Polar envelope correction mechanism for enhancing linearity of RF/microwave power amplifier
a technology of linearity and correction mechanism, applied in the field of communication systems, can solve the problems of inapplicability of baseband correction techniques using baseband signals, inability to achieve practical solutions for correcting distortion, and inability to use conventional correction mechanisms such as feed forward or predistortion schemes, etc., to achieve the effect of improving linearity of non-linear microwave/rf power amplifiers, simple, efficient and effective, and reducing the bandwidth of digital modulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
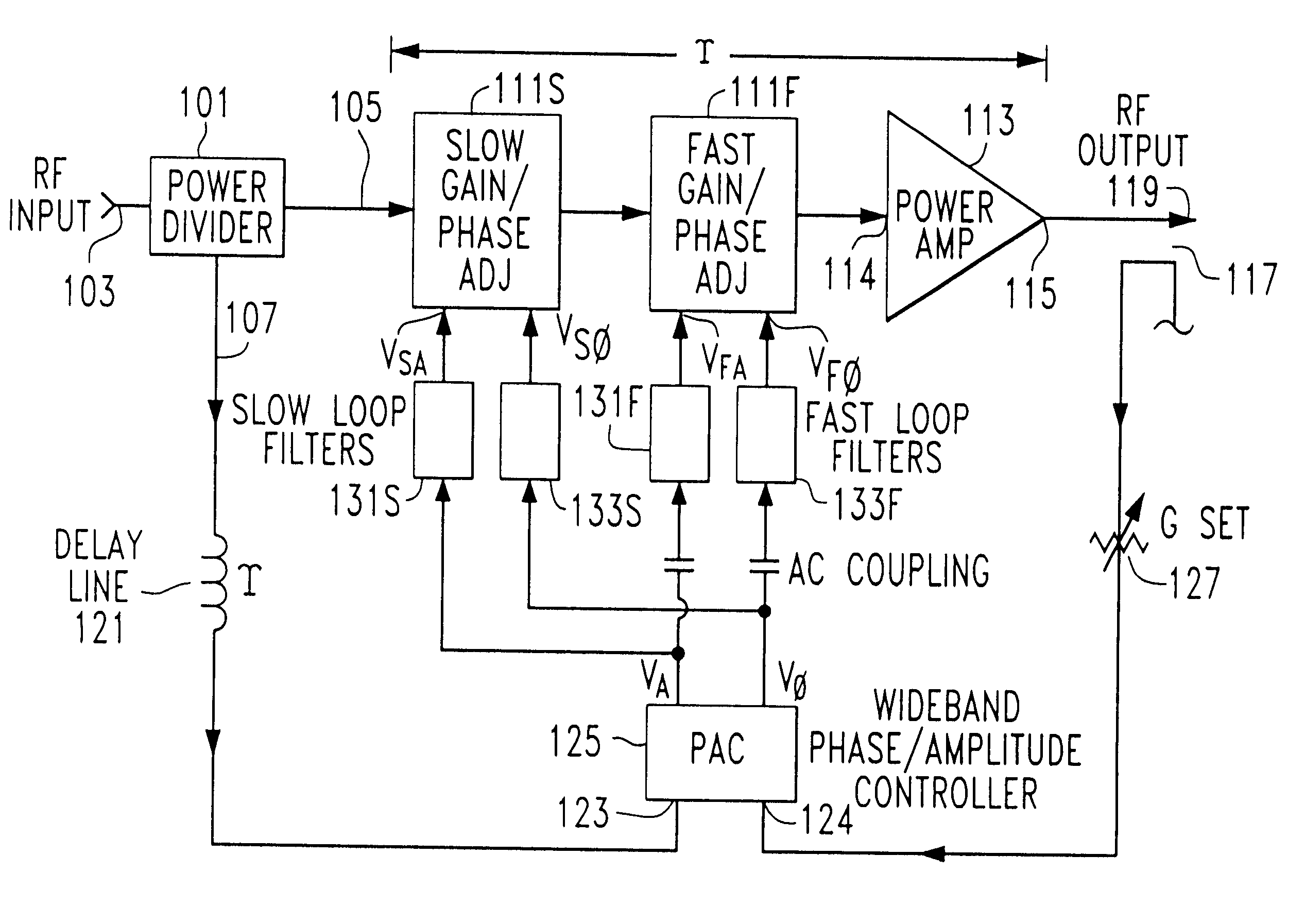
FIG. 17 schematically illustrates a circuit implementation of the high speed phase / amplitude controller 125 of FIG. 4, configured as a differential peak detector 240 for envelope amplitude comparison and a phase bridge 250 serving as a phase detector. In the differential peak detector 240, input signals are coupled to respective R (reference) and M (measure) input ports 123 and 124 through respective dc blocking capacitors 245 and 246, resistors 251 and 253 and peak detector diodes 255 and 256 to (-) and (+) input ports 257 and 258 of differential amplifier 260. The (+) and (-) input ports 257 and 258 of differential amplifier 260 are further coupled through respective capacitors 265 and 266 and resistors 271 and 273 to ground. Isolation resistors 251 and 253, detector diodes 255 and 256, by-pass capacitors 265, 266 and video load resistors 271 and 273 comprise a pair of fast biased peak detectors which measure the amplitude of the envelopes of the signals delivered to the R and M p...
second embodiment
FIG. 18 schematically illustrates a circuit implementation of the high speed phase / amplitude controller 125 of FIG. 4, configured with peak detectors and a Gilbert multiplier. In the embodiment of FIG. 18, the R and M input terminals 123 and 124, respectively, are each split into two paths by quadrature power divider 311 and in phase power divider 312. The in phase R paths and one of the M paths are each peak detected by means of a pair of matched, biased diode detectors 321 and 322, respectively, and coupled to (+) and (-) inputs 331 and 332 of differential amplifier 330. The output of differential amplifier 330 is the control voltage V.sub.A.
The control voltage V.sub..PHI. is obtained by multiplying the remaining quadrature R and in phase M signals limited by respective phase-matched limiters 341 and 343 in a wideband Gilbert cell multiplier 350 and low pass filtering the result by means of a low pass filter 352. The phase matched limiters 341 and 343 remove amplitude information ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com