Support material for laminate shaping, product laminate-shaped by using the same, and laminate-shaped product production method
a technology of supporting materials and laminates, applied in metal-working apparatus, additive manufacturing apparatus, 3d object support structures, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient adhesiveness to model materials, unstable shape of support materials, and prone to deformation of support materials, etc., to achieve excellent peelability and forming stability, excellent shape stability and adhesiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment (
Y)
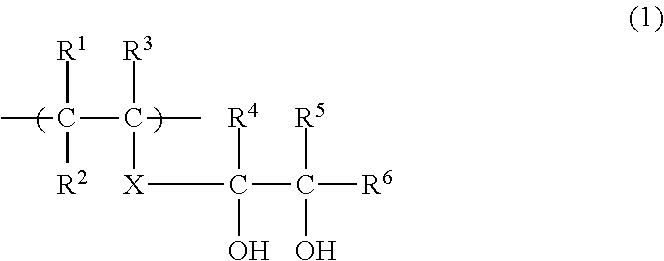
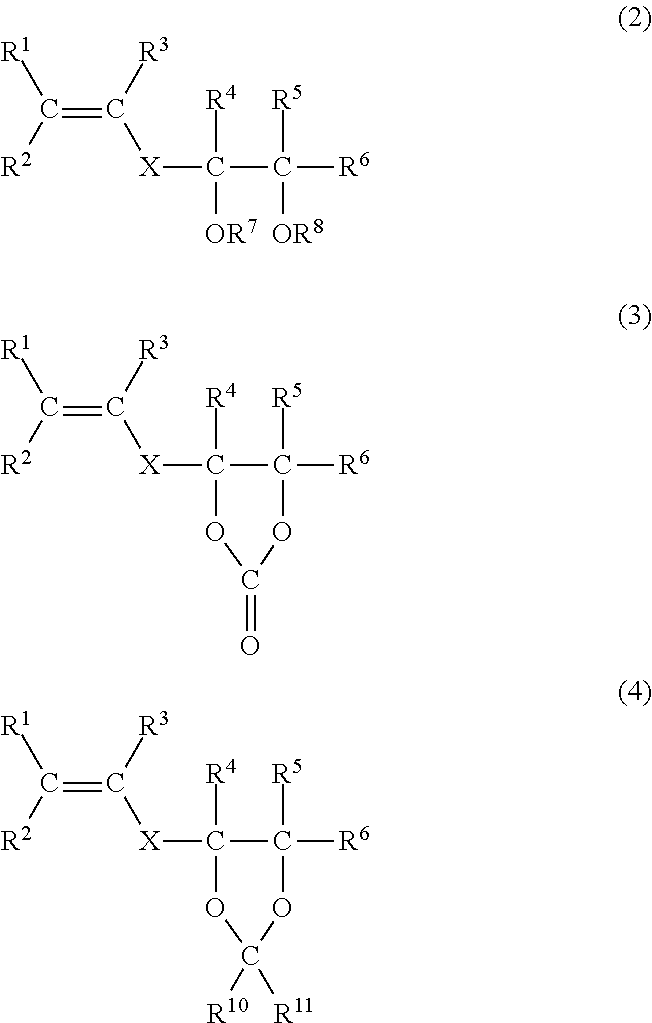
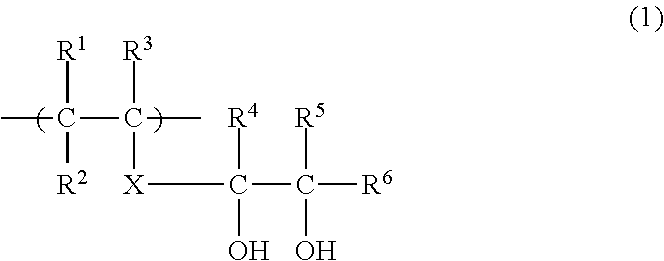
[0064]The laminate shaping support material according to Embodiment (Y) employs a resin composition (Y) which contains a PVA resin, and a block copolymer including a polymer block of an aromatic vinyl compound, at least one of a polymer block of a conjugated diene compound and a block of a hydrogenated conjugated diene compound, and a functional group reactive with a hydroxyl group.
[0065][PVA Resin]
[0066]First, the PVA resin to be used in Embodiment (Y) will be described.
[0067]The PVA resin is a resin mainly including a vinyl alcohol structural unit and prepared by copolymerizing a vinyl ester monomer and saponifying the resulting polyvinyl ester resin. The PVA resin includes the vinyl alcohol structural unit in a proportion corresponding to a saponification degree, and includes an unsaponified vinyl ester structural unit.
[0068]Examples of the vinyl ester monomer include vinyl formate, vinyl acetate, vinyl propionate, vinyl valerate, vinyl butyrate, vinyl isobutyrate, vinyl pivala...
examples
[0136]The present invention will hereinafter be described more specifically by way of examples thereof. It should be understood that the present invention be not limited to these examples within the scope of the invention. In the examples, the term “part(s)” means part(s) by weight.
Examples of Embodiment (X)
Example 1
(i) Preparation of 1,2-Diol-Containing PVA Resin (1)
[0137]In a reaction vessel provided with a reflux condenser, a dropping funnel and a stirrer, 10% of 68.5 parts of vinyl acetate and 20.5 parts of methanol were first fed, and the rest of the vinyl acetate and 11.0 parts (7.2 mol % with respect to the amount of vinyl acetate to be fed) of 3,4-diacetoxy-1-butene were fed dropwise at constant rates in 9 hours. Then, 0.3 mol % (with respect to the amount of the fed vinyl acetate) of azobisisobutyronitrile was fed into the reaction vessel. In turn, the temperature was raised while the resulting mixture was stirred in a nitrogen stream, thereby initiating polymerization. Whe...
example 2
(i) Preparation of 1,2-Diol-Containing PVA Resin (2)
[0145]In substantially the same manner as in Example 1, 40% of 72.1 parts of vinyl acetate and 21.6 parts of methanol were first fed in a reaction vessel, and the rest of the vinyl acetate and 6.3 parts of 3,4-diacetoxy-1-butene were fed dropwise at constant rates in 8 hours. Then, 0.16 mol % (with respect to the amount of the fed vinyl acetate) of azobisisobutyronitrile was fed in the reaction vessel. In turn, the temperature was raised while the resulting mixture was stirred in a nitrogen stream, thereby initiating polymerization. When the polymerization degree of vinyl acetate reached 90%, a predetermined amount of m-dinitrobenzene was added to the reaction vessel to terminate the polymerization. Subsequently, methanol vapor was blown into the reaction vessel, whereby unreacted vinyl acetate monomer was removed out of the reaction vessel. Thus, a copolymer was prepared in the form of a methanol solution.
[0146]The methanol soluti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com