Wire for liquid assisted additive manufacturing of a superalloy component
a superalloy and additive manufacturing technology, applied in the direction of additive manufacturing with solid and fluid, metal-working equipment, welding/cutting media/materials, etc., can solve the problems of high ′ forming nickel-base superalloy materials, additively manufactured or welded superalloy components are sensitive to strain-age cracking and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
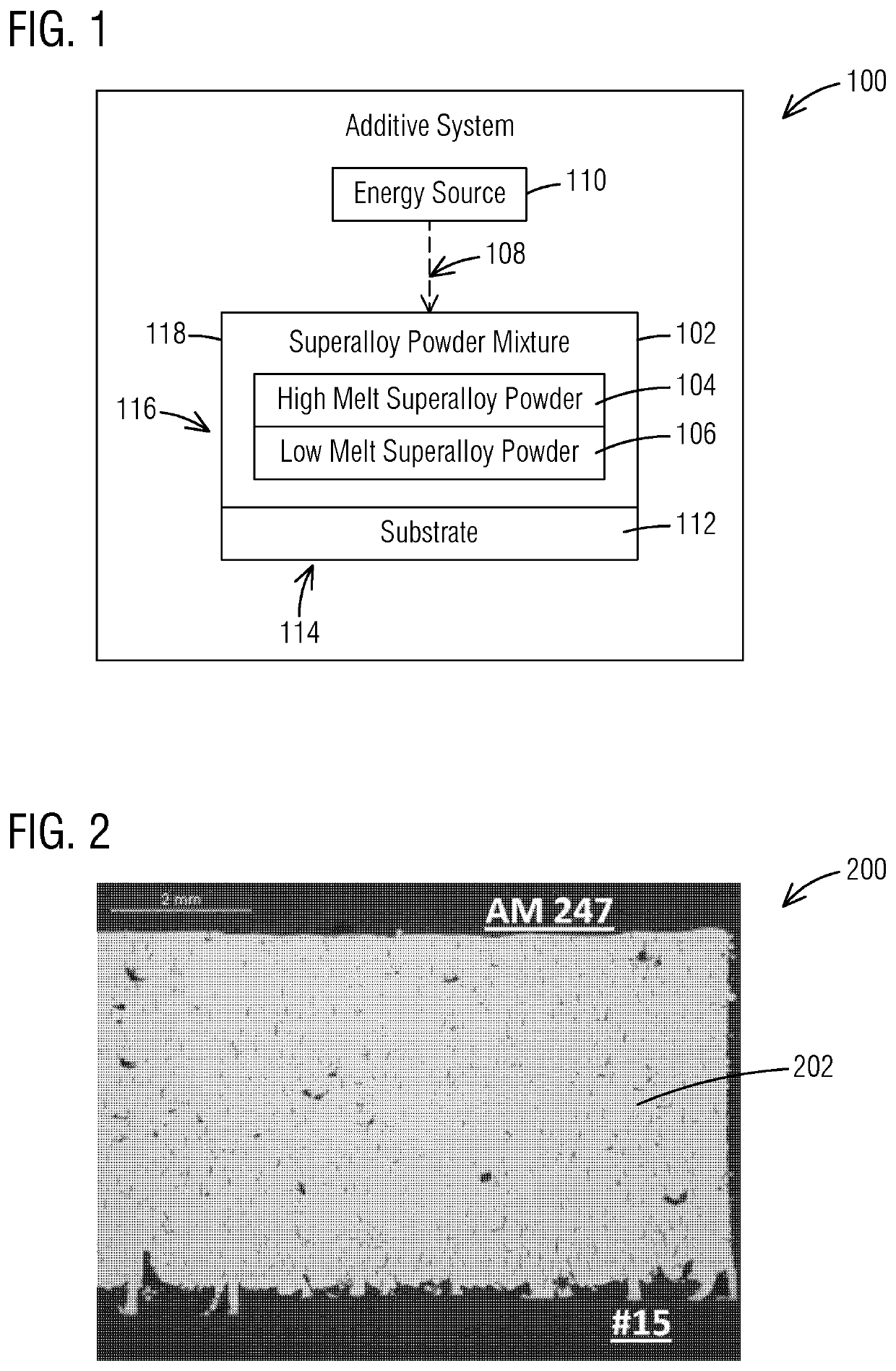
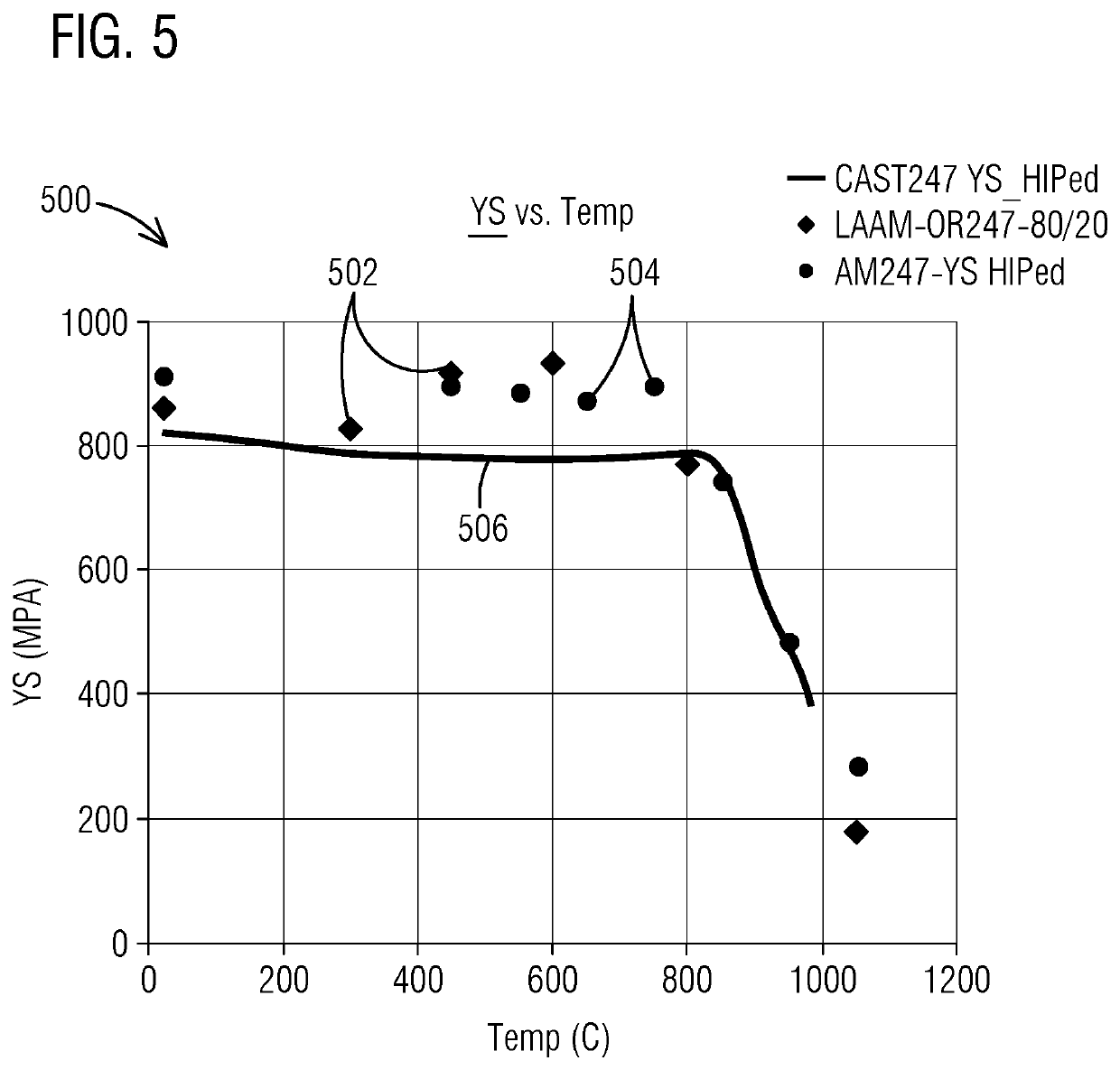
[0111]Various technologies that pertain to systems, methods and materials that facilitate additively manufacturing (and / or welding) components made from superalloy materials will now be described with reference to the drawings, where like reference numerals represent like elements throughout. Before any embodiments of the invention are explained in detail, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited in its application to the details of construction and the arrangement of components set forth in this description or illustrated in the following drawings. The invention is capable of other embodiments and of being practiced or of being carried out in various ways. Also, it is to be understood that the phraseology and terminology used herein is for the purpose of description and should not be regarded as limiting.
[0112]Example embodiments of one or more inventions described herein are directed to making components comprising nickel-base superalloys including greater than 40%...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com