Polymerization process in the presence of antistatic agent
a technology of antistatic agent and polymerization process, applied in the field of polymer chemistry, can solve the problems of limited efficiency, negative impact on the activity of polymerization catalyst, sheeting and lump formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077]The density was determined according to DIN EN ISO 1183-1:2004, Method A (Immersion) with compression molded plaques of 2 mm thickness. The compression molded plaques were prepared with a defined thermal history: Pressed at 180° C., 20 MPa for 8 min with subsequent crystallization in boiling water for 30 min.
[0078]The melt flow rate MFR2.16 was determined according to DIN EN ISO 1133:2005, condition D at a temperature of 190° C. under a load of 2.16 kg.
[0079]The melt flow rate MFR5 was determined according to DIN EN ISO 1133:2005, condition T at a temperature of 190° C. under a load of 5 kg.
[0080]The melt flow rate MFR21.6 was determined according to DIN EN ISO 1133:2005, condition G at a temperature of 190° C. under a load of 21.6 kg.
[0081]The Flow Rate Ratio FRR is the ratio of MFR21.6 / MFR5.
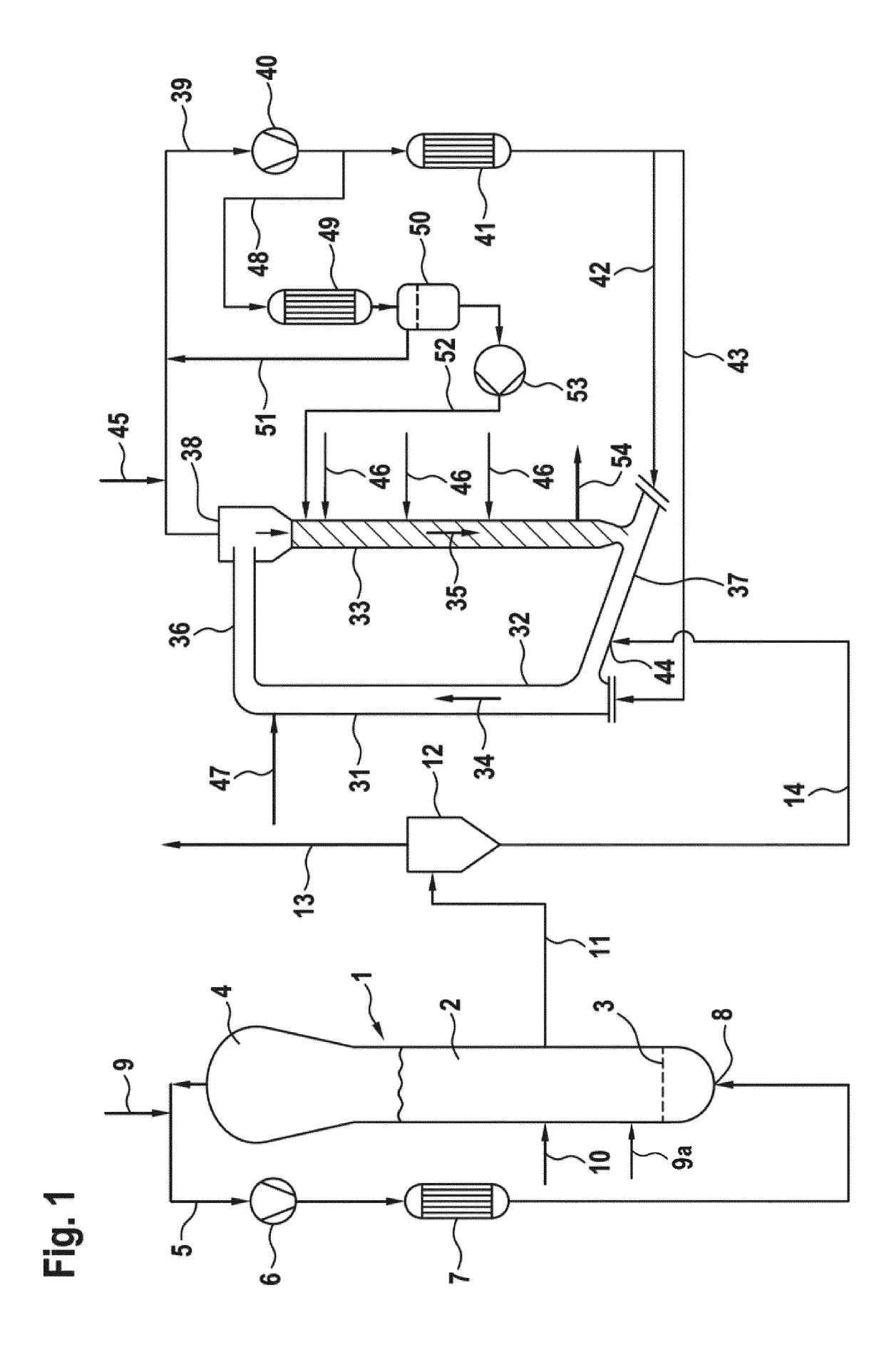
[0082]The electrostatic charges present in the second polymerization reactor of the polymerization reactor cascade were measured by a sensor (Correstat 3410; Progression, Inc., Haverhill,...
example 1
[0106]The polymerization of Comparative Example B was repeated; however, 100 ppm of Polyglykol PE-K 270 (linear random ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymer having a ratio ethylene oxide / propylene oxide of 3:1 and started by a diol of Clariant SE, Frankfurt, Germany) were fed to the first reactor as antistatic agent instead of 80 ppm of Atmer 163. Liquid propane of a flow rate of 5 kg / h was utilized as feed stream for introducing the Polyglykol PE-K 270 into the first reactor. Furthermore, 50 ppm of Polyglykol PE-K 270 were fed to the second reactor as antistatic agent instead of 90 ppm of Atmer 163 and 20 ppm of Cithrol GMS 40-PW-(GD). Liquid propane of a flow rate of 5 kg / h was utilized as feed stream for introducing the Polyglykol PE-K 270 into the second reactor. Moreover, the catalyst feed to the first reactor was reduced to 6.7 g / h in order to have the same ethylene concentration in the fluidized bed reactor as in Comparative Example B.
[0107]The obtained polyethylene polyme...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com