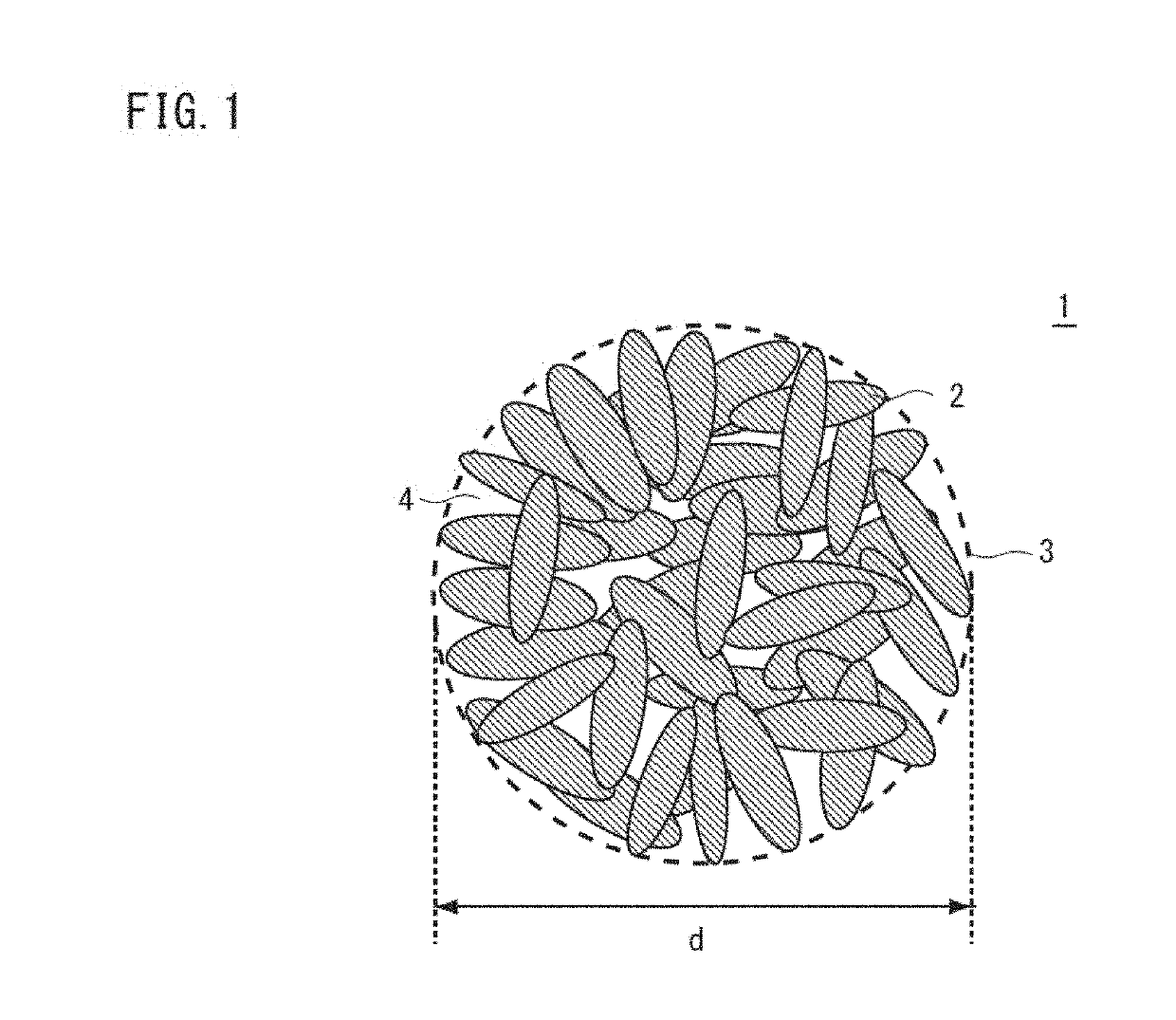
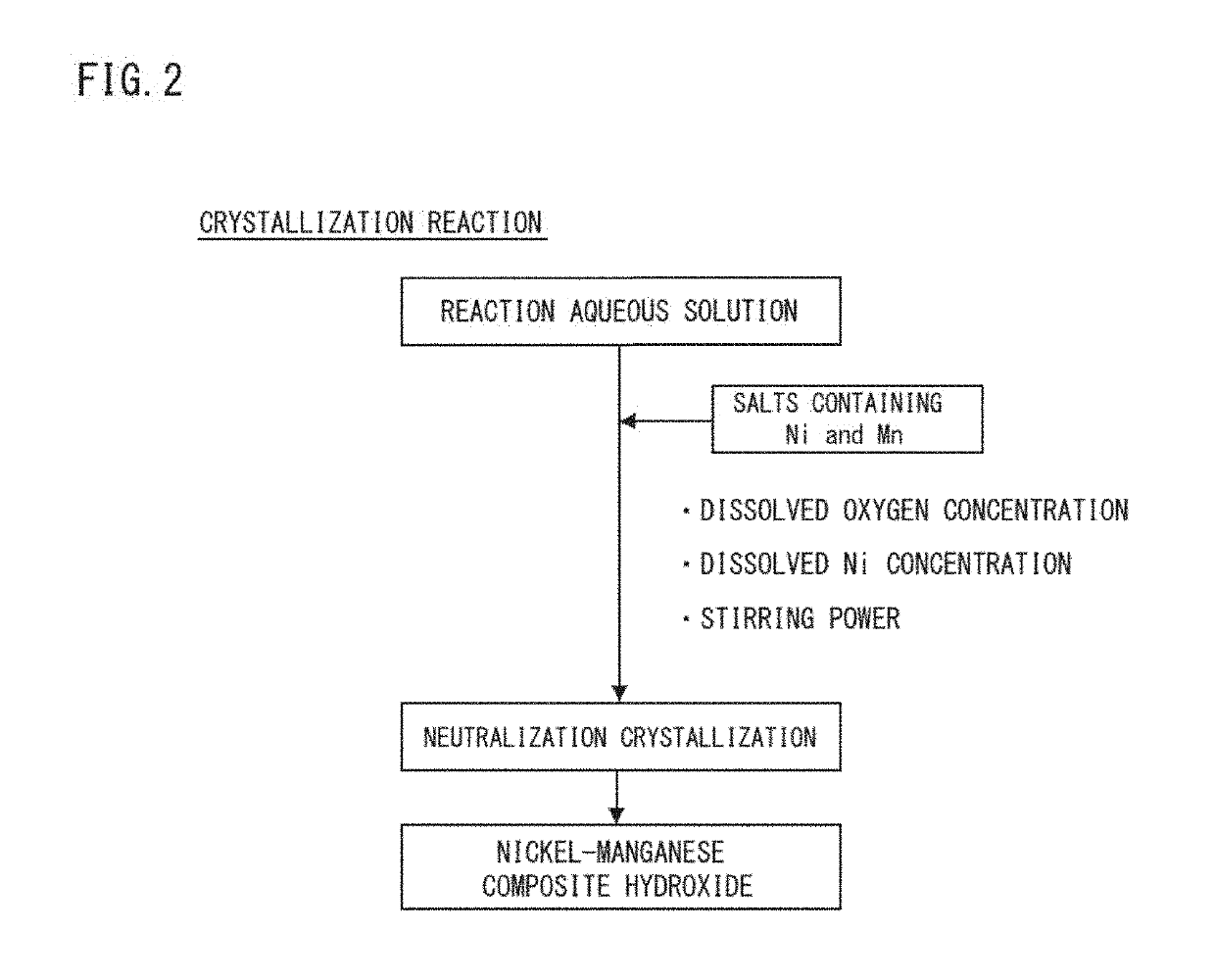
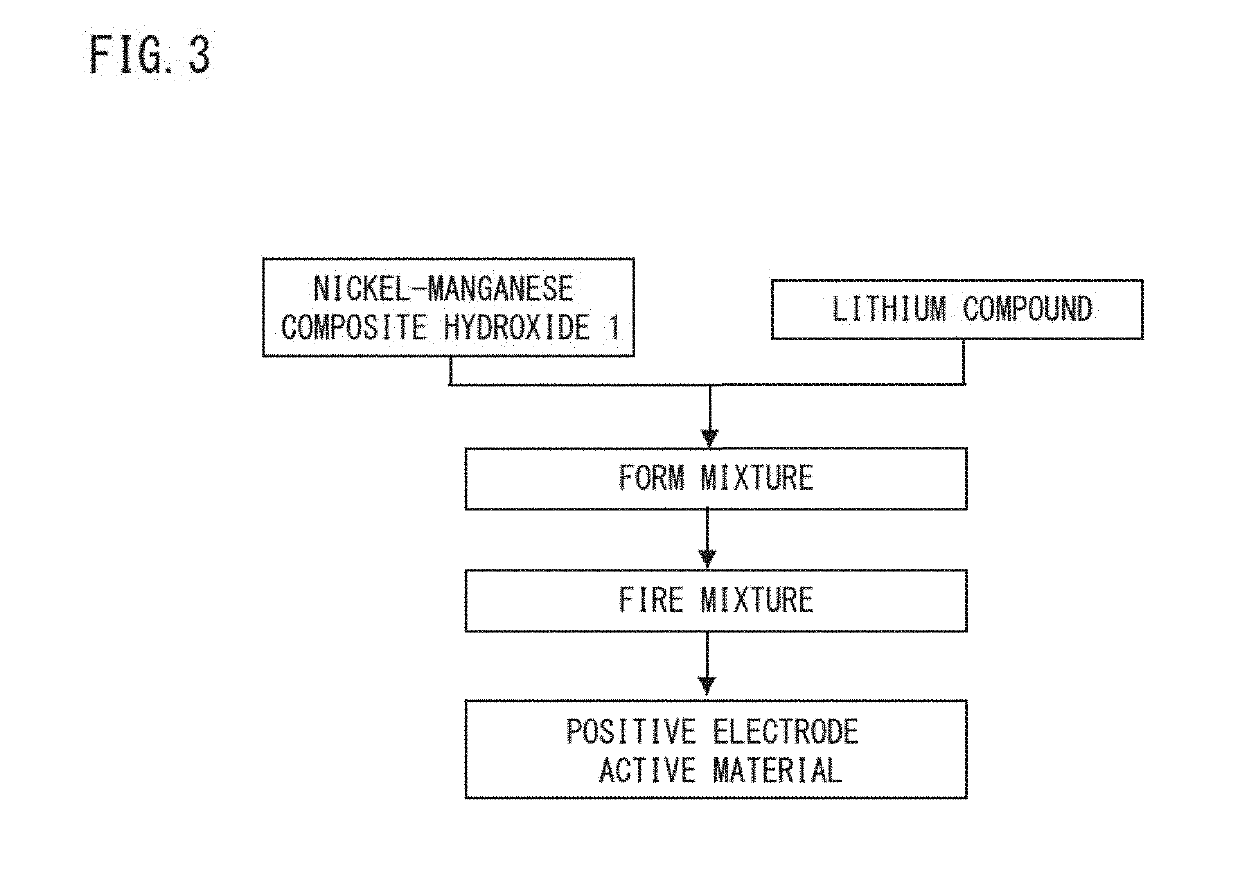
Nickel manganese composite hydroxide, production method for nickel manganese composite hydroxide, positive electrode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, production method for positive electrode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
a nickel manganese and composite hydroxide technology, applied in the field of nickel manganese composite hydroxide, can solve the problems of low fillability of active materials, low volume energy density, and inferior capacity of lithium-nickel composite oxide-based ones, and achieve excellent output characteristics, high energy density, and high industrial value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0117][Production of Composite Hydroxide]
[0118]A prescribed amount of pure water was put into a reaction tank (60 L), and stirring power was adjusted to 5.5 kW / m3. Next, the temperature (liquid temperature) in the reaction tank was set to 45° C. while stirring. In this process, a nitrogen gas (N2) was supplied to the reaction tank, and a N2 flow rate was adjusted so as to give a dissolved oxygen concentration in the liquid in the reaction tank of 5.8 mg / L. Simultaneously and continuously added to this reaction tank were a 2.0 mol / L mixed aqueous solution dissolving nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate, and manganese sulfate so as to give a molar ratio among nickel:cobalt:manganese of 35:35:30, a 25% by mass aqueous sodium hydroxide solution as an alkali solution, and a 25% by mass ammonia water as a complexing agent to perform a neutralization crystallization reaction. A pH value and an ammonium ion concentration were adjusted so as to give a dissolved nickel concentration of 410 mg / L. In...
example 2
[0131]A nickel-manganese composite hydroxide and a positive electrode active material were produced similarly to Example 1 except that the N2 flow rate was adjusted so as to give a dissolved oxygen concentration in the crystallization process of 5.0 mg / L. Table 1 lists characteristics of the obtained nickel-manganese composite hydroxide. Table 2 lists characteristics and electrochemical characteristic evaluation results of the obtained positive electrode active material. The evaluations were performed similarly to those in Example 1.
example 3
[0132]A nickel-manganese composite hydroxide and a positive electrode active material were produced similarly to Example 1 except that the N2 flow rate was adjusted so as to give a dissolved oxygen concentration in the crystallization process of 5.0 mg / L and that the ammonium ion concentration was controlled so as to give a dissolved nickel concentration in the reaction aqueous solution of 600 mg / L. Table 1 lists characteristics of the obtained nickel-manganese composite hydroxide. Table 2 lists characteristics and electrochemical characteristic evaluation results of the obtained positive electrode active material. The evaluations were performed similarly to those in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com