Pharmaceutical Formulation with Improved Solubility and Bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0158]HPMC-Valsartan Microparticles (Percentage of API in the Particle is of 30% by Weight)
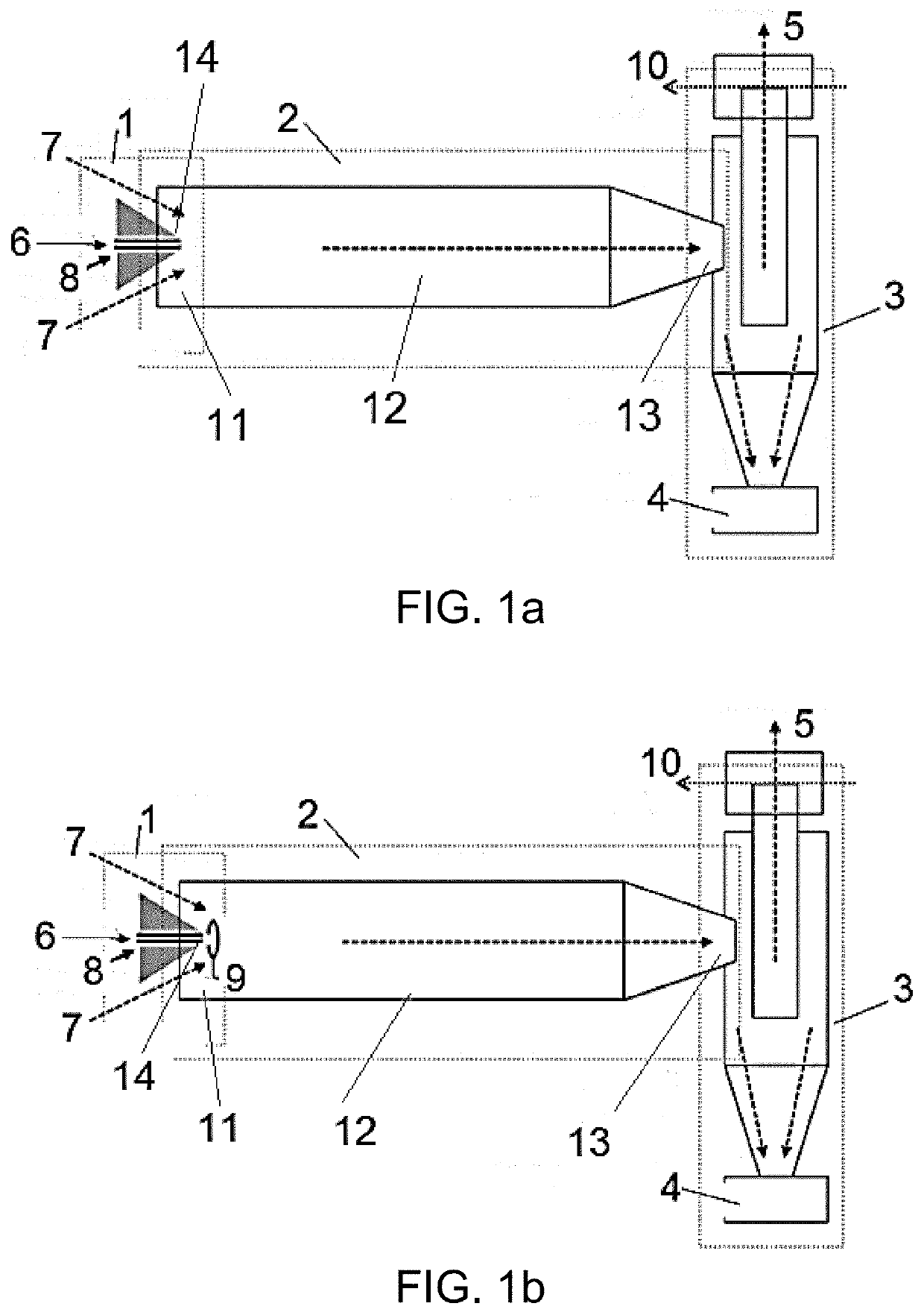
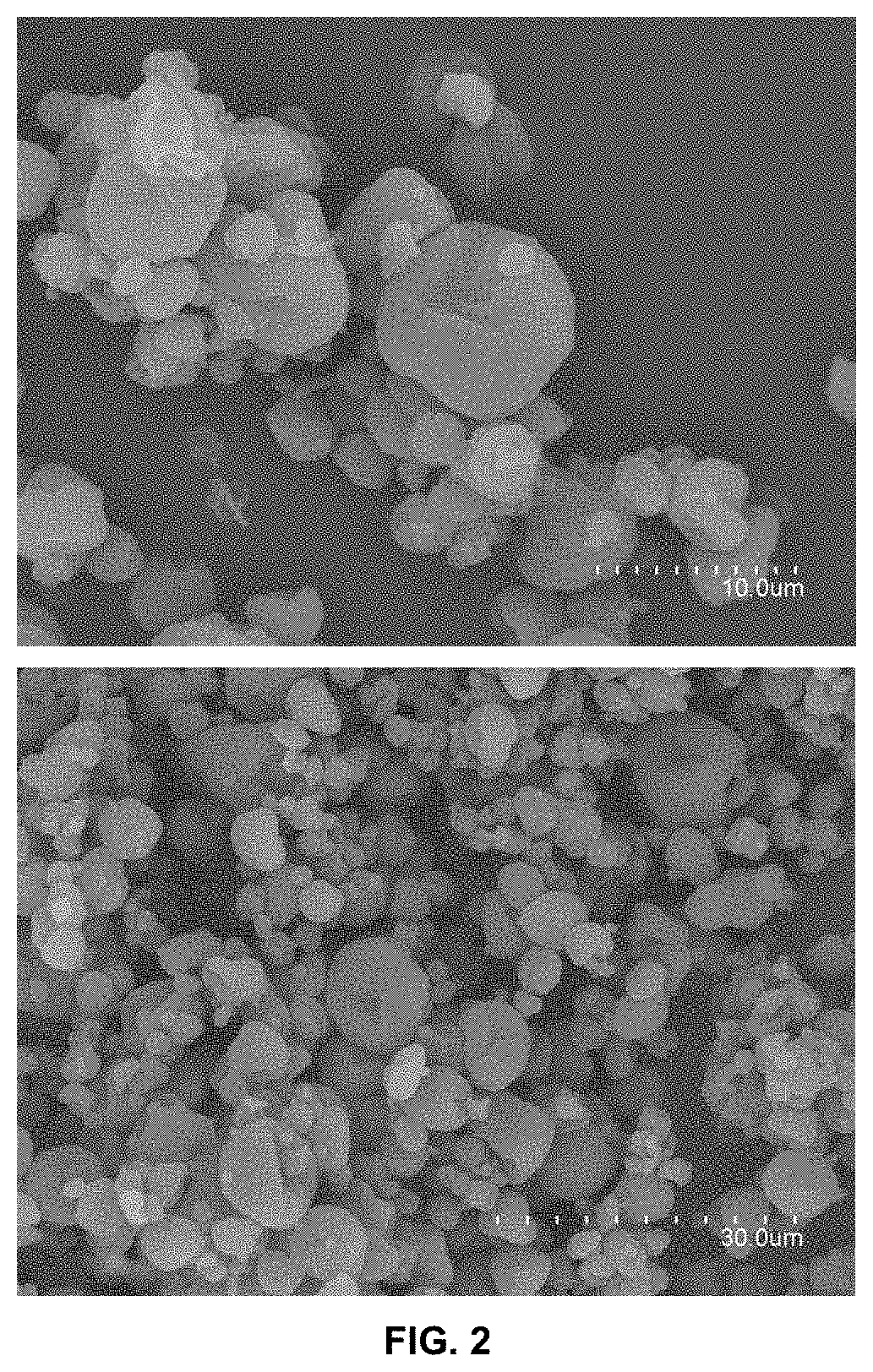
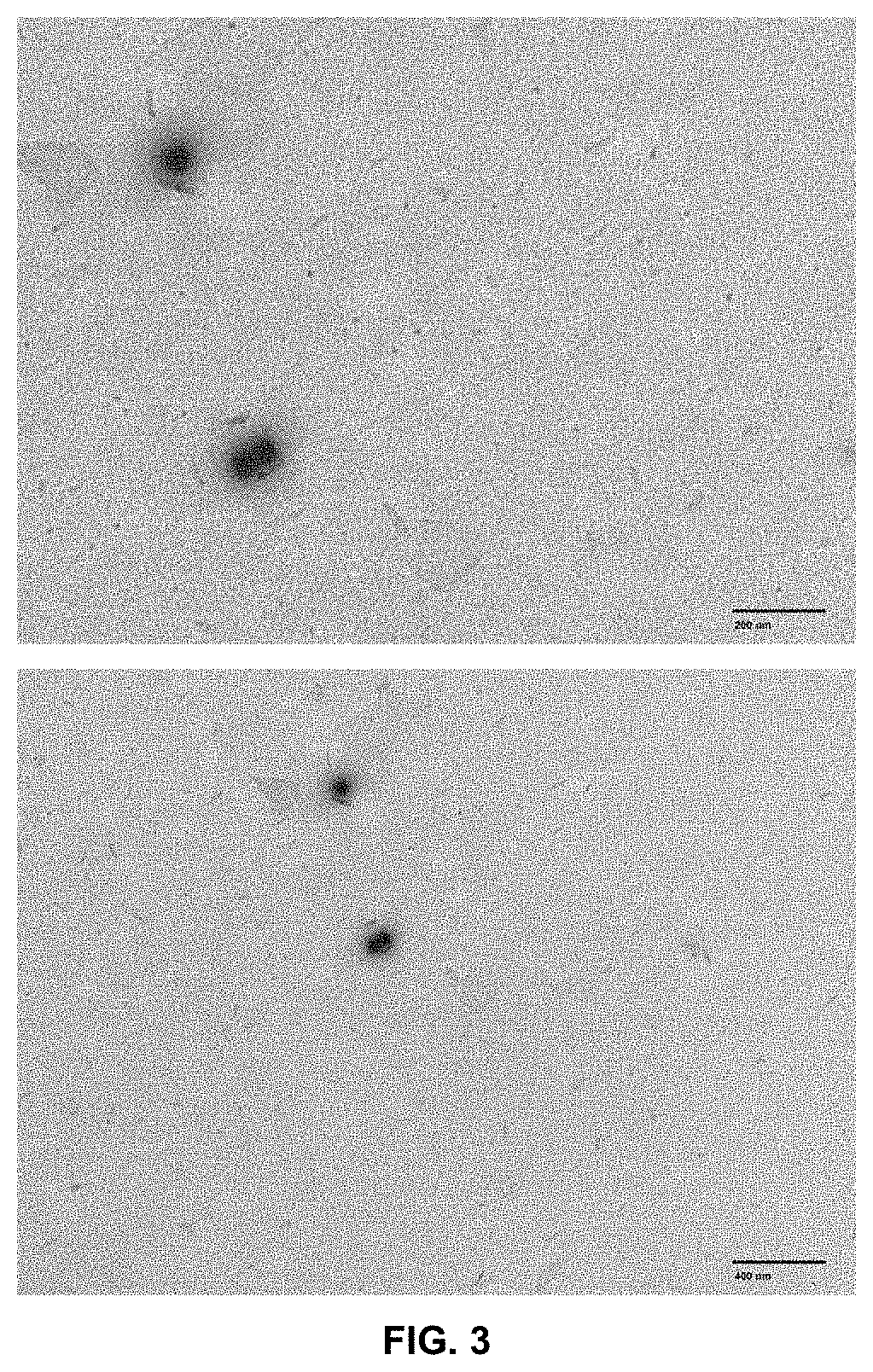
[0159]In this example, the production of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose or hypromellose (HPMC) microparticles containing sub-micron sized valsartan particles is described, using the electro-nebulizer technique, with a percentage of API in the particle of 30% by weight.
[0160]Emulsion Preparation:
[0161]In this case, an oil in water (O / W) emulsion was used, with a ratio organic phase: aqueous phase of 30:70. In a first step, the aqueous phase of the emulsion is prepared. The polymer (HMPC) is dissolved in cold deionized water with a concentration of 20 mg / mL. 10 mg / mL of TEGO (TEGO® SML sorbitan fatty acid ester) is added to this mixture. The organic phase of the emulsion consisted of 30 mg / mL of valsartan in chloroform. The organic phase is slowly added over the aqueous phase and stirred in the ultraturrax for 5 min at 17,000 rpm, followed by 1 min of ultrasounds to achieve a homogeneous size di...
example 2
[0168]HPMC-Valsartan Microparticles (Percentage of API in the Particle is of 63% by Weight)
[0169]In this example, the encapsulation of valsartan in HPMC is described, using the electro-nebulizer technique, with a percentage of API in the particle of 63% by weight.
[0170]Emulsion Preparation:
[0171]An oil in water (0 / W) emulsion was used, with a ratio organic phase: aqueous phase of 30:70. In a first step, the aqueous phase of the emulsion is prepared. The polymer is dissolved in cold deionized water with a concentration of 20 mg / mL. 10 mg / mL of TEGO (TEGO® SML sorbitan fatty acid ester) is dissolved in this mixture. The organic phase of the emulsion consisted of 120 mg / mL of valsartan in ethanol 85%. The organic phase is slowly added over the aqueous phase and stirred in the ultraturrax for 5 min at 17,000 rpm, followed by 1 min of ultrasounds to achieve a homogeneous size distribution of the micelles of the emulsion. During the stirring, the emulsion is maintained in a cold bath to p...
example 3
[0186]HPMC-Valsartan Microparticles (Percentage of API in the Particle is of 82% by Weight)
[0187]In this example, the encapsulation of valsartan in HPMC is described, using the electro-nebulizer, with a percentage of API in the particle of 82% by weight.
[0188]Emulsion Preparation:
[0189]In this case, an oil in water emulsion (O / W) was used, with a ratio organic phase: aqueous phase is of 30:70. In a first step, the aqueous phase of the emulsion is prepared. The polymer with a concentration of 10 mg / mL was dissolved in cold deionized water. 1 mg / mL of TEGO (TEGO® SML sorbitan fatty acid ester) is dissolved in this mixture. The organic phase of the emulsion consisted of 120 mg / mL of valsartan in ethanol 85%. The organic phase is slowly added over the aqueous phase and stirred in the ultraturrax for 5 min at 17,000 rpm, followed by 1 min of ultrasounds to achieve a homogeneous size distribution of the micelles of the emulsion. During the stirring the emulsion is maintained in a cold bat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com