Patents
Literature
65 results about "Screen reader" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
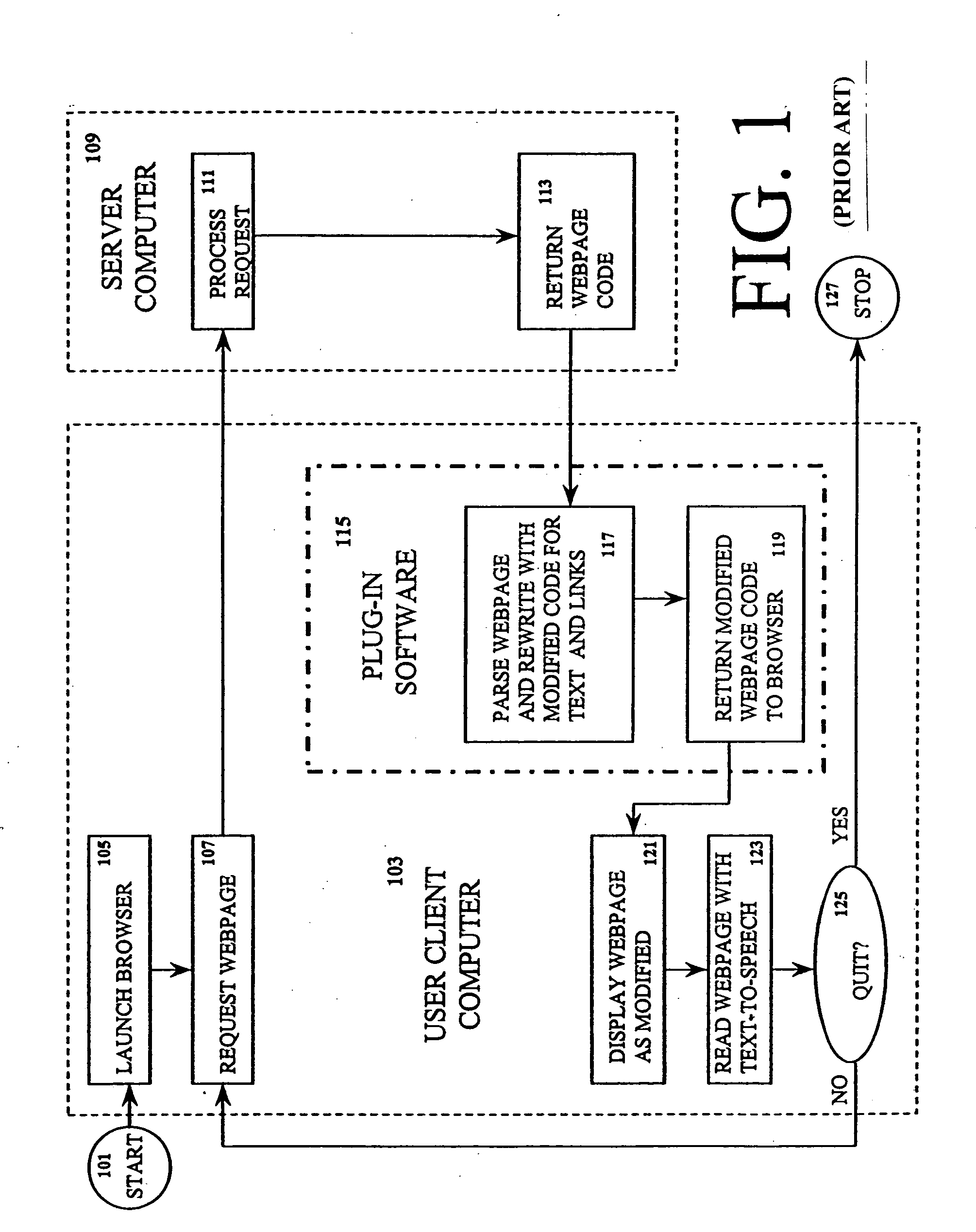
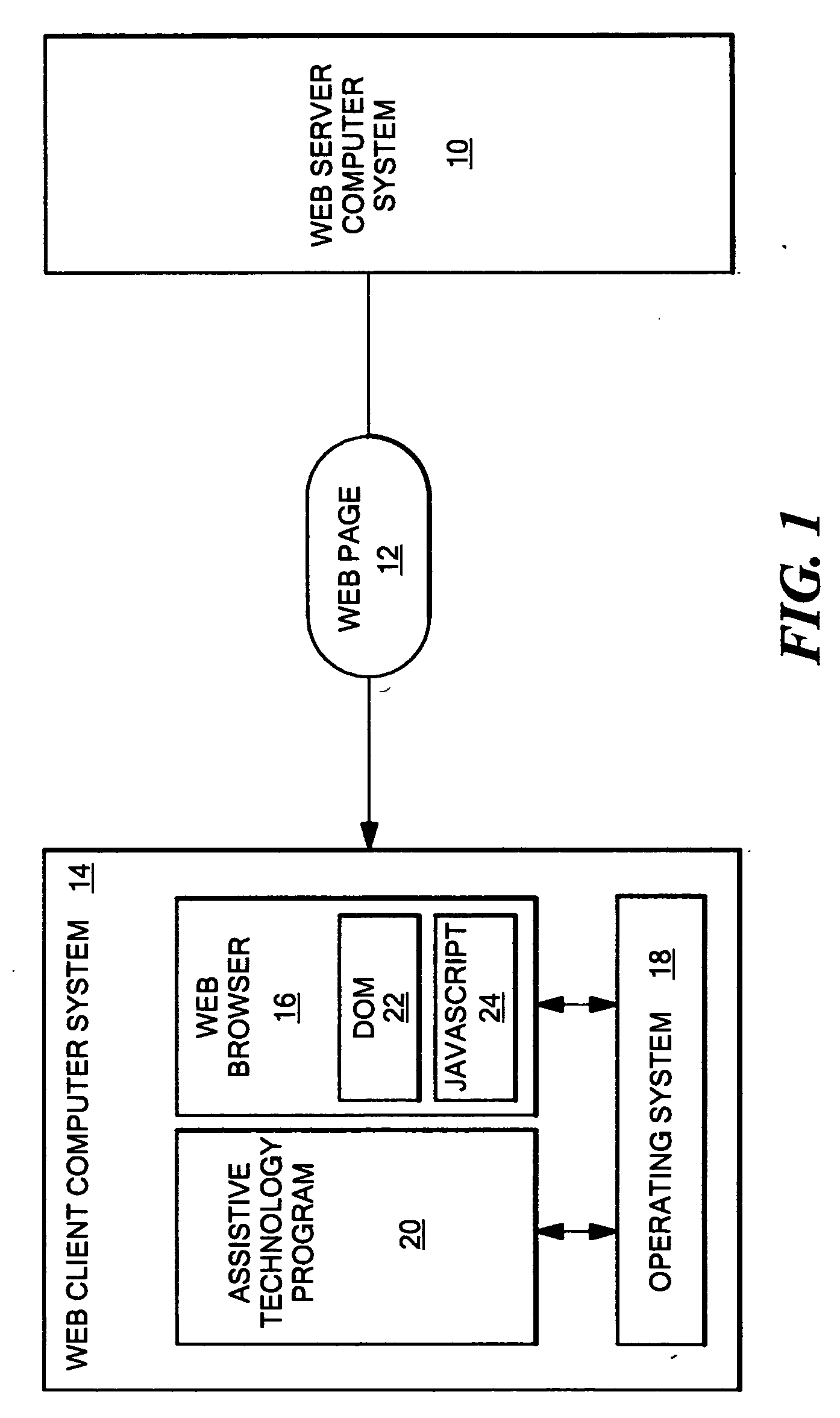
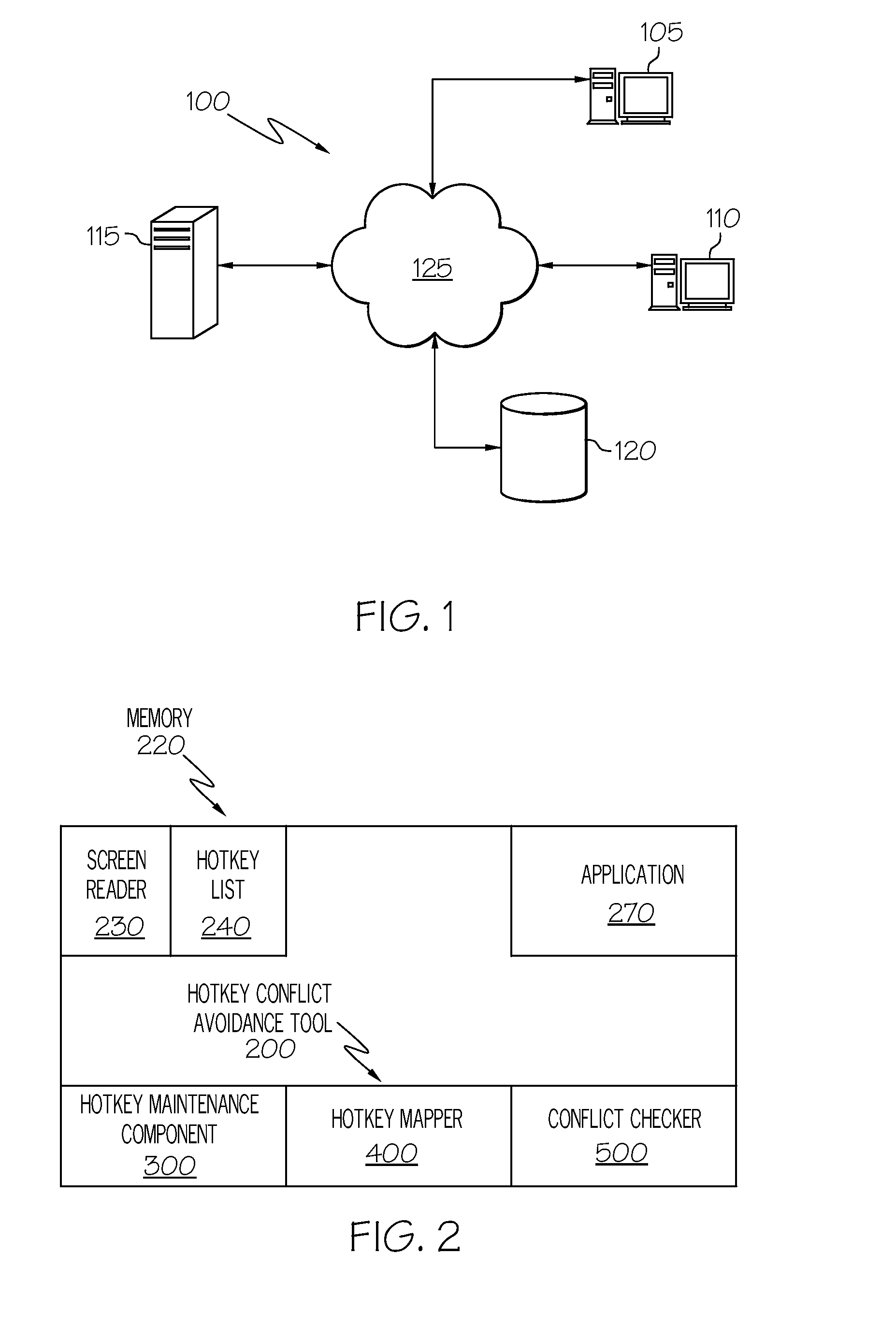
A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) which is essential to people who are blind, as well as useful to people who are visually impaired, illiterate, or have a learning disability. Screen readers are software applications that attempt to convey what people with normal eyesight see on a display to their users via non-visual means, like text-to-speech, sound icons, or a Braille device. They do this by applying a wide variety of techniques that include for example interacting with dedicated accessibility APIs, using various operating system features (like inter-process communication and querying user interface properties) and employing hooking techniques.
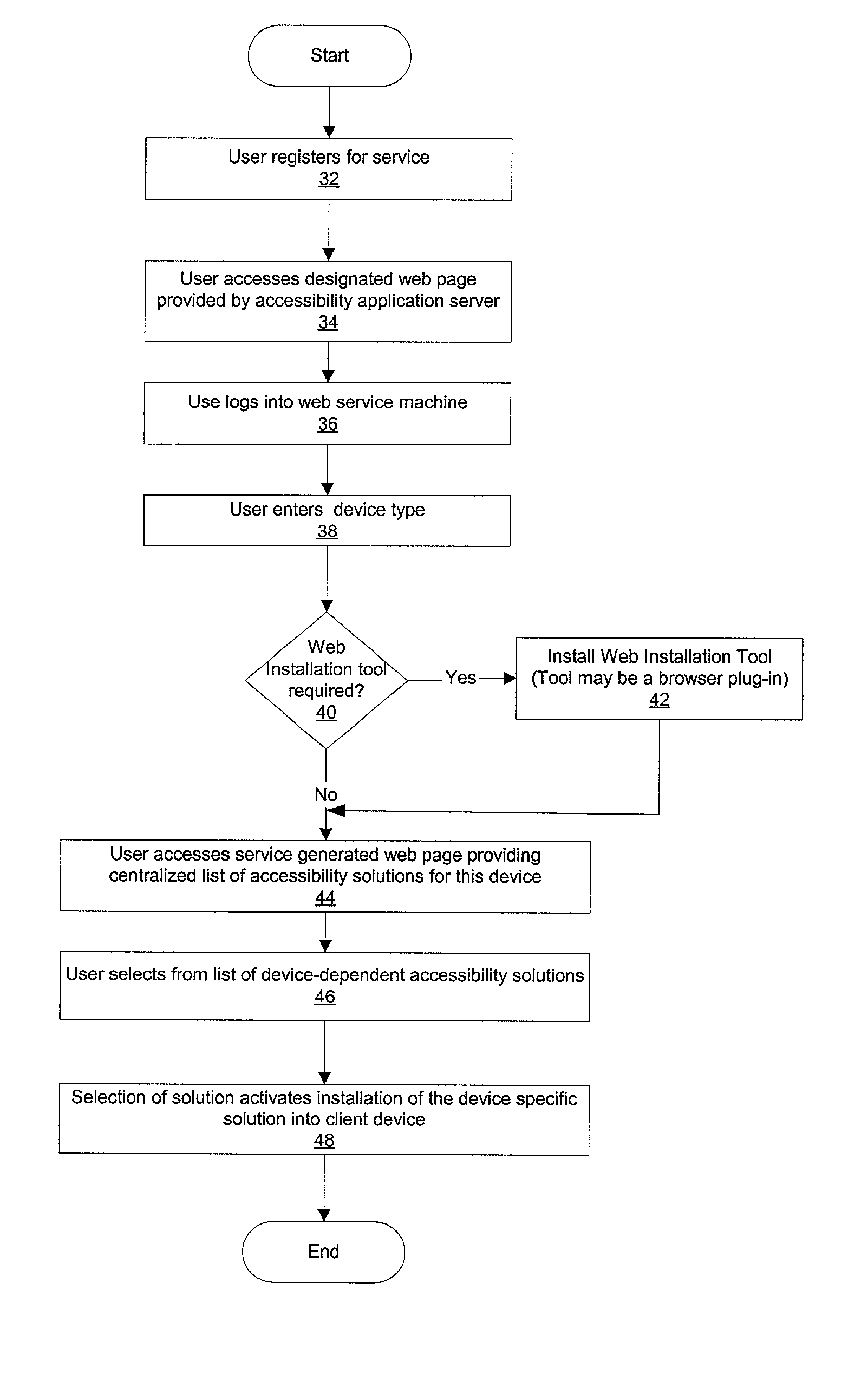
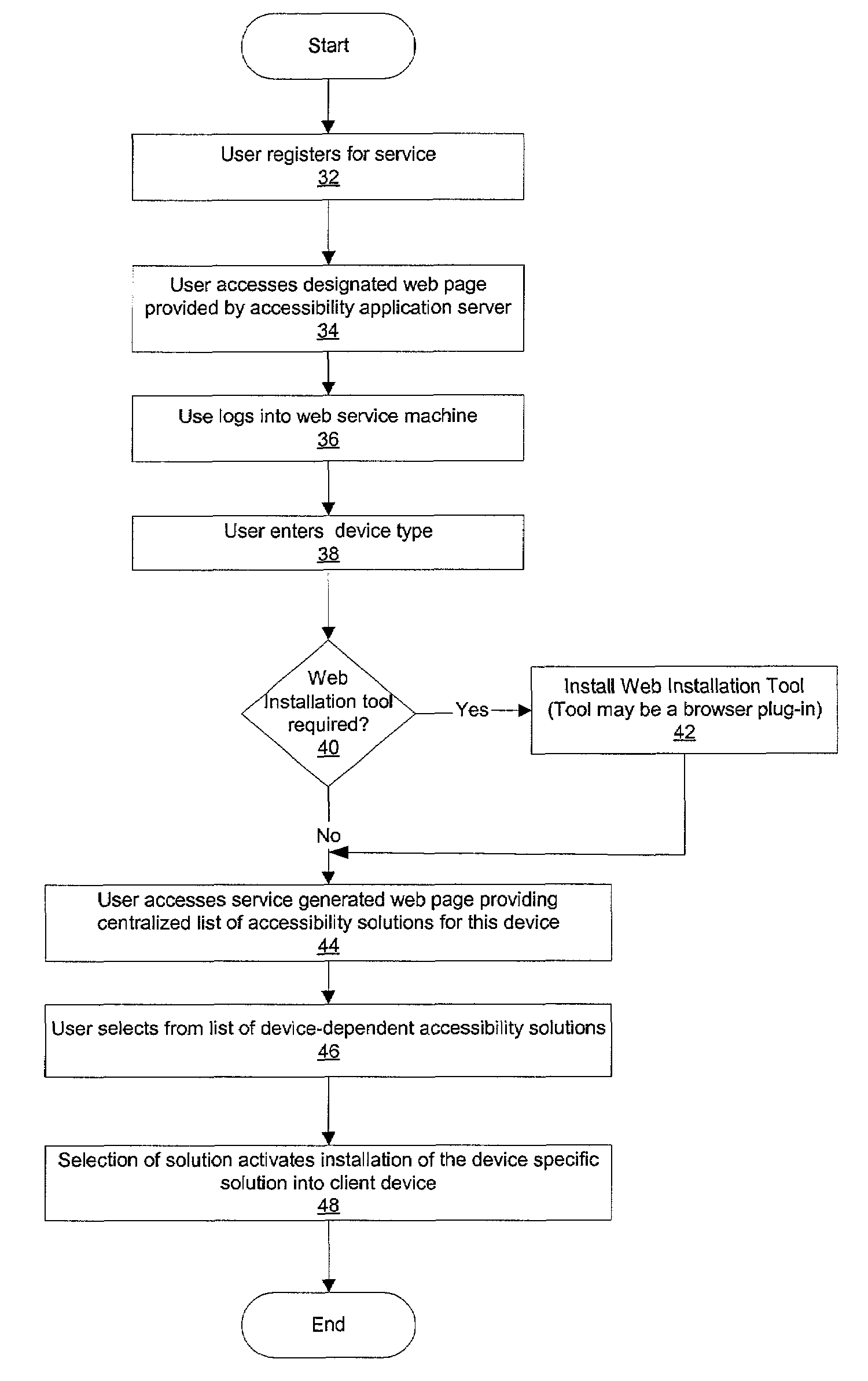
Method and system for providing a central repository for client-specific accessibility
InactiveUS20030061317A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsService provisionTranscoding
A method and system that provide a central repository for client specific accessibility applications to a user from an accessible server. The repository is updated on a periodic basis with new solutions provided by the service provider, who also manages licensing agreements between the user and the owner of the accessibility application. Accessibility programs, such as page magnification, screen readers, background changes, input modification, etc., are downloaded into the client device being used by the user customer by clicking link buttons from a web page generated by the service provider's server. The accessibility programs downloaded are then resident on the client device until changed by the user. In a preferred embodiment, the service provider also provides a universal transcoding service to apply the user selected accessibility transformations to any type of client device used by the user.
Owner:IBM CORP
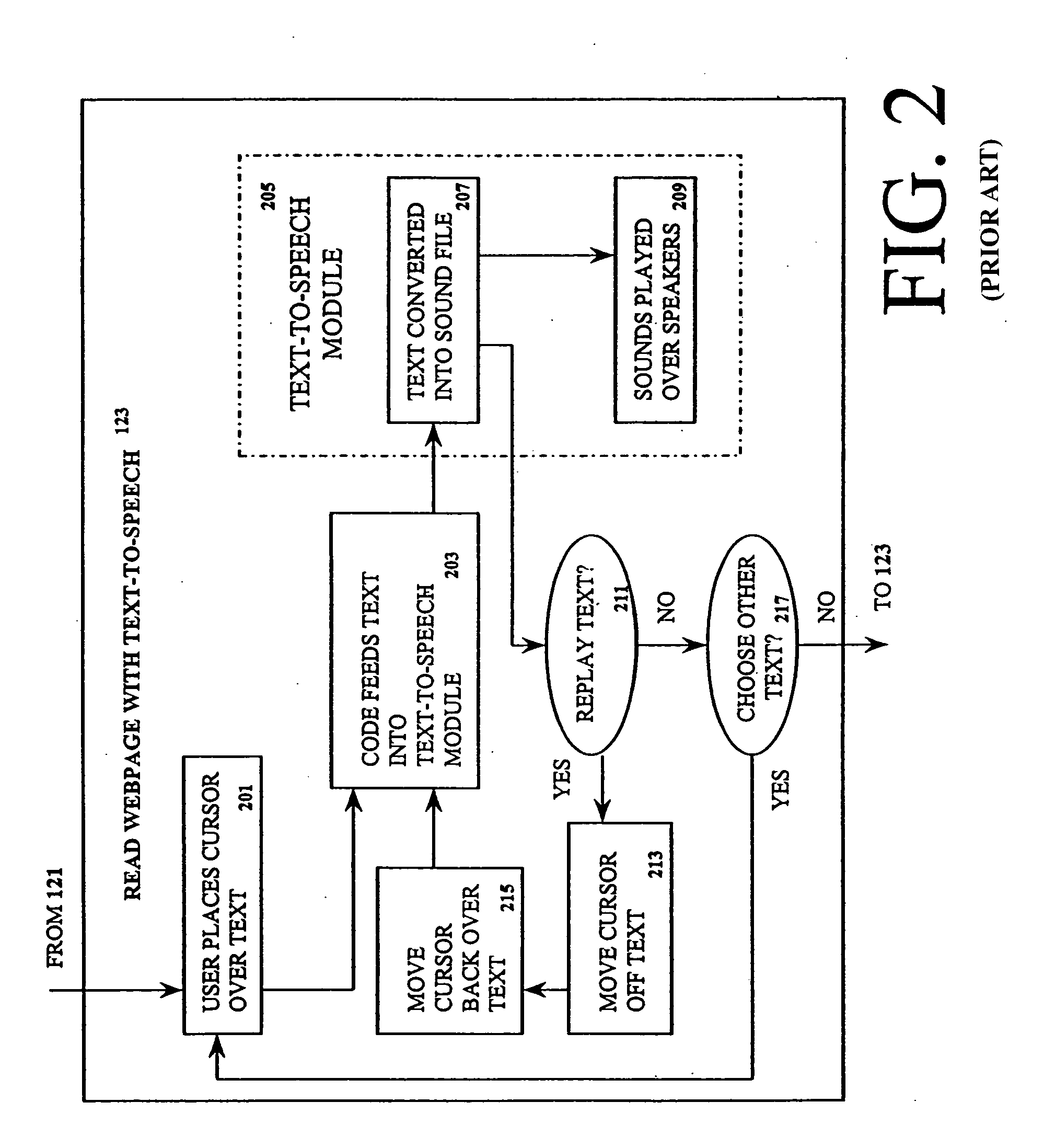
Method and apparatus for interacting with a visually displayed document on a screen reader
InactiveUS20070211071A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
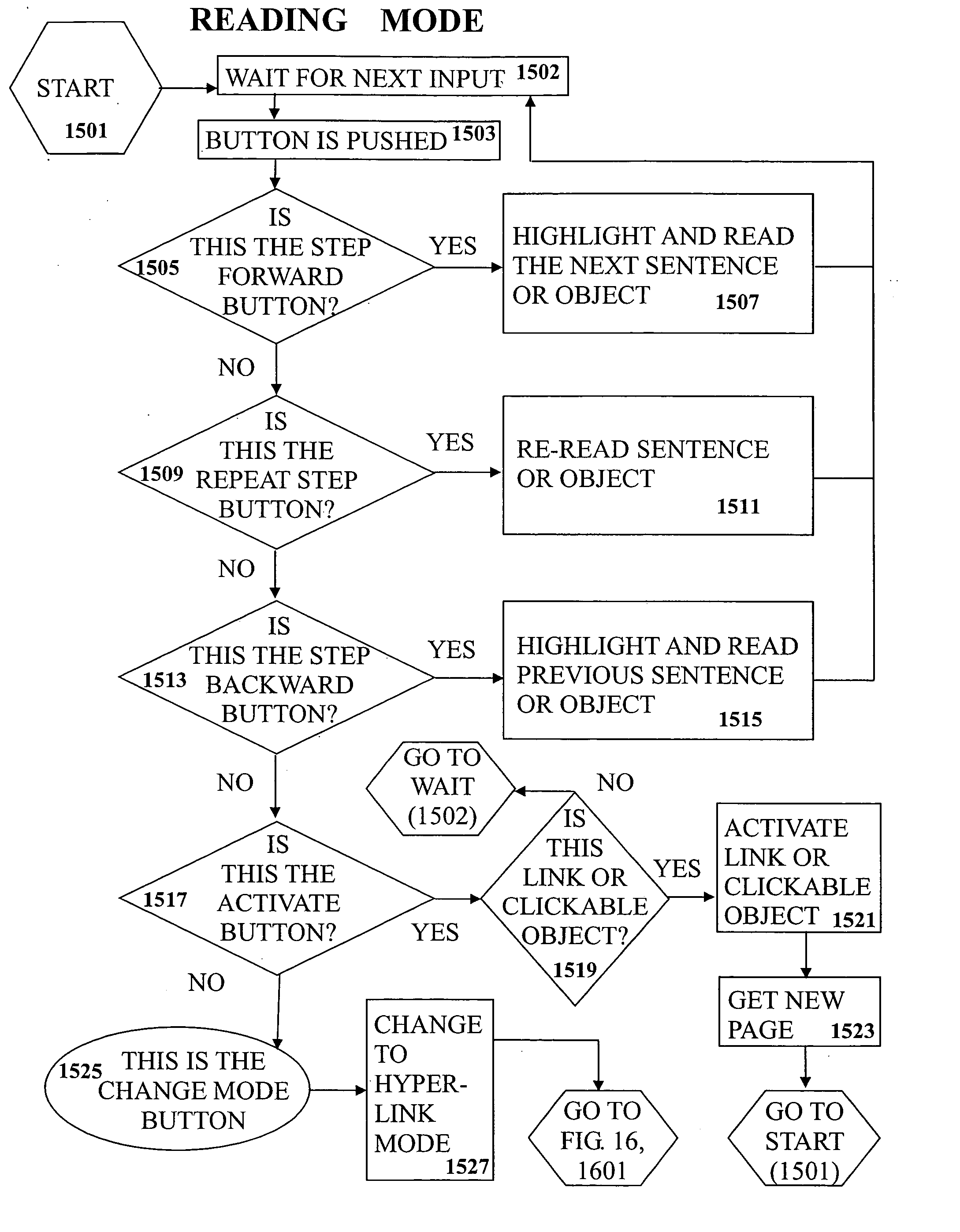
User interaction of a visually displayed document is provided via a graphical user interface (GUI). The document includes, and is parsed into, a plurality of text-based grammatical units. An input device modality is selected from a plurality of input device modalities which determines the type of input device in which a user interacts with to make a selection. One or more grammatical units of the document are then selected using the selected type of input device. Each grammatical unit that is selected is read aloud to the user by loading the grammatical unit into a text-to-speech engine. The text of the grammatical unit is thereby automatically spoken. Furthermore, a switching modality is selected from a plurality of switching modalities. The switching modality determines the manner in which one or more switches are used to make a selection. Using the selected switching modality, a user steps through at least some of the grammatical units in an ordered manner by physically activating one or more switches associated with the GUI. Each activation steps through one grammatical unit. Each grammatical unit that is stepped through is read aloud by loading the grammatical unit into a text-to-speech engine, thereby causing the text of the grammatical unit to be automatically spoken.
Owner:SLOTZNICK BENJAMIN
Audible menu system
InactiveUS20090187950A1Television system detailsColor television detailsHuman–computer interactionGraphical user interface testing
An audible menu system associated with distribution of television content over a service provider network is disclosed. The menu system includes a speech synthesizer and screen reader. Electronic programming guide (EPG) elements are read by a screen reader and provided to a speech synthesizer for presenting audible representations of EPG elements to a user. The user may provide inputs to a remote control device to navigate an EPG that may also be presented through a graphical user interface. As a user navigates a cursor over selectable EPG elements, disclosed embodiments provide audible outputs that correspond to the selectable EPG elements. In some embodiments, users may provide customized audio inputs that are played as audio outputs during future menu navigation sessions.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
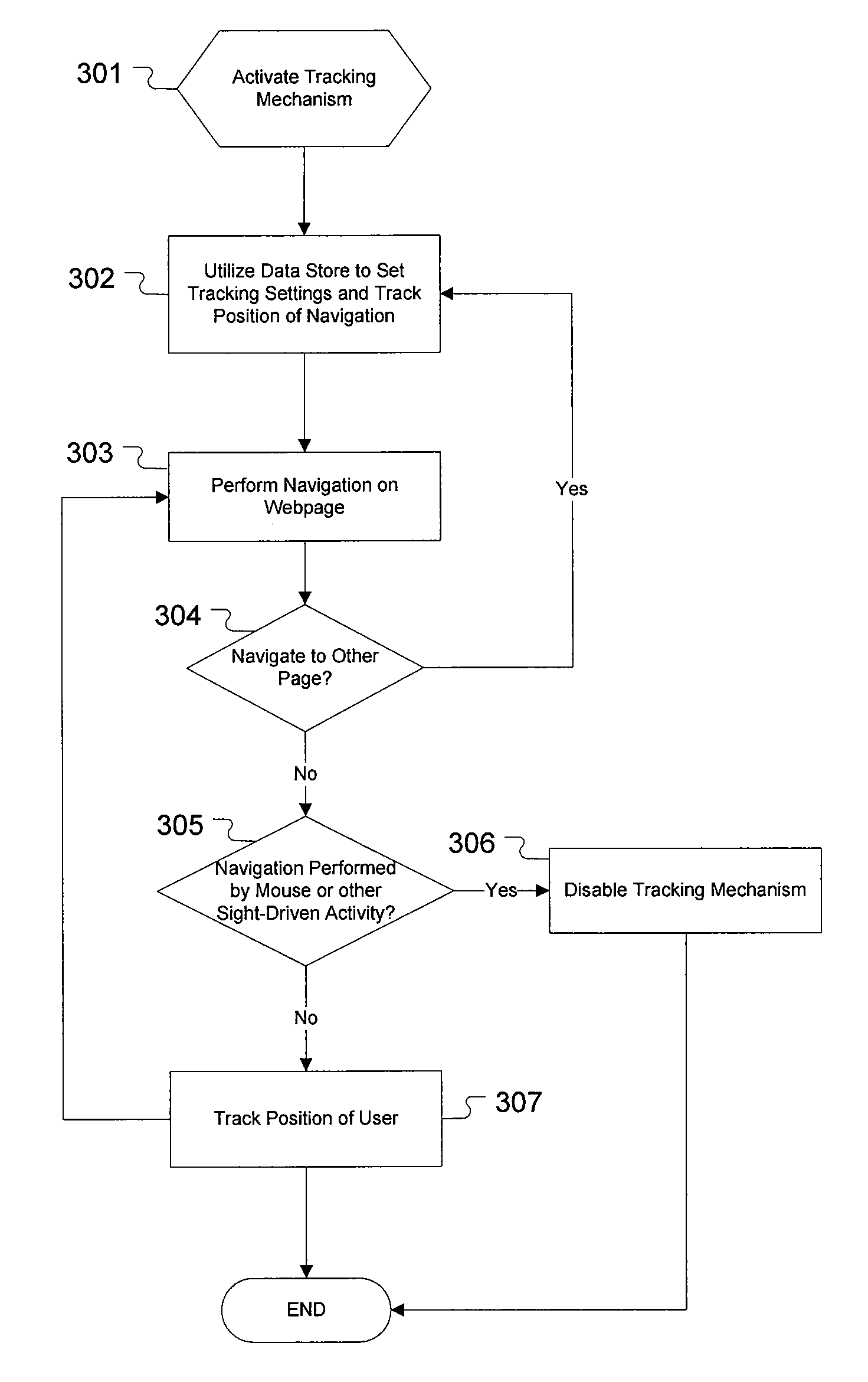
Adaptive technique for sightless accessibility of dynamic web content
ActiveUS20100070872A1Improve accessibilitySimple methodSpeech analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsScreen readingApplication software
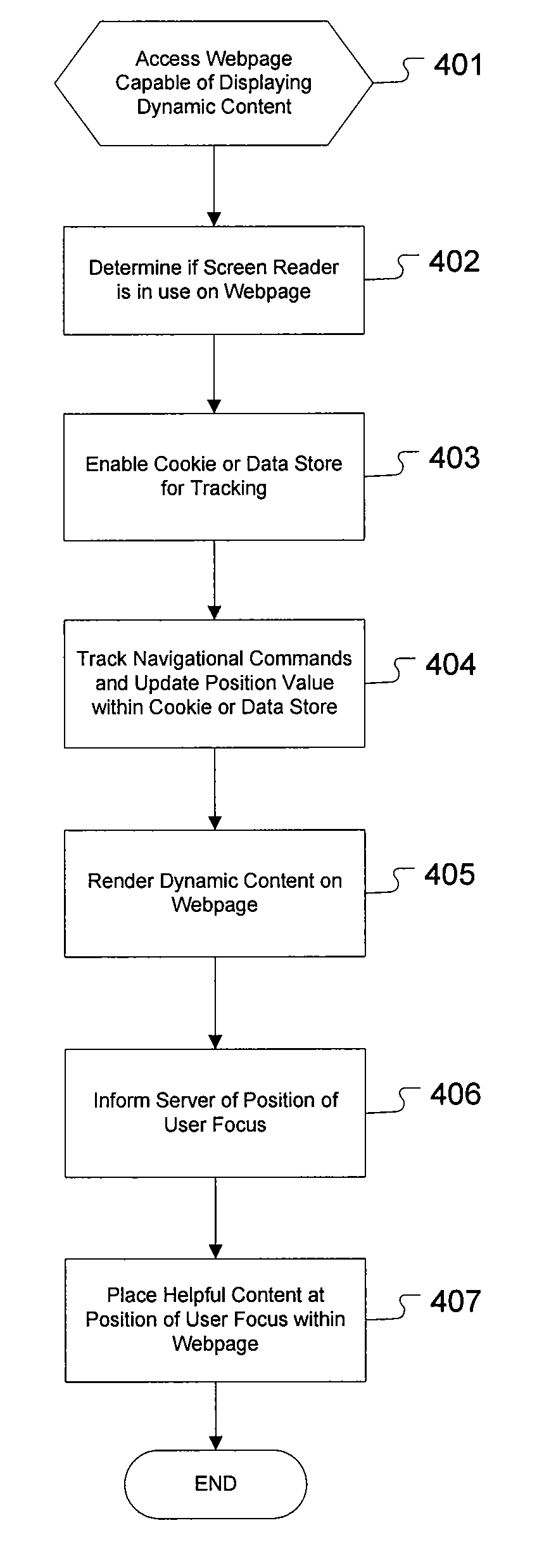
One aspect of the present invention includes adaptive techniques used to render dynamic web content for accessibility software applications, such as screen readers. In one embodiment, an operation for improving webpage browsing with accessibility software includes detecting if an accessibility software application is in use, tracking the position of user focus on the webpage, and presenting information to the user based on the position of user focus on the webpage. In a further embodiment, additional content is rendered on the webpage to screen reader applications, and is placed at the position of the screen reader focus in response to dynamic content appearing or changing on the webpage. This additional content is read by the screen reader to inform the user of the dynamic content change, and / or enable the user to quickly perform a specific action on the webpage.
Owner:ACCESSIBE LTD
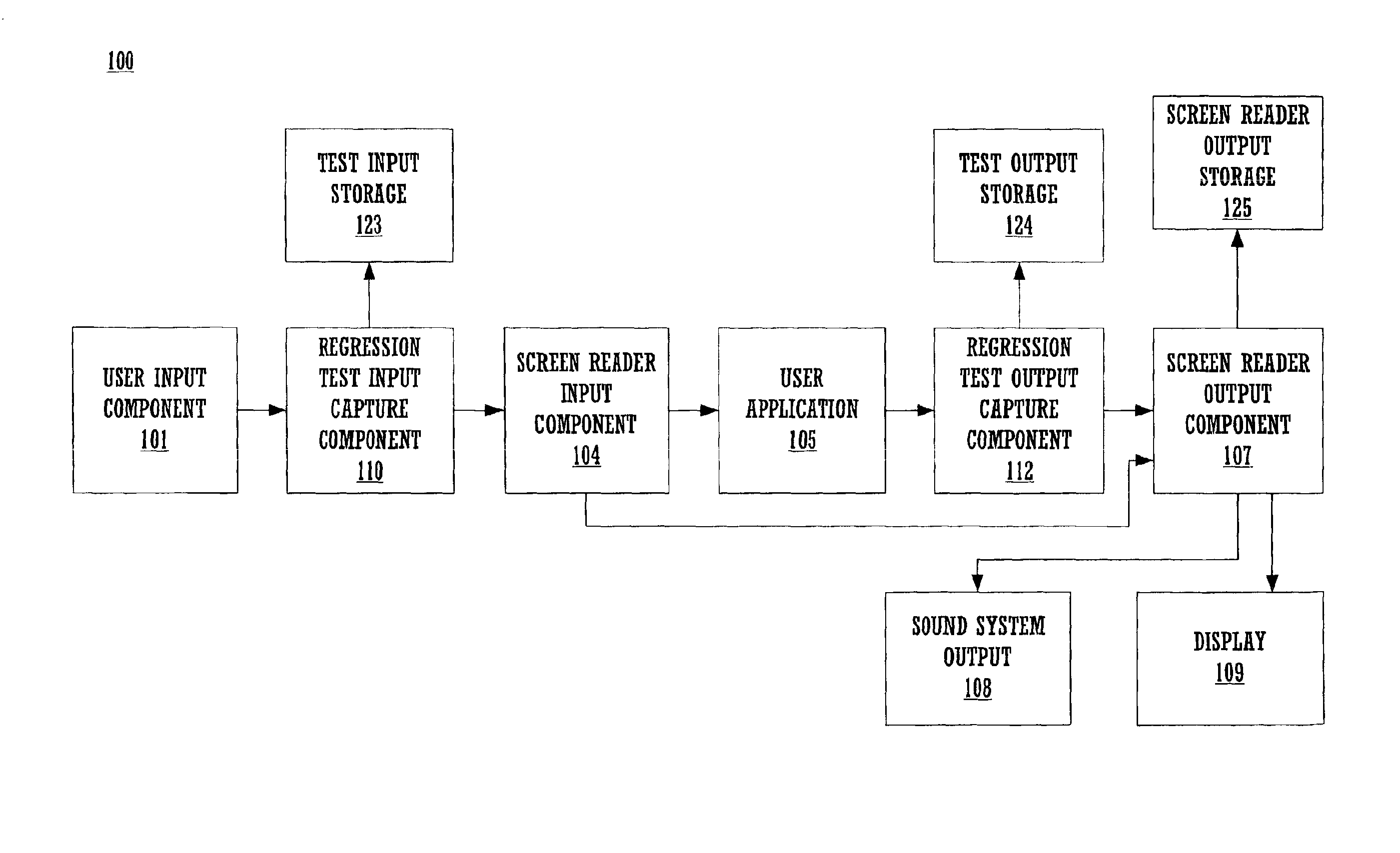
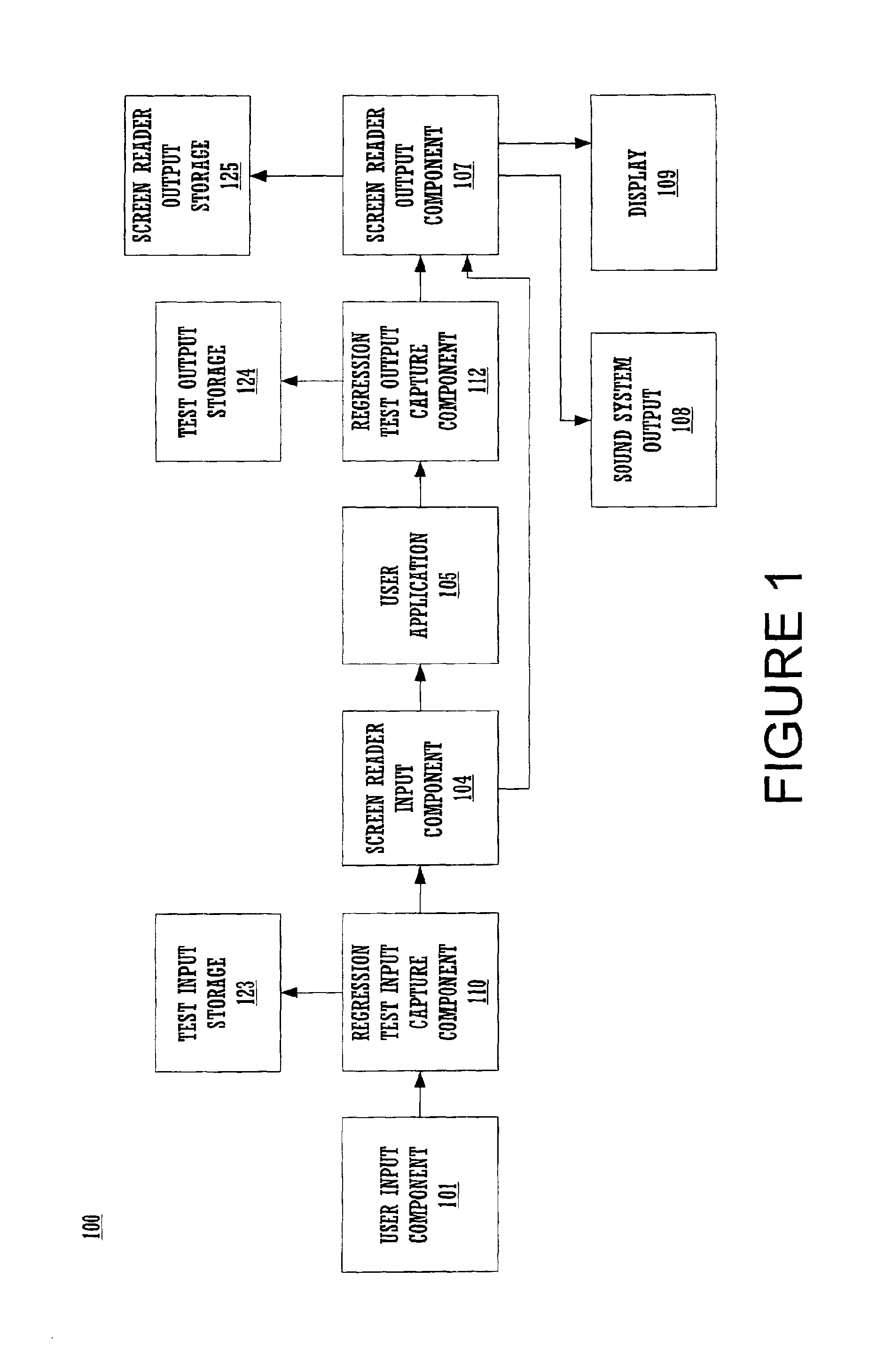
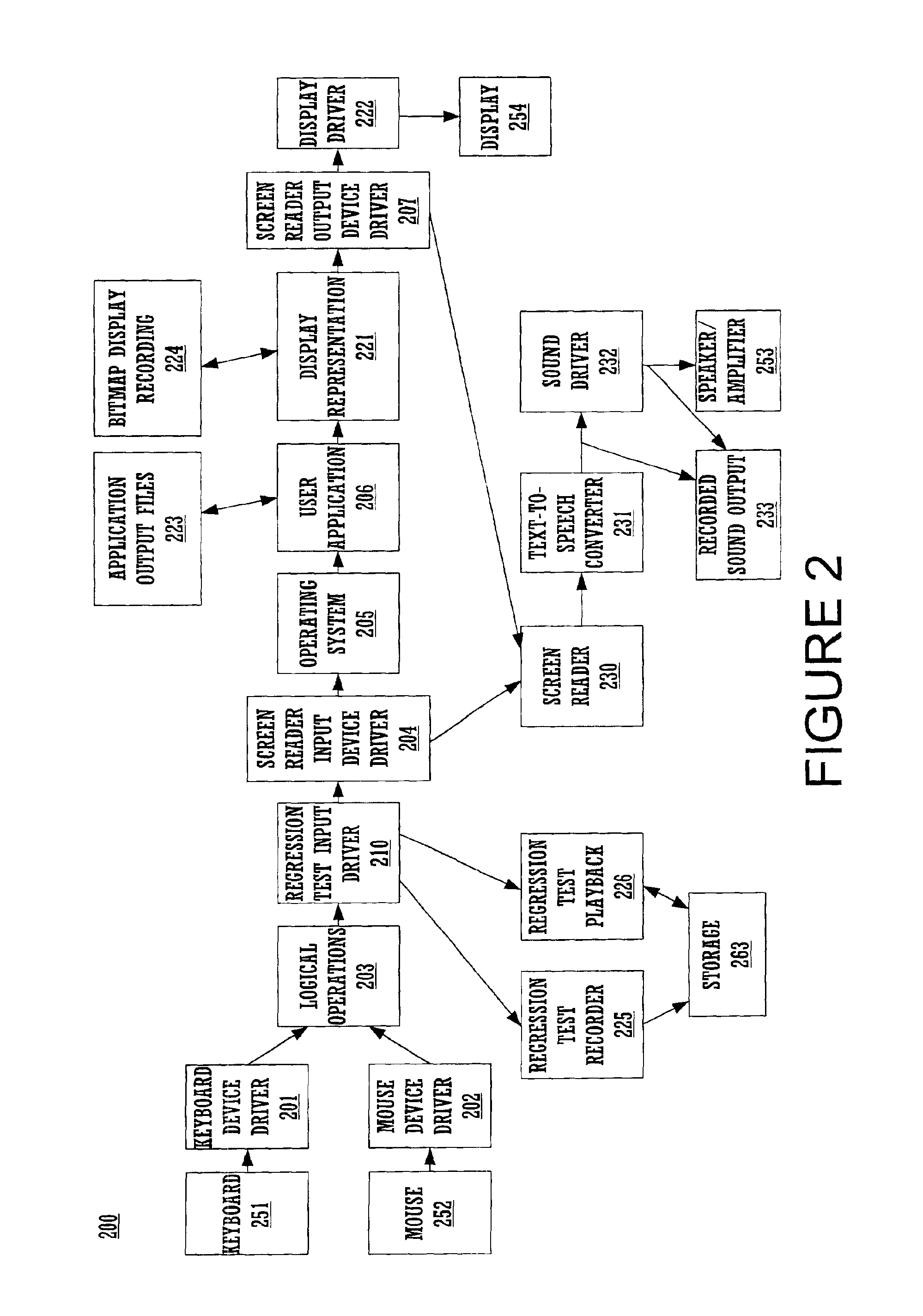
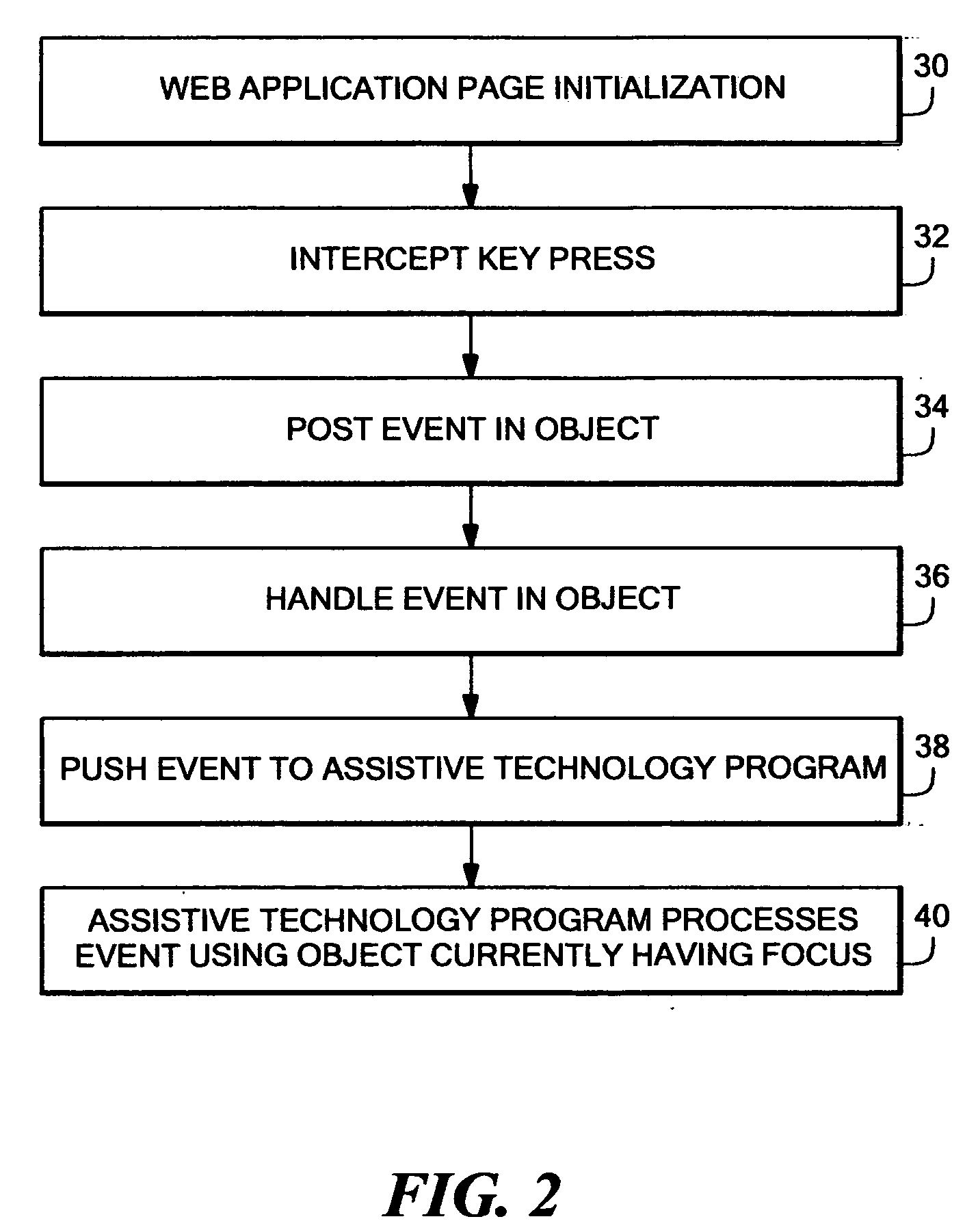
Method and system for screen reader regression testing
A method for repeatable application testing on a computer system for audible output generated by the application in conjunction with a screen reader or similar assistive technology. The method includes recording user inputs to a user application using a test input component. The user inputs are also accessed by a screen reader input component. Outputs of the user application are recorded using a test output component. The outputs of the user application are also accessed by a screen reader output component. The resulting screen reader outputs are recorded and are analyzed with respect to the recorded user inputs and the recorded outputs of the user application. The user inputs to the user application can be keyboard inputs or mouse inputs, and inputs of other input devices. The outputs of the user application can be graphical outputs or alphanumeric outputs for a display of the computer system. The resulting screen reader outputs can be sound output signals (or representations thereof) for a sound system of the computer system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for providing a central repository for client-specific accessibility
InactiveUS7062547B2Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsService provisionTranscoding
A method and system that provide a central repository for client specific accessibility applications to a user from an accessible server. The repository is updated on a periodic basis with new solutions provided by the service provider, who also manages licensing agreements between the user and the owner of the accessibility application. Accessibility programs, such as page magnification, screen readers, background changes, input modification, etc., are downloaded into the client device being used by the user customer by clicking link buttons from a web page generated by the service provider's server. The accessibility programs downloaded are then resident on the client device until changed by the user. In a preferred embodiment, the service provider also provides a universal transcoding service to apply the user selected accessibility transformations to any type of client device used by the user.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
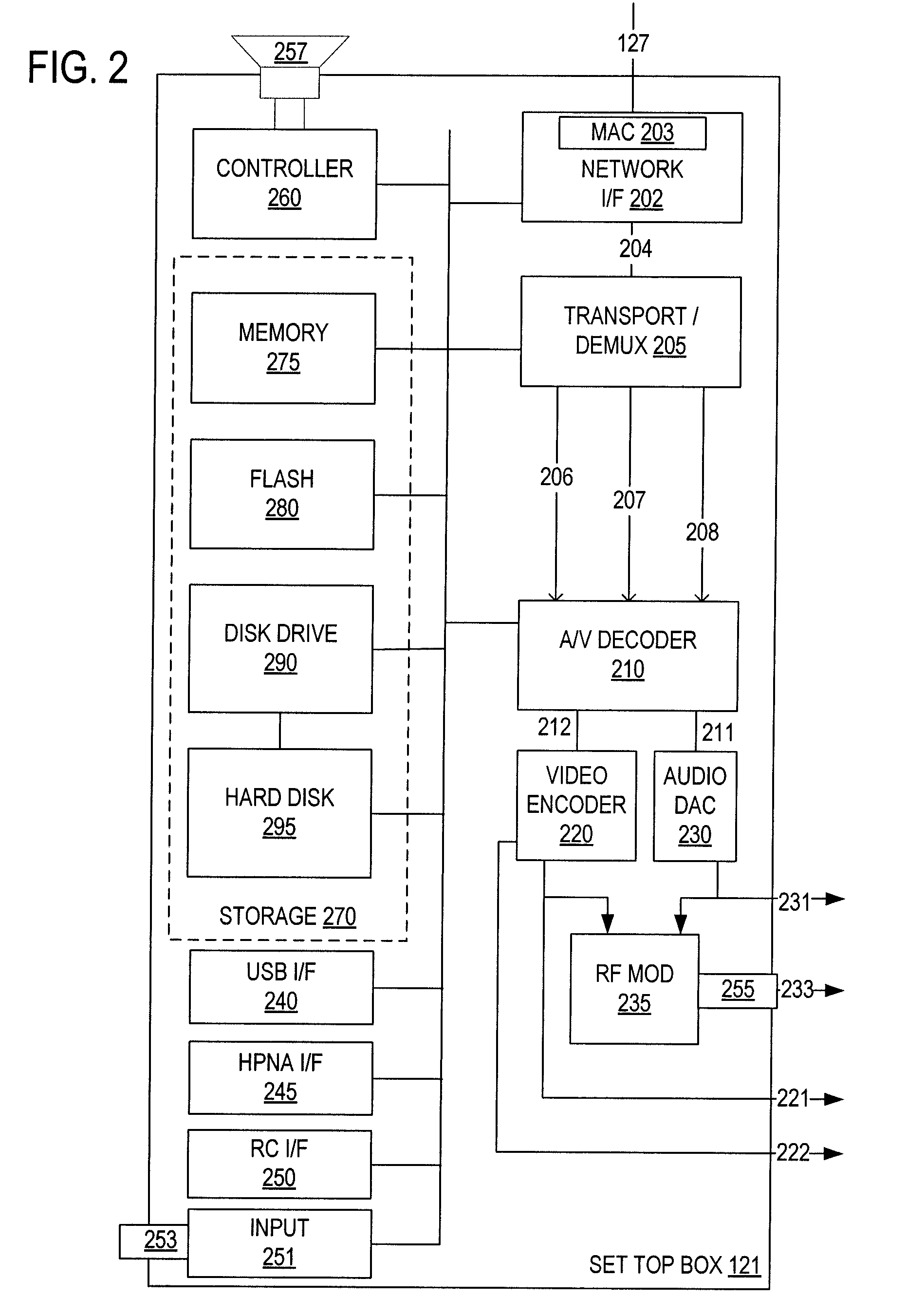
Method and apparatus for providing DHTML accessibility
InactiveUS20060090138A1Execution for user interfacesSpecial data processing applicationsWeb applicationComputer graphics (images)
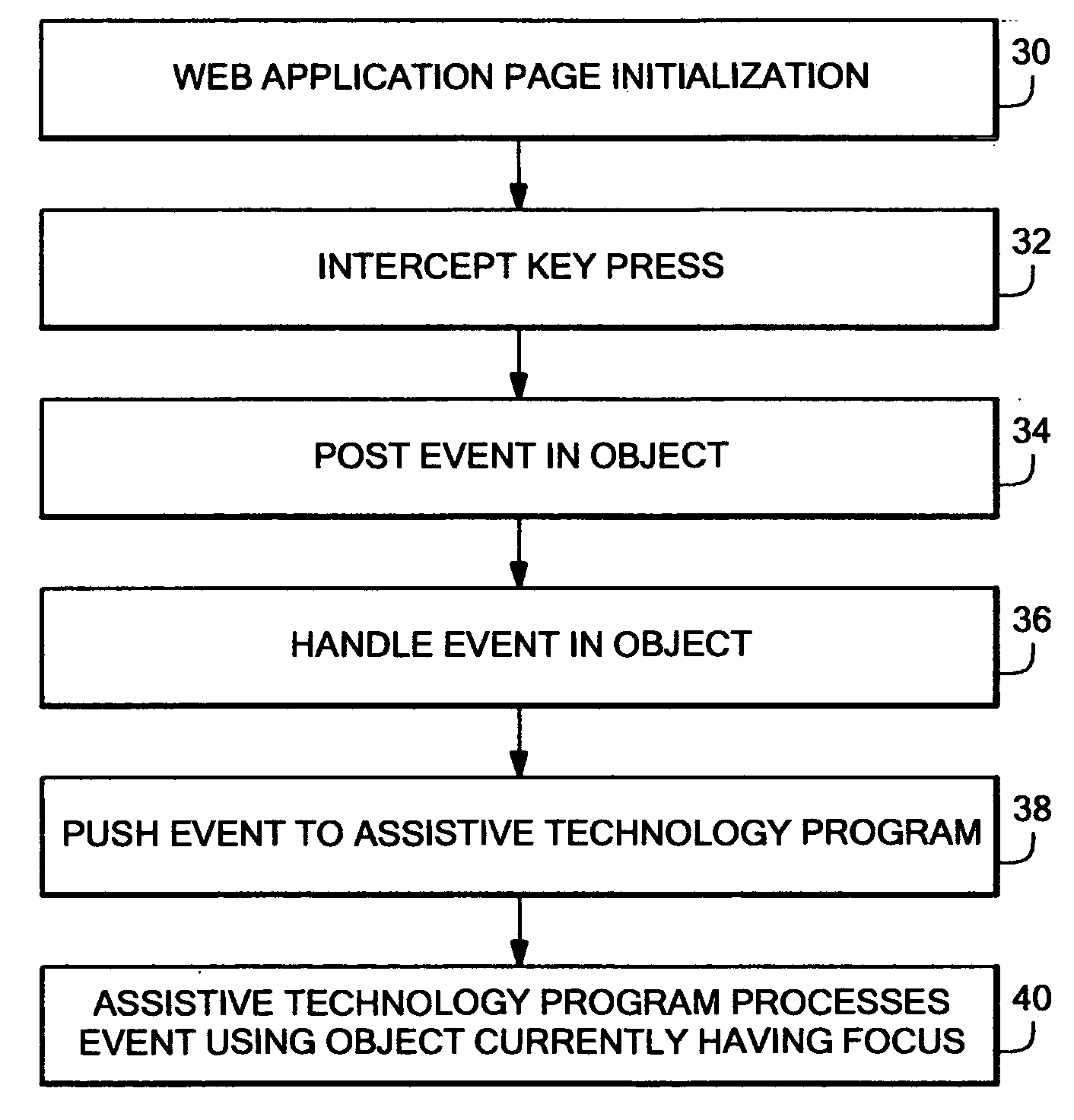
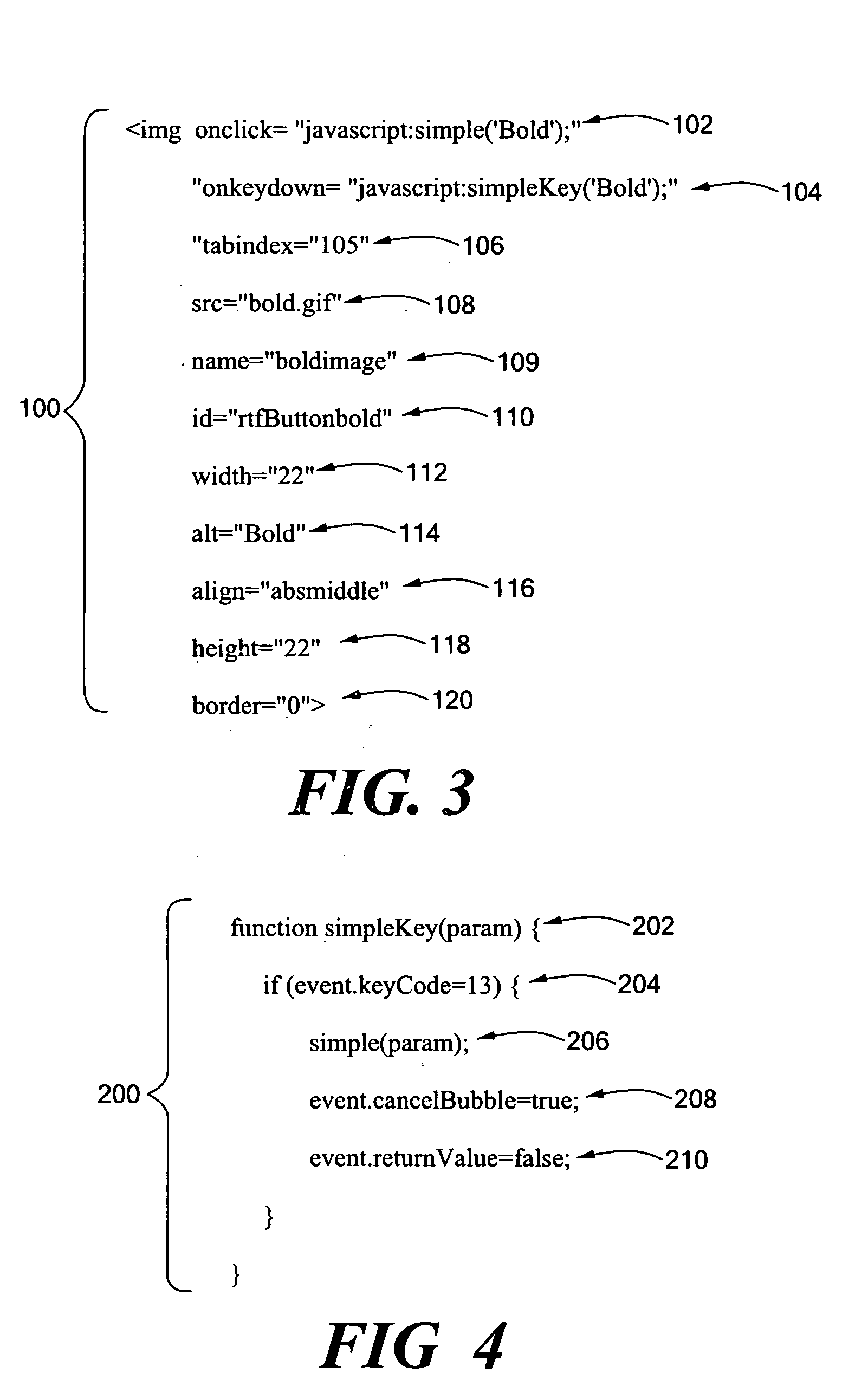
A system for providing DHTML (“Dynamic Hyper-Text Markup Language”) accessibility. Rich keyboard and other assistive technology (“AT”) accessibility is provided for sophisticated Web applications. When a user downloads a Web page, the system performs initialization that includes loading at least one display object, and binding the object to a predetermined event, such as, for example, a focus event. The event the object is bound to may be any semantic, device independent event. The disclosed system may also load a device handling function, such as a keyboard handling function. The device handling function associates one or more display objects with corresponding device actions, such as key presses. A keyboard handling function may operate to intercept at least one key press, and determine that an intercepted key press matches a key press corresponding to a previously loaded display object. The device handling function may create a focus event for the previously loaded display object, and post the event to the display object. The display object then handles the event by visually responding to the intercepted key press, for example by changing the visual representation of the display object to be highlighted, or to otherwise indicate that the display object has been selected. The event may then also be sent to an assistive technology program, such as a screen reader program. Using the values of attributes in that display object, such as the value of the role attribute, the assistive technology program responds to the event as appropriate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for providing an accessible object on a modal dialog box
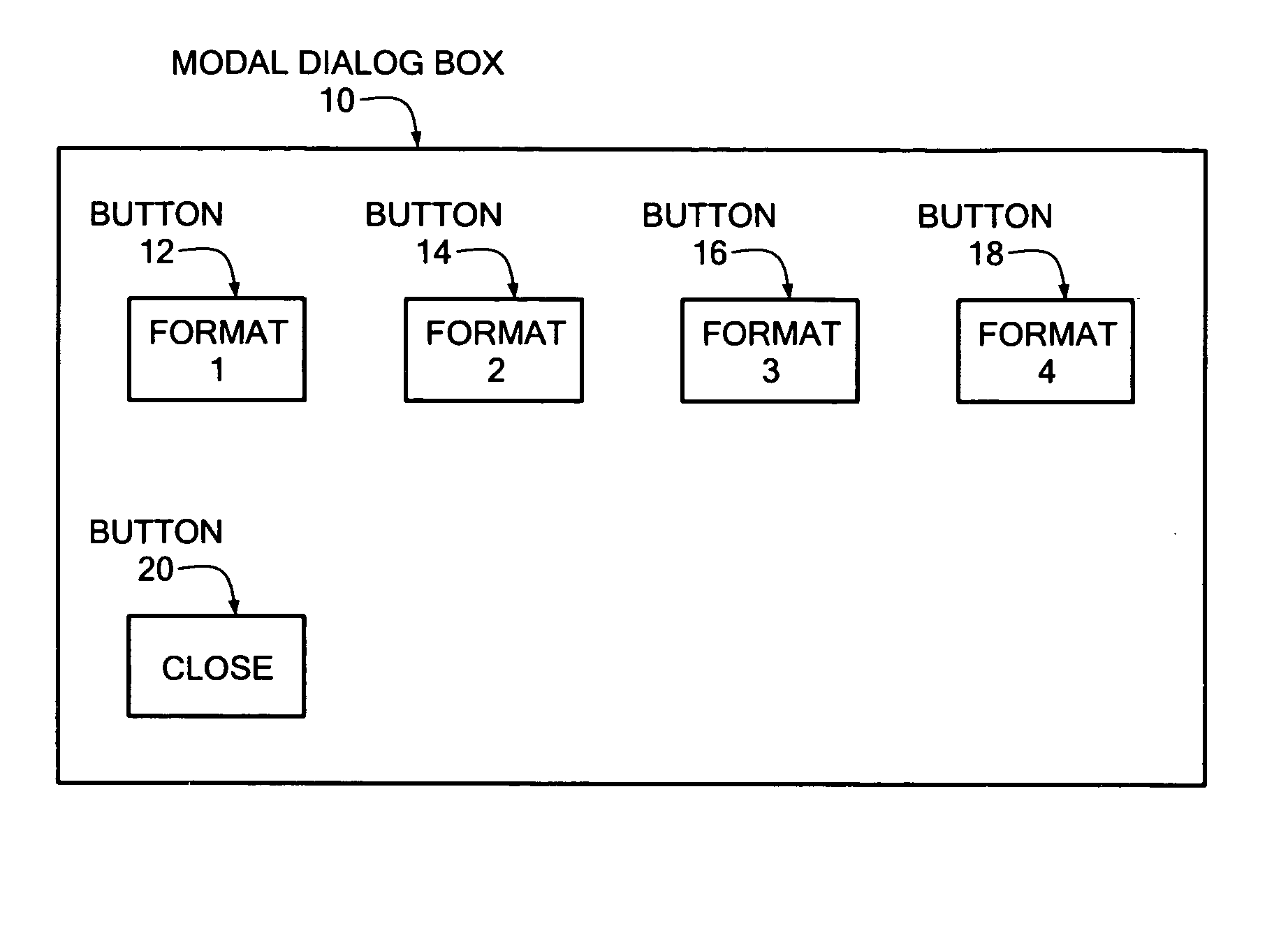
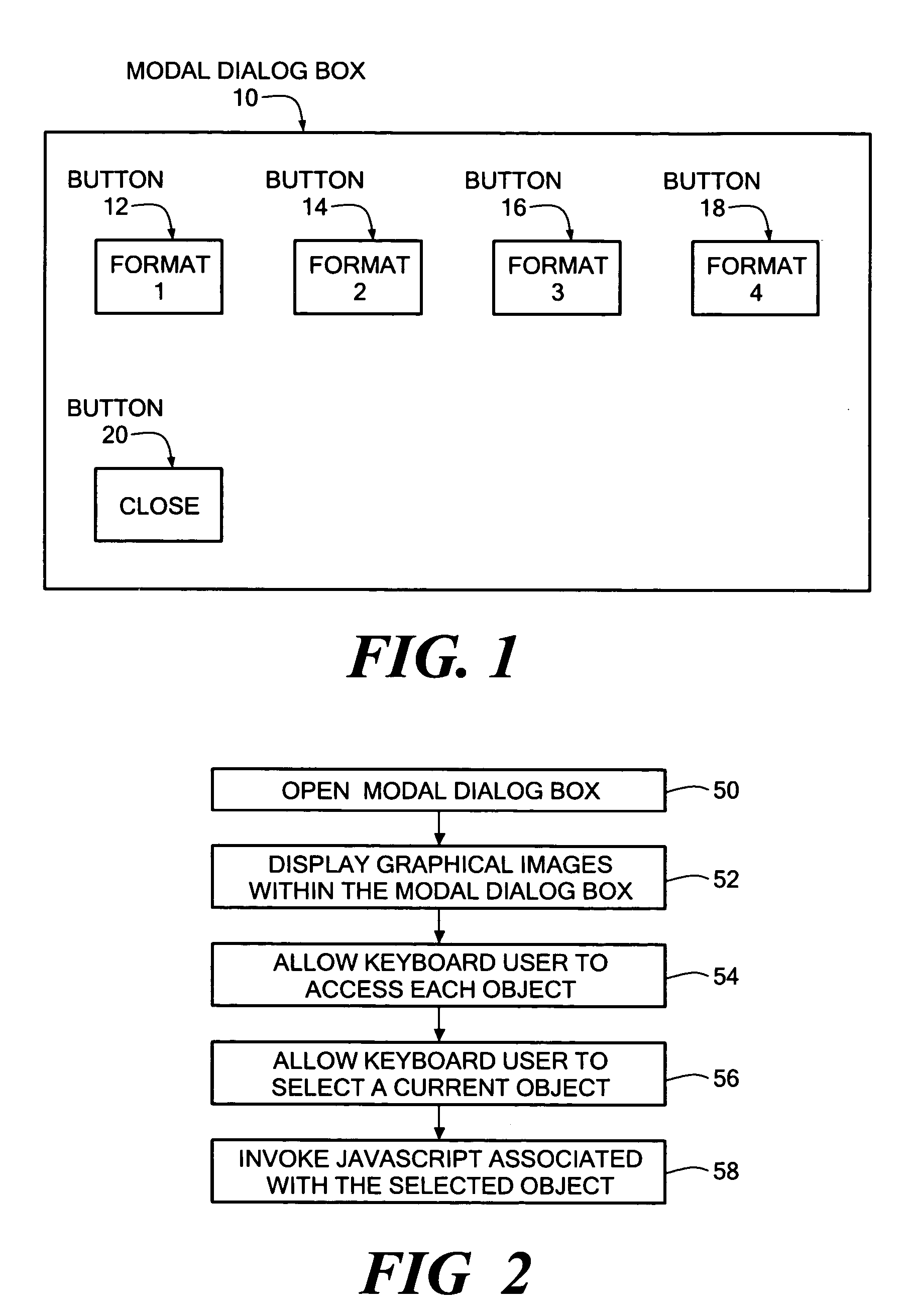
InactiveUS20050120308A1Execution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsPaper document
A method and system for creating a fully accessible display object is disclosed, that may advantageously be used to provide a fully accessible object within a modal dialog box displayed in association with Web page. A fully accessible object is formed using an image command, and associated parameters, within a document containing formatting information for a user interface. The image command associates a graphical image with an software script event handler used to respond to keyboard actions of the user, such as pressing the enter key, as well as mouse actions, and also enables screen reader program access to the object. The display object formed with the disclosed system may be specifically identified and accessed with respect to the other objects of the modal dialog box through use of a the tab key on the keyboard.
Owner:IBM CORP
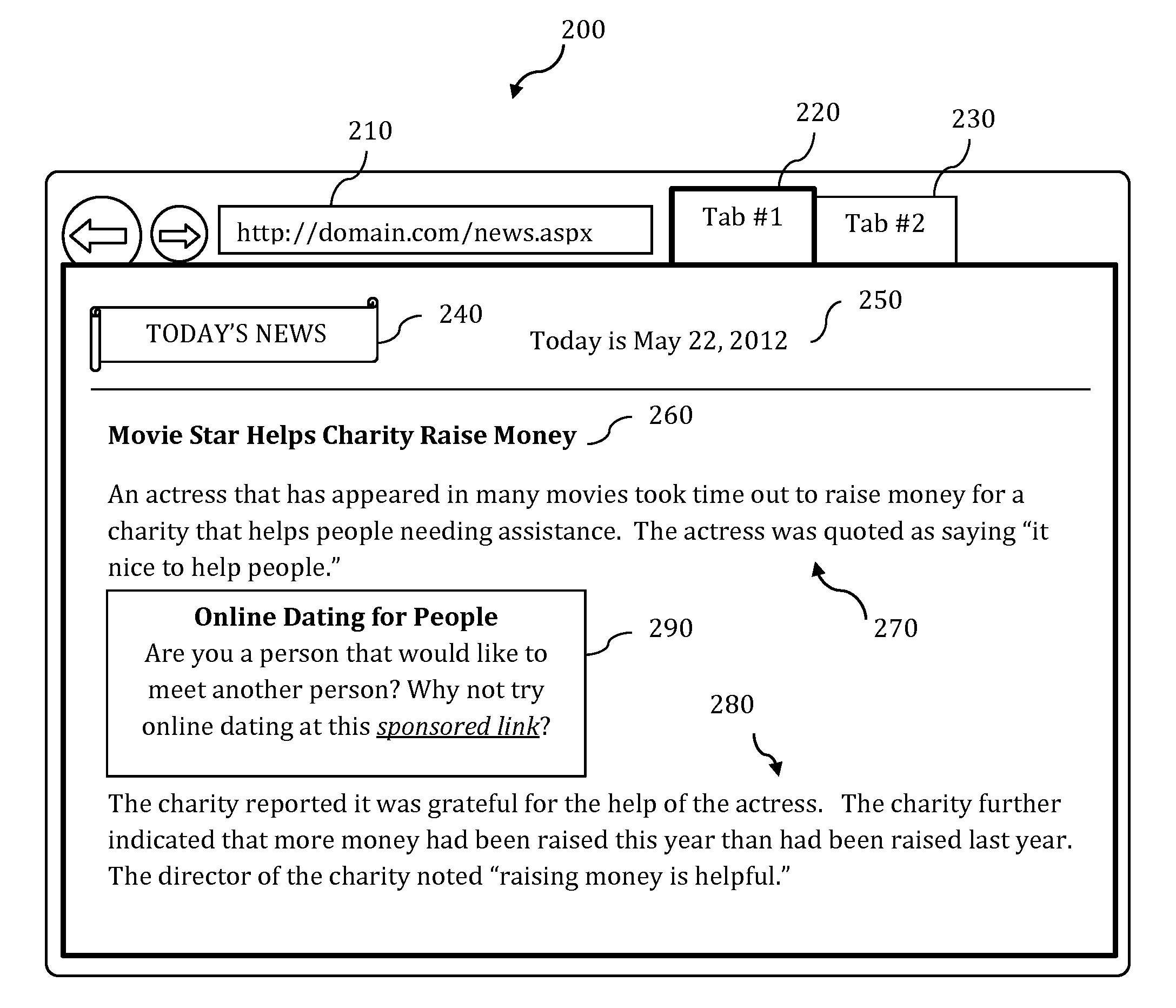
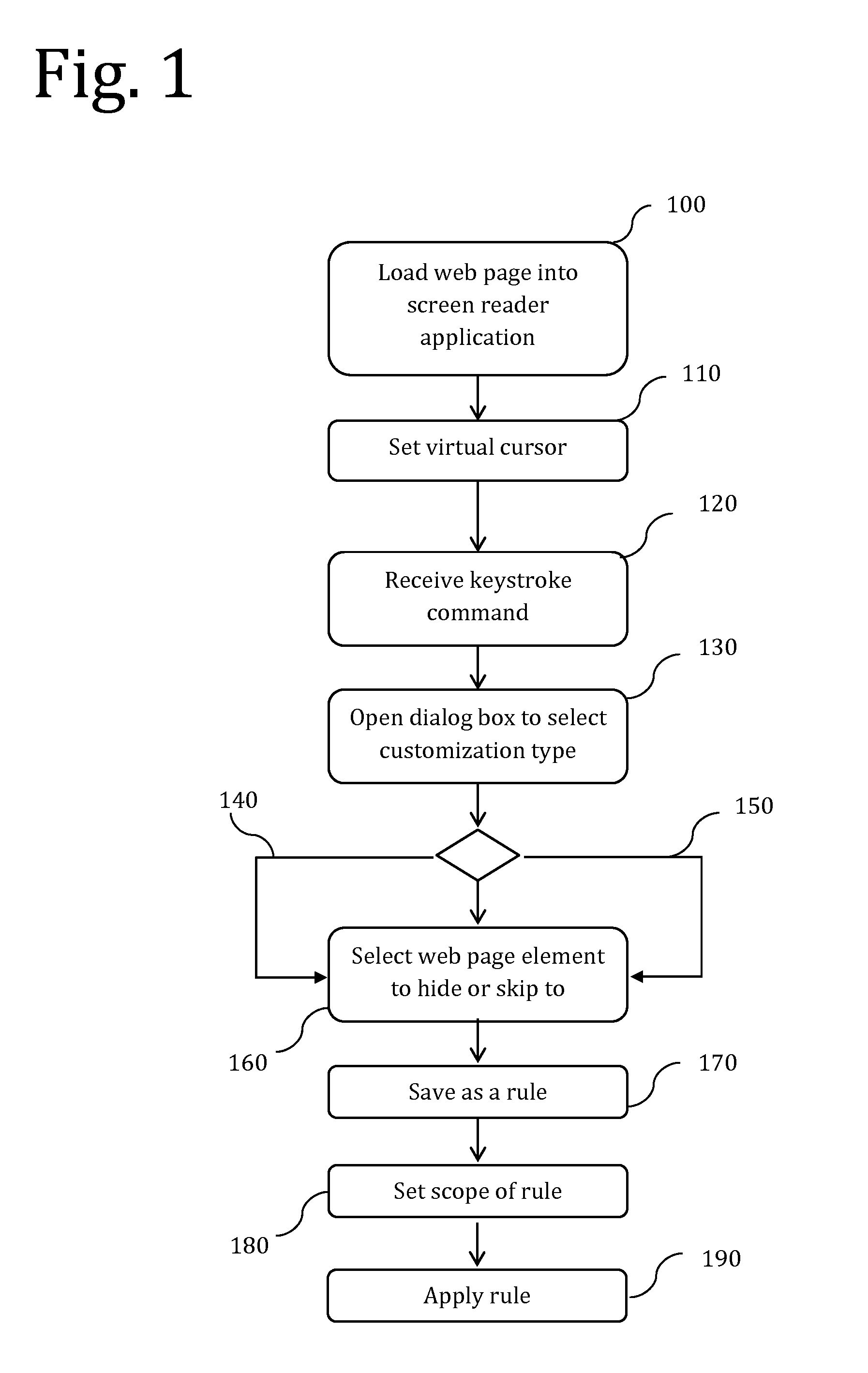
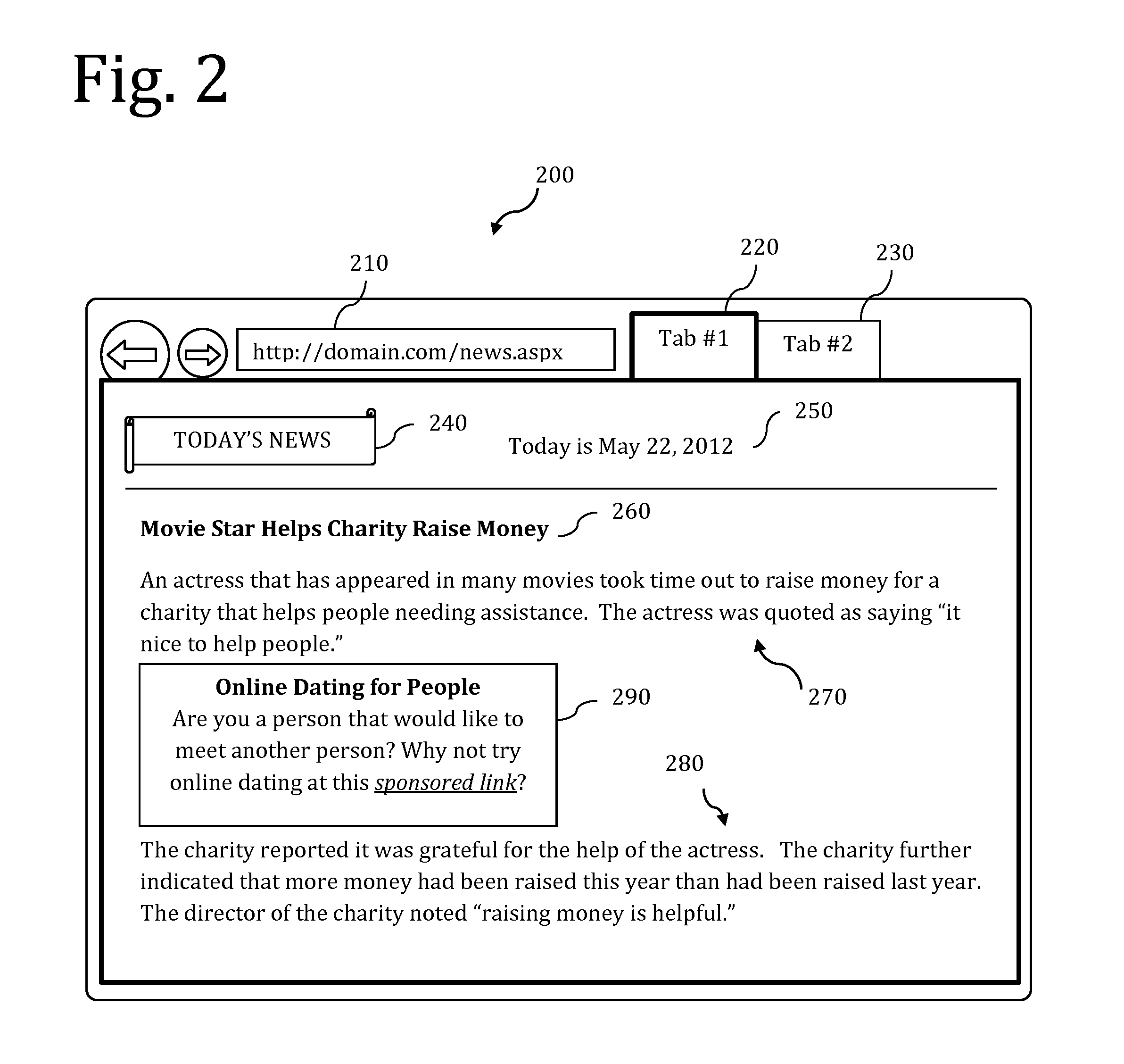
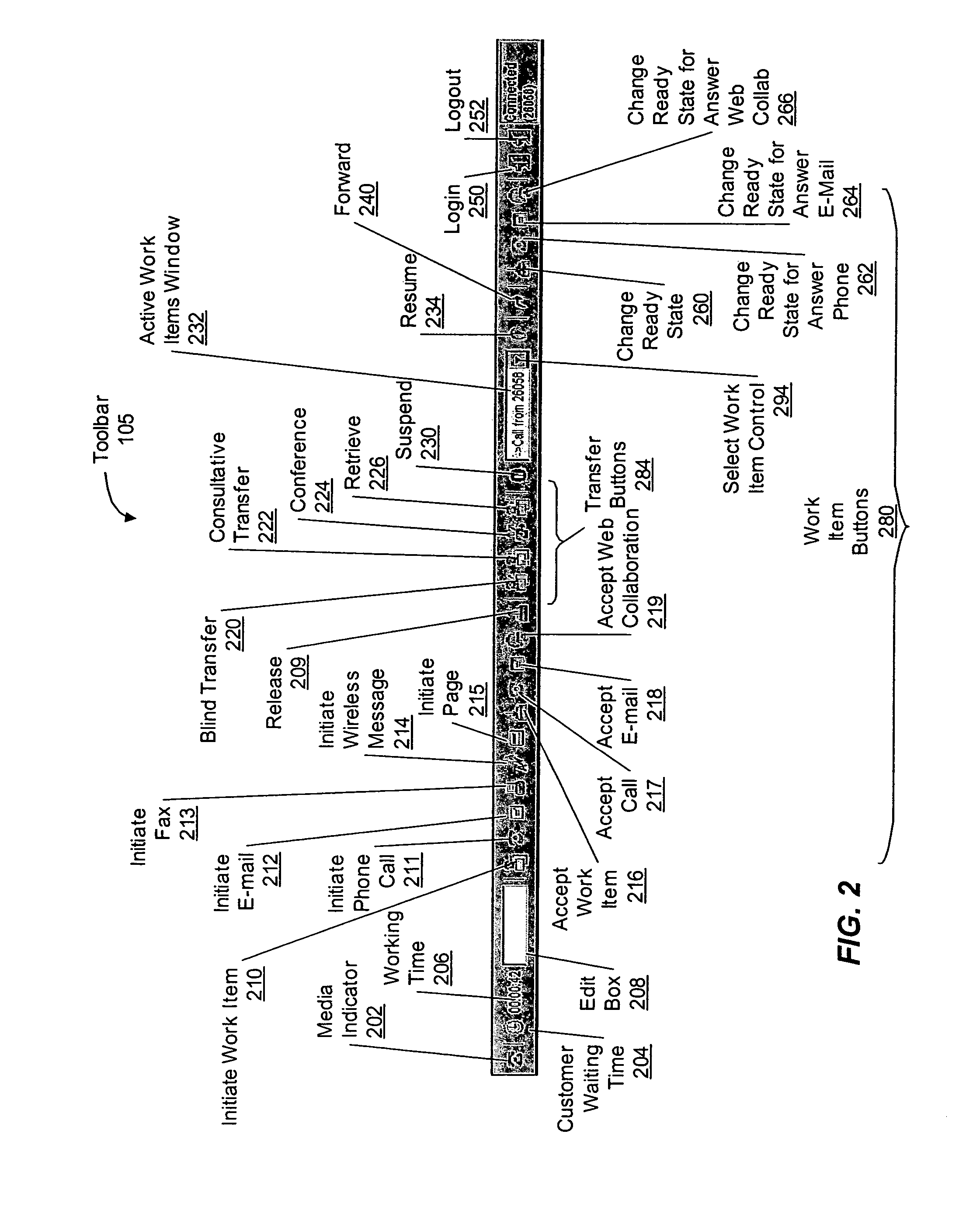
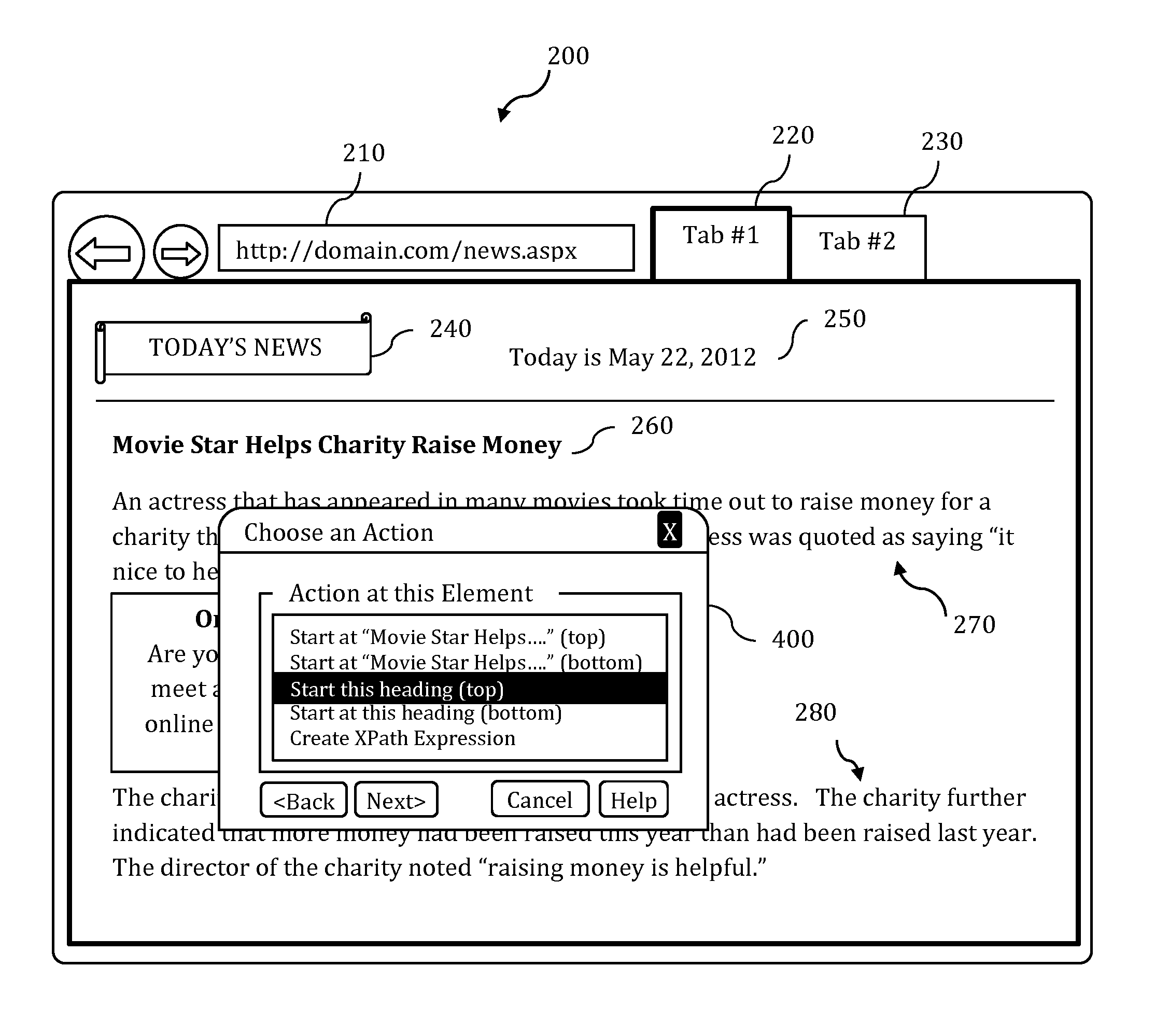
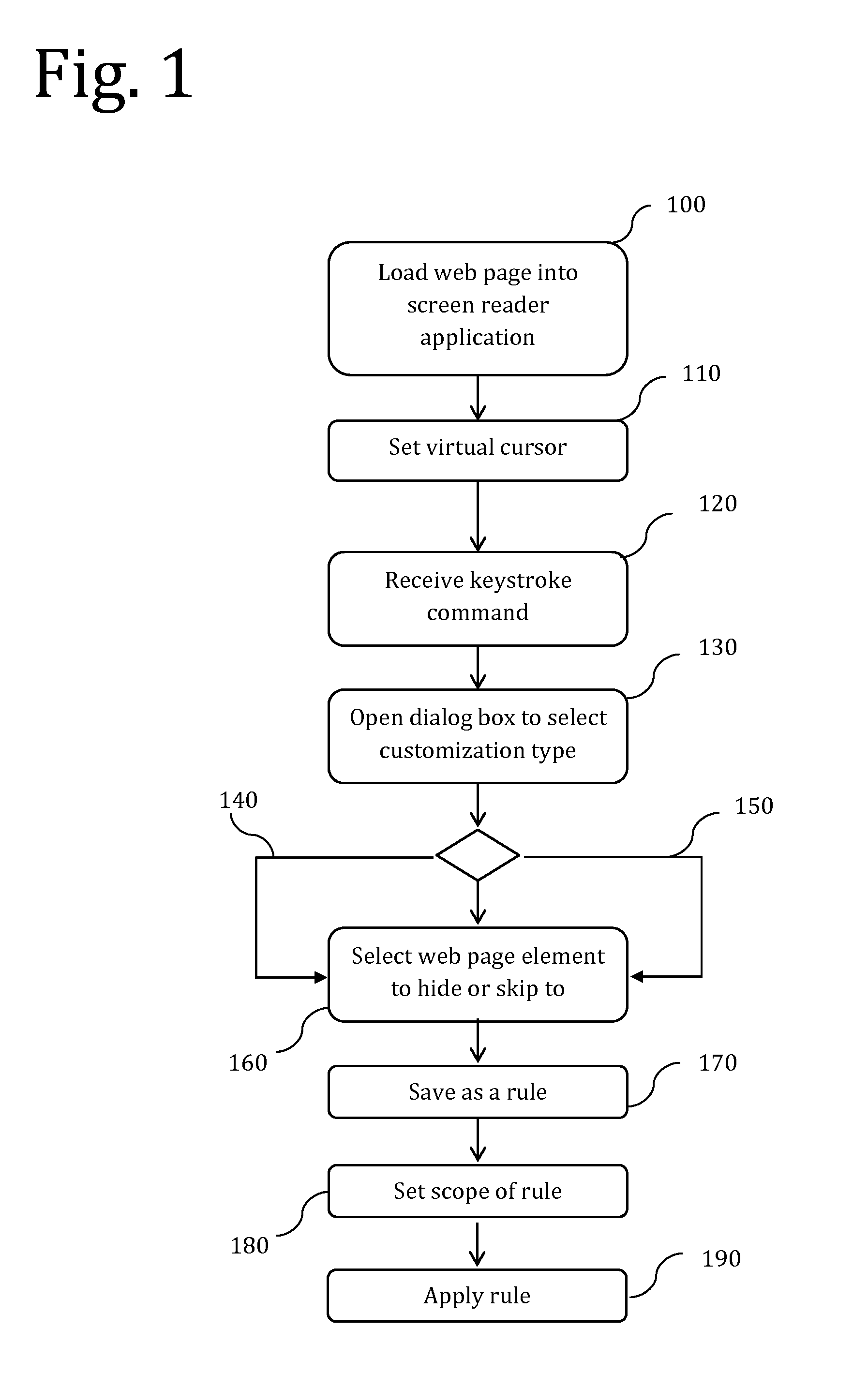
Screen reader with customizable web page output
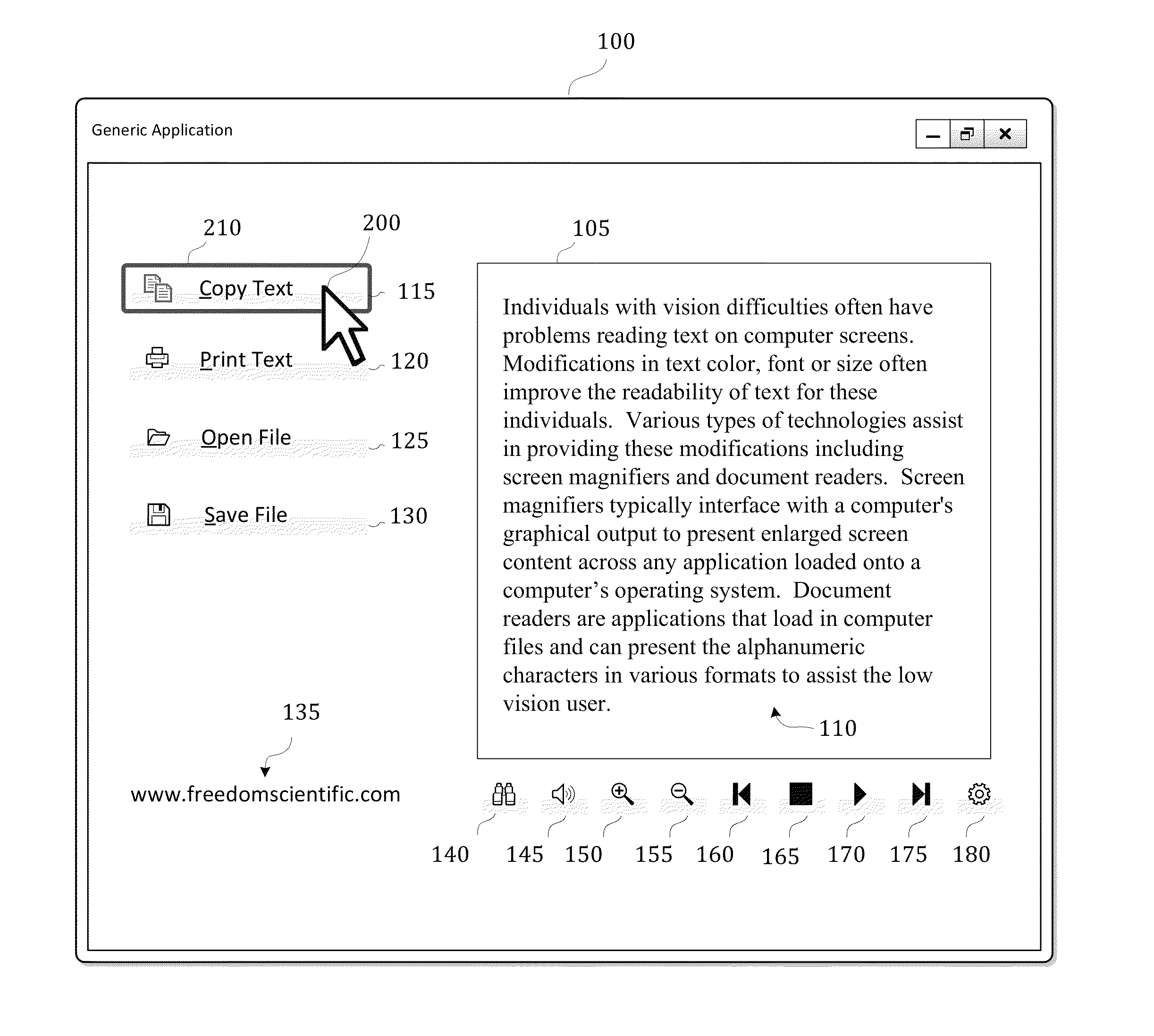
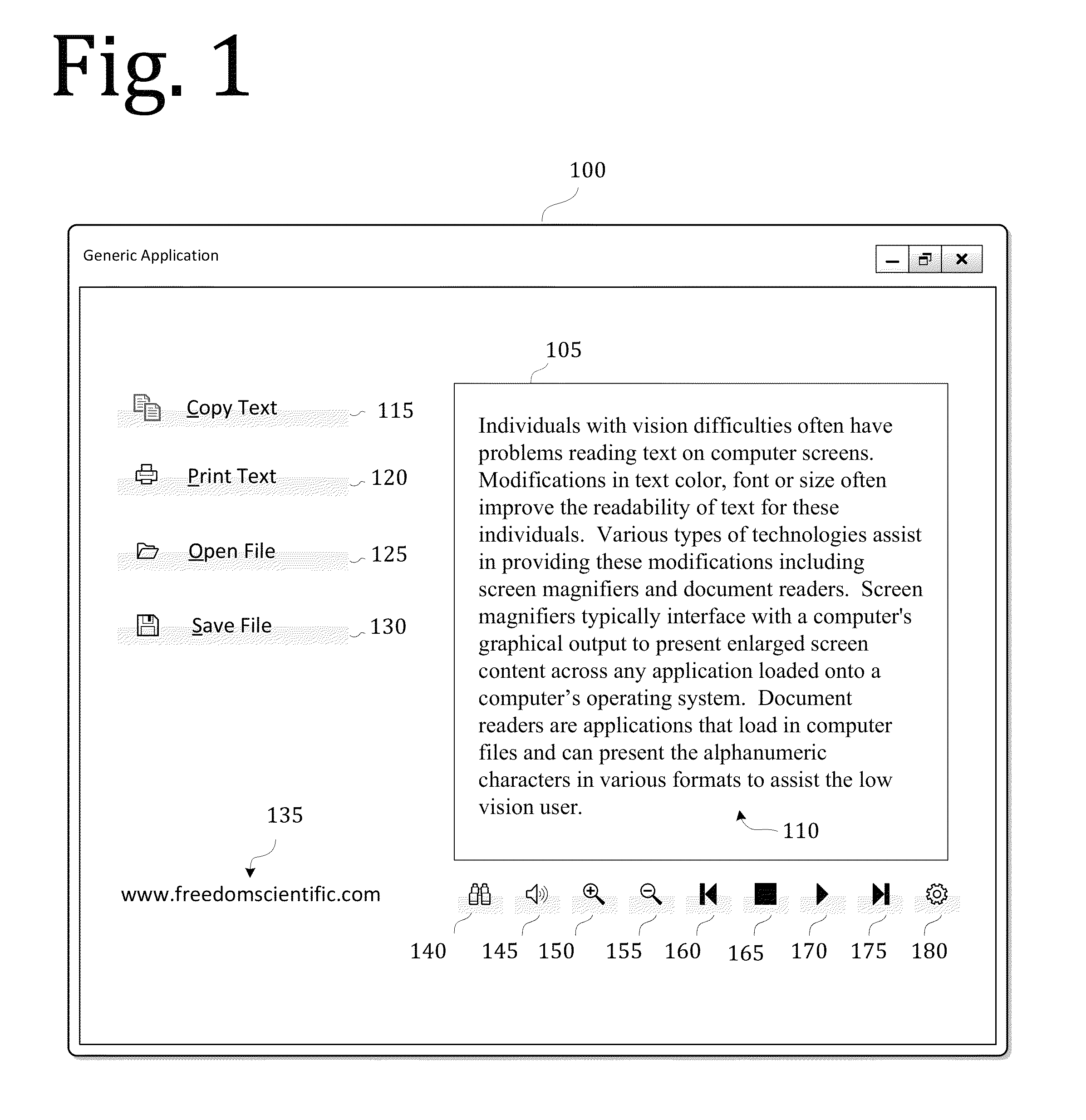
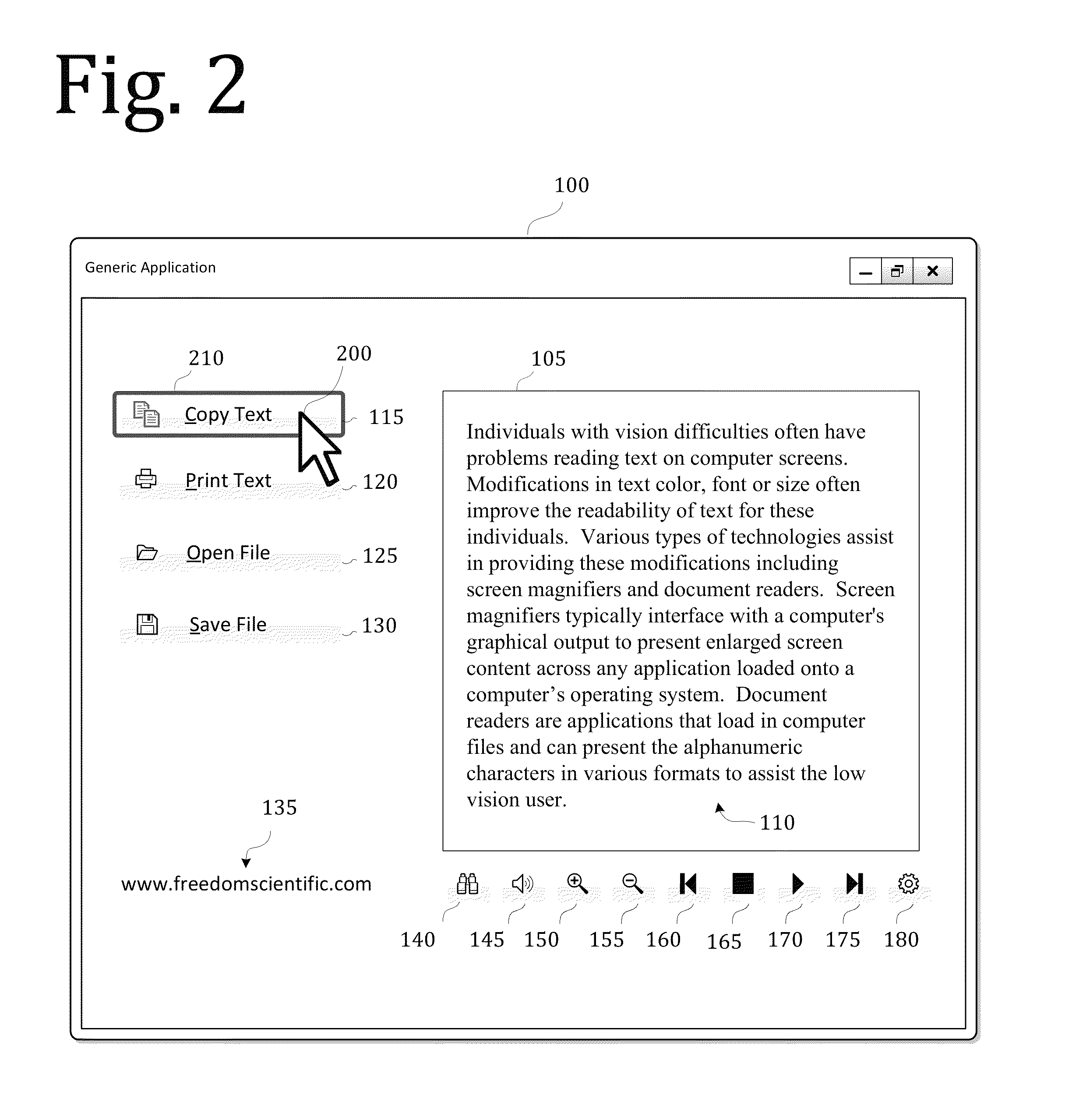
A screen reader application for visually impaired users suppresses unwanted content that is output by Braille or text-to-speech. The invention accesses, but does not modify, the document object model of the web page and enumerates web page elements for the end user to either hide or skip to. The end user selections are saved as rules which may be applied according to various levels of scope include web page specific, site specific or web-wide. A screen magnification application for visually impaired users automatically sets the visual focus and magnification level on a web page element according to end-user selection.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
User interface for multi-media communication for the visually disabled
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
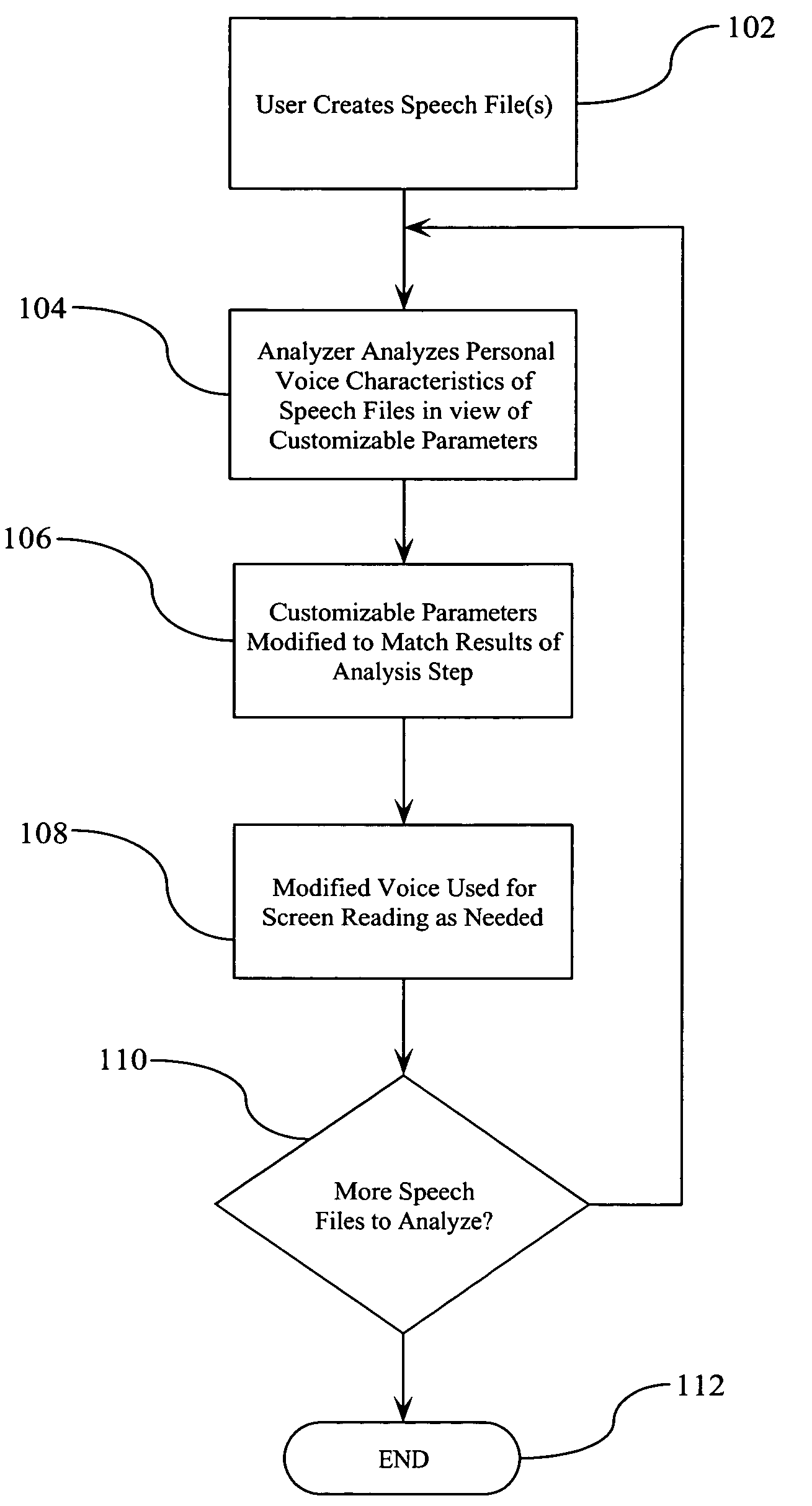
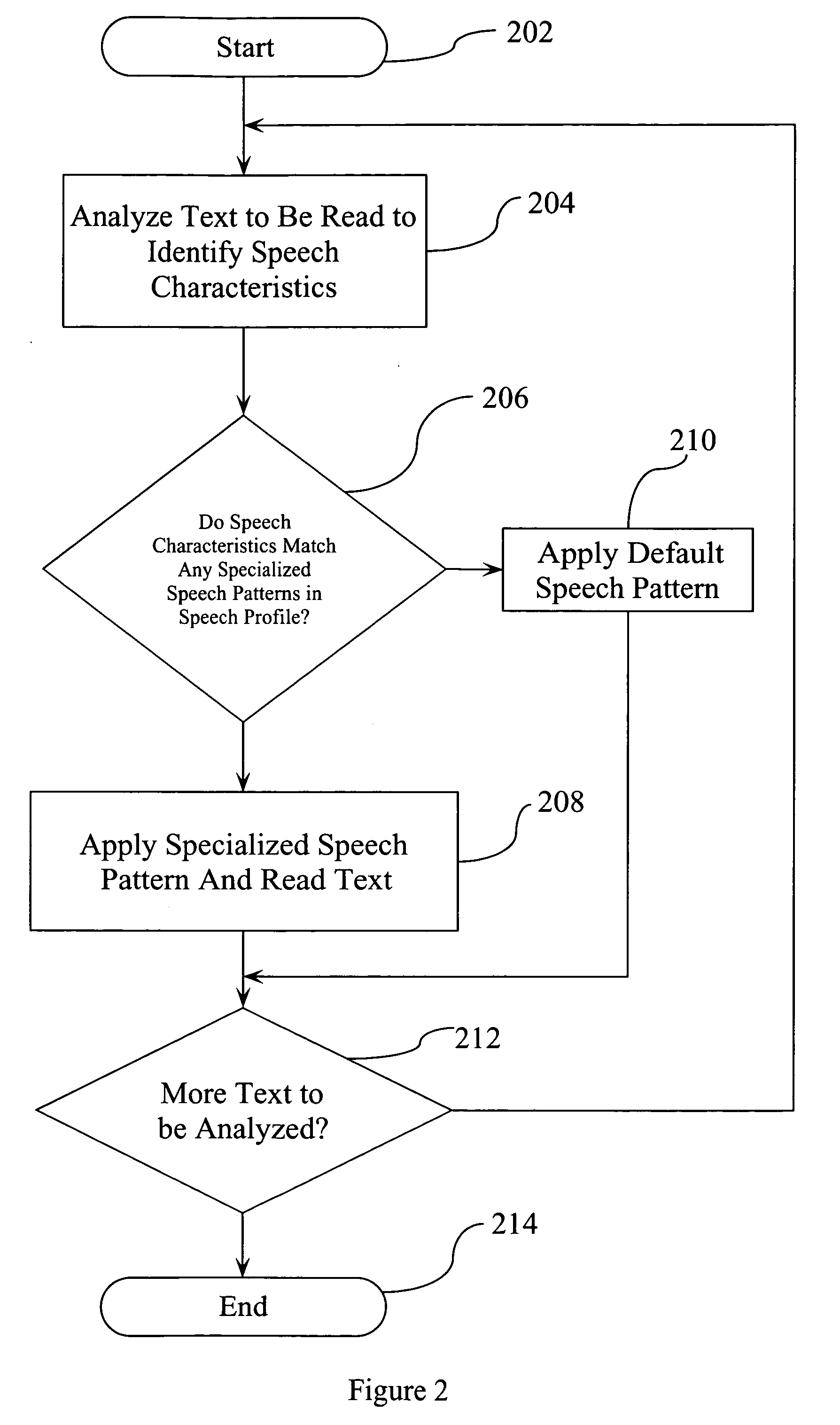
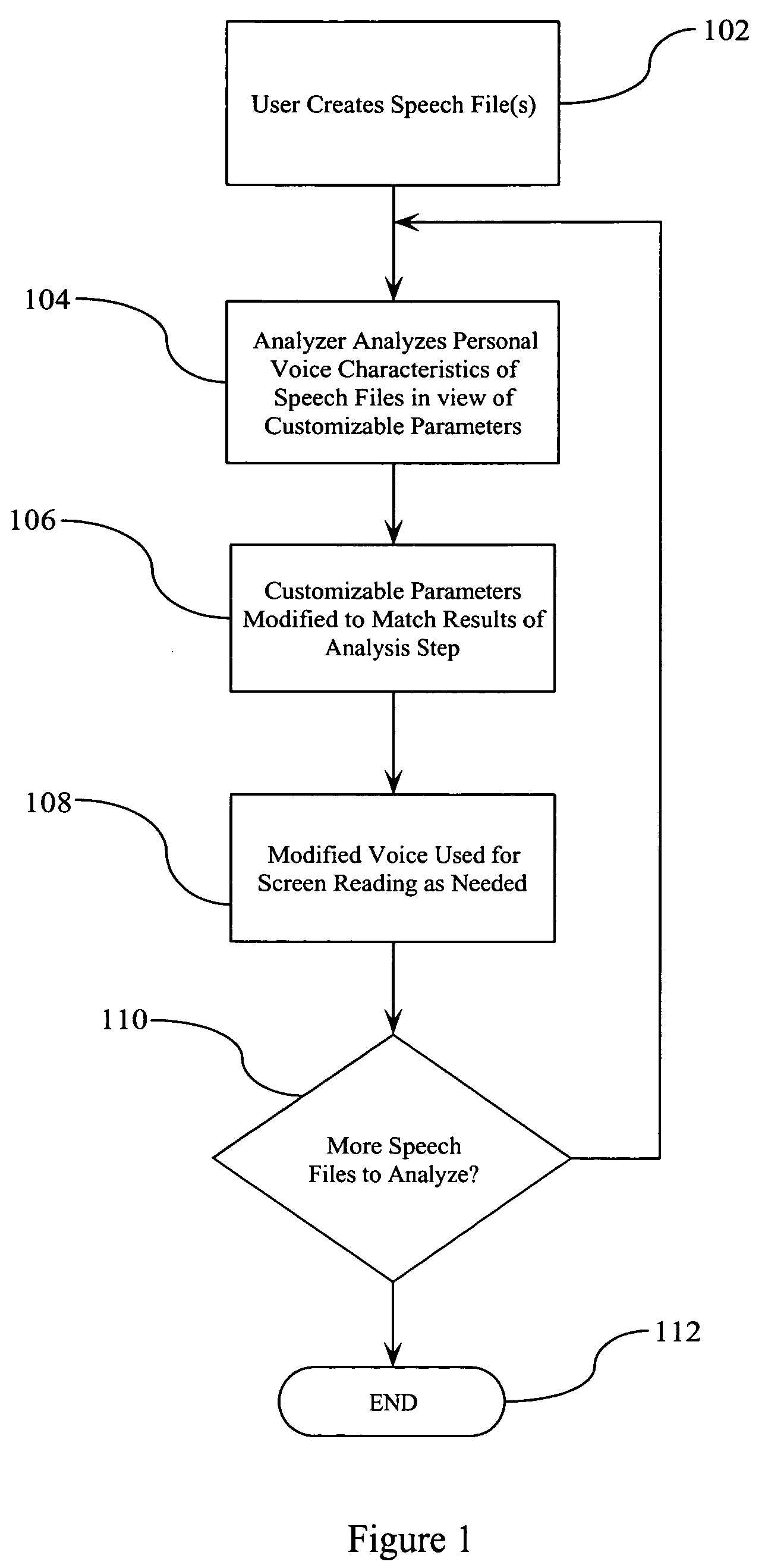
Personalized voice playback for screen reader
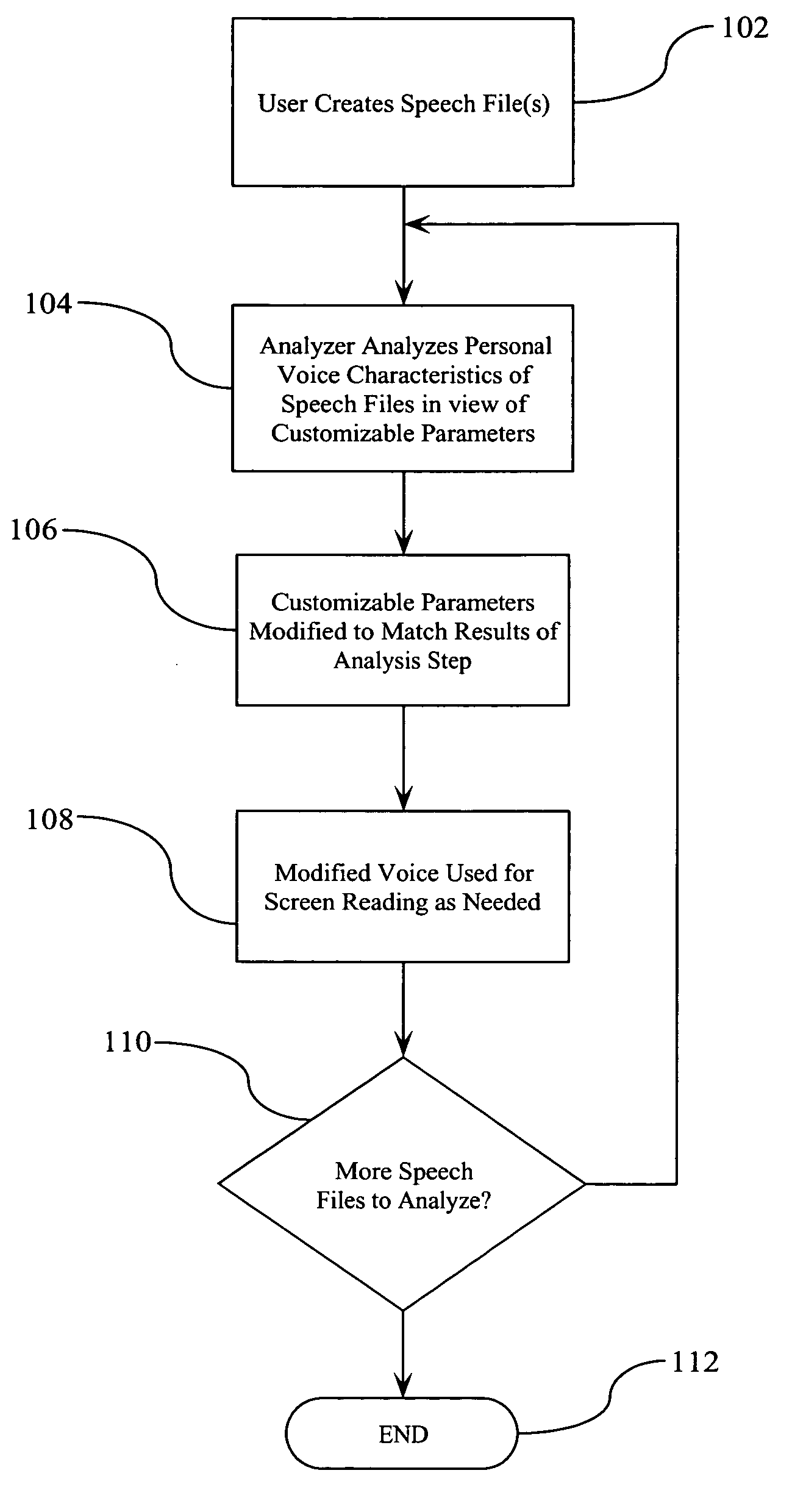
ActiveUS20060031073A1Easily and automatically createSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisPersonalizationScreen reading
A method, system, and computer program product is disclosed for customizing a synthesized voice based upon audible input voice data. The input voice data is typically in the form of one or more predetermined paragraphs being read into a voice recorder. The input voice data is then analyzed for adjustable voice characteristics to determine basic voice qualities (e.g., pitch, breathiness, tone, speed; variability of any of these qualities, etc.) and to identify any “specialized speech patterns”. Based upon this analysis, the characteristics of the voice utilized to read text appearing on the screen are modified to resemble the input voice data. This allows a user of the system to easily and automatically create a voice that is familiar to the user.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Adaptive technique for sightless accessibility of dynamic web content
ActiveUS8103956B2Improve accessibilitySimple methodSpeech analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsApplication softwareHuman–computer interaction
One aspect of the present invention includes adaptive techniques used to render dynamic web content for accessibility software applications, such as screen readers. In one embodiment, an operation for improving webpage browsing with accessibility software includes detecting if an accessibility software application is in use, tracking the position of user focus on the webpage, and presenting information to the user based on the position of user focus on the webpage. In a further embodiment, additional content is rendered on the webpage to screen reader applications, and is placed at the position of the screen reader focus in response to dynamic content appearing or changing on the webpage. This additional content is read by the screen reader to inform the user of the dynamic content change, and / or enable the user to quickly perform a specific action on the webpage.
Owner:ACCESSIBE LTD
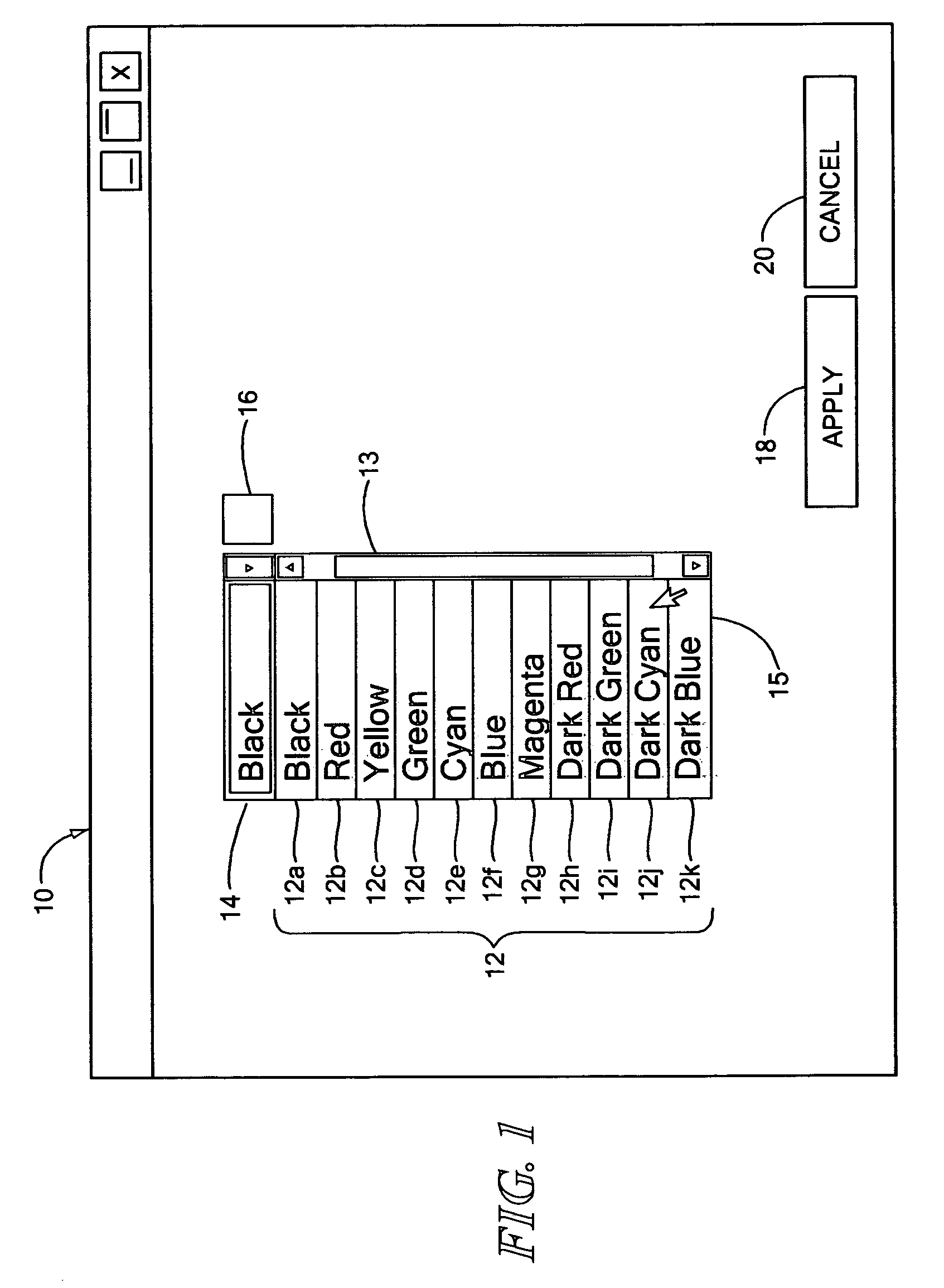
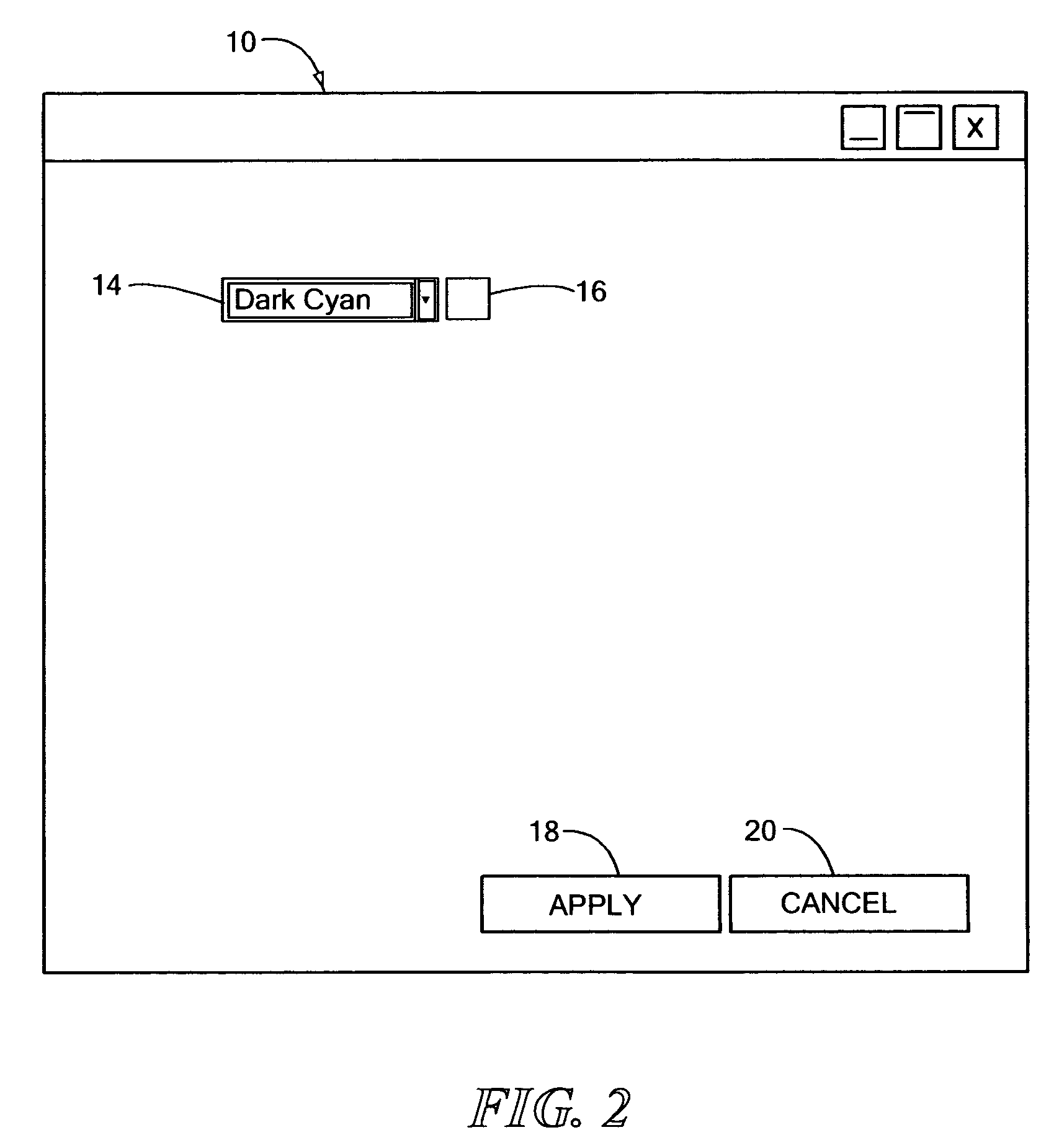
Method and system for providing a fully accessible color selection component in a graphical user interface
InactiveUS20070028178A1Reduce ambiguityExecution for user interfacesMemory systemsGraphicsGraphical user interface
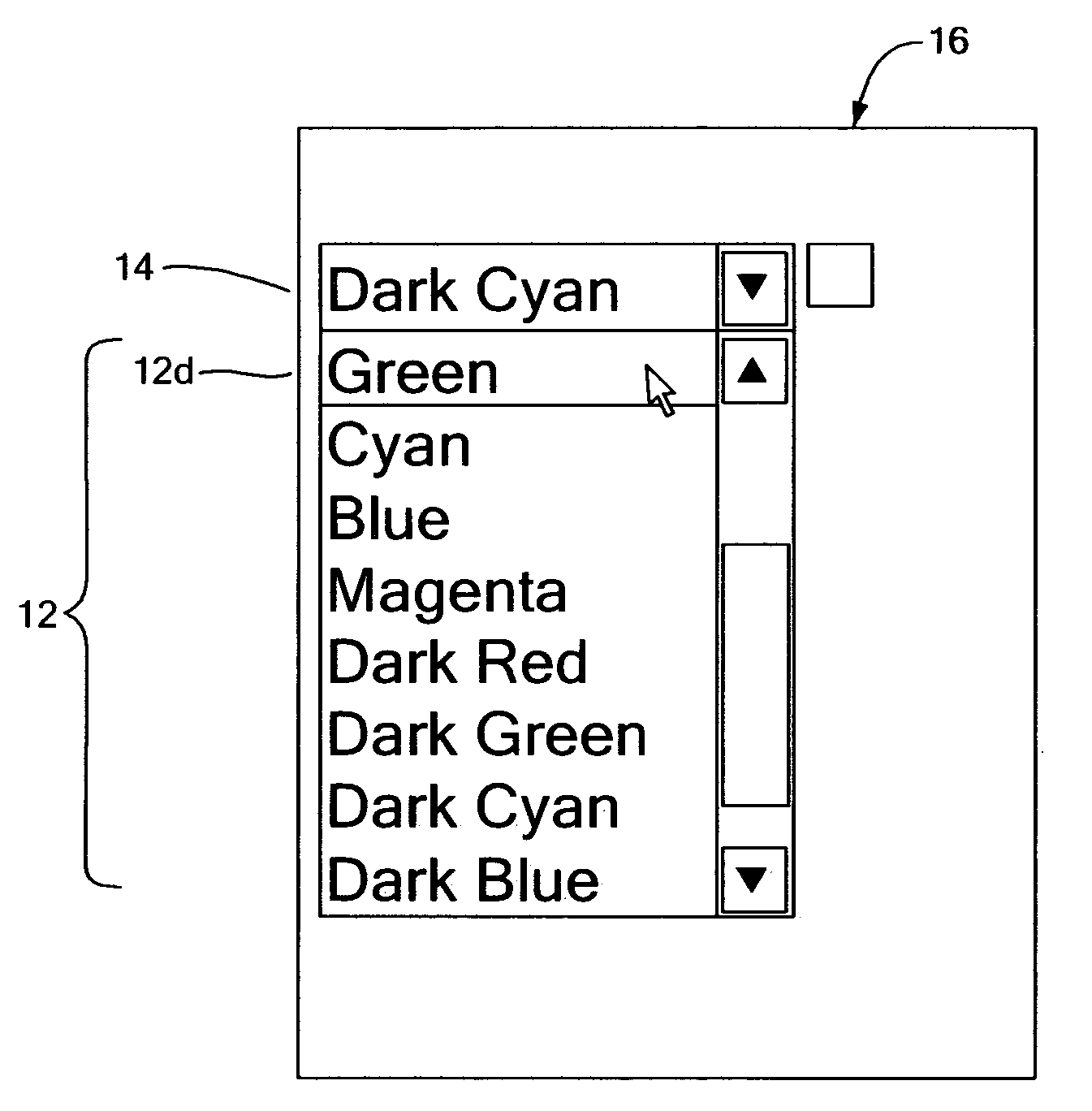
A system for providing a fully accessible color selection component in a graphical user interface, in which multiple selectable colors are represented using a set of selectable color name display regions, each of which includes a text name for a color and has a background color made up of the selectable color. Additionally, and external to the color name display regions, the disclosed system provides a sample color display region made up of a currently selected color. The background colors in the color name display regions reduce ambiguity in normal display settings by showing the user samples of colors that can be selected. The sample color display region supports high contrast settings that are likely to be used by low vision users. When a user has a high contrast setting selected, the background colors in the color name display regions may not be displayed, and accordingly the color name display regions may only display textual names. However, by providing an image of a currently selected color in the sample color display region, the actual color that is currently selected is still displayed, since images are typically not modified by high contrast settings, which may be useful when selecting a color for an off-screen application. The disclosed system can be implemented using an HTML <select> component. A screen reader program can also be used to speak the color names for each color name display region, and the user does not hear any redundant information about the currently selected color.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for rendering documents
Generally, the systems and methods described herein are directed to rendering a document containing textual elements and graphical elements. The systems and methods include separating the graphical elements from the textual elements, and generating a bitmap rendering of the graphical elements and an HTML rendering of the textual elements. The HTML rendering may then be overlaid on the bitmap rendering to generate a composite document having textual elements that are accessible to screen reader software.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Audio clutter reduction and content identification for web-based screen-readers
InactiveUS7058887B2Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsScreen readingWeb page
A method and apparatus for reading a web page according to a set of user-configurable settings. In one embodiment, a set of user-configurable settings configured for reading the web page is determined. An initial reading position on the web page is determined as specified by the user-configurable settings. The web page is then read from the initial reading position according to the set of user-configurable settings.
Owner:IBM CORP
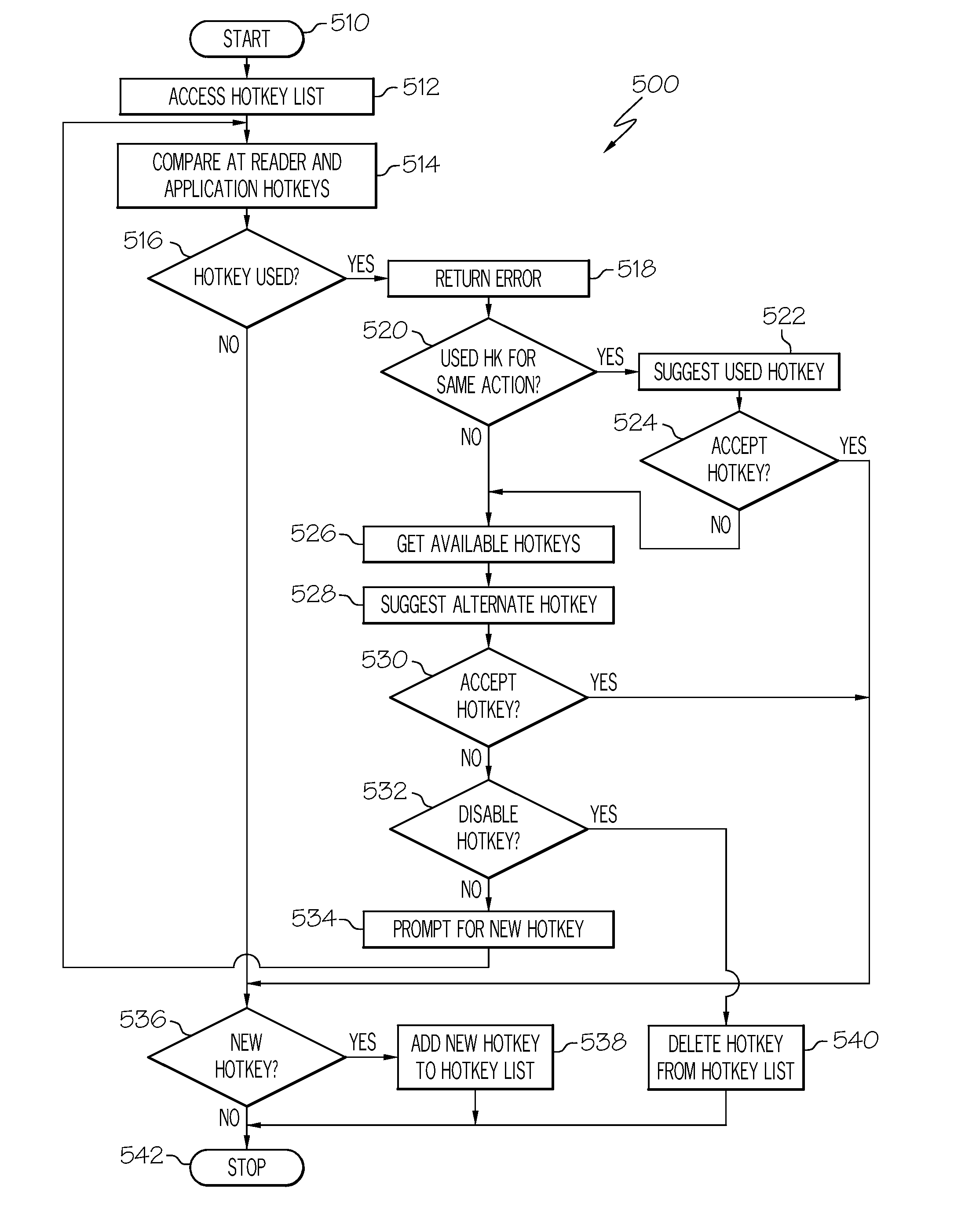
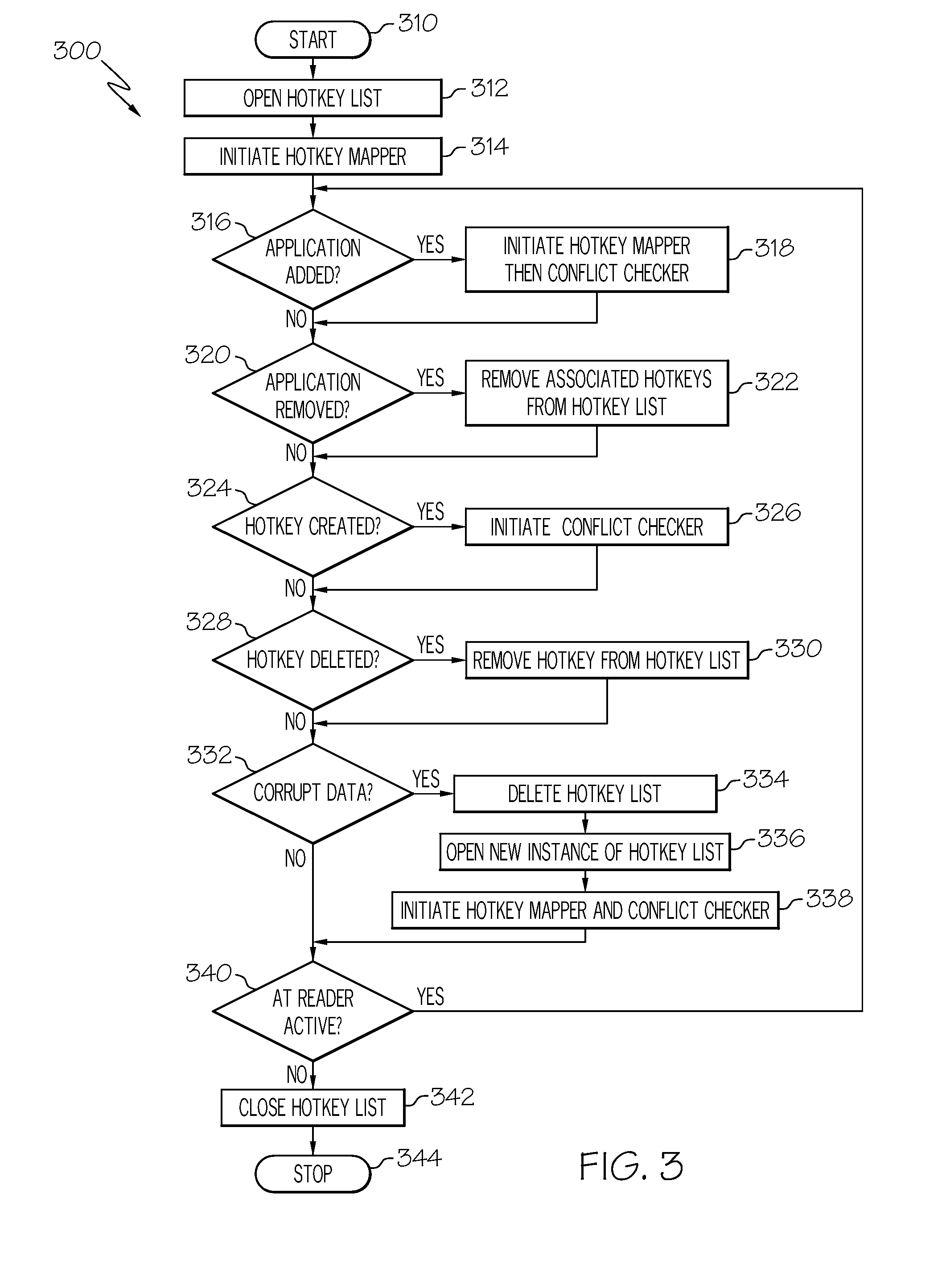
Method and apparatus for identifying hotkey conflicts
The hotkey conflict avoidance program identifies a set of hotkeys in a first application and a second set of hotkeys in a simultaneously running second application, compares a first hotkey in the first set of hotkeys to a second hotkey in the second set of hotkeys and returns an error if the first hotkey conflicts with the second hotkey. Each hotkey in the first set of hotkeys is compared to each of the hotkeys in the second set of hotkeys. Other features of the hotkey conflict avoidance program include suggesting alternative hotkeys when a conflict is found and saving identified hotkeys and the corresponding actions to a persistent list. In a preferred embodiment, the first application is a screen reader for use by the visually impaired, and the simultaneously running second application is an application with which the screen reader interacts.
Owner:IBM CORP
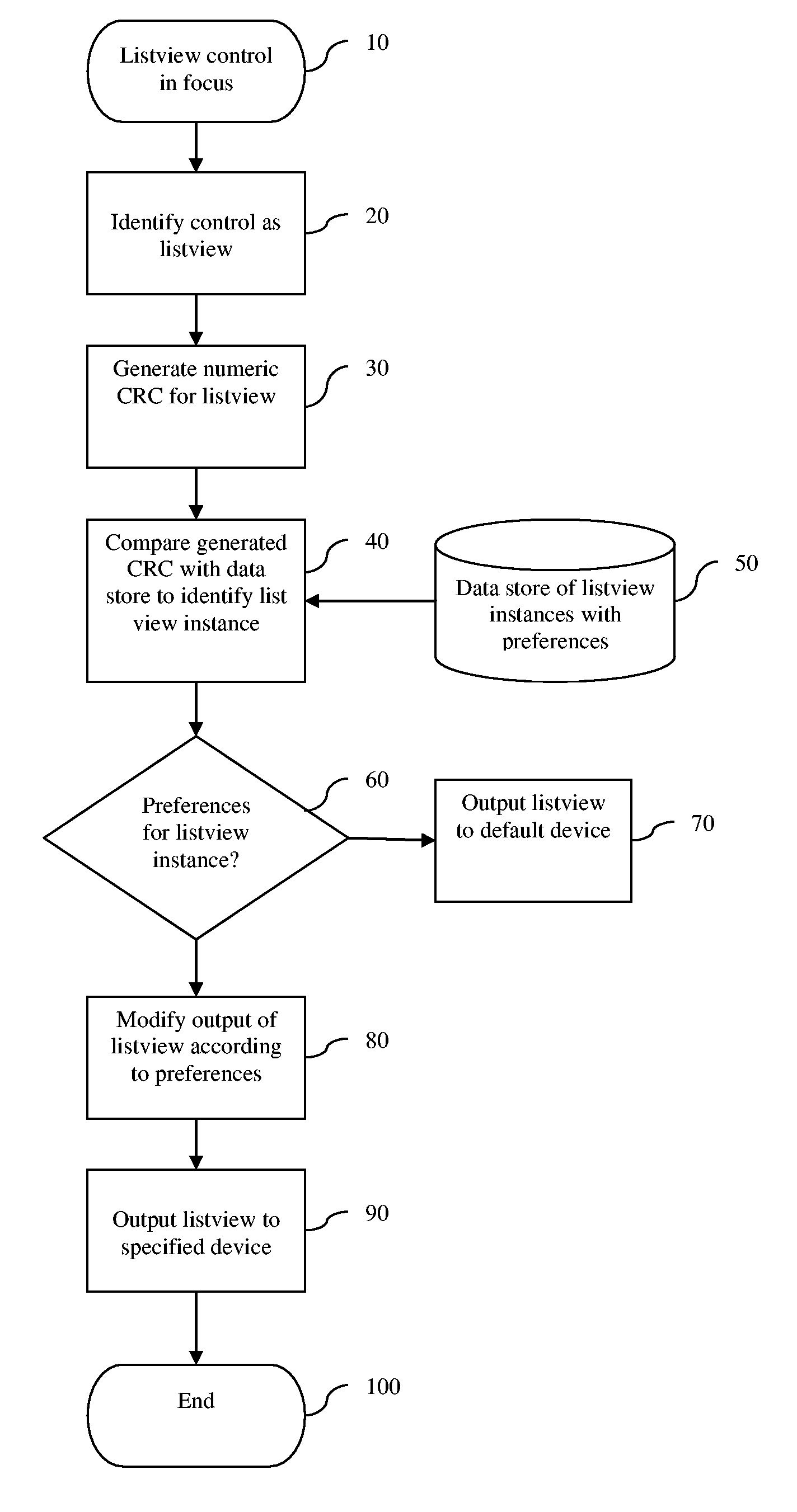
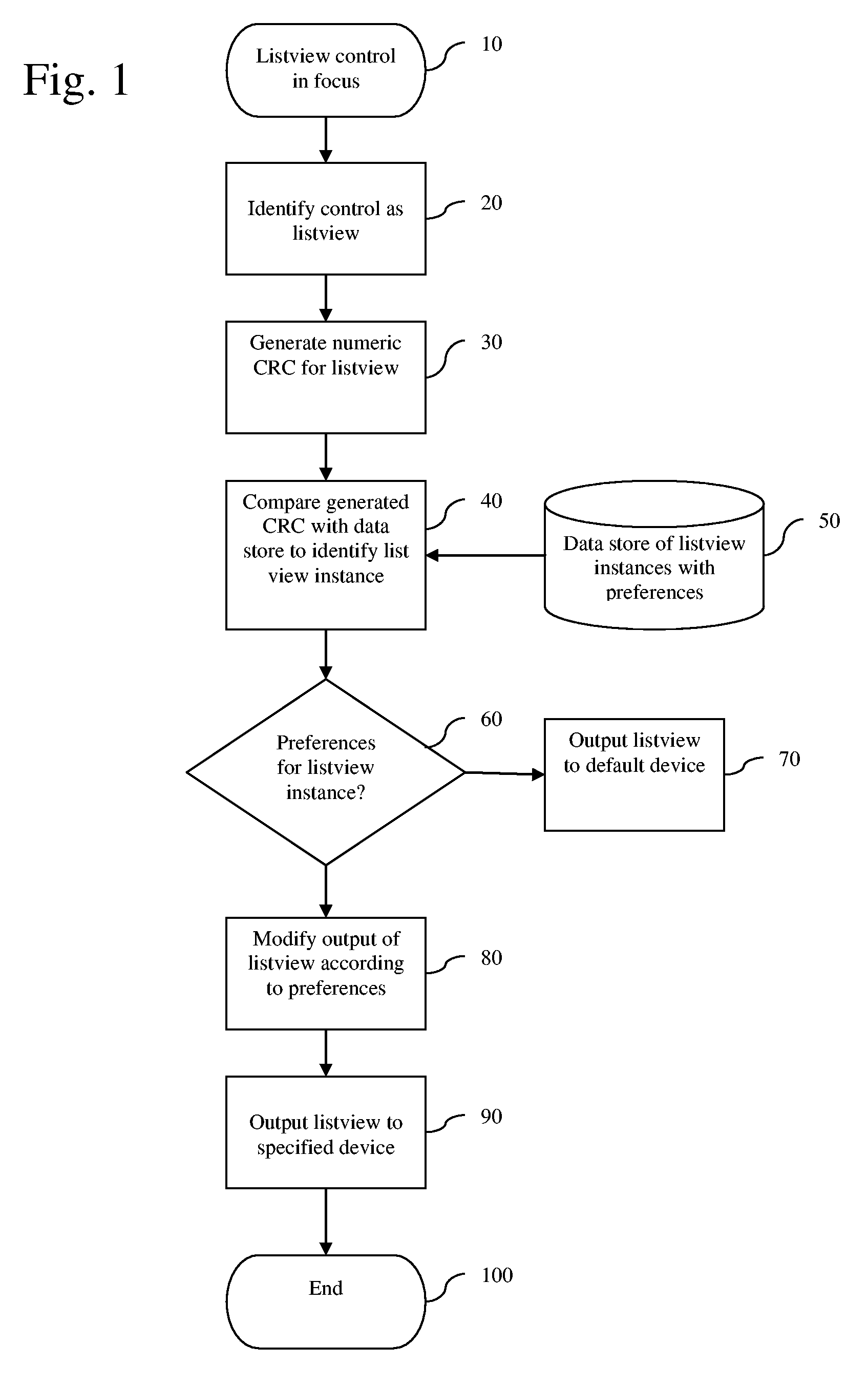
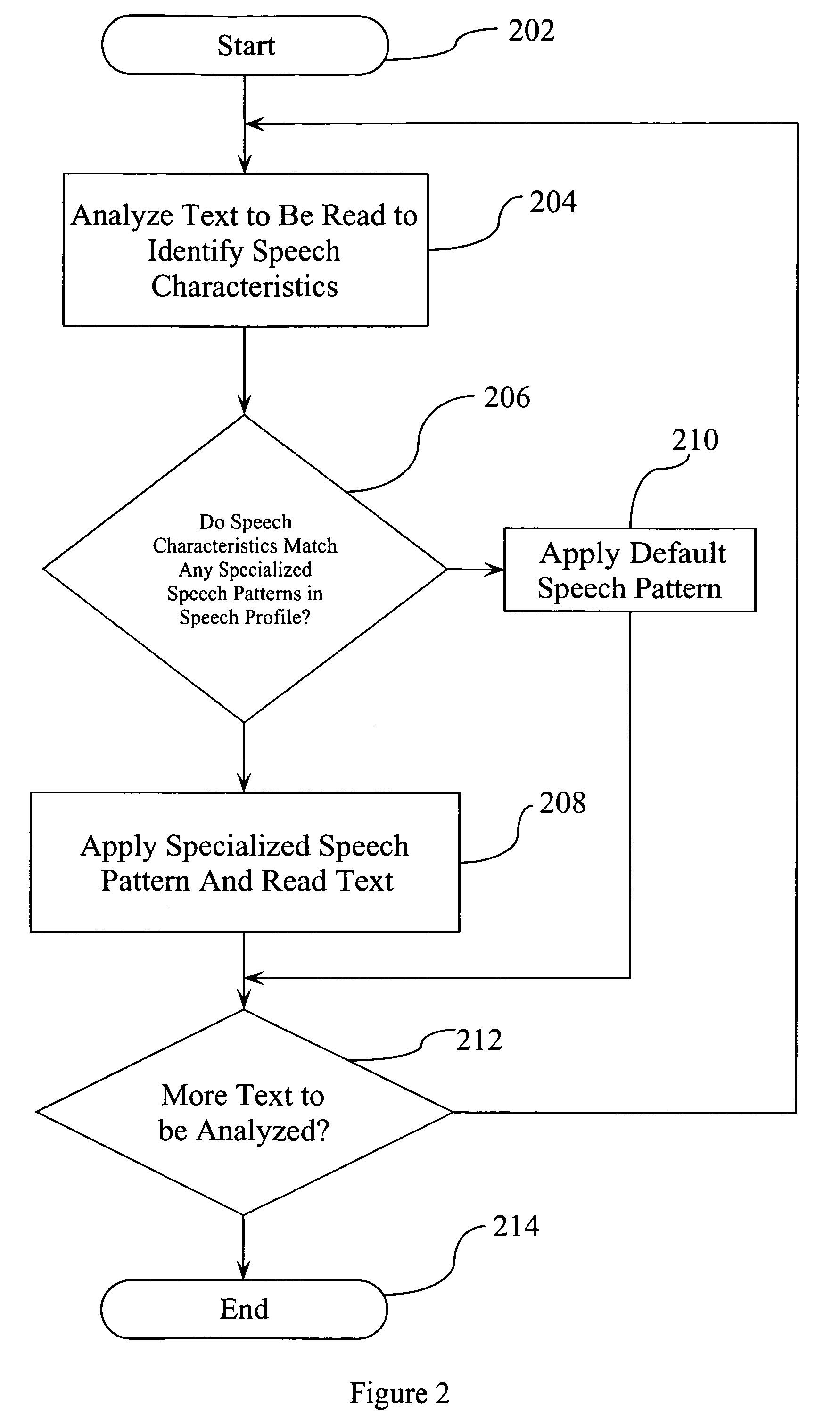
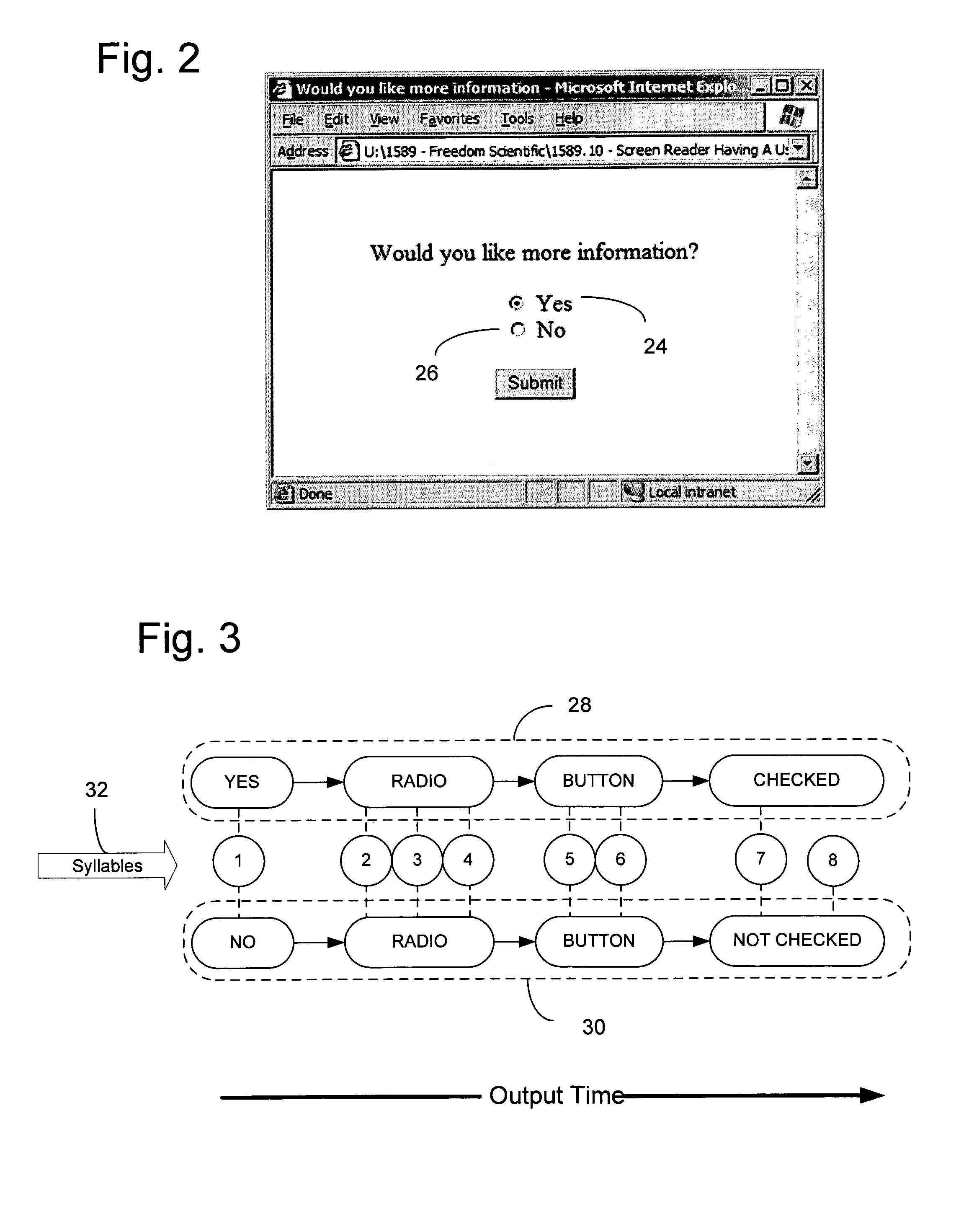
Screen Reader List View Presentation Method
A speech-generating product for controlling the output of tabular or other composite data in a computer having a screen reader function. The product provides a customized control presentation tool that configures a screen reader to present tabular or other composite data to a user in the order most useful to the user. The tool includes the ability to configure the screen reader independently for both speech and Braille output on a control by control basis. This customized control presentation is saved in permanent storage. Consequently, each time the screen reader is presented with this instance of the control, the screen reader immediately knows how to present it to the user. The software product allows a user to modify the output by the screen reader of the data according to preferences configurable by the user. These preferences may include the ability to skip display information, to specify the order in which the screen reader presents the display information and the ability to alter the headers associated with the display information. By altering the headers the user may annotate the headers to provide additional information about the underlying data. The headers may also be output in an alternative voice by a speech synthesizer to queue a user to a change of information. The user may also specify that certain display information is sent by the screen reader to one display device while other display information is sent to an alternative display device.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
Systems and methods for dynamic menus
InactiveUS8645848B2Avoid obstaclesExecution for user interfacesSpecial data processing applicationsScreen readingDatabase
Systems and method for dynamically loaded menus and objects are provided that can provide cross-platform capability and accessibility features. Objects in a page that are dynamic or are not human-readable (e.g., executable or images) can be identified and enhanced for compatibility with screen readers. HTML corresponding to the object can be generated and loaded in storage for use within the web page. The loaded HTML can be copied into the HTML of the web page. A blank placeholder may be displayed in the area in which the corresponding HTML is to be displayed and the corresponding HTML is displayed over the placeholder to provide a replacement object such as to display a list of URL menu items.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
Method and system to create and access an object on a computing system
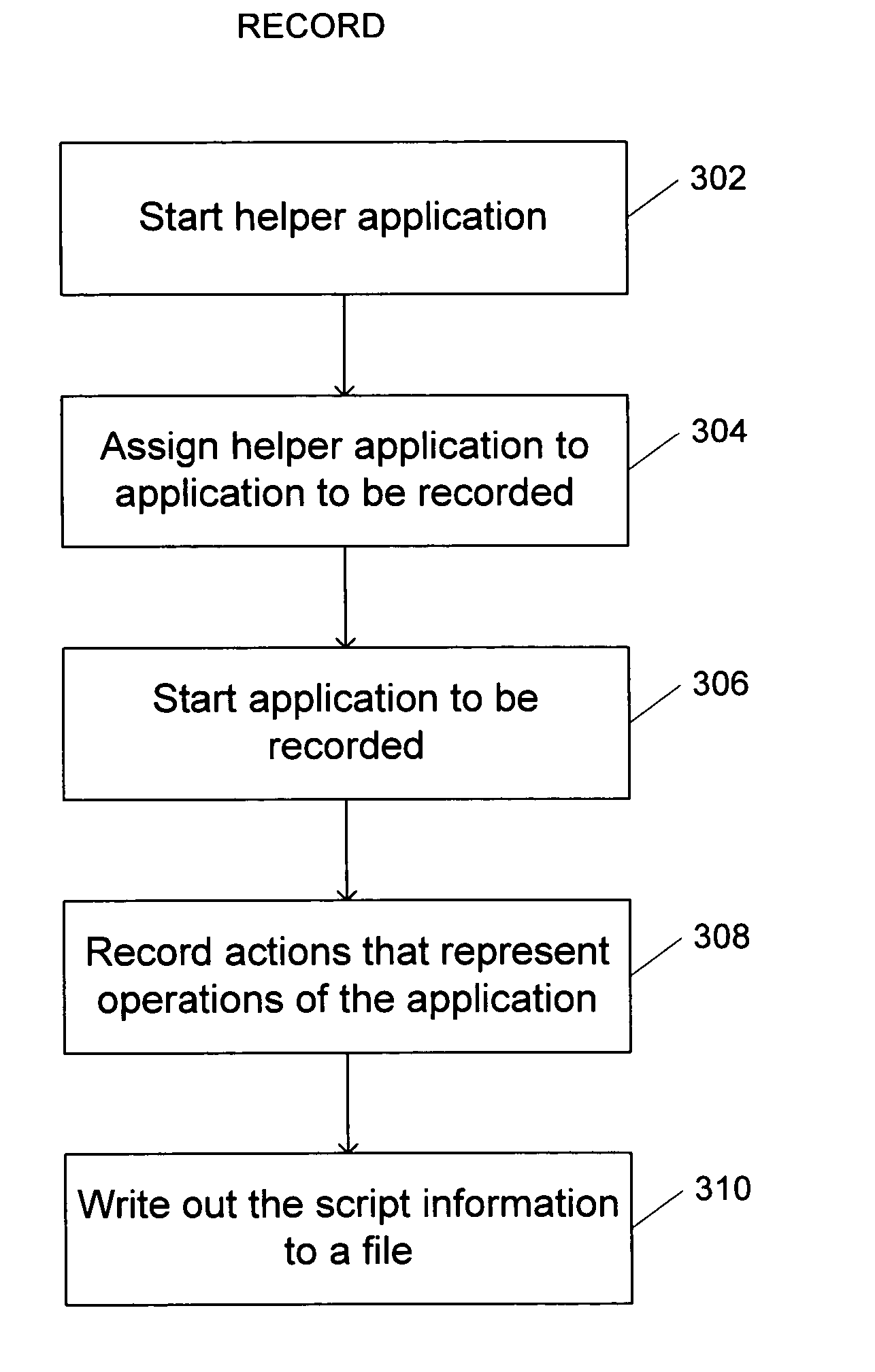
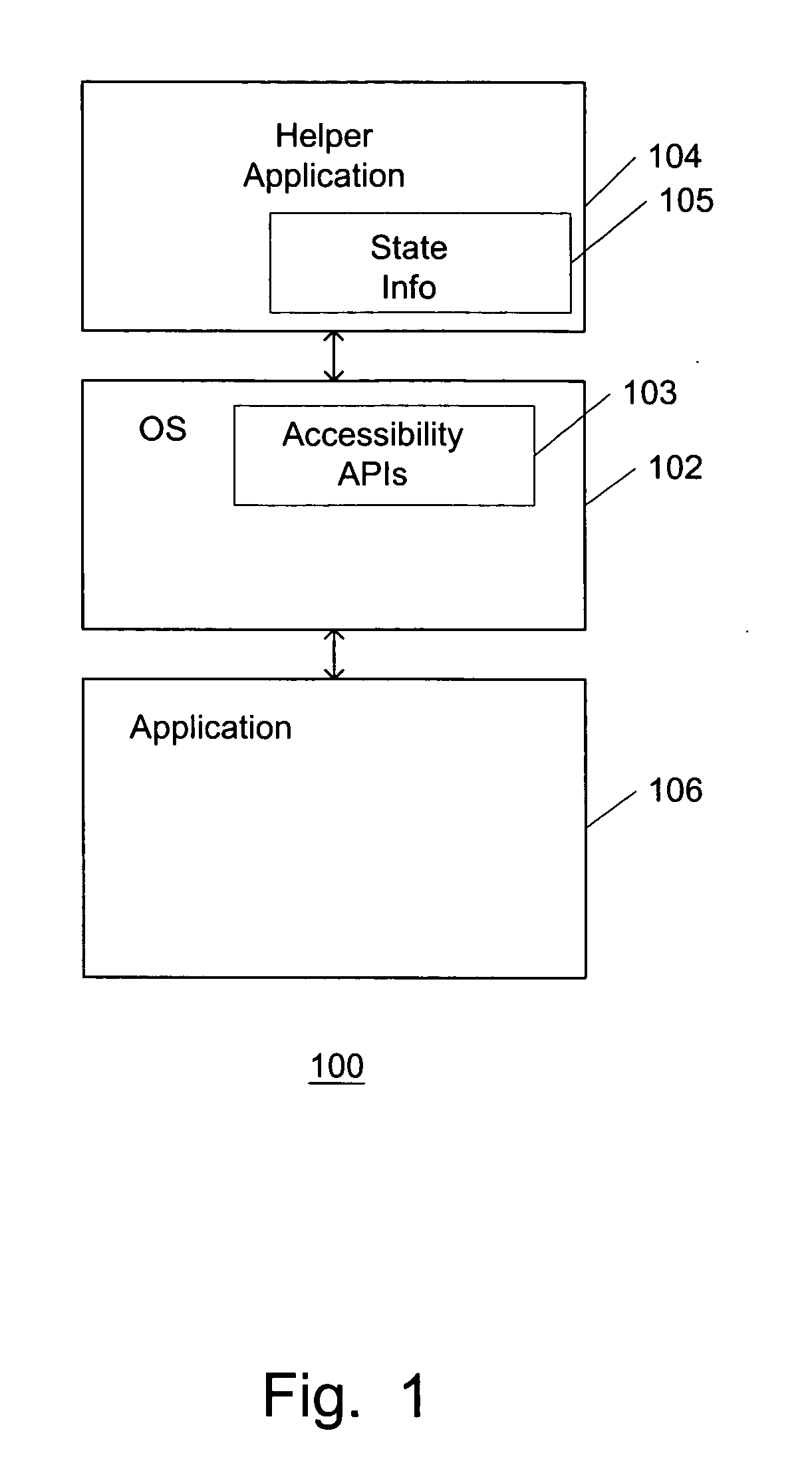
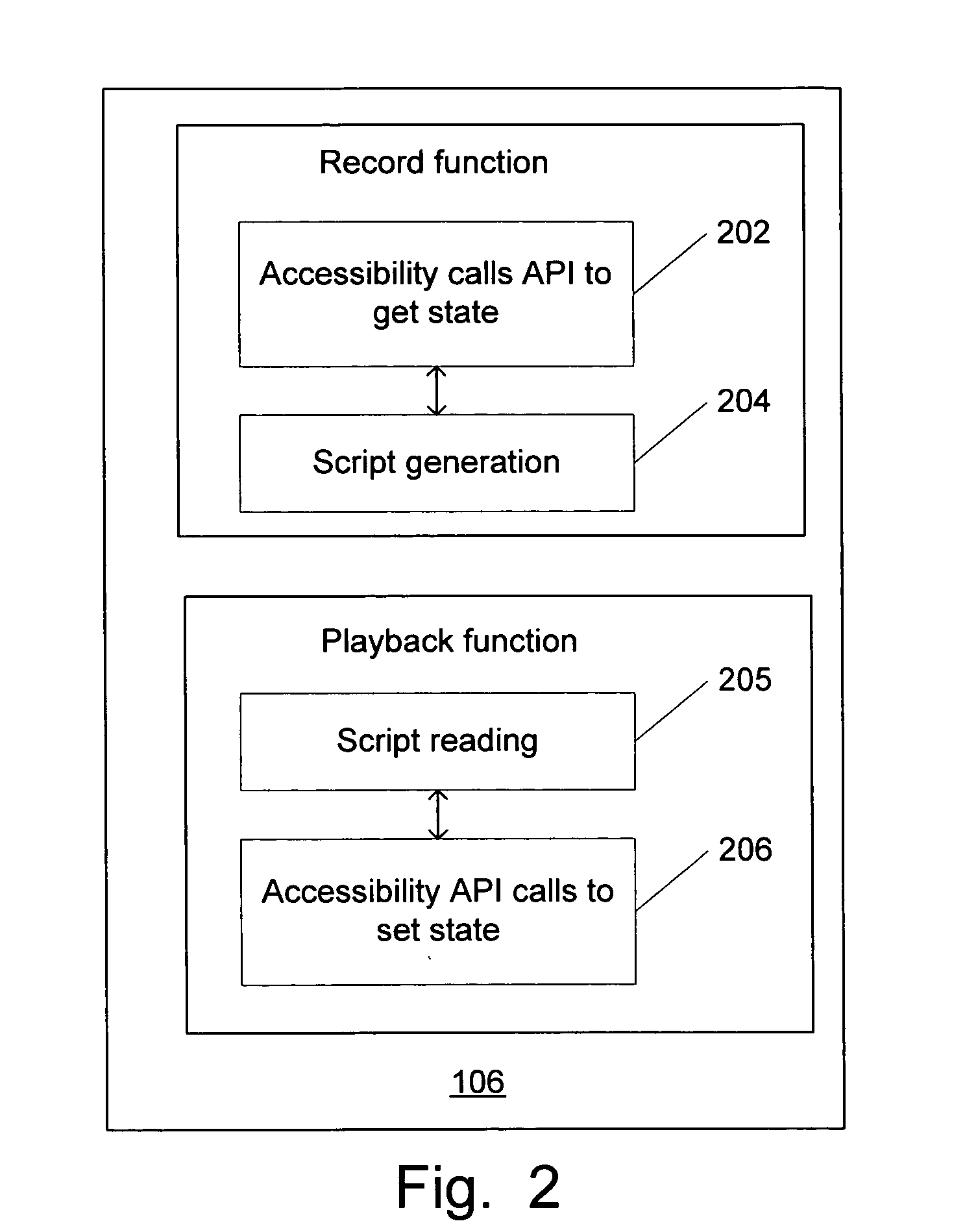
InactiveUS20050138646A1Execution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemApplication programming interface
A system and method for creating and accessing an object in a computer system is disclosed. The computer system including an application and an operating system. The system and method comprises a plurality of application programming interfaces (APIs) calls in the operating system. The plurality of API calls being utilized to obtain and set state information related to the application. The system further comprises a record / playback application on the computer, the record / playback application being capable of generating and reading script based upon the API calls to record actions that represent the operations of the applications and to reply actions that represent operations of the application. A system and method in accordance with the present invention utilizes existing accessibility screen reader technologies in order to create automated script files to launch program events. This can be accomplished by capturing the actions that the user's mouse and keyboard events create during of launching of a program or application including, mouse clicks, commands, pull down menu selections, etc., by utilizing API calls to retrieve state information concerning the program application.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Personalized voice playback for screen reader
ActiveUS7865365B2Easily and automatically createSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisPersonalizationSpeech patterns
A method, system, and computer program product is disclosed for customizing a synthesized voice based upon audible input voice data. The input voice data is typically in the form of one or more predetermined paragraphs being read into a voice recorder. The input voice data is then analyzed for adjustable voice characteristics to determine basic voice qualities (e.g., pitch, breathiness, tone, speed; variability of any of these qualities, etc.) and to identify any “specialized speech patterns”. Based upon this analysis, the characteristics of the voice utilized to read text appearing on the screen are modified to resemble the input voice data. This allows a user of the system to easily and automatically create a voice that is familiar to the user.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Screen reader with customizable web page output
A screen reader application for visually impaired users suppresses unwanted content that is output by Braille or text-to-speech. The invention accesses, but does not modify, the document object model of the web page and enumerates web page elements for the end user to either hide or skip to. The end user selections are saved as rules which may be applied according to various levels of scope include web page specific, site specific or web-wide. A screen magnification application for visually impaired users automatically sets the visual focus and magnification level on a web page element according to end-user selection.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
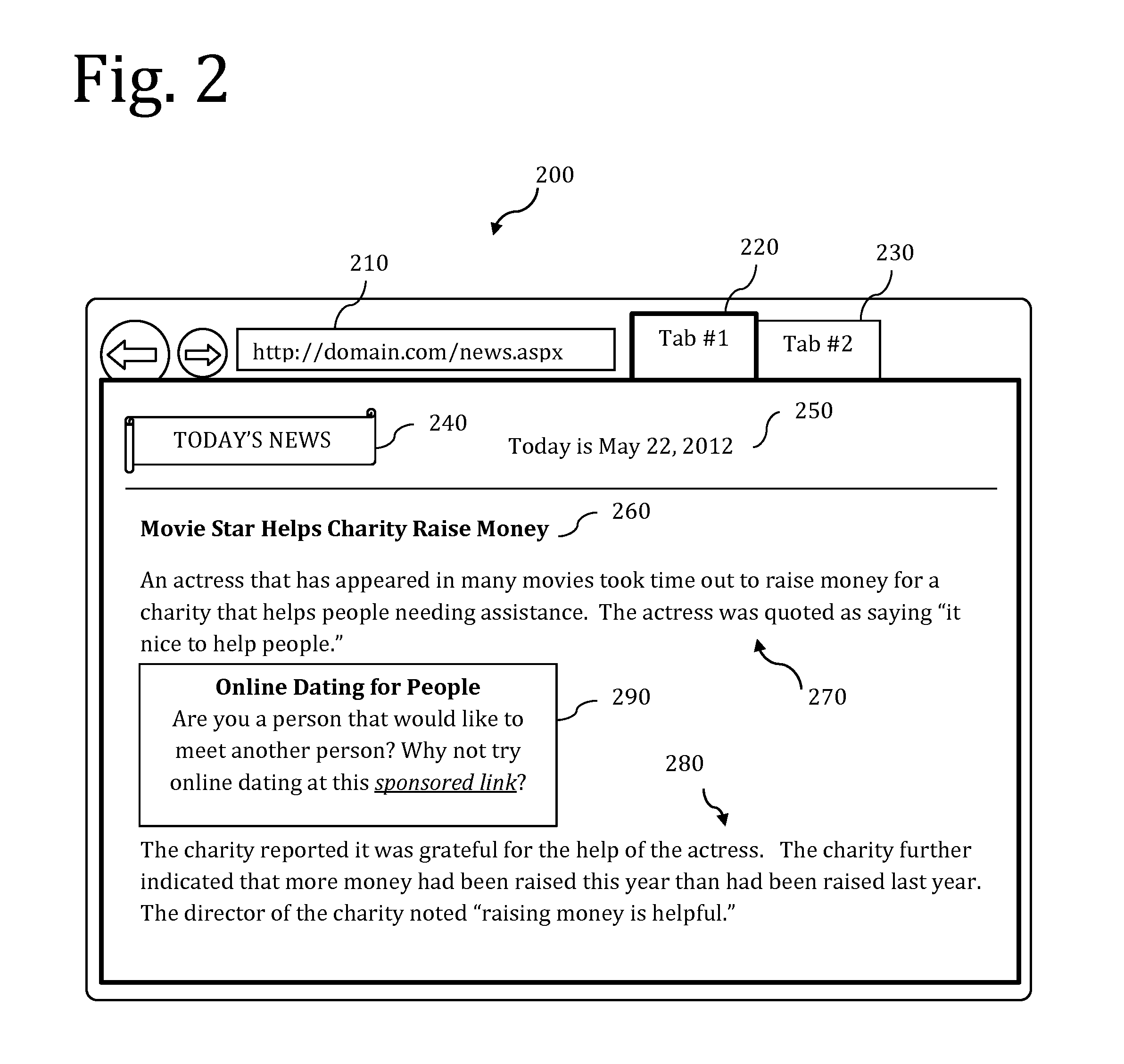
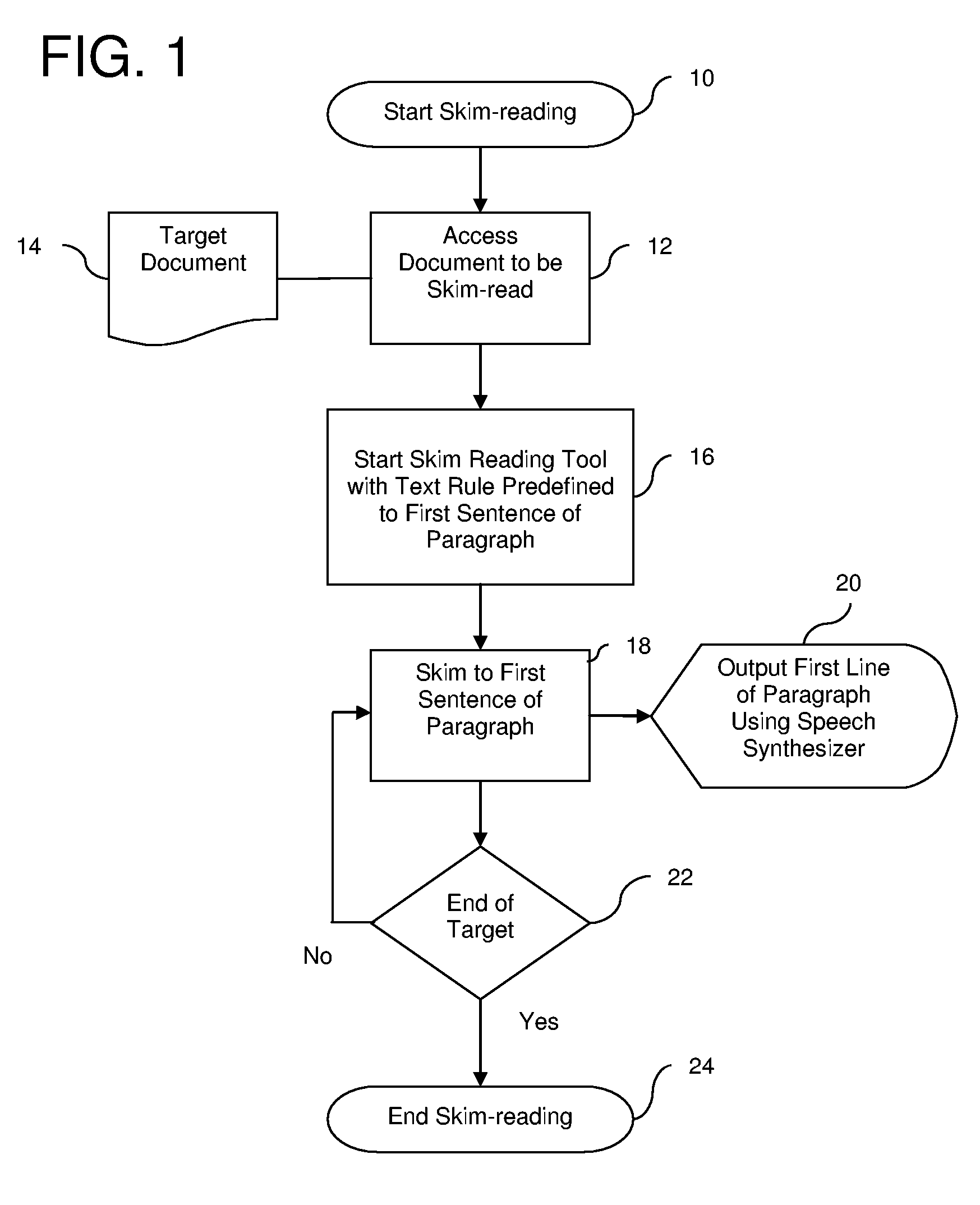
Reading Alerts and Skim-Reading System
ActiveUS20060080310A1Enhanced communication and access to informationDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionScreen readingDocumentation
A screen reader software product including a pattern store containing at least one user-definable array of keywords relating to a subject of interest and skim reading module adapted to apply the at least one array of keywords to a target document whereby only portions of the target document matching the at least one array of keywords are output by the screen reader software to an end user.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
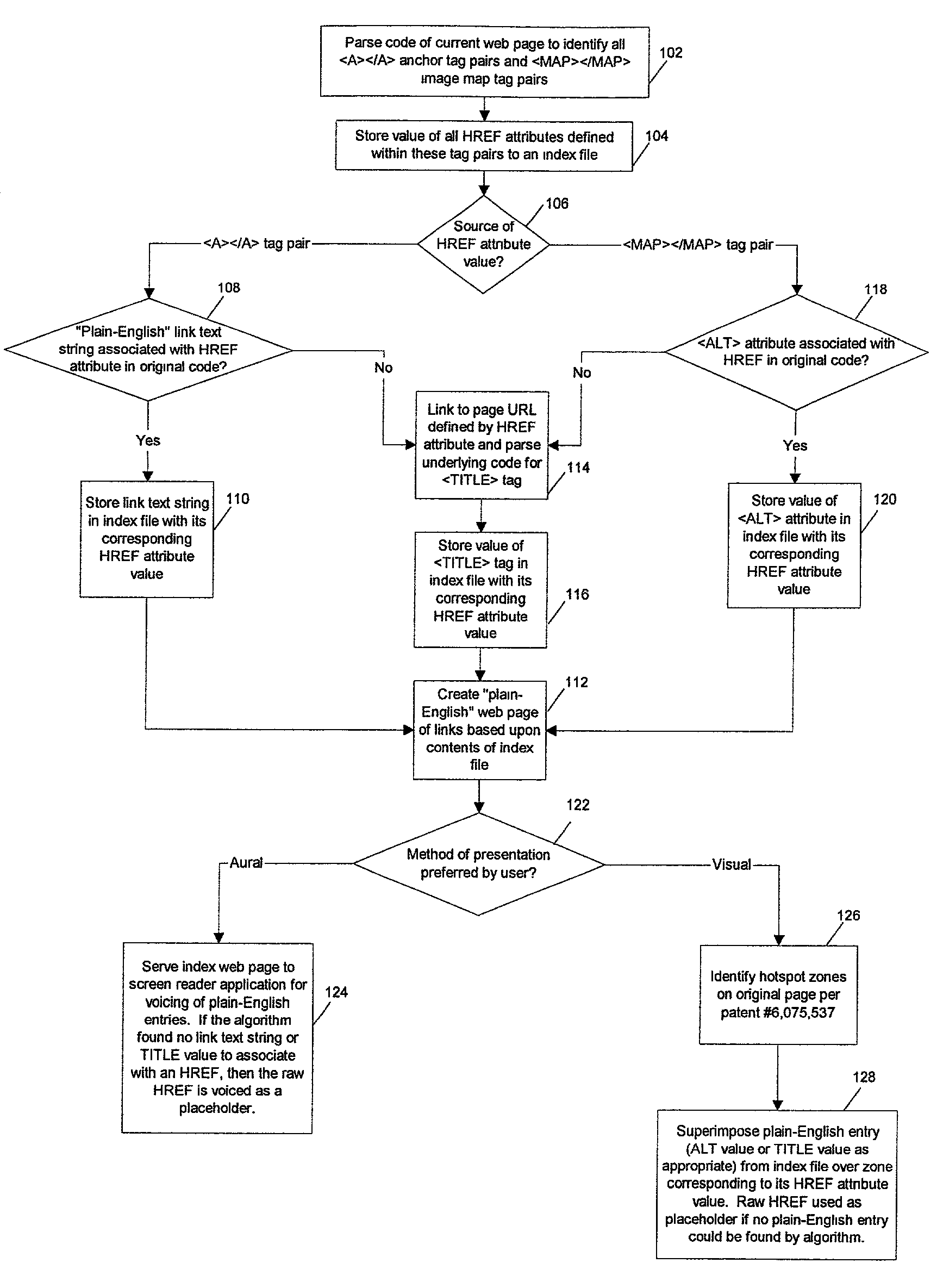
Method and system for providing an index to linked sites on a web page for individuals with visual disabilities
InactiveUS7228495B2Quick identificationDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsWeb pageVisual perception
A system and method in accordance with the present invention allows blind and visually impaired users to quickly identify links to relevant material when “viewing” web pages that consist primarily of either plain text or images. By generating an aural or visual index to the links on the page being “viewed”, blind and visually impaired users can quickly jump to interesting sites that are linked from the current page without having to wait for the entire page to be voiced by a screen reader application.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
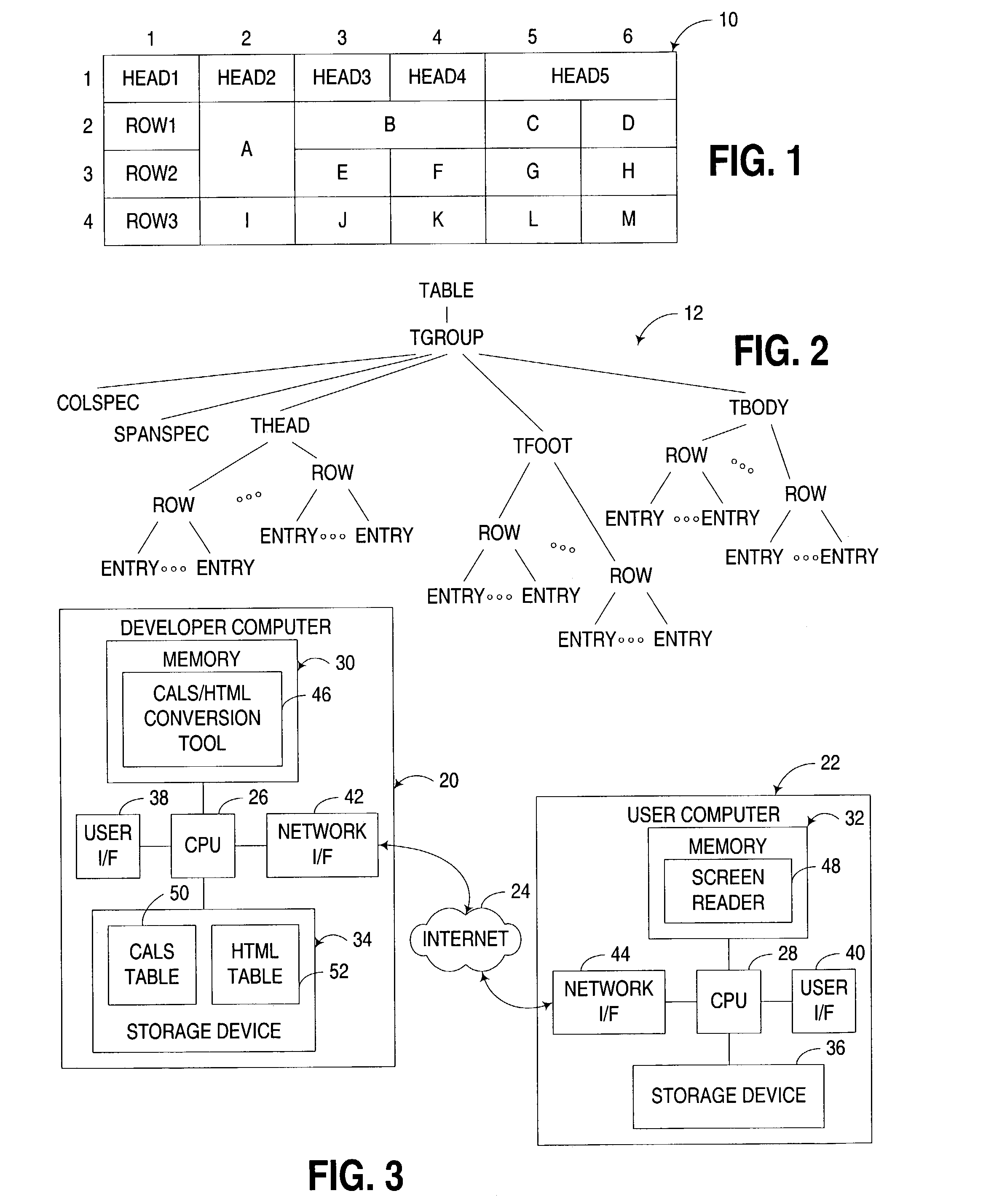
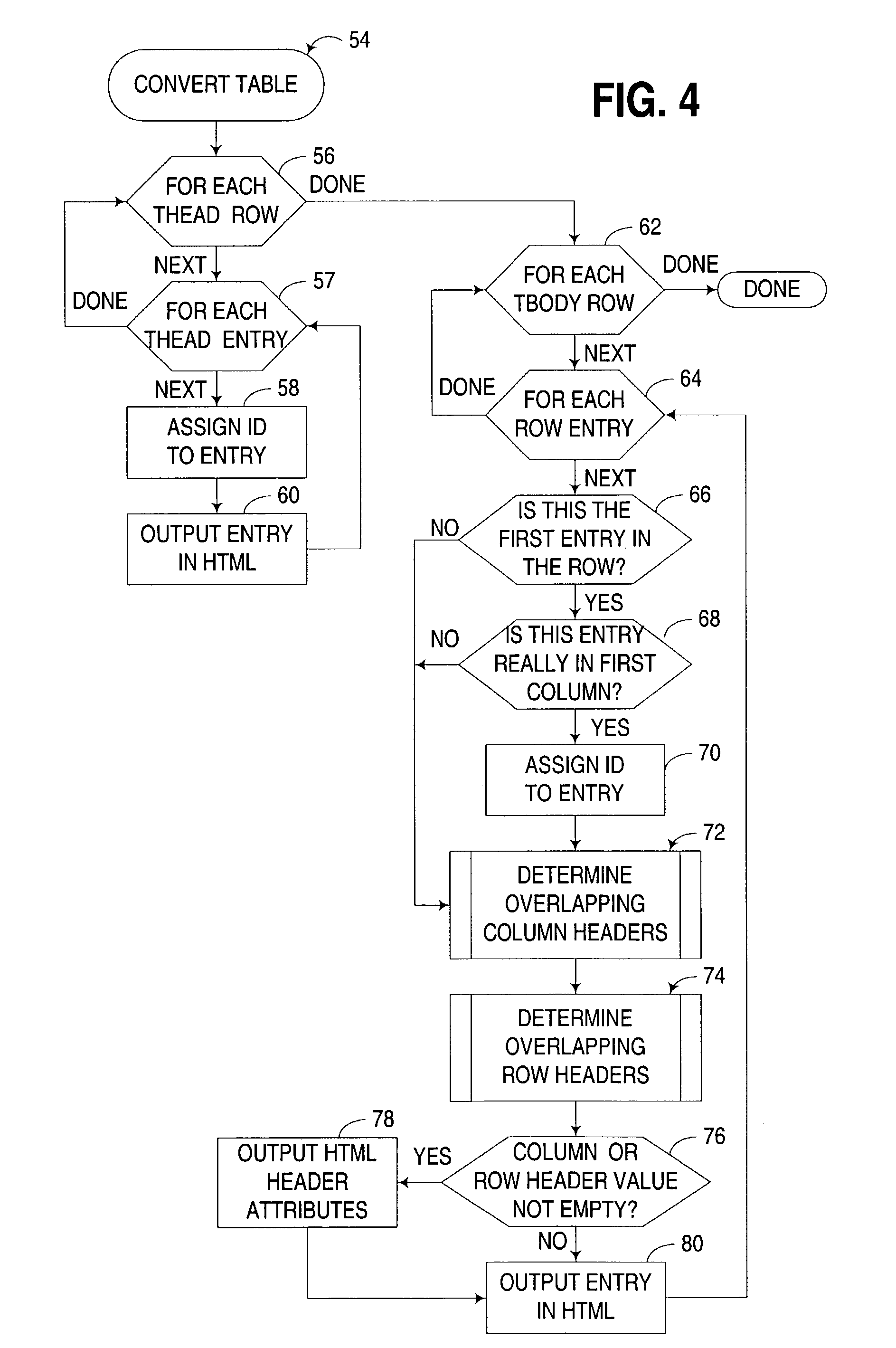
Automated conversion of CALS-compatible tables to accessible HTML tables
An apparatus, program product and method support the automated conversion of a table formatted in a CALS-compatible format to an HTML-compatible format, e.g., for use by presentation of the table by a screen reader or other application requiring knowledge of what headers apply to a given cell in a table. A table may be converted from a CALS-compatible format to an HTML-compatible format by assigning an identifier to each header cell in the table, in particular by embedding the identifier in an HTML identifier attribute for such header cell. Then, for each non-header cell in the table, any overlapping header cells therefor may be detected, and the identifier for any detected overlapping header cell may be embedded in an HTML headers attribute for such non-header cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
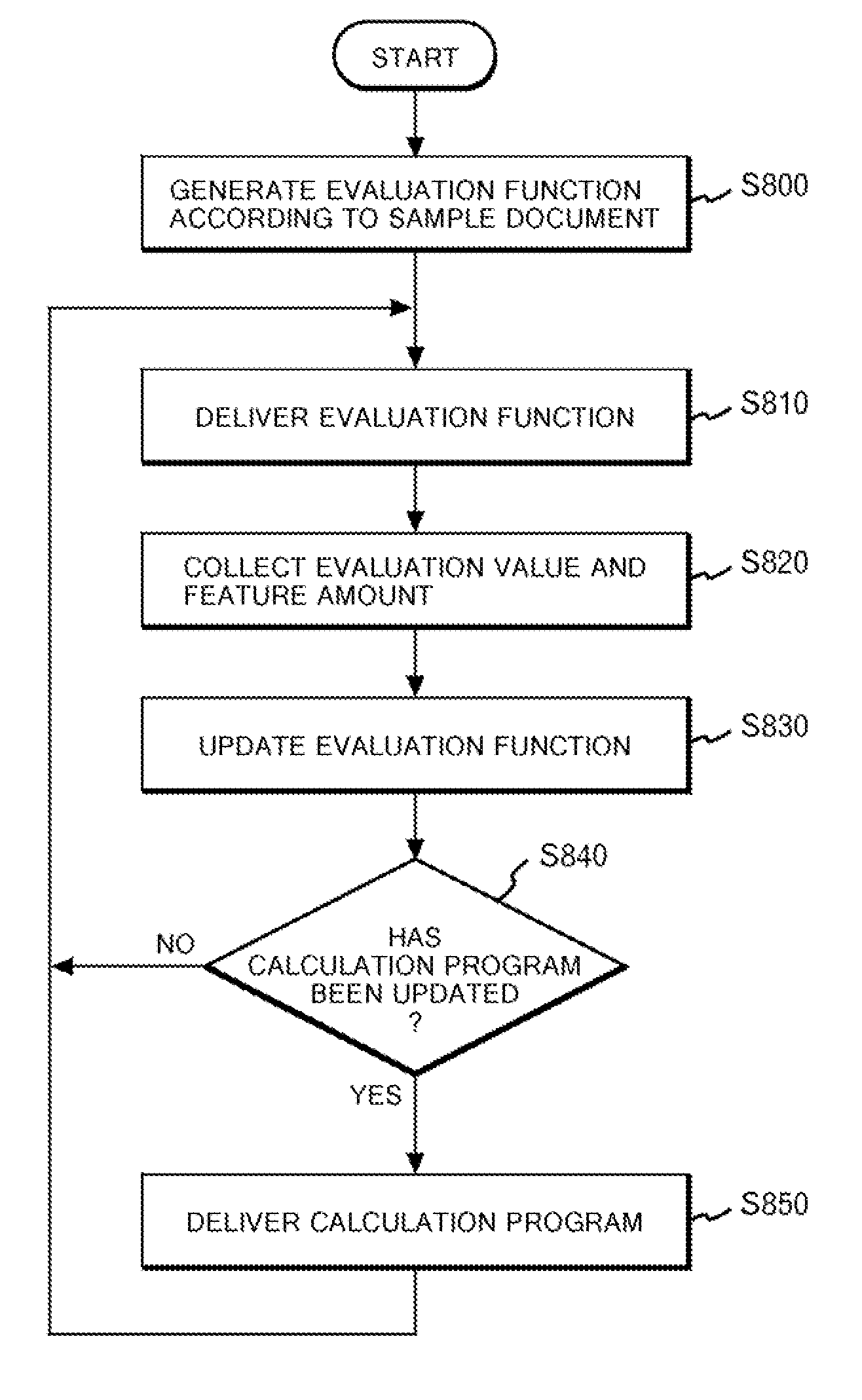
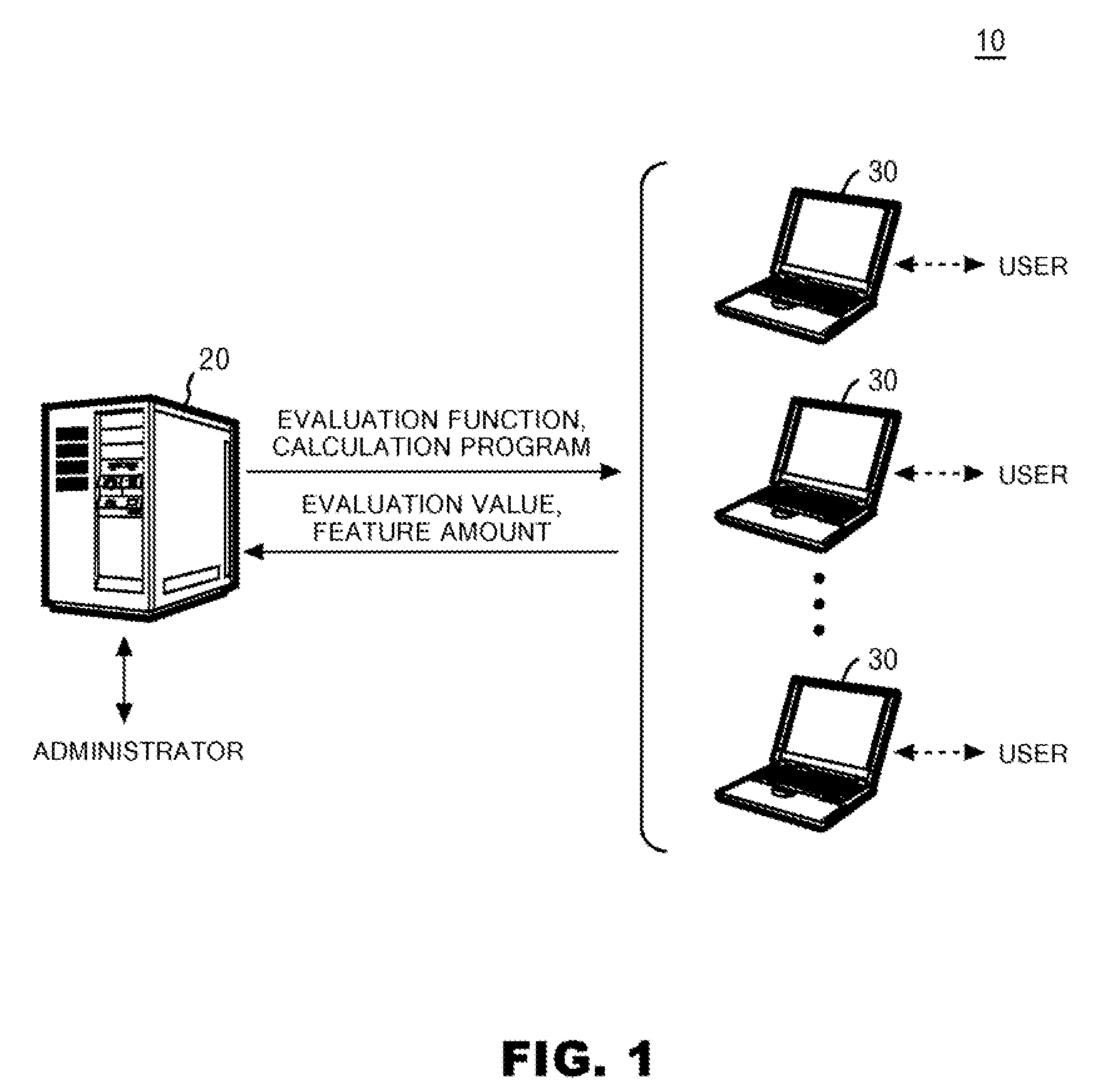
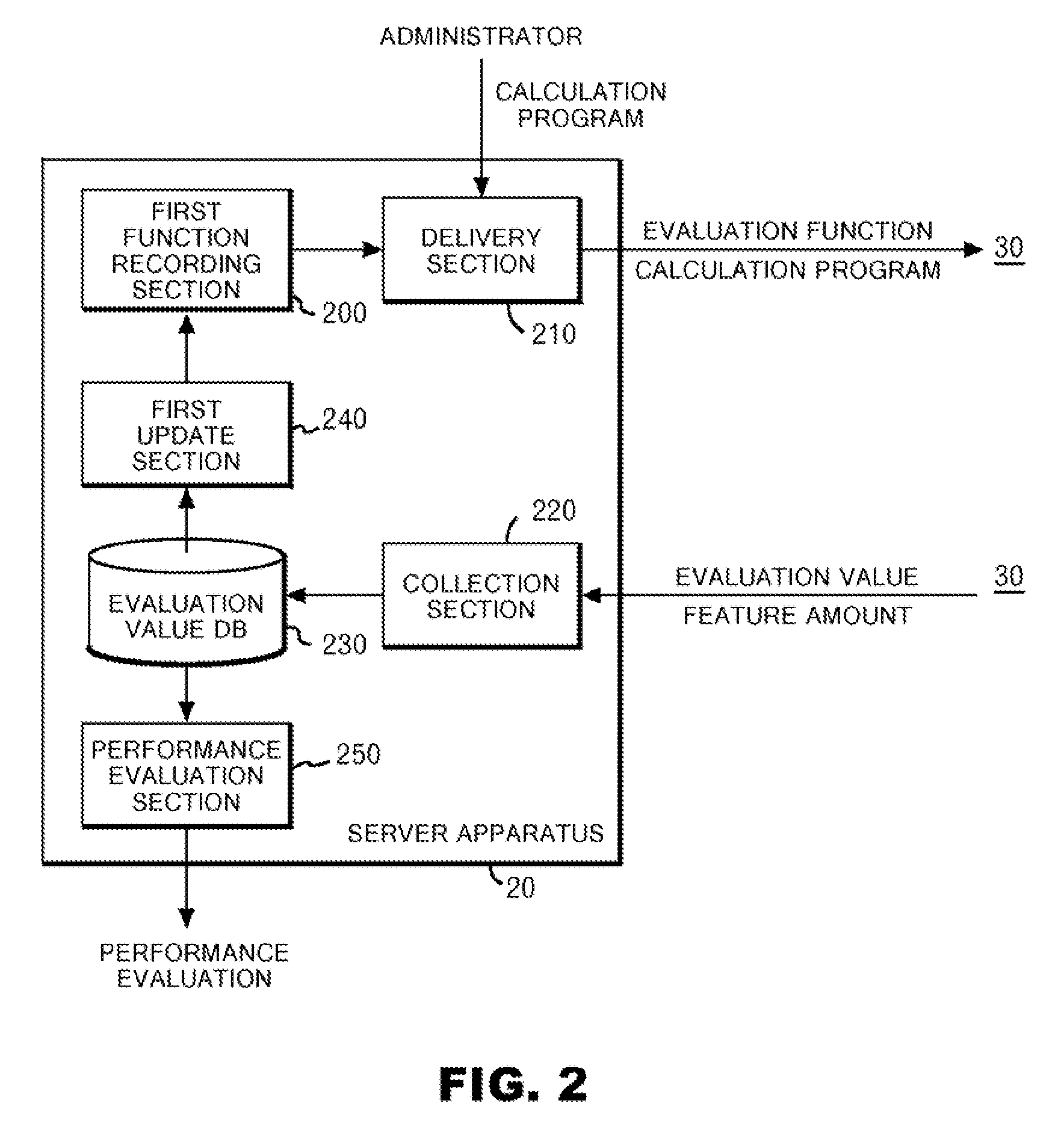
System and method for evaluating the difficulty of understanding a document
InactiveUS20080040115A1Low accuracySound input/outputSpecial data processing applicationsPaper documentDocument preparation
A system is provided for evaluating the degree of difficulty a user is likely to encounter when trying to understanding the contents of one or more document pages by listening to a voice output from a screen reader. An evaluation value representing the likely degree of difficulty is generated based on a feature amount representing a feature of the page. A collection section collects the user's actual evaluation value of the difficulty and the feature amount of one or more pages where the generated evaluation value is inconsistent with the user's evaluation of the difficulty. A first update section updates the evaluation function on the basis of the feature amount and the evaluation value collected from the user.
Owner:IBM CORP
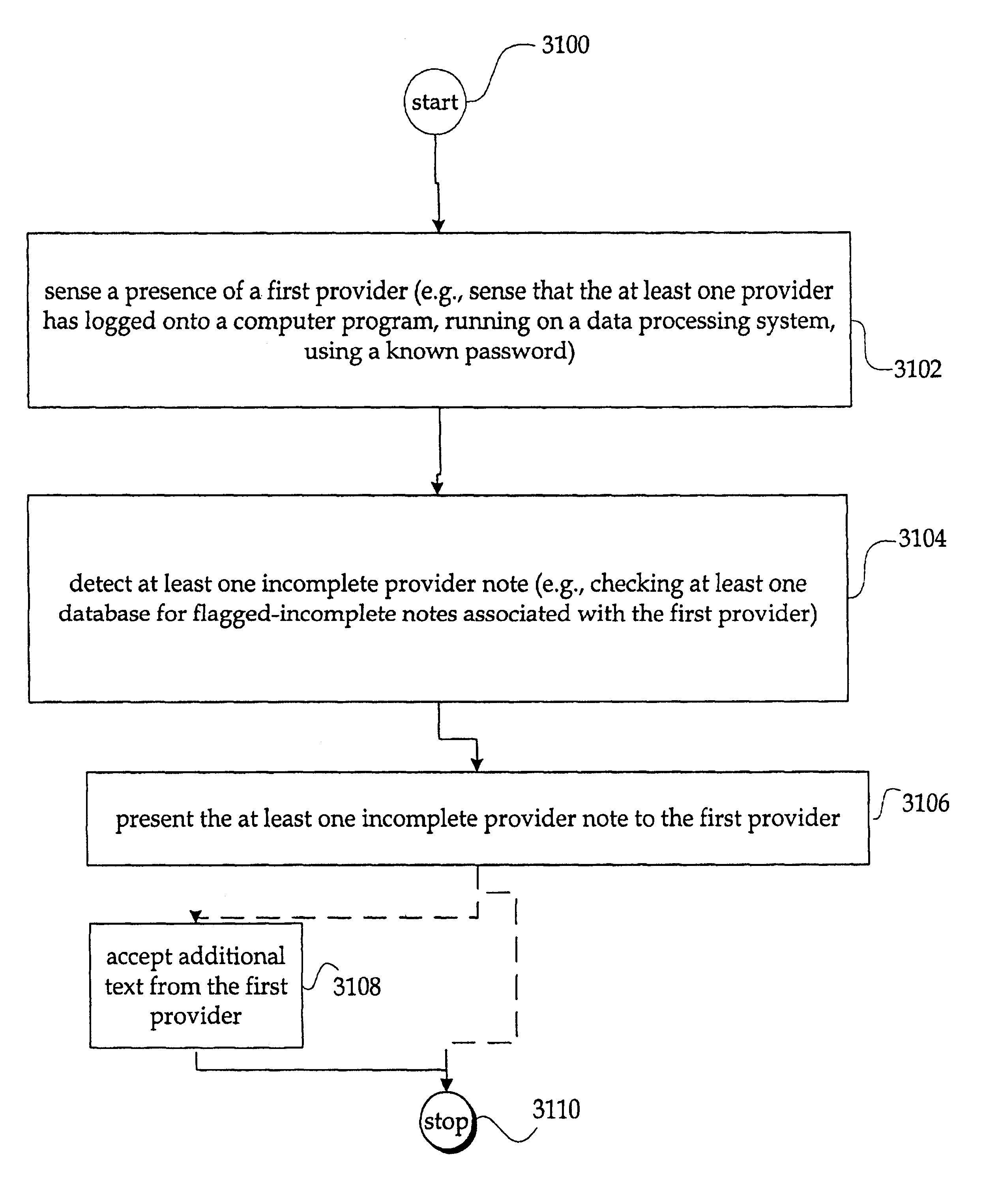
Providing for automated note completion
InactiveUS6876780B1Character and pattern recognitionPatient personal data managementScreen readerGraphical user interface
A method and system which provide for automated note completion. In one embodiment, the method is characterized by sensing a presence of a first provider; detecting at least one incomplete provider note; and presenting the at least one incomplete provider note to the first provider. In another embodiment of the method, the sensing a presence of a first provider is characterized by accepting an identifier associated with the first provider. In another embodiment of the method, the accepting an identifier associated with the first provider is characterized by accepting user input of the identifier via either a keyboard, a touch-screen reader, a graphical user interface, or a biometrics identifier. In another embodiment of the method, the detecting at least one incomplete provider note is characterized by checking at least one database for flagged-incomplete notes associated with the at least one provider. In one or more various embodiments, related systems include but are not limited to circuitry and / or programming for effecting the foregoing-referenced method embodiments; the circuitry and / or programming can be virtually any combination of hardware, software, and / or firmware configured to effect the foregoing-referenced method embodiments depending upon the design choices of the system designer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
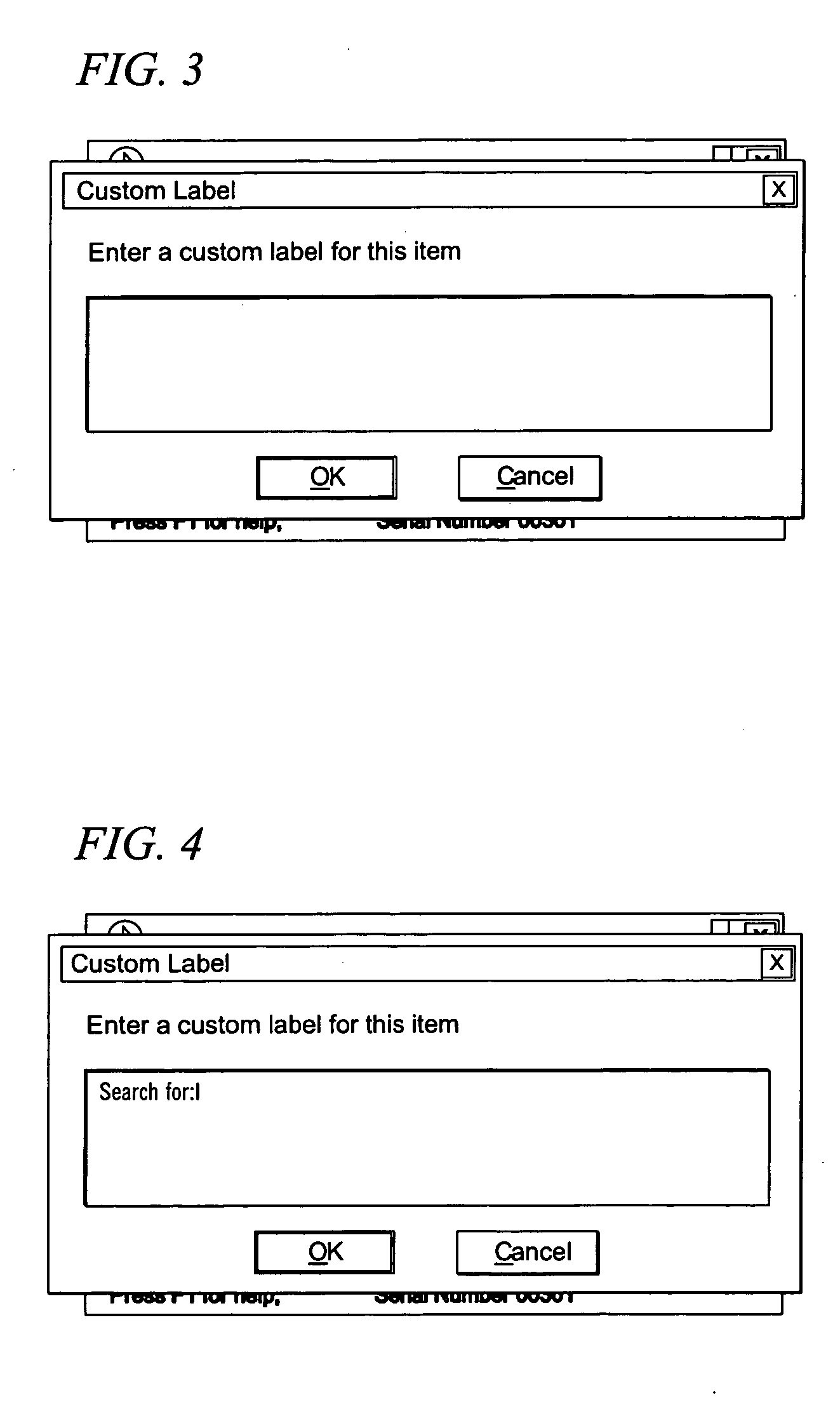
Custom Labeler for Screen Readers
ActiveUS20060200757A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsWord processingPaper document
A screen reader feature is described that enables end users to assign their own descriptions to forms and navigational elements in electronic documents such as web pages, word processing documents and portable document formats. The form or navigational element is identified by the end user. A dialog box provides a text entry box for accepting a user-defined description. The description is saved in association with the document and its particular form or navigational element.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
Device, method, and graphical user interface for integrating recognition of handwriting gestures with a screen reader
ActiveUS20170185285A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyDigital data authenticationSound input/outputGraphicsGraphical user interface
While an electronic device with a display and a touch-sensitive surface is in a screen reader accessibility mode, the device displays a character input area and a keyboard, the keyboard including a plurality of key icons. The device detects a sequence of one or more gestures on the touch-sensitive surface that correspond to one or more characters. A respective gesture of the one or more gestures that corresponds to a respective character is a single finger gesture that moves across the touch-sensitive surface along a respective path that corresponds to the respective character. The respective path traverses one or more locations on the touch-sensitive surface that correspond to one or more key icons of the plurality of key icons without activating the one or more key icons. In response to detecting the respective gesture, the device enters the corresponding respective character in the character input area of the display.
Owner:APPLE INC
Screen reader with focus-based speech verbosity
ActiveUS8868426B2Improve productivityImprove the level ofSpeech synthesisTeaching apparatusGraphicsGraphical user interface
The amount of speech output to a blind or low-vision user using a screen reader application is automatically adjusted based on how the user navigates to a control in a graphic user interface. Navigation by mouse presumes the user has greater knowledge of the identity of the control than navigation by tab keystroke which is more indicative of a user searching for a control. In addition, accelerator keystrokes indicate a higher level of specificity to set focus on a control and thus less verbosity is required to sufficiently inform the screen reader user.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
Screen reader having concurrent communication of non-textual information
ActiveUS8826137B2Input/output for user-computer interactionNatural language data processingWeb browserWord processing
A screen reader software product for low-vision users, the software having a reader module collecting textual and non-textual display information generated by a web browser or word processor. Font styling, interface layout information and the like are communicated to the end user by sounds broadcast simultaneously rather than serially with the synthesized speech to improve the speed and efficiency in which information may be digested by the end user.
Owner:FREEDOM SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com