Selective liquid-liquid extraction of oxidative desulfurization reaction products
a liquid-liquid extraction and desulfurization technology, applied in the field of system and process, can solve problems such as safety and environmental problems, other deleterious effects, and corrosion of processing equipment and engine parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
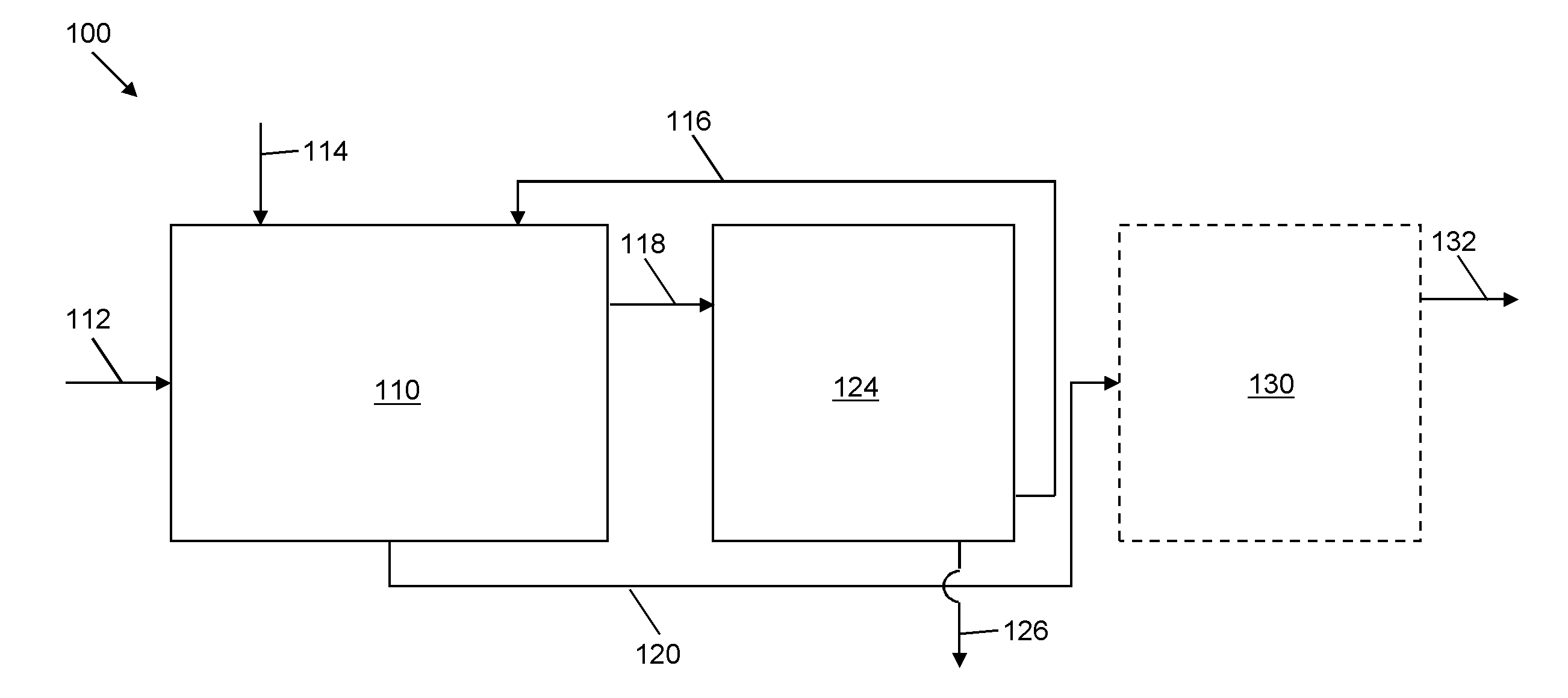
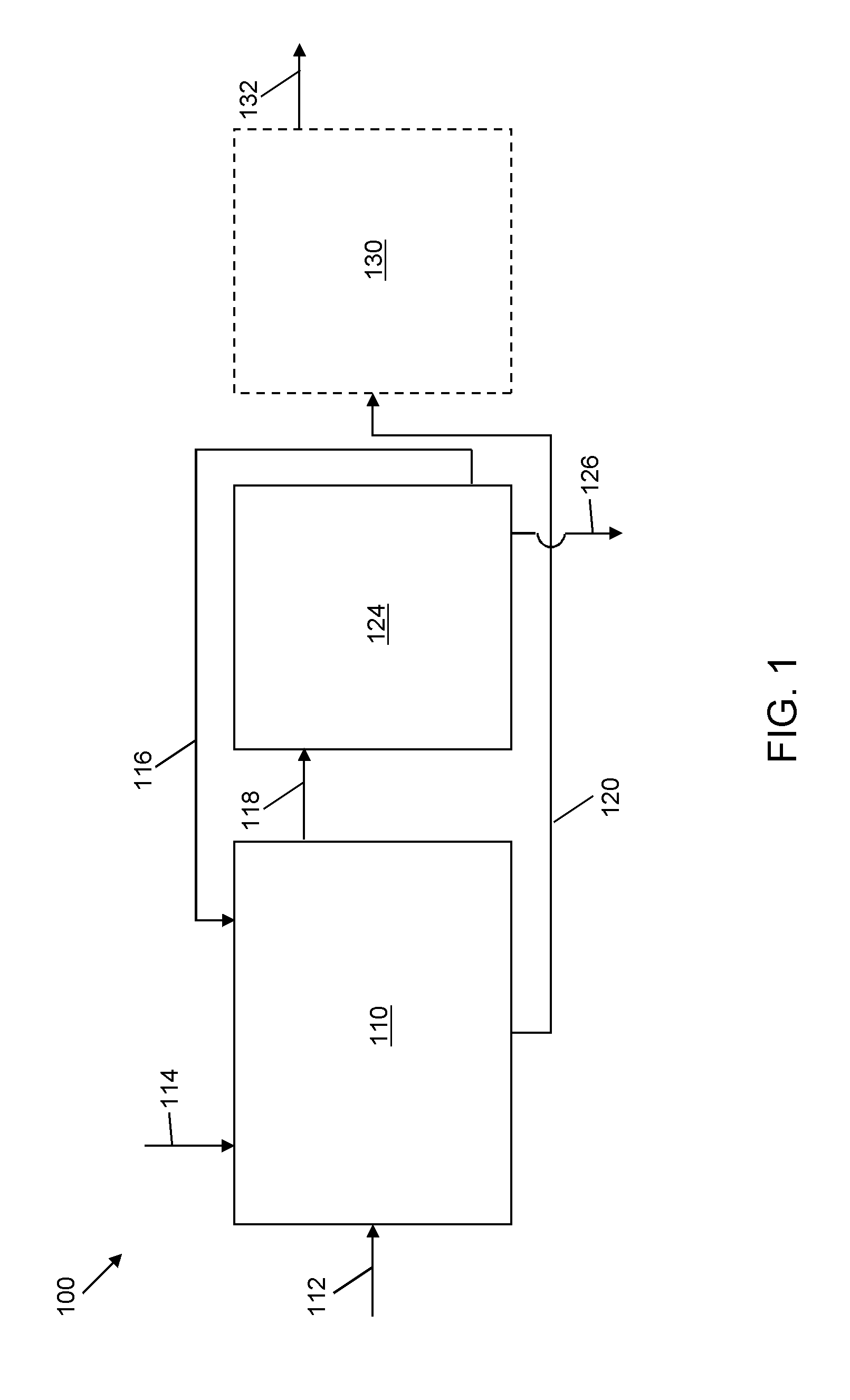
[0094]A quantity of 100 mL of a model diesel feed formed of xylene, DBT, DBT sulfoxide and DBT sulfone (with a total sulfur content of 1635 ppmw) was oxidized by 30 W % aqueous hydrogen peroxide at a temperature of 37° C. and at a pressure of 1 atmosphere for a period of 70 minutes with solid ZnO catalyst (1.2 g) and a ratio of oxidant (H2O2) to organic sulfur of 4:1 in acetic acid, about 10 mL. After the sold catalyst settled, the model diesel was removed for extraction of sulfoxidation products and removal of aqueous H2O2 using an embodiment of the selective solvent formulation of the present invention.
[0095]DBT sulfoxide and DBT sulfone were extracted using a selective solvent formulation of 50 W % aqueous acetic acid. Two batch extractions were sequentially conducted using a solvent-to-model diesel ratio of about 1:1 at a temperature of 23° C. and at a pressure of 1 atmosphere for a period of 2 minutes, during which the contents were stirred. Table 10A represents the abundance u...
example 2
[0096]A quantity of oxidized model diesel feed as used in Example 1 was subjected to extraction to remove DBT sulfoxide and DBT sulfone using a selective solvent formulation of 70 W % aqueous formic acid. Two batch extractions were sequentially conducted using a solvent to model diesel ratio of about 1:1 at a temperature of 23° C. and at a pressure of 1 atmosphere for a period of 2 minutes, during which the contents were stirred. Table 11A represents the abundance units as a result of gas chromatography. The total extraction of DBT sulfoxide and DBT sulfone was 94 W % and 56 W % respectively. Furthermore, the co-extraction of xylene was limited to 2 W % after the first extraction, and increased by 3.8 W % after the second extraction, based on the normalization percentage of the peak regions for the GC analysis for each extraction. The normalization method is qualitative and quasi-quantitative, so that the peak area varies. The slight positive (3.8%) of xylene is due to the normaliza...
example 3
[0098]A quantity of oxidized model diesel feed as used in Example 1 was subjected to extraction to remove DBT sulfoxide and DBT sulfone using a selective solvent formulation of 50 W % aqueous methanol. One extraction was conducted using a solvent to model diesel ratio of about 1:1 at a temperature of 23° C. and at a pressure of 1 atmosphere for a period of 2 minutes, during which the contents were stirred. Table 12A represents the abundance units as a result of gas chromatography. The total extraction of DBT sulfoxide was 51.5 W %. Furthermore, there was no co-extraction of xylene, as the amount of xylene increased by 2.8 W % after extraction (based on the normalized GC results). The co-extraction of DBT (not oxidized) was limited to 3.1 W %. The total sulfur measured by sulfur speciation determined that the overall sulfur content was reduced by 16 W % as shown at Table 12B.
TABLE 12AXyleneDBTDBT(aromatic)(untreated sulfur)sulfoxideDBT sulfoneModel diesel9283.724.4424.0225.09oxidized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com