Clone of gene RID1 for controlling rice floral conversion and heading stage and application thereof
A heading date and genetic technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as non-existence and non-discovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
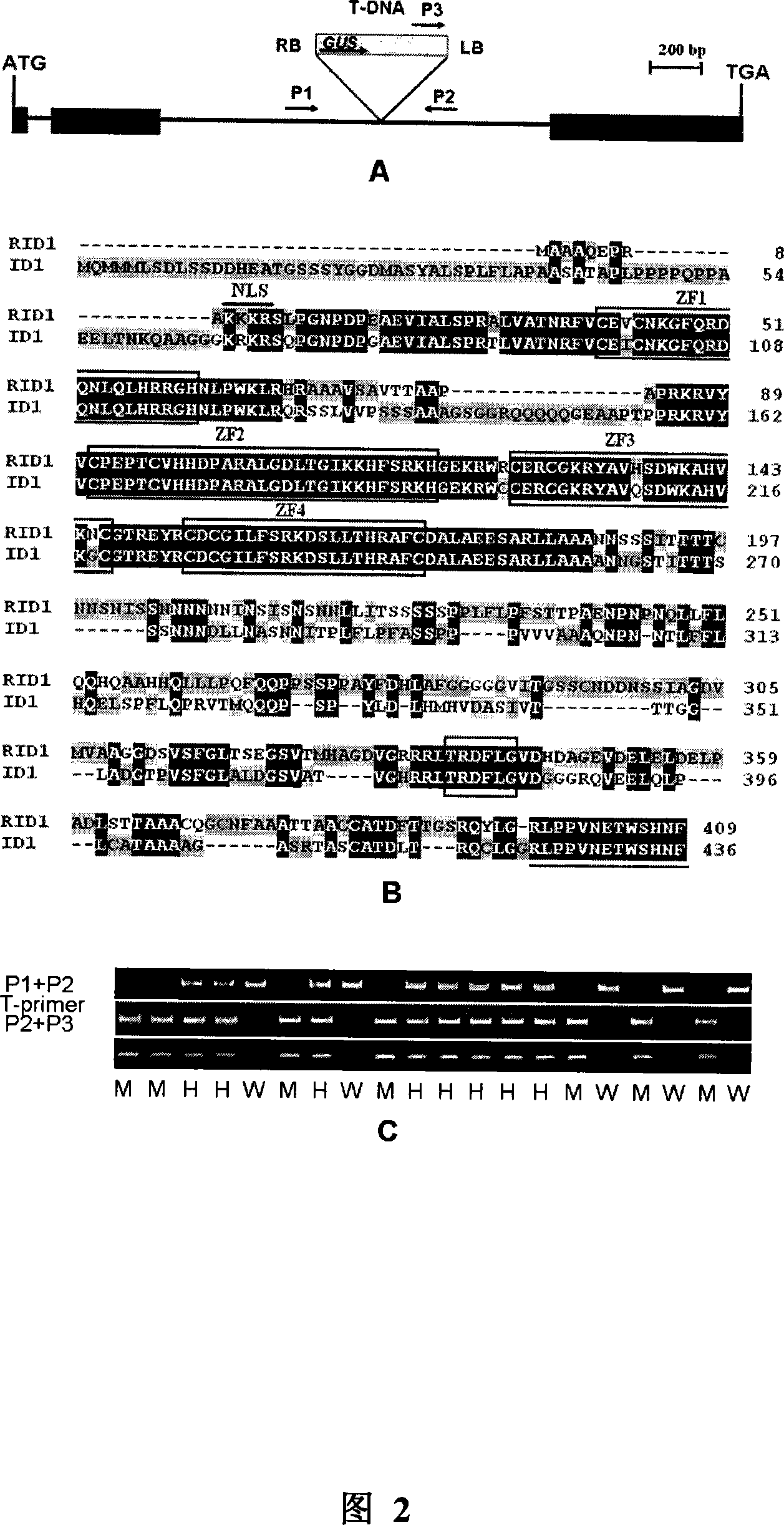
[0027] Example 1: Isolation and cloning of RID1 gene
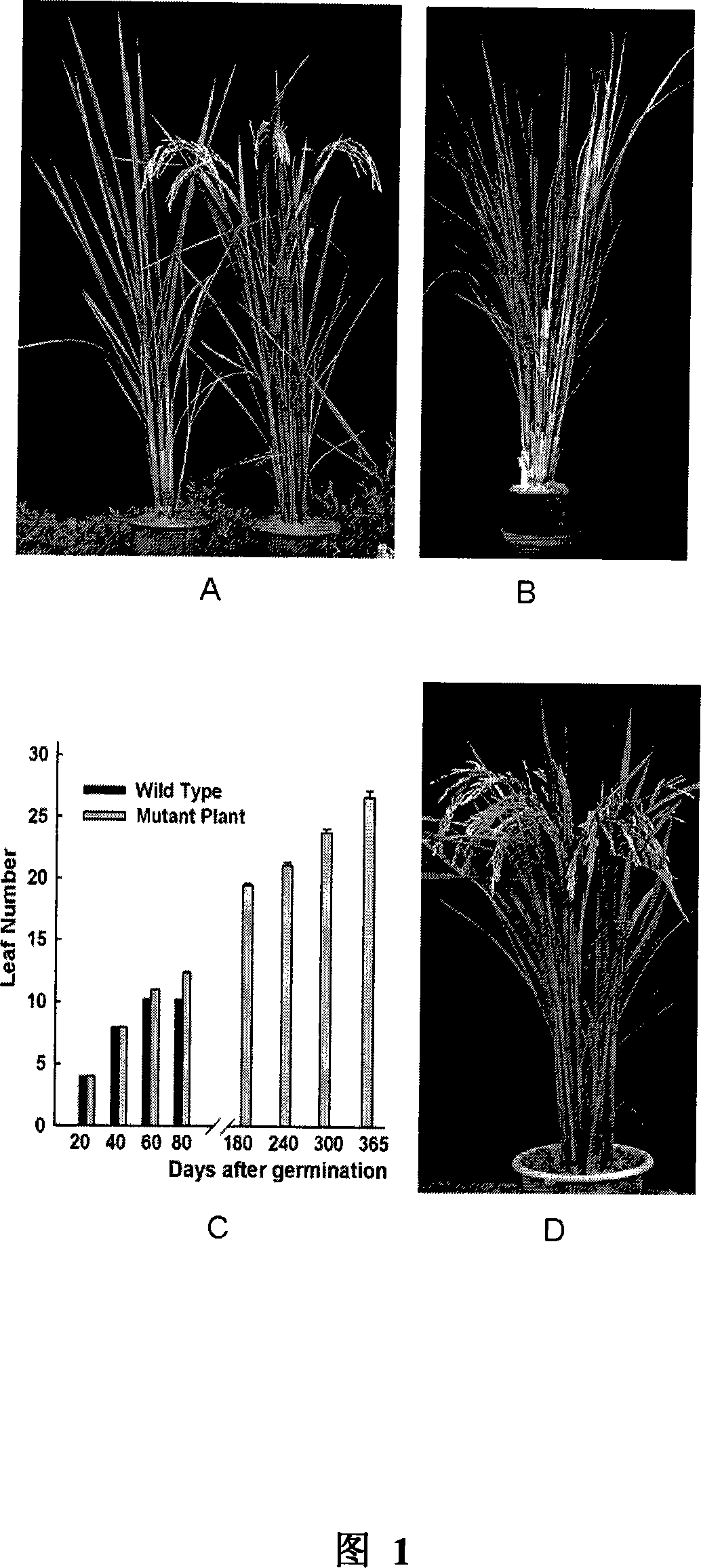
[0028] 1. Obtaining non-heading mutants
[0029] The mutants identified in the present invention are from rice T-DNA insertion mutants (the creation method of the mutant library has published papers, see Wu et al., Development of enhancer trap lines for functional analysis of the rice genome, Plant J (2003): 418-427; Zhang et al., Non-random distribution of T-DNA insertions at various levels of the genome hierarchy as revealed by analyzing 13, 804 T-DNA flanking sequences from an enhancer-trap mutant library, Plant J(2007): 947- 959). The screening identification method of mutant is: from above-mentioned rice T-DNA insertion mutant library (see http: / / rmd.ncpgr.cn / ), the T0 transgenic rice seeds were planted in the field after conventional soaking and germination procedures to obtain each T 1 A total of 20 plants were planted in the generation family. The plants were planted in the experimental field of Huazhong Agricu...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: RID1 gene is expressed in immature leaves and localized in the nucleus
[0039] The present invention at first utilizes semi-quantitative RT-PCR to analyze the expression pattern of RID1 gene, plant tissue total RNA sample extraction, reverse transcription and RT-PCR reaction conditions see references (Huang etc., Down-Regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2-RelatedHistone Deacetylase Gene, OsSRT1, Induces DNA Fragmentation and Cell Death in Rice, Plant Physiol (2007): 1508-1519). The total RNA was obtained from the plant tissues of the wild-type rice variety "Zhonghua 11" and the rid1 mutant grown under artificially controlled diurnal neutral conditions (12 hours day / 12 hours night): leaves and leaf sheaths 35 days after germination Total RNA was extracted from , immature leaves, roots, shoot apex tissues and flower organ meristems 41 days after germination. RT-PCR results showed that the RID1 gene was only expressed at a very low level in the immatur...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: RID1 regulates known heading date-related regulatory genes
[0046] In order to analyze the molecular mechanism of RID1 gene regulating rice flowering, the present invention uses quantitative RT-PCR technology to detect the expression of related heading date regulation genes in rid1 mutants and wild-type plants. The results are shown in Figure 4, no matter in two consecutive days under long-day conditions (14 hours day / 10 hours night) or short-day conditions (10 hours day / 14 hours night), compared with the expression in wild-type rice plants, The expression of Ehd1 and Hd3a in the rid1 mutant was severely suppressed, almost undetectable; while the expression of Hd1 gene in the rid1 mutant was lower than that of the wild-type plant during the day, but the difference was not obvious at night. This shows that the RID1 gene mainly affects the flowering of rice by regulating the expression of Ehd1 and Hd3a. The study also found that the expression of the RID1 gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com