Amorphous boron carbon alloy and photovoltaic application thereof
A boron carbon and amorphous technology, applied in the field of semiconductor material production, can solve the problems of not eliminating the n-p junction effect, difficulty in conductivity, and not being easily applied, and achieve the effect of improving photoelectric conversion performance and good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
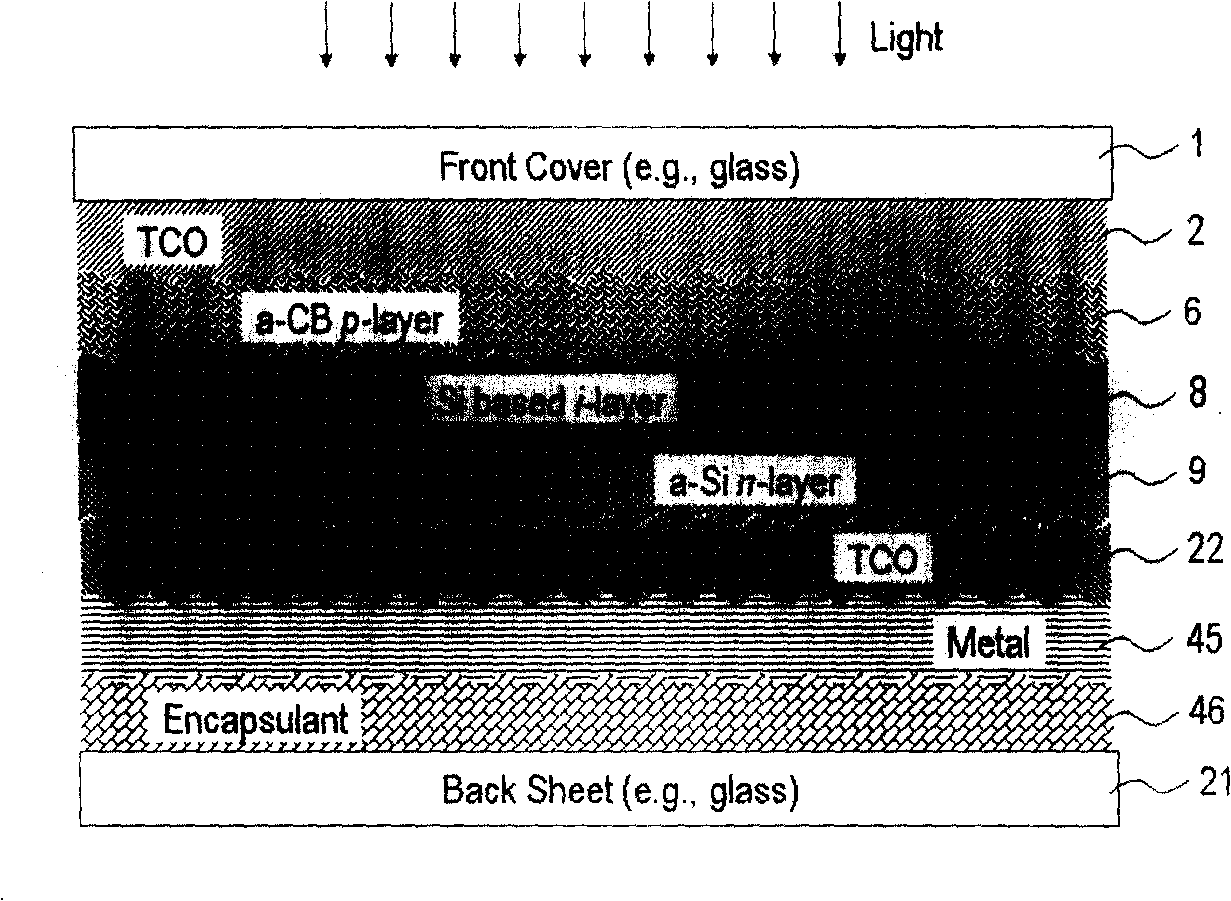
[0030] The p-layer has a significant impact on the conversion efficiency of p-i-n solar cells based on silicon thin films. The hydrogenated amorphous boron carbon film has an optical energy band gap greater than 2.0 eV, which can be used to replace the traditional wide band gap p-layer based on amorphous silicon (usually boron-doped amorphous silicon carbon, a-SiC) . For example Figure one In the pin-type photovoltaic cell shown, the p-layer 6 is composed of a hydrogenated amorphous boron carbon film with a thickness of no more than 15 nanometers and a light energy band gap of 2.0-2.2 eV, which is directly on the transparent conductive oxide front electrode 2. Generated by plasma coating method. The i-layer 8 may be based on an amorphous silicon film or a nano-silicon layer. The phosphorus-doped n-layer 9 is formed of ordinary amorphous silicon. The interface formed by the hydrogenated amorphous boron carbon p-layer 6 and the undoped intrinsic i-layer 8 is a unique heterojunction ...
Embodiment 2
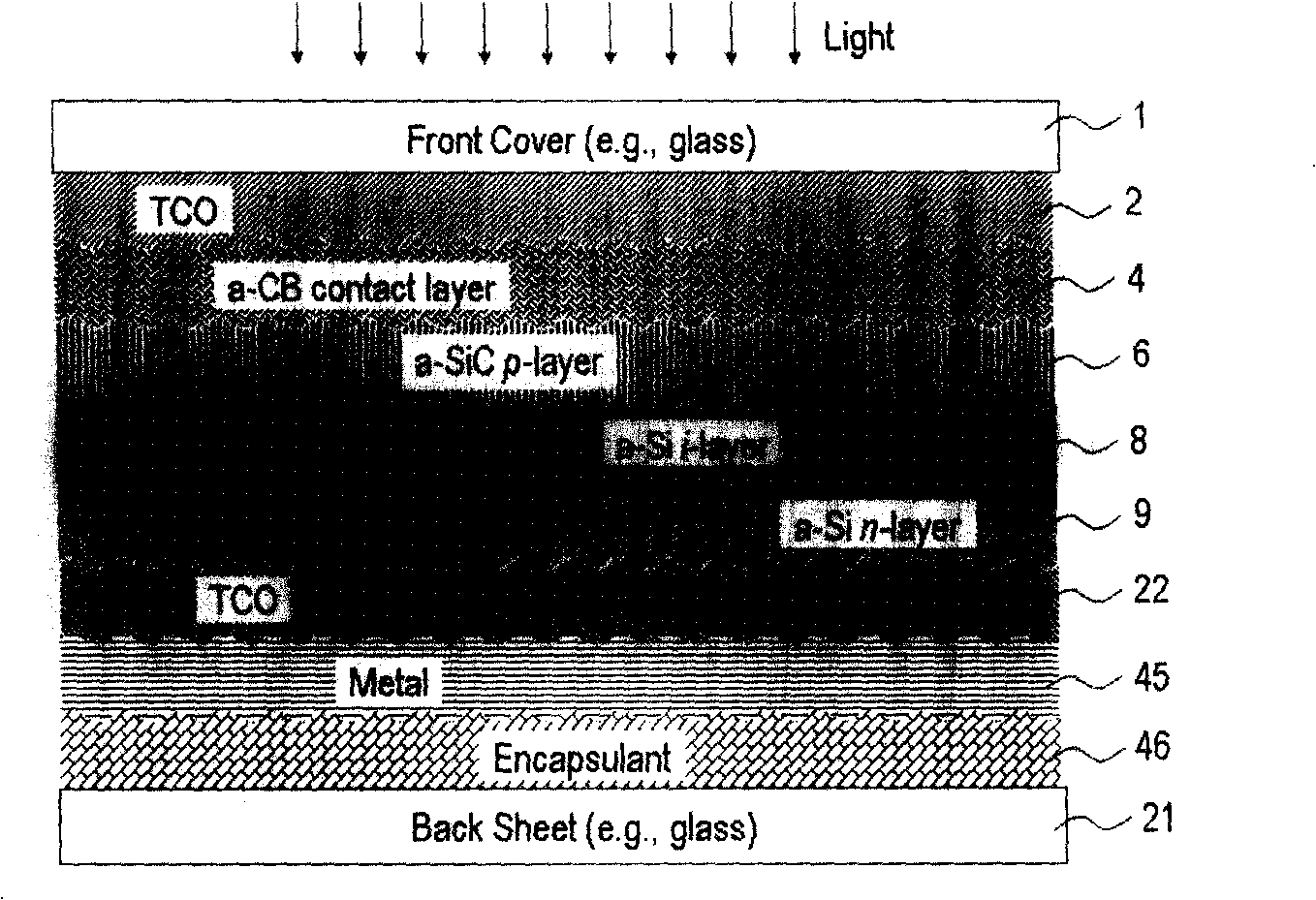
[0032] figure 2 In the single junction photovoltaic cell based on amorphous silicon, except that the p-layer 6 is composed of a conventional amorphous silicon-carbon alloy, it is basically the same as figure 1 The p-i-n device used in the first embodiment shown has the same structure. The difference and uniqueness is that it has a hydrogenated amorphous boron carbon contact layer 4, which is placed on the front electrode 2 and the hydrogenated amorphous silicon carbon p-layer 6. The function of the hydrogenated amorphous boron-carbon contact layer 4 is to reduce the resistance (electrical barrier) between the transparent conductive oxide and the amorphous silicon-carbon p-layer. Since a high concentration of carbon atoms must be used to minimize the amount of light loss and increase the light transmission rate as much as possible, the p-layer is almost completely electrically insulated. The ultra-thin hydrogenated amorphous boron carbon layer with a thickness of less than 3 nan...
Embodiment 3
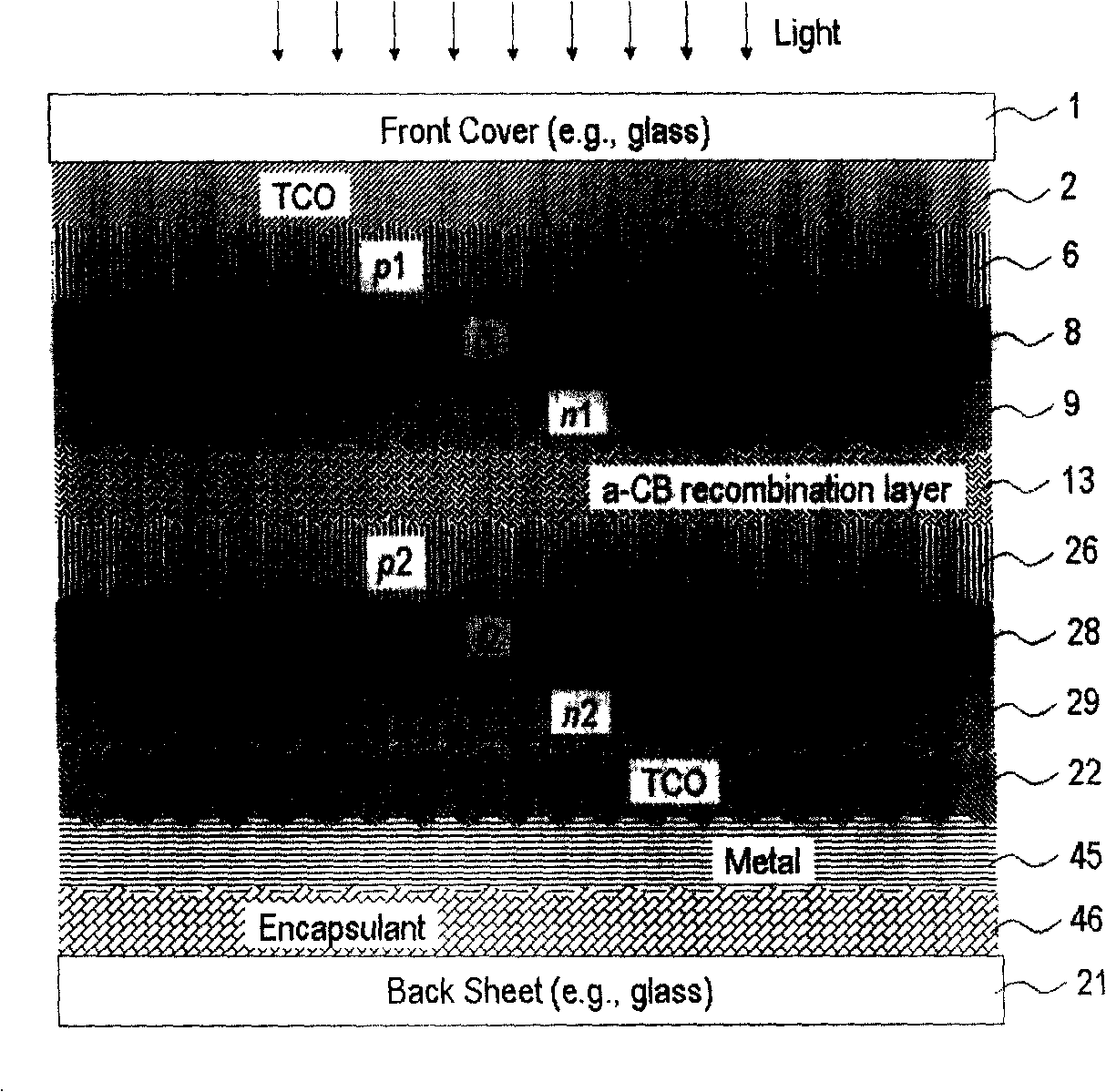
[0034] Multi-junction photovoltaic cells based on silicon thin films are composed of two or more p-i-n photovoltaic units connected with the same optical path and circuit, superimposed on top of each other. Each p-i-n photovoltaic unit is called a junction. The band gap widths of multiple i-layers based on silicon thin films in a multi-junction photovoltaic cell can be the same or different. In order to eliminate resistance or reverse n-p junctions between adjacent photovoltaic cells, multi-junction photovoltaic devices require a composite layer or tunnel junction. To image 3 The double-junction stacked photovoltaic device shown is taken as an example. Two photovoltaic units (top junction and bottom junction) are connected end to end and stacked on top of each other to form an integrated photovoltaic device. The top junction is composed of p1-i1-n1 (6-8-9), the bottom junction is composed of p2-i2-n2 (26-28-29), and there is a composite layer 13 between the two junctions. The othe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com