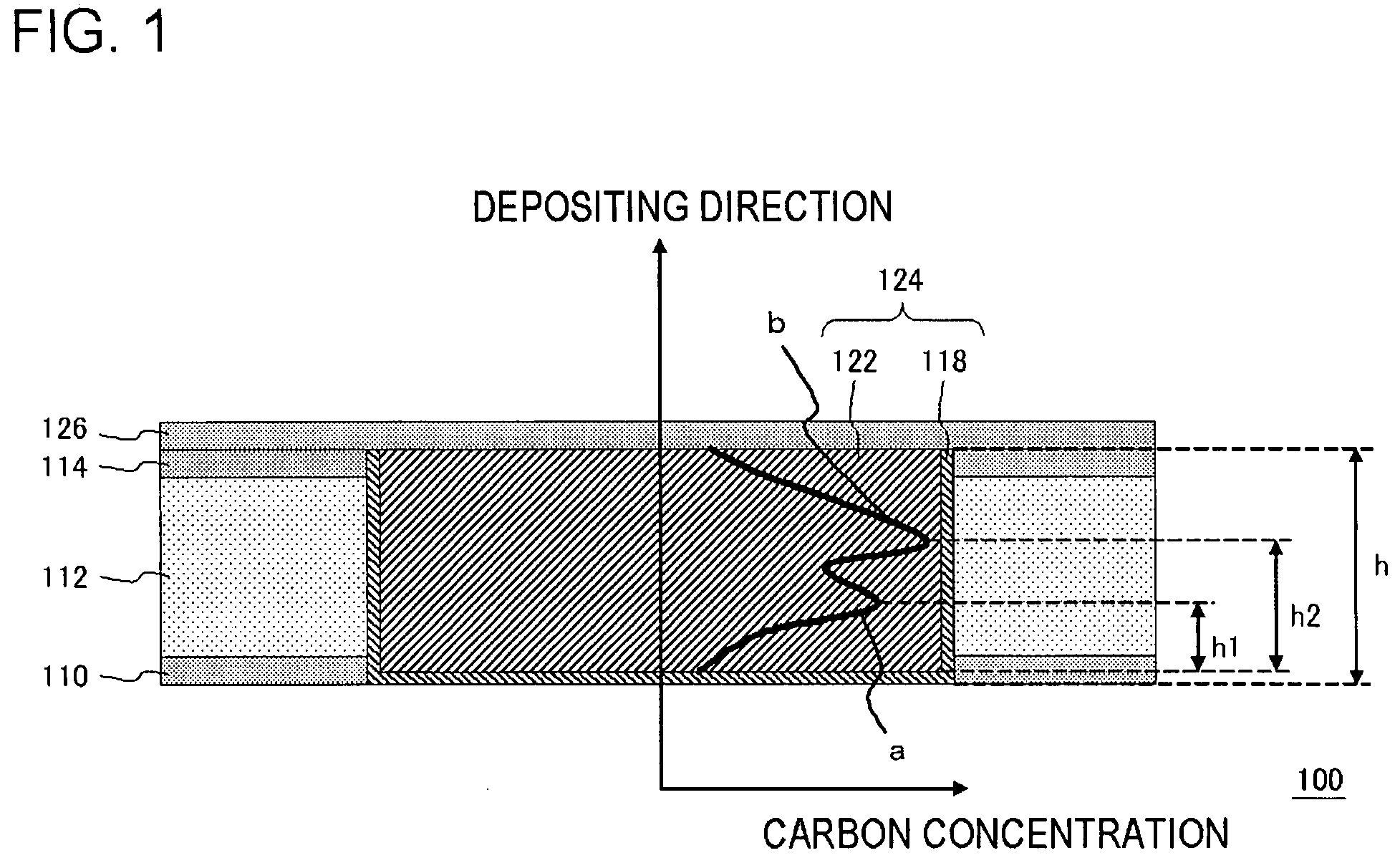
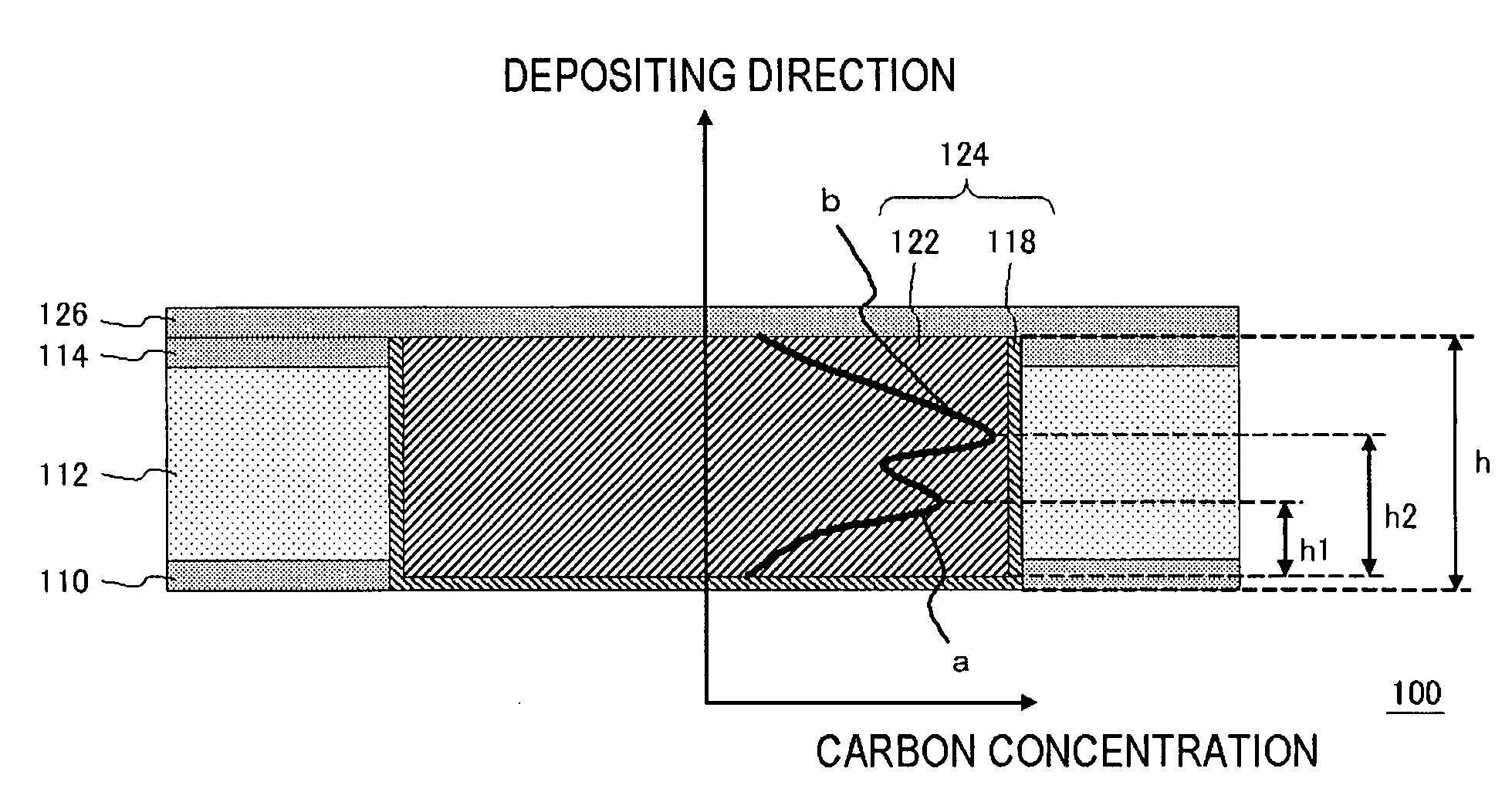
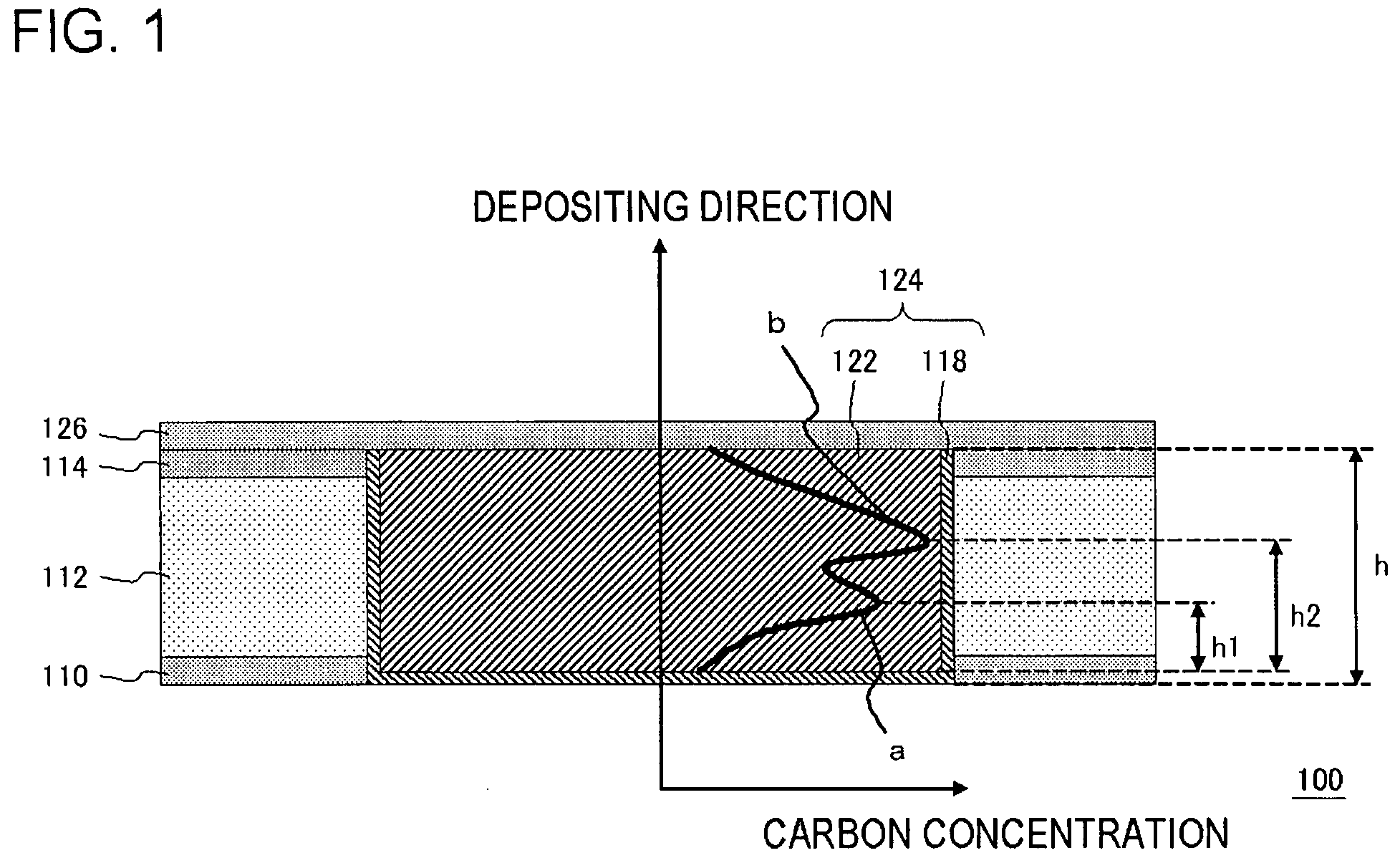
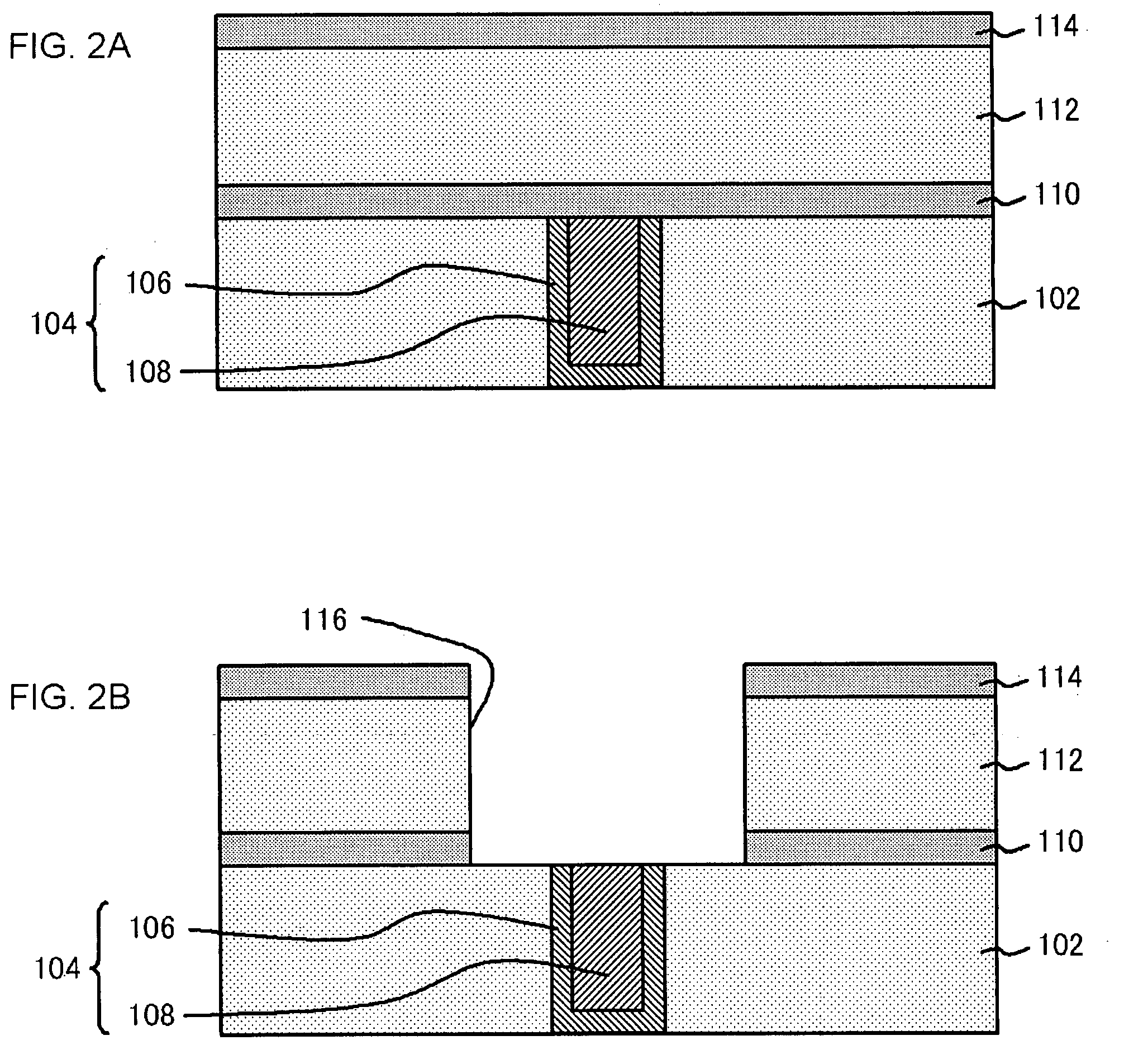
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20070190341A1Improved SIV resistanceCarbon concentration can be reducedElectrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
An improved SIV resistance and an improved EM resistance are achieved in the coupling structure containing copper films. A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a second insulating layer formed on or over the semiconductor substrate; a second barrier metal film, formed on the second insulating film, and being capable of preventing copper from diffusing into the second insulating film; and an electrically conducting film formed on the second barrier metal film so as to be in contact with the second barrier metal film, and containing copper and carbon, wherein a distribution of carbon concentration along a depositing direction in the second electrically conducting film includes a first peak and a second peak.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
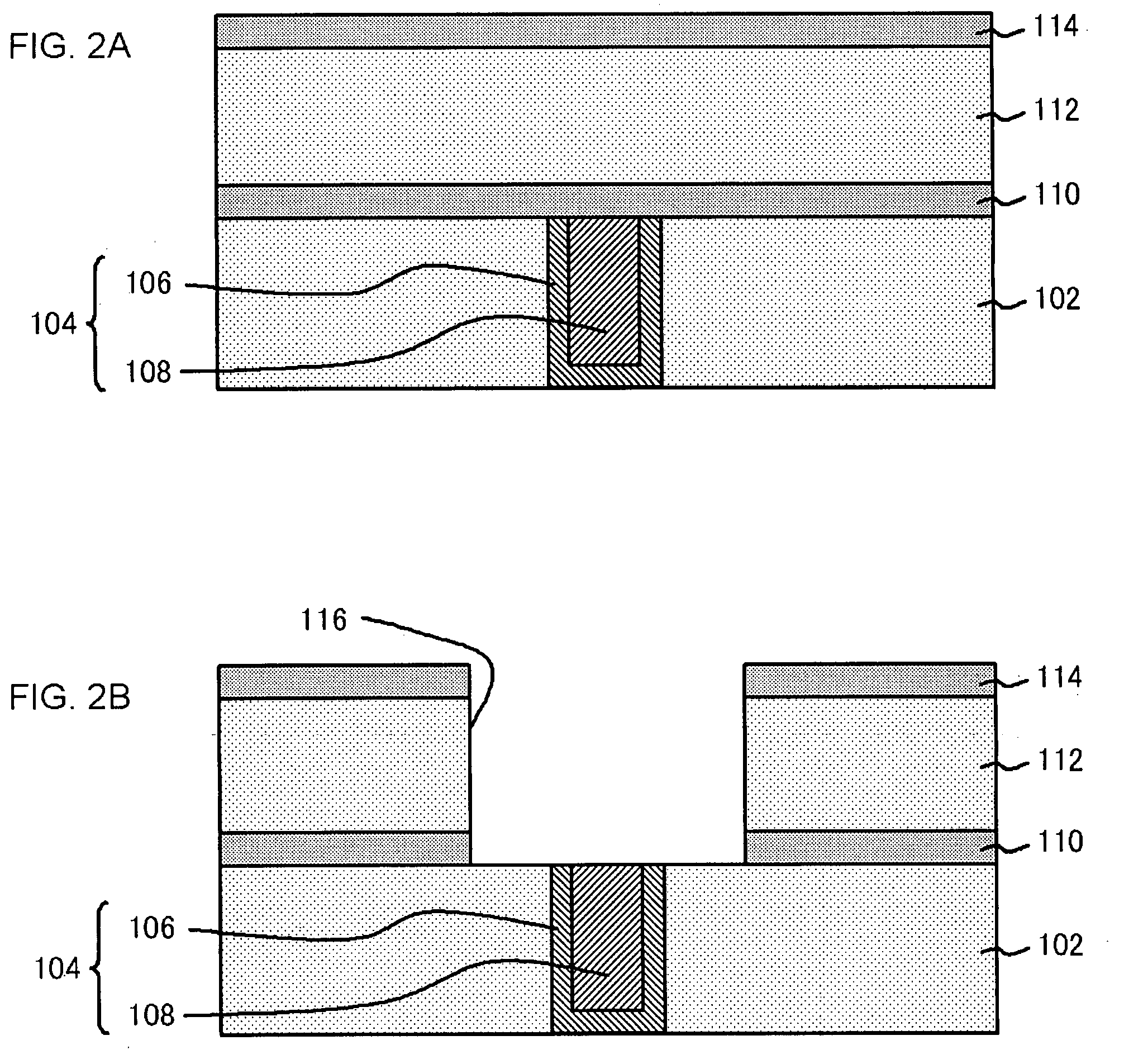
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with less leakage current induced by carbon implant
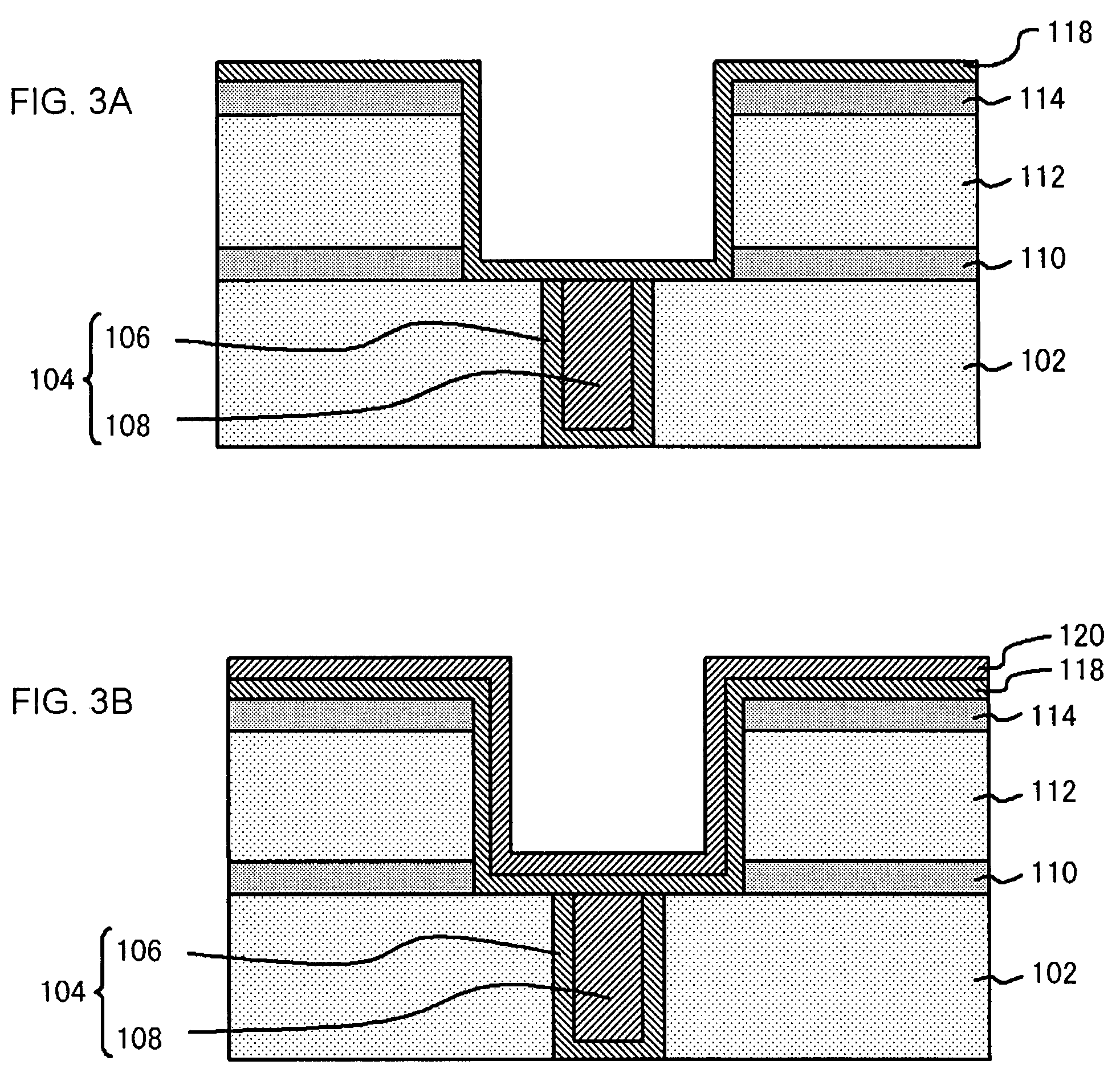
ActiveUS8211784B2Minimize the possibilityReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceFree interface
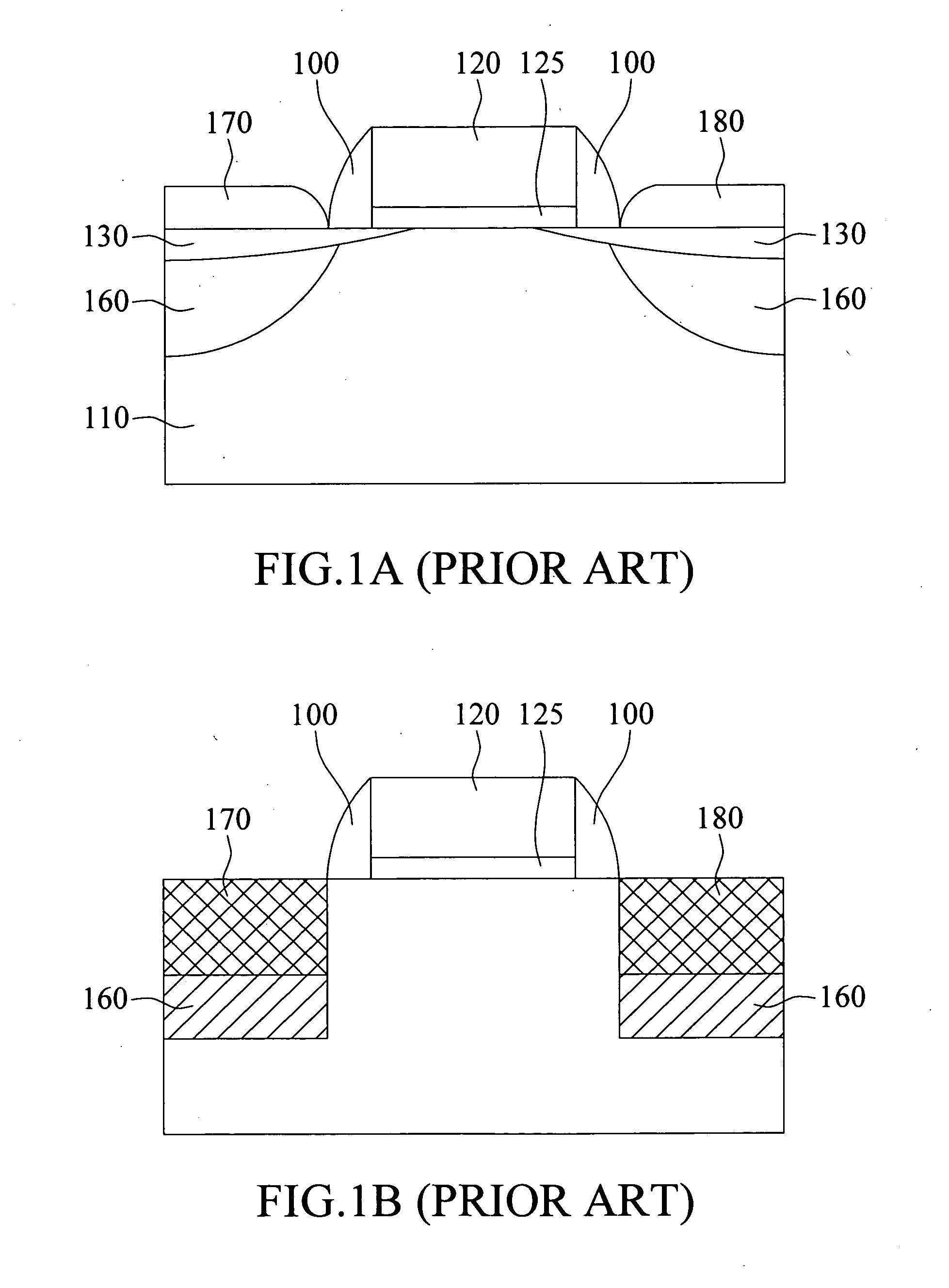
A semiconductor device has at least two main carbon-rich regions and two additional carbon-rich regions. The main carbon-rich regions are separately located in a substrate so that a channel region is located between them. The additional carbon-rich regions are respectively located underneath the main carbon-rich regions. The carbon concentrations is higher in the main carbon-rich regions and lower in the additional carbon-rich regions, and optionally, the absolute value of a gradient of the carbon concentration of the bottom portion of the main carbon-rich regions is higher than the absolute value of a gradient of the carbon concentration of the additional carbon-rich regions. Therefore, the leakage current induced by a lattice mismatch effect at the carbon-rich and the carbon-free interface can be minimized.
Owner:ADVANCED ION BEAM TECHNOLOGY INC
Carburizing treatment method
InactiveCN106086769AIncrease carbon concentrationHigh hardnessSolid state diffusion coatingHardnessCarburizing
The invention provides a carburizing treatment method. The carburizing treatment method adopts a composite carburizing method. A workpiece is placed in a carburizing medium with the temperature being 900-980 DEG C at first, heat preservation and cooling are conducted, then the workpiece continues to be placed in the carburizing medium with the temperature being 900-980 DEG C, and heat preservation is conducted. According to the carburizing treatment method, after the first time of carburizing, the workpiece surface has the carbon concentration distribution and macro thickness to a certain extent. Meanwhile, the carbon concentration on the workpiece surface is increased through the second time of carburizing in the step (b), so that the macro hardness and surface hardness of the workpiece surface are improved. Experimental results show that the macro thickness of the workpiece treated through the method is 0.78-1 mm, and the hardness of the position, 0.15 mm thick, of the workpiece is greater than 700 HV.
Owner:南通三荣实业有限公司
Surface-treated mold and method of producing surface-treated mold
ActiveUS20110127403A1Improve adhesionAdhesionFoundry mouldsSolid state diffusion coatingCarbon filmNichrome
A surface-treated mold that includes a mold, a metal layer that is provided on a surface of the mold and contains at least one metal selected from nickel, chromium, tungsten and brass, and a carbon film that is provided on a surface of the metal layer, wherein the metal layer contains carbon, and the carbon concentration in the metal layer is higher between the boundary with the carbon film and the center of the metal layer than that between the boundary with the mold and the center of the metal layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Methods for Fabricating Semiconductor Devices Including Surface Treatment Processes
ActiveUS20180102280A1Improve performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
Methods for fabricating semiconductor devices may provide enhanced performance and reliability by recovering quality of a low-k insulating film damaged by a plasma process. A method may include forming a first interlayer insulating film having a trench therein on a substrate, filling at least a portion of the trench with a metal wiring region, exposing a surface of the metal wiring region and a surface of the first interlayer insulating film to a plasma in a first surface treatment process, then exposing the surface of the first interlayer insulating film to a recovery gas containing a methyl group (—CH3) in a second surface treatment process, and then forming an etch stop layer on the metal wiring region and the first interlayer insulating film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
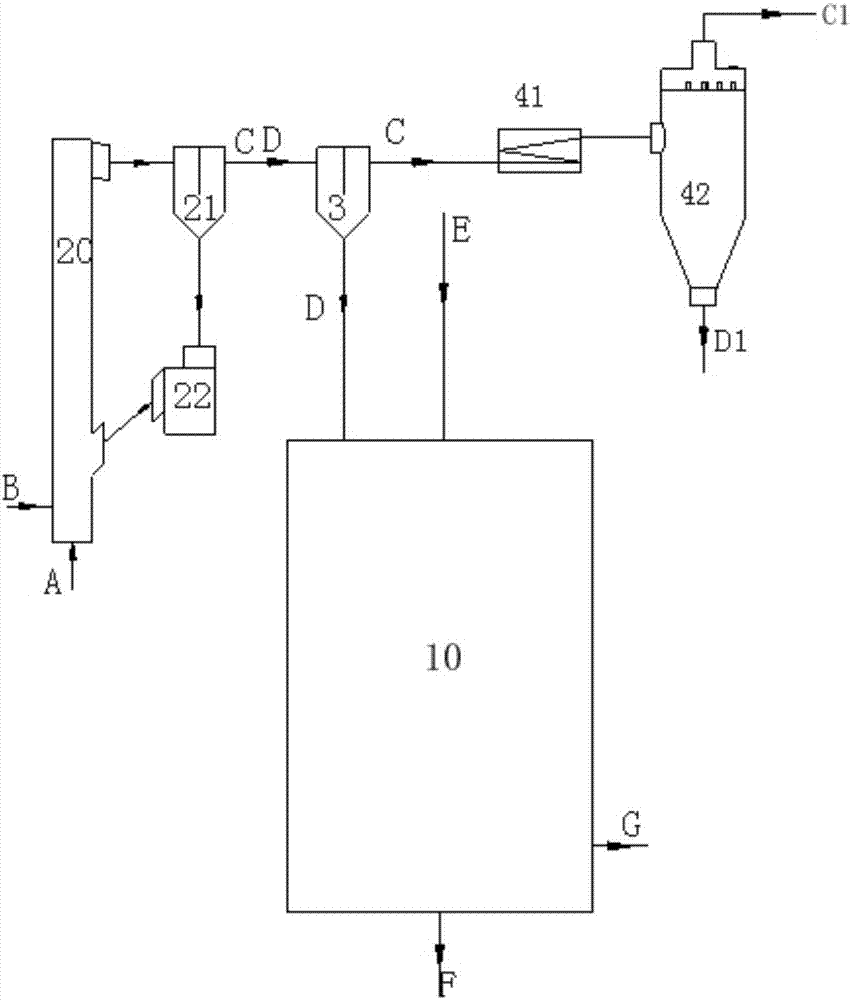
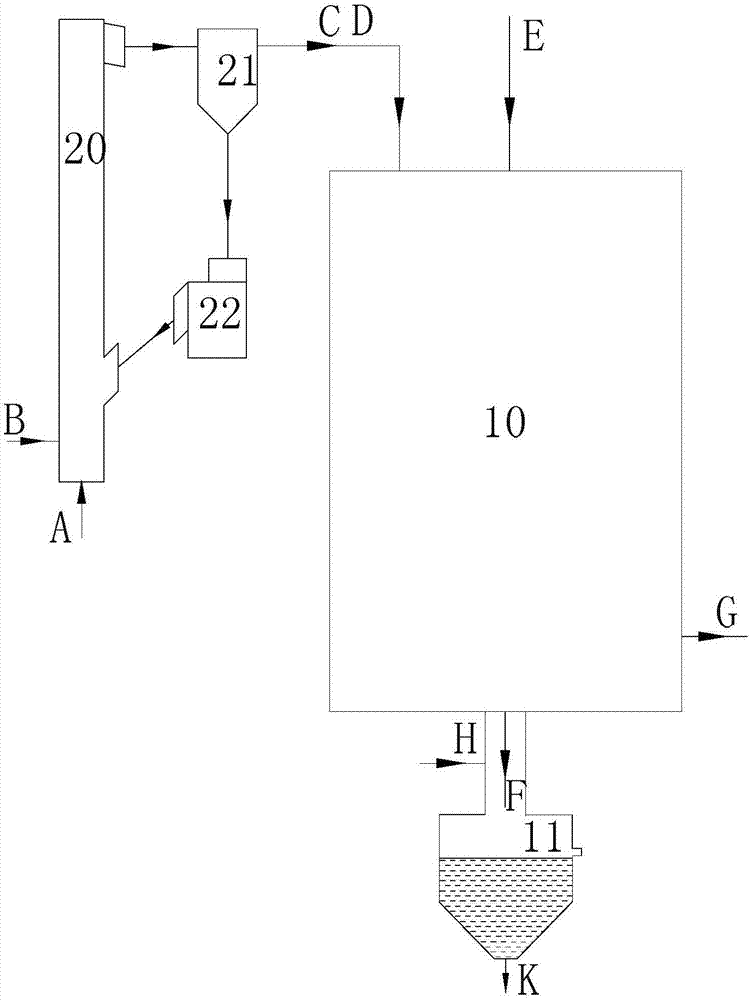
Preheating type graded gasification method and device
PendingCN107880938AHigh reactivityLower requirementGasification processes detailsGranular/pulverulent flues gasificationSlagCoal
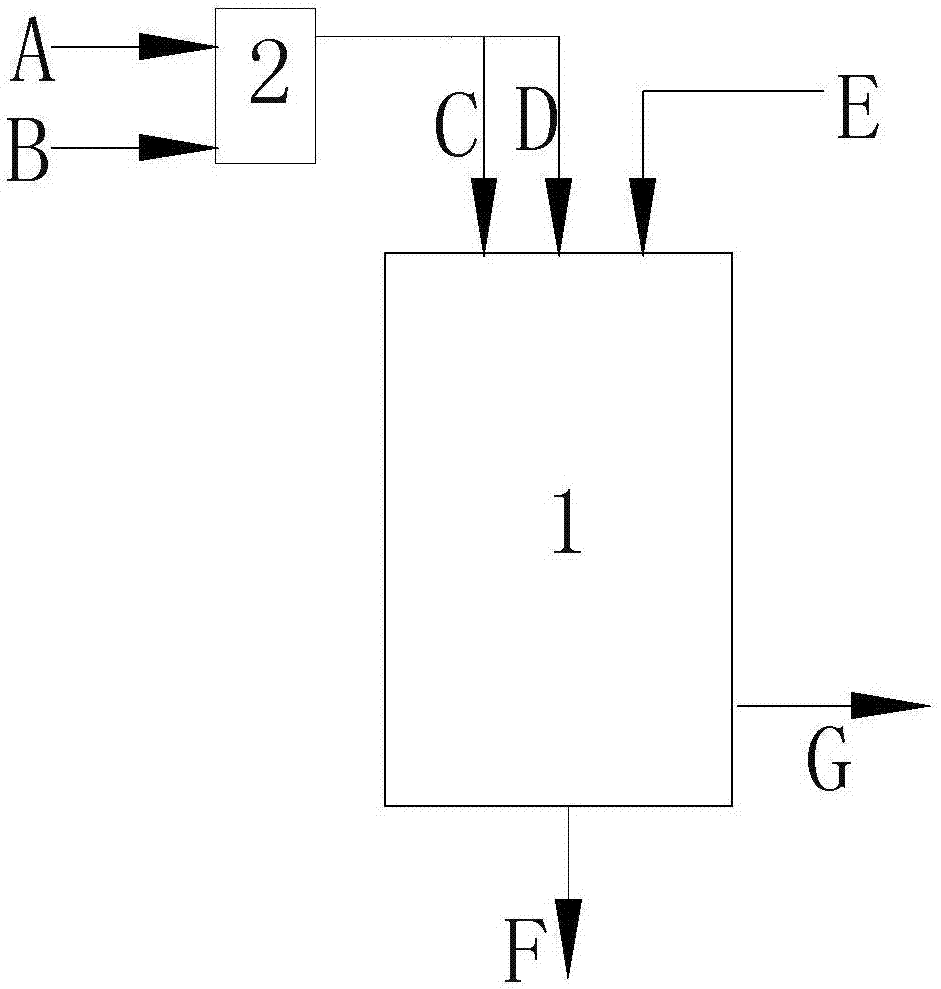
The invention provides a preheating type graded gasification method which comprises the following steps: (a) introducing fuel (A) and a first gasifying agent (B) into a front-loading preheating chamber (2), and preheating so as to generate a preheated gas-solid mixture (CD); (b) performing gas-solid separation on the preheated gas-solid mixture (CD) by using a separation device (3) so as to form reductive fume (C) and preheated fuel (D); (c) introducing a second gasifying agent (E) and the preheated fuel (D) into an entrained-flow gasifier (1), and enabling the two components to react to generate a crude coal gas (G) and bottom slag (F); and (d) collecting the reductive fume (C) and the crude coal gas (G), and discharging the bottom slag (F) outside the entrained-flow gasifier (1). The invention further provides a preheating type graded gasification device. By adopting the preheating type graded gasification method and the preheating type graded gasification device provided by the invention, no burner is used, wide coal applicability is achieved, coal can be prepared easily, and product gas is rich in CH4.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
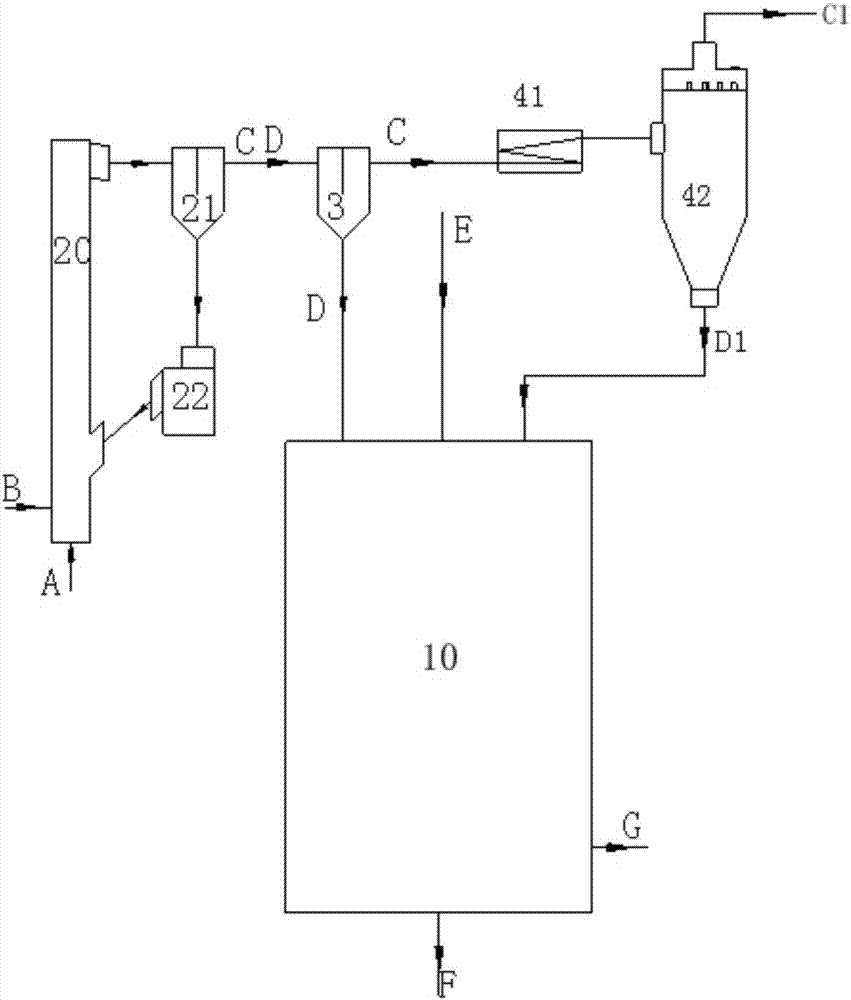
Preheating type gasification method and device
ActiveCN107880940AIncrease carbon concentrationImprove carbon conversionGasification processes detailsGranular/pulverulent flues gasificationSlagFront loading
The invention provides a preheating type gasification method which comprises the following steps: (a) introducing fuel (A) and a first gasifying agent (B) into a front-loading preheating chamber (2),and preheating so as to generate reductive fume (C) and preheated fuel (D); (b) introducing a second gasifying agent (E), the preheated fuel (D) and the reductive fume (C) into an entrained-flow gasifier (1), and carrying out reaction on the three components to generate crude coal gas (G) and bottom slag (F); and (c) collecting the crude coal gas (G), and discharging the bottom slag (F) outside the entrained-flow gasifier (1). The invention further provides a preheating type gasification gasification device. By adopting the preheating gasification method and the preheating gasification deviceprovided by the invention, the problems that a burner is short in service life and needs to be replaced at regular time are solved, wide coal applicability is achieved, coal can be prepared easily, high gasification efficiency and high carbon conversion rates are achieved, and in addition, no pure oxygen is needed.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
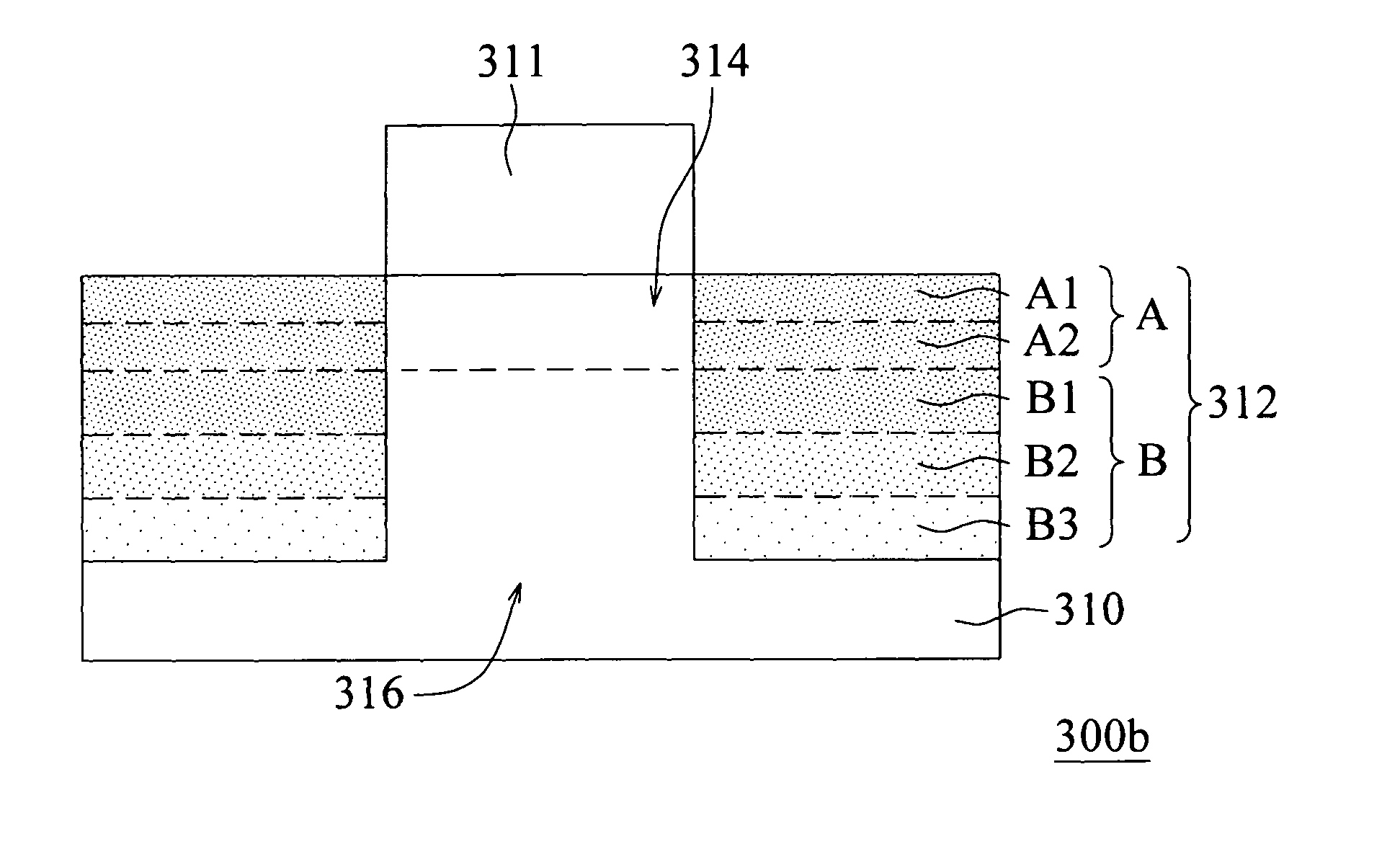
ActiveUS20110095339A1Minimize the possibilityReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFree interfaceLattice mismatch
A semiconductor device has at least two main carbon-rich regions and two additional carbon-rich regions. The main carbon-rich regions are separately located in a substrate so that a channel region is located between them. The additional carbon-rich regions are respectively located underneath the main carbon-rich regions. The carbon concentrations is higher in the main carbon-rich regions and lower in the additional carbon-rich regions, and optionally, the absolute value of a gradient of the carbon concentration of the bottom portion of the main carbon-rich regions is higher than the absolute value of a gradient of the carbon concentration of the additional carbon-rich regions. Therefore, the leakage current induced by a lattice mismatch effect at the carbon-rich and the carbon-free interface can be minimized.
Owner:ADVANCED ION BEAM TECHNOLOGY INC
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, method of processing substrate, substrate processing apparatus and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS8815751B2Improve productivityIncrease carbon concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenHalogen
There is provided a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, including: forming a film containing a specific element, nitrogen, and carbon on a substrate, by alternately performing the following steps a specific number of times: a step of supplying a source gas containing the specific element and a halogen element, to the substrate; and a step of supplying a reactive gas composed of three elements of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen and having more number of a carbon atom than the number of a nitrogen atom in a composition formula thereof, to the substrate.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Aromatic hydrocarbon resin and composition for forming underlayer film for lithography
ActiveUS8586289B2Increase carbon concentrationReduce oxygen concentrationPhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingResistLithographic artist
The aromatic hydrocarbon resin can be used as a coating material and a resist resin for a semiconductor, and has a high carbon concentration and a low oxygen concentration. A composition for forming an underlayer film for lithography that has excellent etching resistance as an underlayer film for a multilayer resist process, an underlayer film formed with the same, and a pattern forming method using the same are disclosed. An aromatic hydrocarbon is reacted with an aromatic aldehyde in the presence of an acidic catalyst, thereby providing an aromatic hydrocarbon resin that has a high carbon concentration of from 90 to 99.9% by mass and a low oxygen concentration of from 0 to 5% by mass. A composition for forming an underlayer film for lithography contains the resin and an organic solvent, an underlayer film is formed with the same, and a pattern forming method uses the same.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Method of preparing potable water
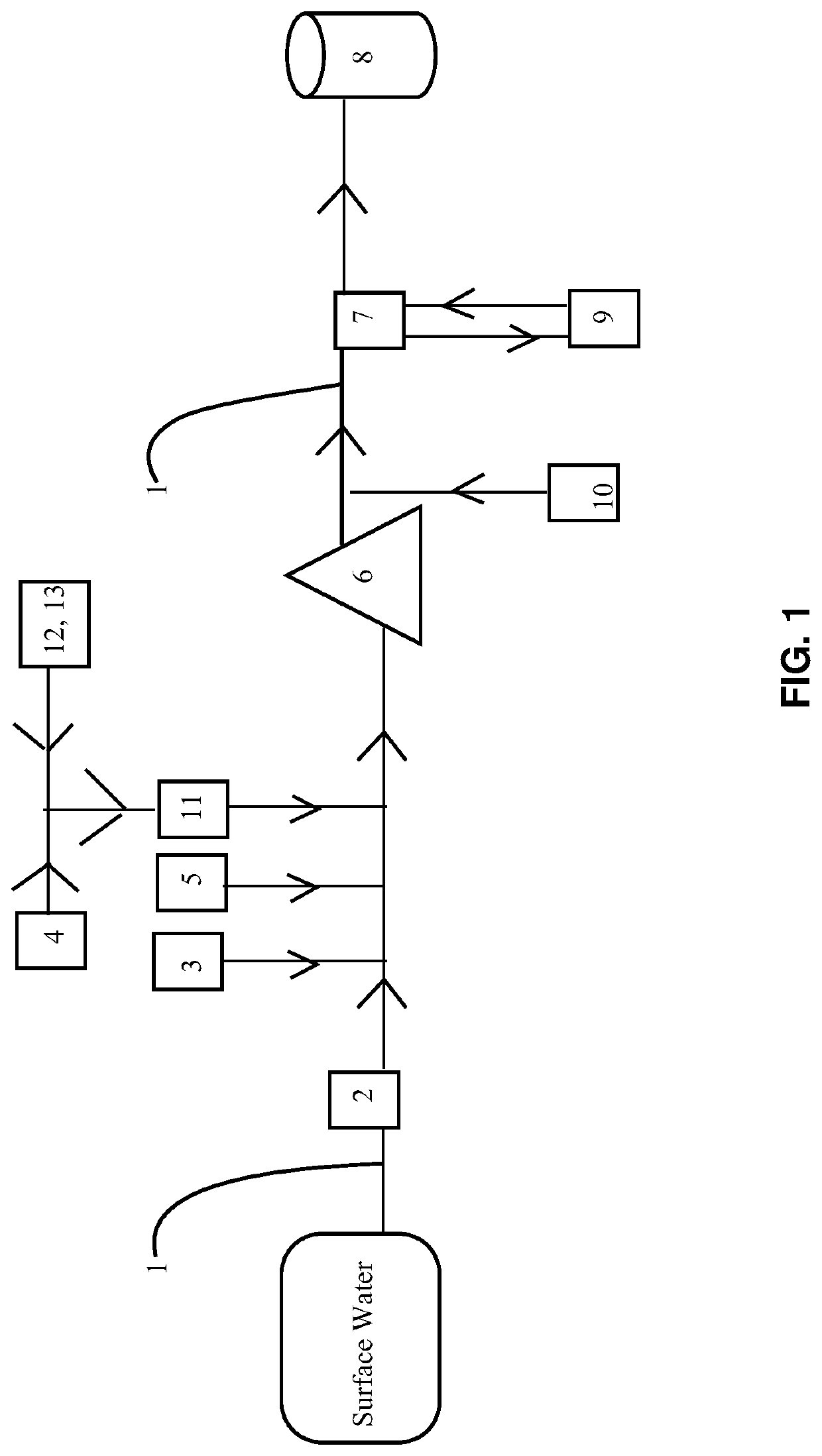
ActiveUS11008228B1High viscosityEasy to transportOther chemical processesCarbon compoundsActivated carbonHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A method of removing organic carbon and other contaminants from a water stream. The method comprises screening large solids from the stream. Pre-oxidation chemicals may then be added. A coagulant is fed into the stream. An activated carbon, preferably formed from lignite, is added by pumping a highly concentrated activated carbon slurry into the stream. The stream, including the activated carbon and coagulant, next flows into a clarifier, where the coagulant will flocculate and enmesh the activated carbon. The activated carbon adsorbs organic carbon and other contaminants, including bacteria, pharmacological agents, and hydrocarbons, as the stream flows through the clarifier. Eventually, the flocculate will agglomerate and settle out in the clarifier, where it, the enmeshed carbon, and the contaminants they contain may be removed. The stream's organic carbon content exiting the clarifier will be much reduced. Accordingly, less primary oxidizing agent will be needed to treat any remaining organic carbon.
Owner:KINETIX PERFORMANCE SOLUTIONS LLC
Methods for fabricating semiconductor devices including surface treatment processes
ActiveUS10128148B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMethyl groupSemiconductor
Methods for fabricating semiconductor devices may provide enhanced performance and reliability by recovering quality of a low-k insulating film damaged by a plasma process. A method may include forming a first interlayer insulating film having a trench therein on a substrate, filling at least a portion of the trench with a metal wiring region, exposing a surface of the metal wiring region and a surface of the first interlayer insulating film to a plasma in a first surface treatment process, then exposing the surface of the first interlayer insulating film to a recovery gas containing a methyl group (—CH3) in a second surface treatment process, and then forming an etch stop layer on the metal wiring region and the first interlayer insulating film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS7800229B2Decrease in dislocation energyIncrease carbon concentrationElectrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
An improved SIV resistance and an improved EM resistance are achieved in the coupling structure containing copper films. A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a second insulating layer formed on or over the semiconductor substrate; a second barrier metal film, formed on the second insulating film, and being capable of preventing copper from diffusing into the second insulating film; and an electrically conducting film formed on the second barrier metal film so as to be in contact with the second barrier metal film, and containing copper and carbon, wherein a distribution of carbon concentration along a depositing direction in the second electrically conducting film includes a first peak and a second peak.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
A rapid carburizing heat treatment process for drive gears used in automobile differentials
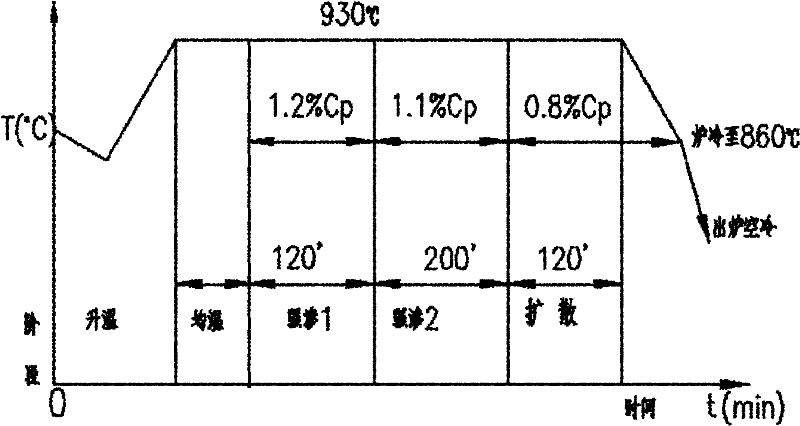
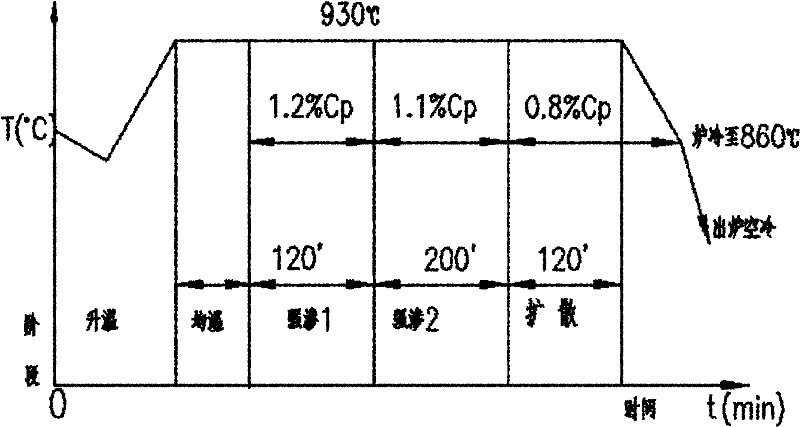
ActiveCN105154633BIncrease pressureIncrease carbon concentrationSolid state diffusion coatingGear driveQuenching
The invention provides a rapid carburizing heat treatment process for a driving gear used in an automobile differential, comprising the following steps: 1) heating up; 2) strong infiltration; 3) diffusion; 4) quenching; 5) cleaning; 6) tempering. The carburizing period of the treatment process is obviously shortened, the production efficiency is improved, the output is increased, the energy saving effect is achieved, the carburizing cost is obviously reduced, and the economic benefit is significantly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU BAOJIE FORGING
Method for producing Group III nitride semiconductor including growing Group III nitride semiconductor through flux method
ActiveUS10329687B2High crystallinityHigh yieldPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthAbnormal grain growthIsoetes triquetra
To reduce ungrown region or abnormal grain growth region in growing a Group III nitride semiconductor through a flux method. A seed substrate has a structure in which a Group III nitride semiconductor layer is formed on a ground substrate as a base, and a mask is formed on the Group III nitride semiconductor layer. The mask has a plurality of dotted windows in an equilateral triangular lattice pattern. A Group III nitride semiconductor is grown through flux method on the seed substrate. Carbon is placed on a lid of a crucible holing the seed substrate and a molten mixture so that carbon is not contact with the molten mixture at the start of crystal growth. Thereby, carbon is gradually added to the molten mixture as time passes. Thus, ungrown region or abnormal grain growth region is reduced in the Group III nitride semiconductor crystal grown on the seed substrate.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Surface-treated mold and method of producing surface-treated mold
A surface-treated mold that includes a mold, a metal layer that is provided on a surface of the mold and contains at least one metal selected from nickel, chromium, tungsten and brass, and a carbon film that is provided on a surface of the metal layer, wherein the metal layer contains carbon, and the carbon concentration in the metal layer is higher between the boundary with the carbon film and the center of the metal layer than that between the boundary with the mold and the center of the metal layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for producing group iii nitride semiconductor
ActiveUS20180066378A1Uniform thicknessLarge caliberPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthAbnormal grain growthCrucible
To reduce ungrown region or abnormal grain growth region in growing a Group III nitride semiconductor through a flux method. A seed substrate has a structure in which a Group III nitride semiconductor layer is formed on a ground substrate as a base, and a mask is formed on the Group III nitride semiconductor layer. The mask has a plurality of dotted windows in an equilateral triangular lattice pattern. A Group III nitride semiconductor is grown through flux method on the seed substrate. Carbon is placed on a lid of a crucible holing the seed substrate and a molten mixture so that carbon is not contact with the molten mixture at the start of crystal growth. Thereby, carbon is gradually added to the molten mixture as time passes. Thus, ungrown region or abnormal grain growth region is reduced in the Group III nitride semiconductor crystal grown on the seed substrate.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
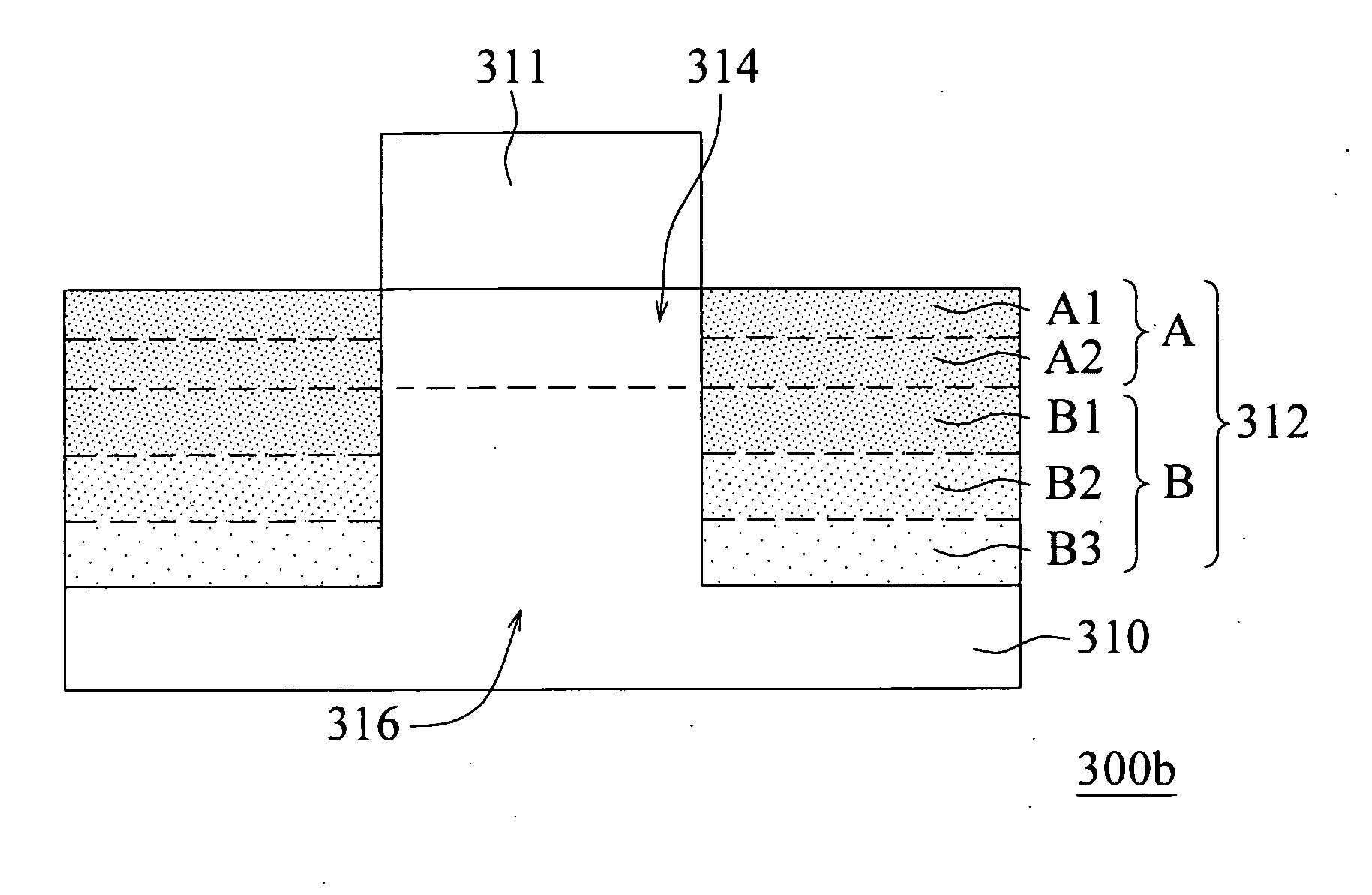
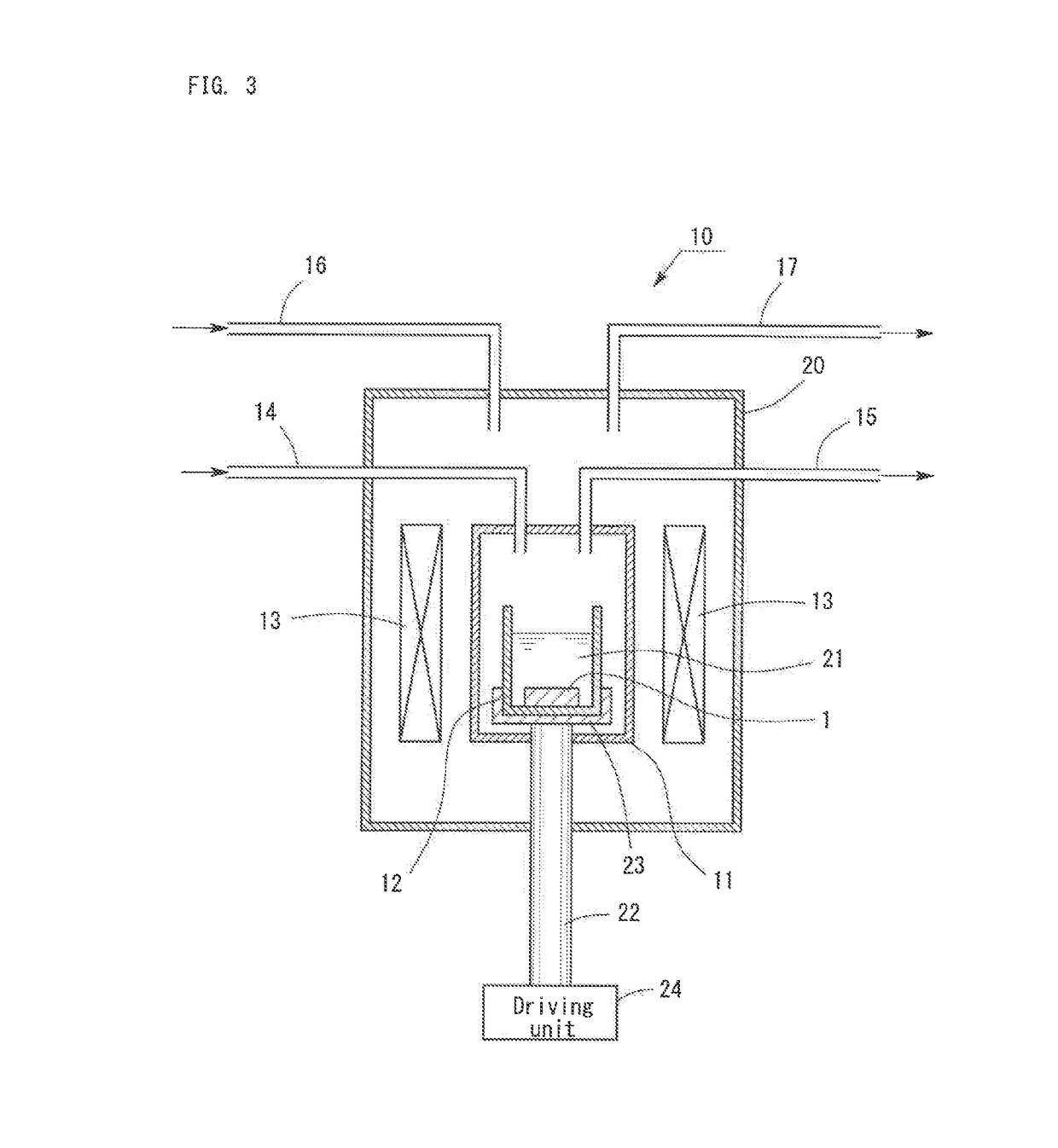
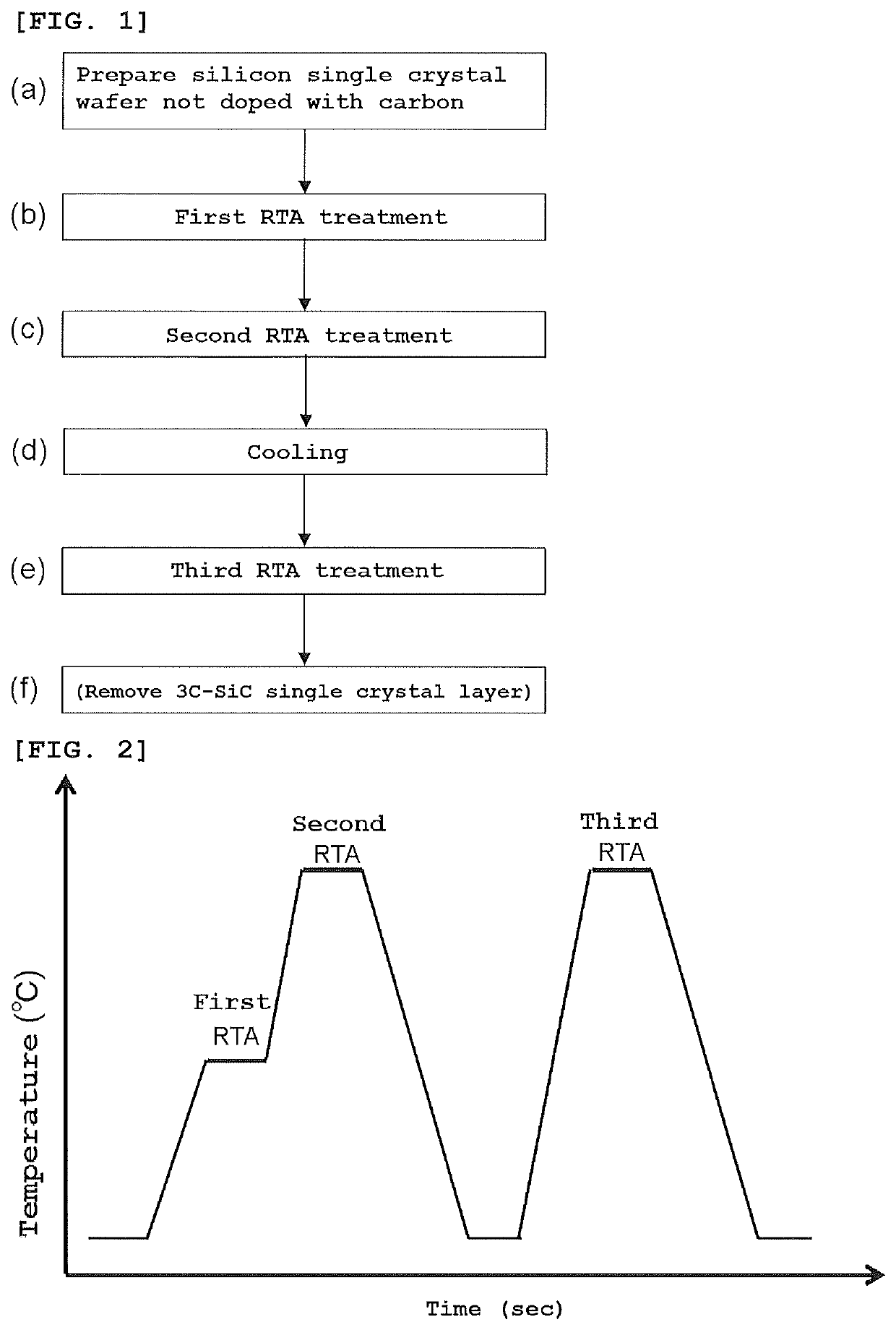
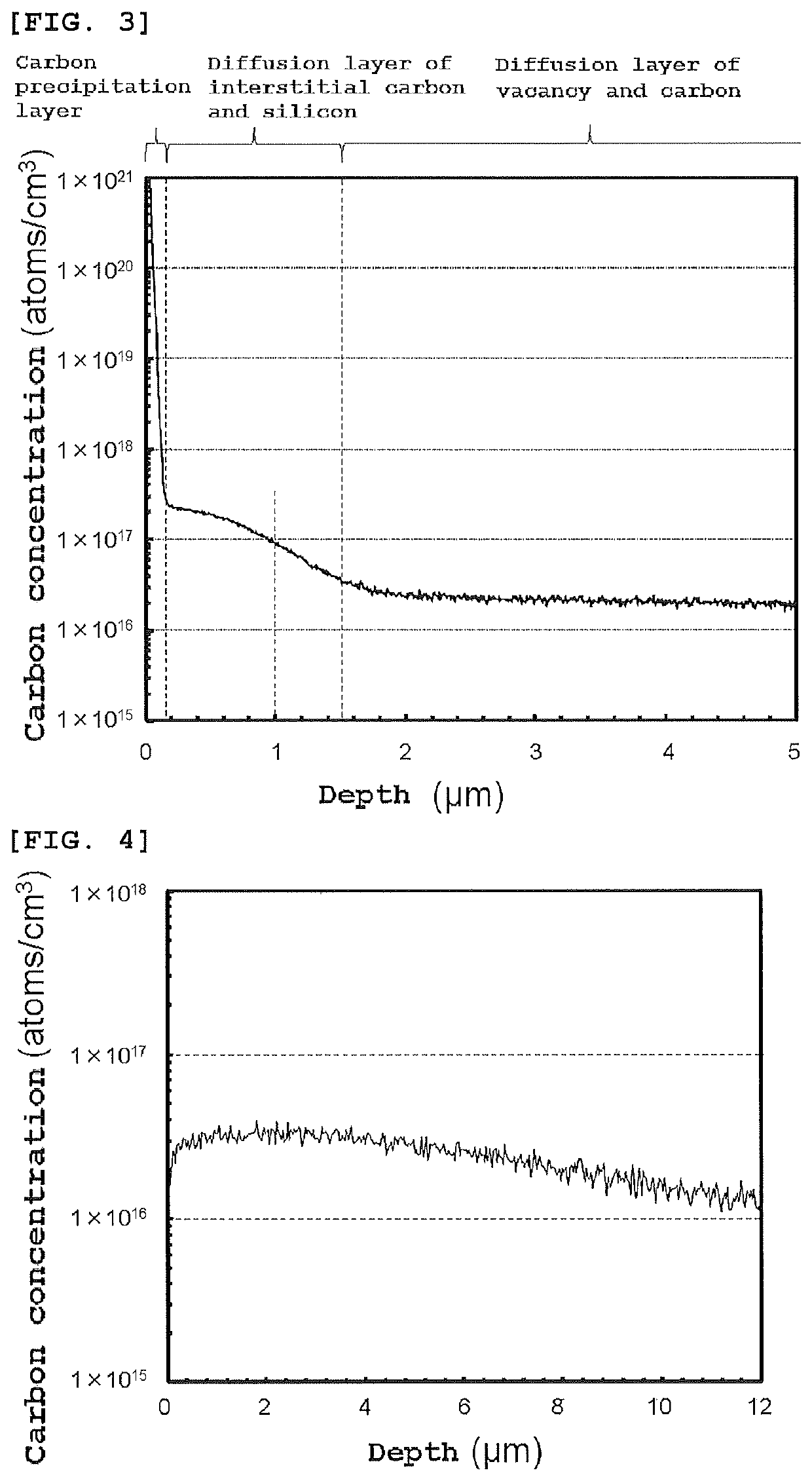
Carbon-doped silicon single crystal wafer and method for manufacturing the same
PendingUS20220259767A1High strengthIncrease successPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsPhysicsCarbon doped
A method for manufacturing a carbon-doped silicon single crystal wafer, including steps of: preparing a silicon single crystal wafer not doped with carbon; performing a first RTA treatment on the silicon single crystal wafer in an atmosphere containing compound gas; performing a second RTA treatment at a higher temperature than the first RTA treatment; cooling the silicon single crystal wafer after the second RTA treatment; and performing a third RTA treatment. The crystal wafer is modified to a carbon-doped silicon single crystal wafer, sequentially from a surface thereof: a 3C-SiC single crystal layer; a carbon precipitation layer; a diffusion layer of interstitial carbon and silicon; and a diffusion layer of vacancy and carbon. A carbon-doped silicon single crystal wafer having a surface layer with high carbon concentration and uniform carbon concentration distribution to enable wafer strength enhancement; and a method for manufacturing the carbon-doped silicon single crystal wafer.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
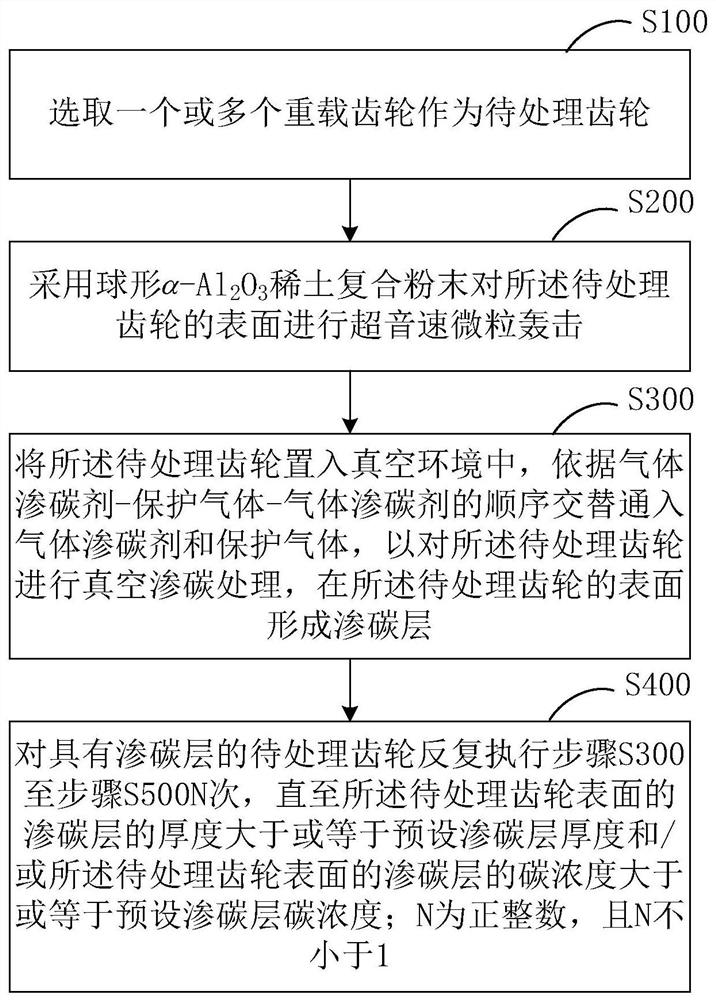
Cyclic carburizing treatment method for surface carburizing layer of heavy-duty gears
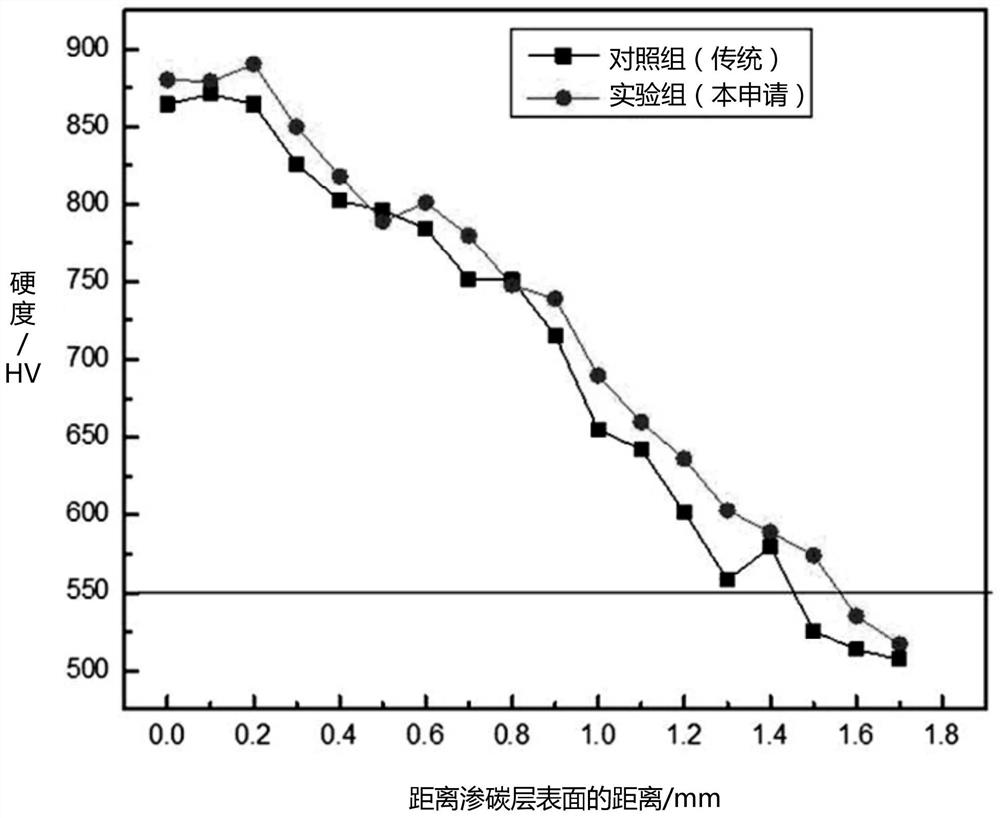
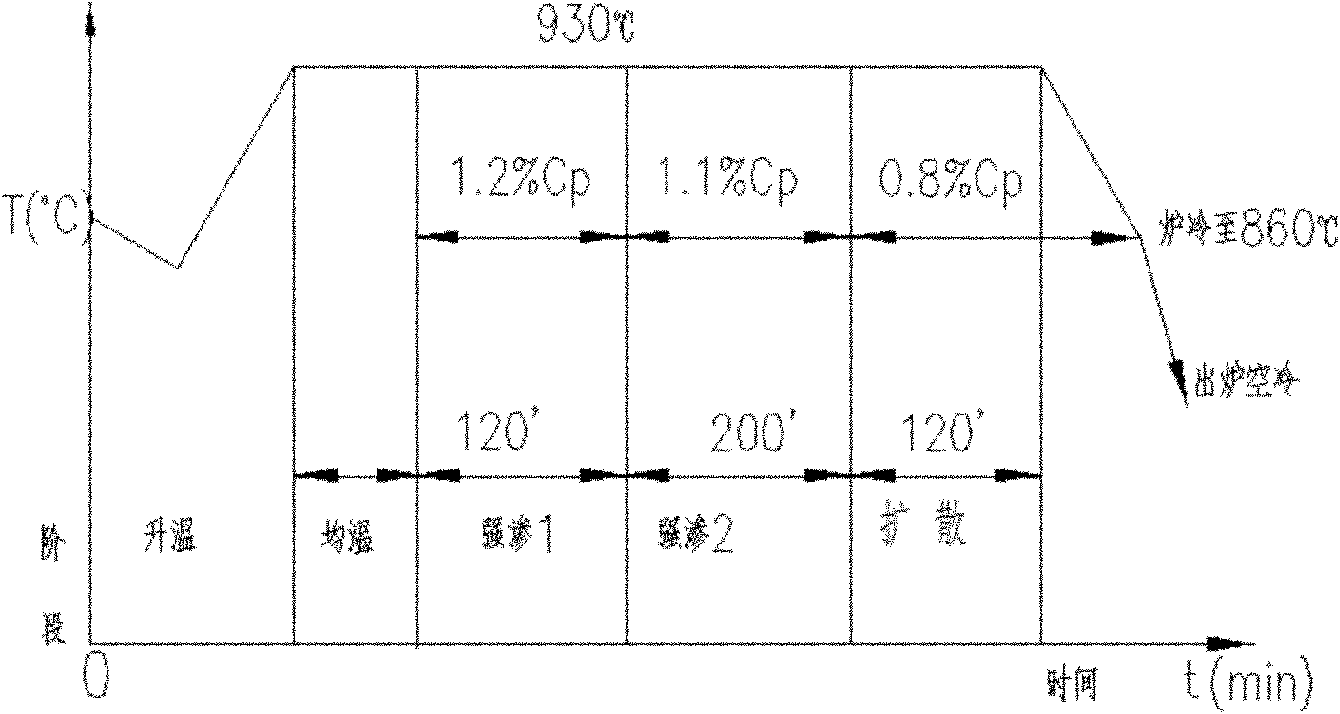
ActiveCN111304581BMeet service needsIncrease concentrationSolid state diffusion coatingMetallurgyGear wheel
The present application relates to a cyclic carburizing treatment method for a carburized layer on the surface of a heavy-duty gear. The surface of the gear to be treated is bombarded with supersonic particles before the gear to be treated is subjected to vacuum carburizing treatment, so that the surface of the gear to be treated is subjected to compound catalytic infiltration. The treatment causes plastic deformation on the surface of the gear to be treated, forming a composite modified layer with fine grains and many grain boundaries, which facilitates the diffusion and penetration of carbon atoms into the surface of the gear to be treated. After completing a cyclic carburizing cycle of composite catalysis-vacuum carburizing, by repeatedly performing multiple cyclic carburizing cycles of composite catalysis-vacuum carburizing, the surface of the gear to be treated generates a higher carbon concentration, a larger thickness, Carburized layer with strong surface hardness. The cyclic carburizing treatment method for the surface carburizing layer of a heavy-duty gear involved in the present application can obtain a higher carbon concentration, greater thickness, and greater surface strength and hardness in a relatively short period of time compared with the traditional atmosphere carburizing method. Carburized layer to meet the service requirements of heavy-duty gears.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Carburization processing method
ActiveCN102676983BIncrease carbon concentrationHigh hardnessSolid state diffusion coatingThermal insulationHardness
An embodiment of the invention discloses a carburization processing method. Composite carburization is adopted in the carburization processing method. First a workpiece is placed in a carburization medium of 900-980 DEG C, thermal insulation and cooling are carried out, then the workpiece is continuously placed in the carburization medium of 900-980 DEG C, and thermal insulation is performed. After carburization for the first time, the surface of the workpiece has a certain carbon concentration distribution and macroscopic thickness. Meanwhile, carburization for the second time in the step (b) is utilized to improve carbon concentration of the surface of the workpiece, and accordingly macrohardness and surface hardness of the surface of the workpiece are improved. Experimental results show that the macroscopic thickness of the workpiece processed by the method is 0.78-1mm, and the hardness at the position of 0.15mm is larger than 700HV.
Owner:青岛德盛机械制造有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com