Process for producing sintered ore
A production method and technology for sintered ore, which are applied in the field of sintered ore production for blast furnaces, can solve the problems of no particle drying, collapse of sintered raw material particles, no drying, etc., and achieve the effects of improving ventilation resistance and reducing the amount of carbon material.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1、2、3
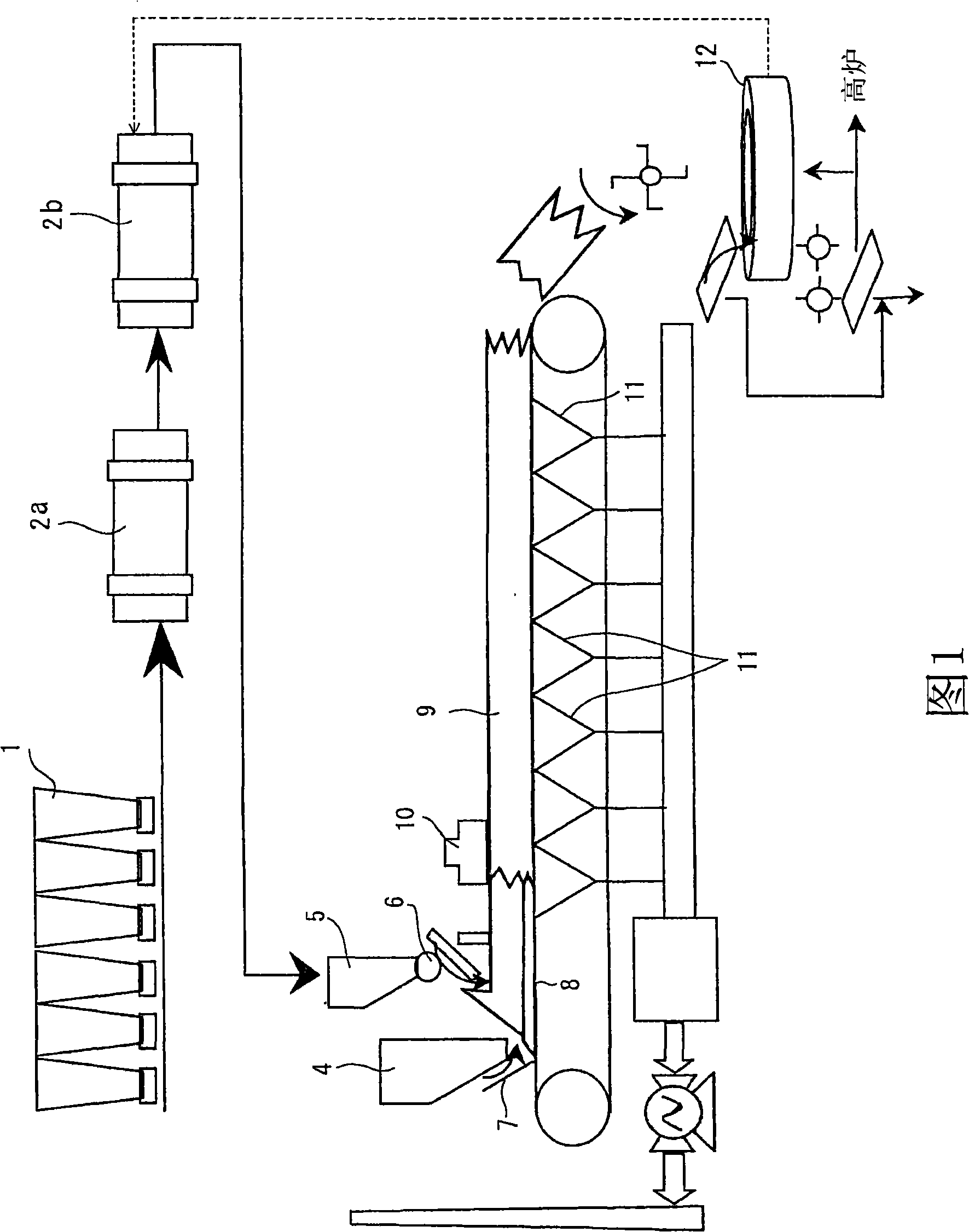
[0157] Invention examples 1 to 3 are application examples suitable for the process of the present invention shown in FIG. 4 . This method is an example of the following: First, between the mixing tumbler mixer 2a and the granulation tumbler mixer 2b, adding characteristics of maintaining granulation strength) and an organic binder having a carboxylic acid group are granulated, and then dried using a rotary kiln 3 for drying. In the above example, the organic binder is added to the mixed sintered raw material particles at the inlet side of the drum mixer (primary mixer) 2b for granulation. Immediately thereafter, in the drum mixer (secondary mixer) 2b for granulation, pseudo particles are formed by the main action of the above-mentioned organic binder, and the pseudo particles are supplied to the rotary kiln 3 for drying.
[0158] The heating medium for drying blown into the furnace from the outlet side of the drying rotary kiln 3 utilizes the exhaust gas supplied from the win...
Embodiment 2
[0163] Under various conditions shown in Table 5, the sintering raw materials were granulated and dried to conduct a sintering experiment. The effect is good when there is no return ore, and the sintering time is also shortened.
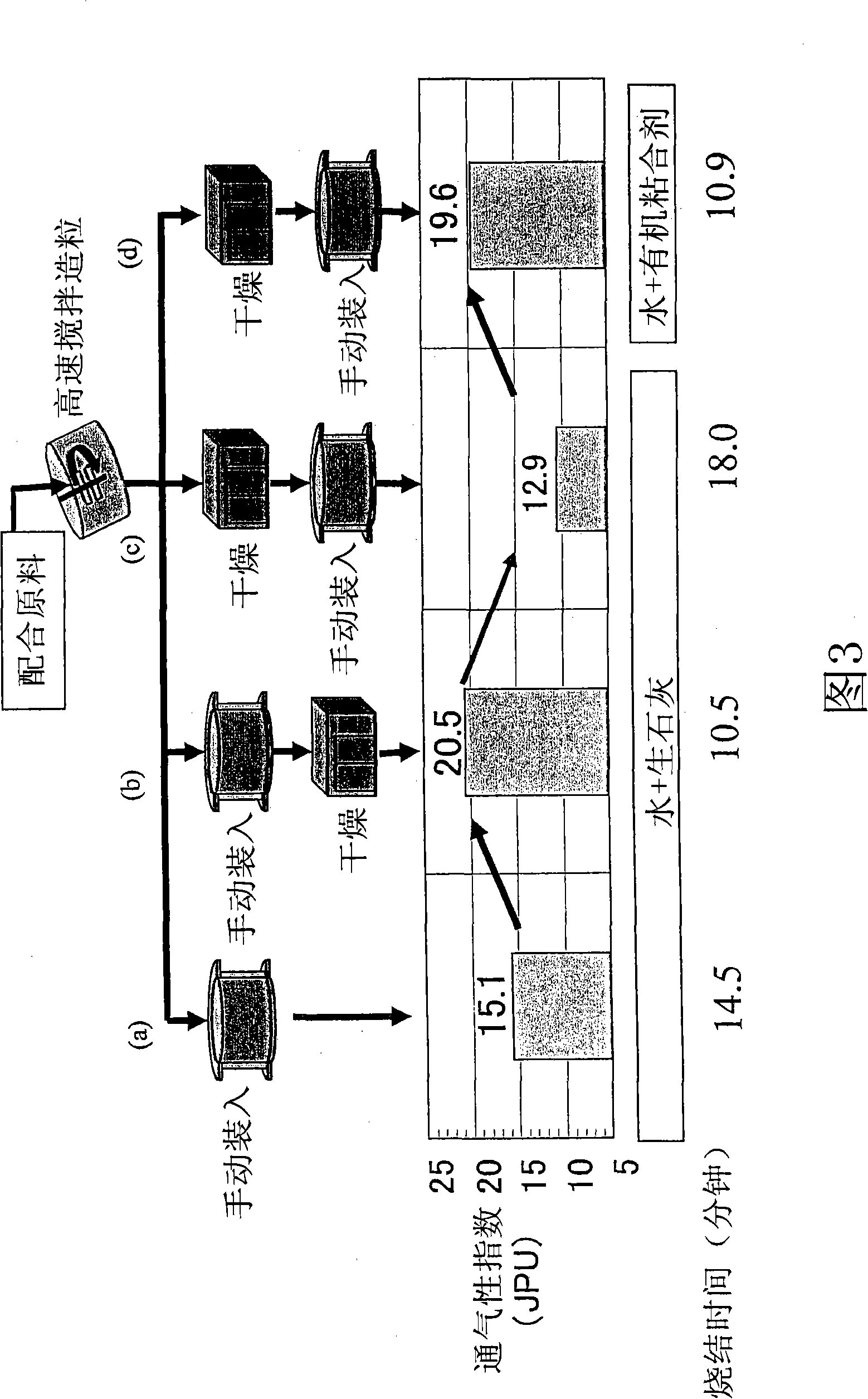
[0164] Fig. 16 shows the following: comparison of the general process A in which water and quicklime are added as binders to the sintered raw materials through a drum mixer without drying and sintered, and the process B in which gum arabic is added in a powder state instead of the quicklime in the above-mentioned general process A As well as process C in which gum arabic is added as an aqueous solution, the effect of the addition method of the organic binder on the sinterability is compared. From this result, it can be seen that the organic binder is preferably directly added in a powder state.
[0165] In addition, FIG. 17 shows the following: In the case of using an organic binder (gum arabic), in order to further observe the influence on the sint...
Embodiment 3
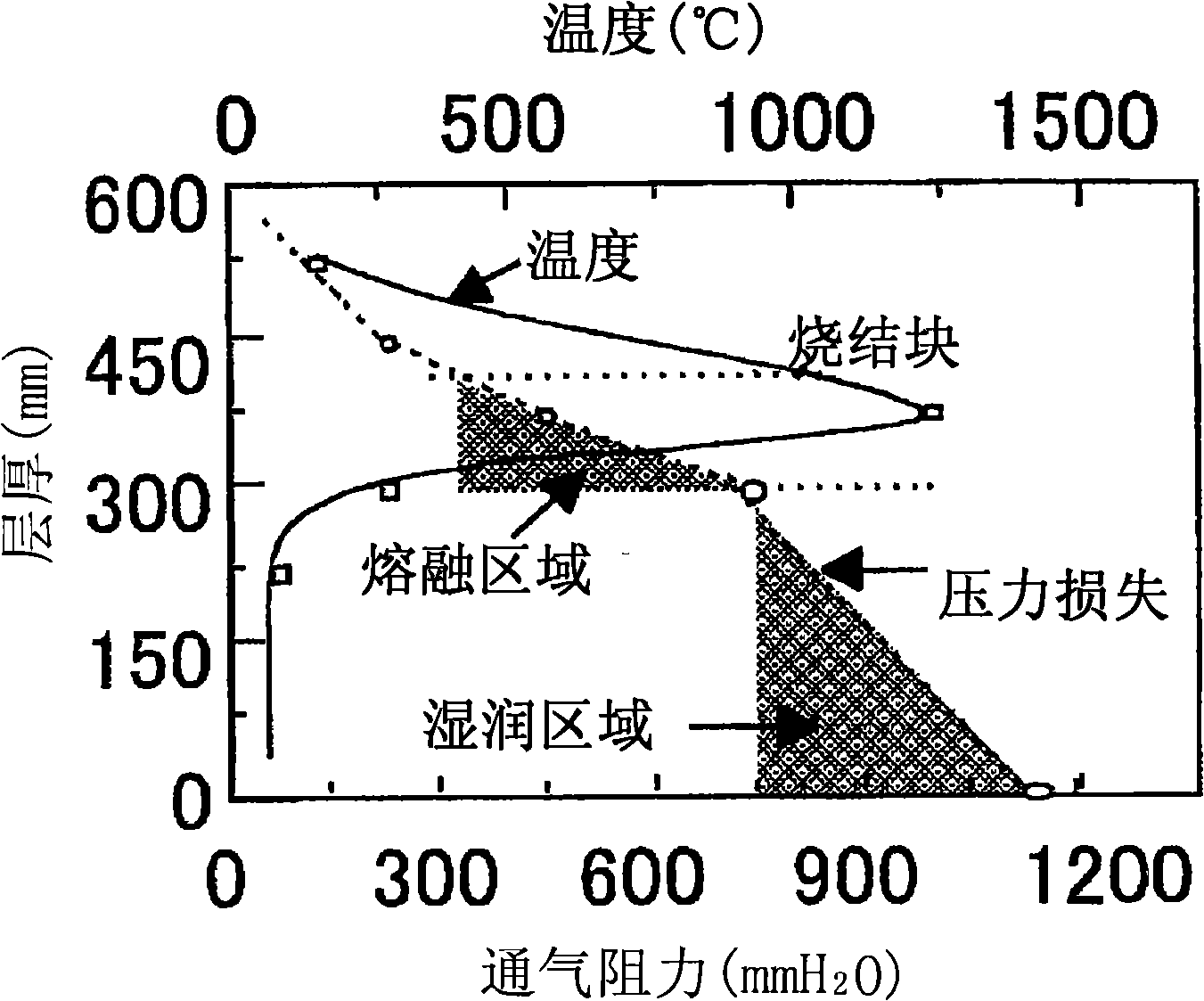
[0169] Under various conditions shown in Table 6, the sintered raw materials were granulated and dried, and the sintering experiment was carried out with a real machine to measure the air volume, sintering time and productivity during sintering, and record the results in Table 6 together. The sintering experiment was carried out under the respective conditions at two levels when the layer thickness was set as the standard 600mm and when it was raised to 900mm. In the sintering machine operation of 600mm, the carbon material was 5.5mass% as a benchmark, and the sintering at 900mm In machine operation, due to the increase of layer thickness, 4.0mass% of carbon material is used as a benchmark.
[0170] Comparative Example 1 is an example using a conventional inorganic binder. The sintering time in the sintering machine operation is 30 minutes when the layer thickness is 600 mm, and the time is only extended by 45 minutes when the layer thickness is 900 mm. .
[0171] On the othe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com