Recombinated multi shape ttansenula yeast, its structural method and application
A technology for Hansenula polymorpha and yeast is applied in the field of recombinant Hansenula polymorpha and its construction and application, which can solve the problem of difficulty in obtaining ideal transformants, inconvenience in large-scale industrial production, and low genetic stability. problems, to achieve the effect of maintaining physiological and biochemical characteristics, high industrial application value, and high genetic stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
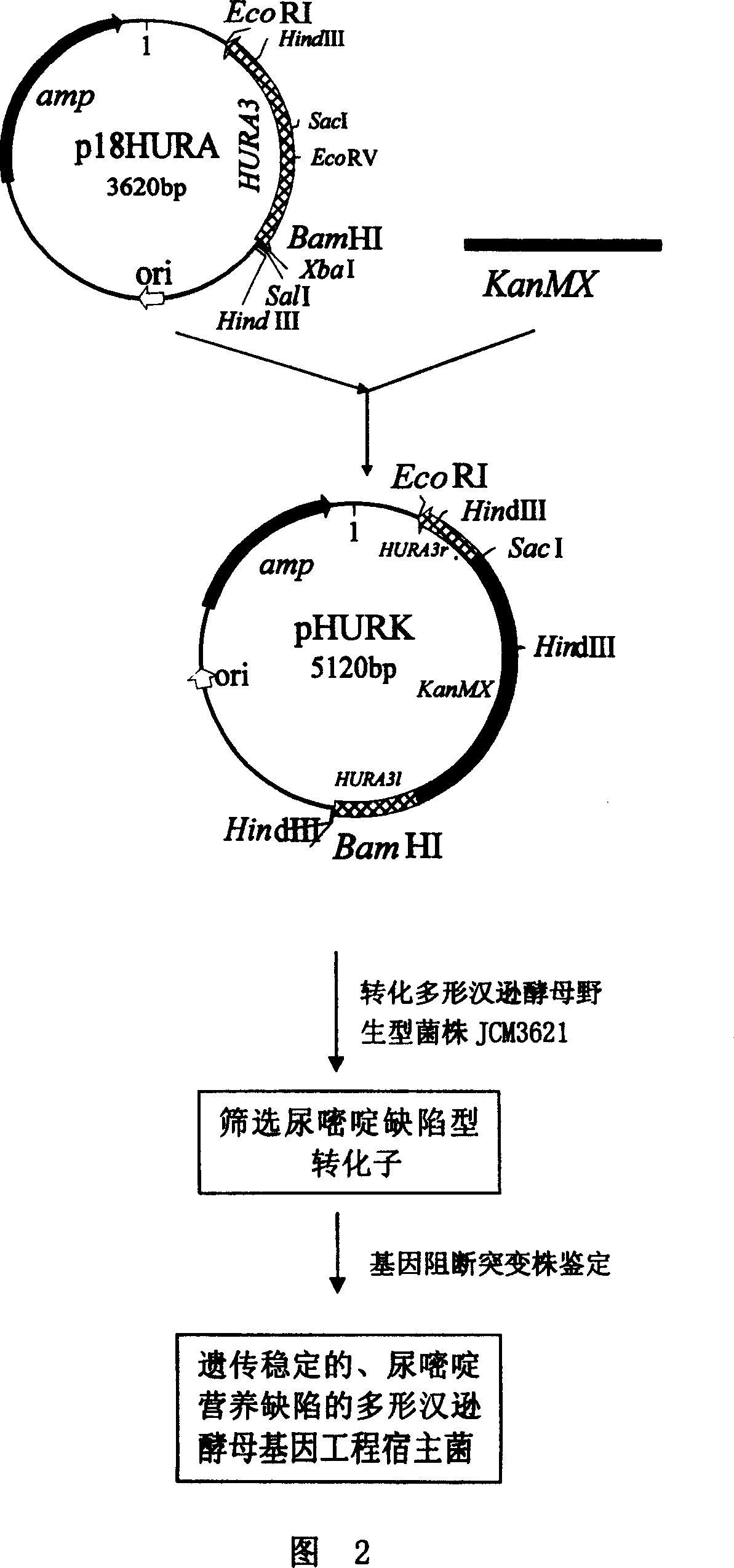
[0029] Example 1, Construction of Hansenula polymorpha (Hansenula polymorpha) HU-11 CGMCC No.1218 and detection of its biomass and biological activity
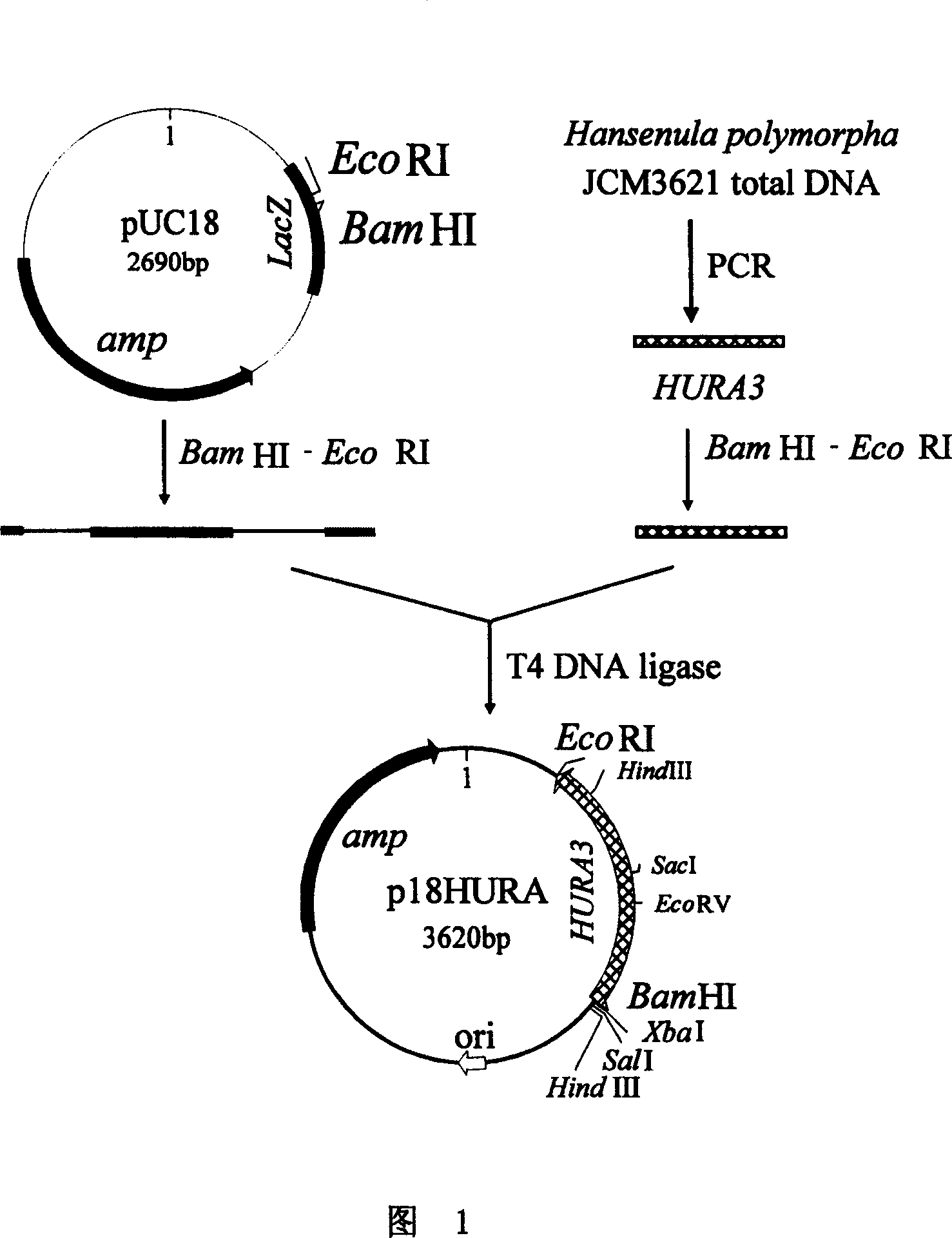
[0030] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmid p18HURA containing the orotidine-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene (HURA3) of Hansenula polymorpha
[0031] As shown in Figure 1, the construction process of the recombinant plasmid p18HURA is as follows:
[0032] 1. Acquisition of orotic acid-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene (HURA3) of Hansenula polymorpha
[0033] The primer sequences designed according to the reported HURA3 nucleotide sequence of Hansenula polymorpha are as follows:
[0034] Primer 1: 5′-CCA GGATCC TCAACATTTCCCTGAATAAT-3' (sequence 1 in the sequence listing) (the bases underlined are BamH I recognition sites)
[0035] Primer 2: 5′-CGA GAATTC TCACTAGTATTC CCGCGACT-3' (sequence 2 in the sequence listing) (the underlined part of the base is the EcoR I recognition site)
[0036] Using the total DNA of Hansenula pol...
Embodiment 2
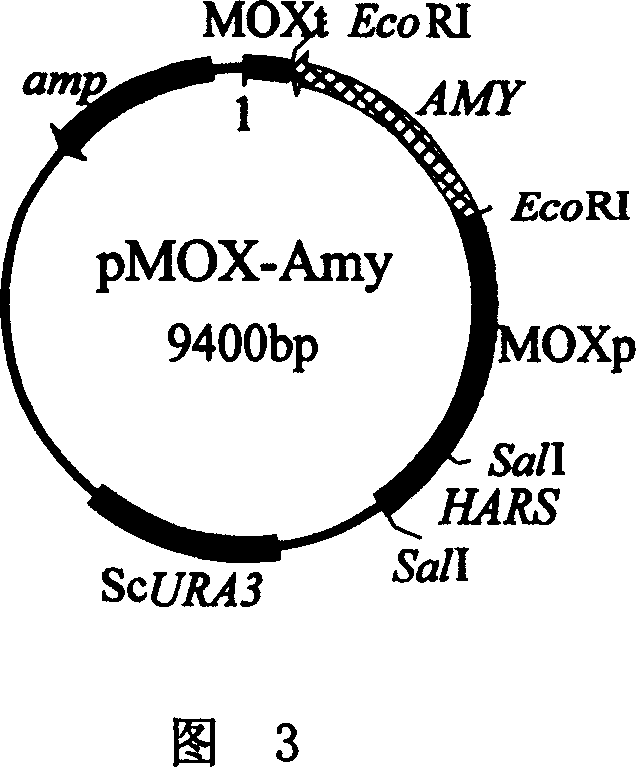
[0062] Example 2, Intracellular expression of amylase gene in Hansenula polymorpha (Hansenula polymorpha) HU-11 CGMCCNo.1218
[0063] 1) The vector YIp5 (Struhl K, St inchcomb DT, et al. High-frequency transformation of yeast: Autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. ProcNatl Acad Sci USA, 1979, 76: 1035-1039) was used as the starting vector. Digest plasmid YIp5 and pHARS (Roggenkamp R, Hansen H, et al. Transformation of themethylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorphabby autonomous replication and integration vectors. Mol Gen Genet, 1986, 202: 302-308) respectively with restriction endonuclease SalI, low melting point The 5.6kb linear YIp5 DNA fragment and the 0.5kb Hansenula polymorpha self-replicating sequence HARS were recovered by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the recovered DNA fragments were dissolved in TE buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, 1mM EDTA, pH8. 0), the ligation reaction was performed, and the ligation reaction system was: 3 μl deionized water, 1 μl 10× ligation buf...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3, Secretory expression of amylase gene in Hansenula polymorpha (Hansenula polymorpha) HU-11 CGMCCNo.1218
[0072] 1) Design and synthesize primer amy3(5'-CC CTGCAG AATATGCAAATTTCAAAAGC-3 ', the underlined part is the PstI recognition site), and together with the primer amy2 in Example 2, the chromosome of Saccharomyces spp. Using DNA as a template, the PCR reaction was performed to amplify the α-amylase gene (AMY).
[0073] Design and synthesis of primer αP1(5′-TAA GAATTC AAAATGAGATTTCCTT-3′, the underlined part is EcoRI recognition site) and αP2 (5′-CGT CTGCAG CTCAGCTTCAGCCTCTCTT-3', the underlined part is the PstI recognition site), and the plasmid pMETαB (Invitrogen Company) was used as a template to perform PCR reaction to amplify about 0.3kb of the sequence MFα1s encoding the α-factor signal peptide of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
[0074] The plasmid pHAM1 constructed in Example 2 was digested with the restriction endonuclease EcoRI, and the PCR amplif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com