Method for producing sodium carboxymethylcellulose from waste coated paper
A technology of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and coating, applied in papermaking, paper recycling, waste paper processing, etc., to achieve low production costs, realize resource regeneration, and protect the ecological environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
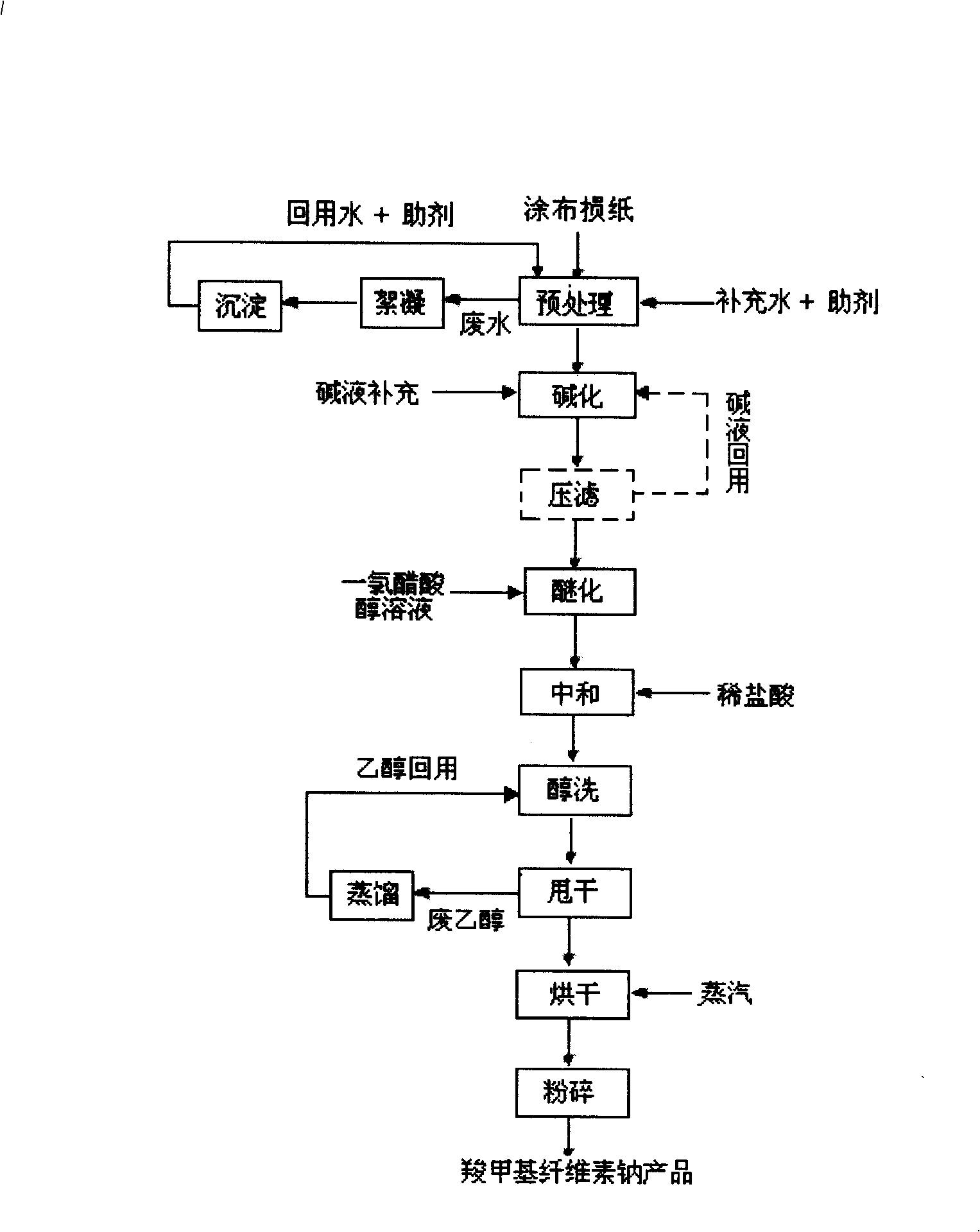
[0025] Take 8.3g of the coated broken paper dry material pretreated by hydrochloric acid, add 100mL of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 18%, stir continuously at room temperature for 45min, filter the alkali cellulose with a filter press, and reuse the filtered alkali solution Add alkali fiber in the reaction flask, add 120mL mass concentration of 95% ethanol and stir, then add 8.9g monochloroacetic acid and 30mL mass concentration of 95% ethanol mixed solution, react at 40°C for 1 After 1 hour, heat up to 75°C and react for 3 hours; adjust the pH value to neutrality with dilute hydrochloric acid; wash three times with ethanol with a mass concentration of 75%, and wash once with ethanol with a mass concentration of 95%; dry the product, and the waste ethanol solution is distilled back to use; finally the product is dried and pulverized.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Take 1Kg of the coated broken paper dry material pretreated by sulfuric acid, add 12L of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 20%, stir continuously at room temperature for 45min, filter the alkali cellulose with a filter press, and reuse the filtered alkali liquor; Add the alkali fiber into the reactor, add 15L of ethanol with a mass concentration of 95% and stir well, then add 14Kg of monochloroacetic acid and 4L of ethanol with a mass concentration of 95%, and react at 40°C for 1.5 hours. Raise the temperature to 75°C and react for 3.5 hours; adjust the pH value to neutral with dilute hydrochloric acid; wash three times with ethanol with a mass concentration of 75%, and wash once with ethanol with a mass concentration of 95%; dry the product, and reuse the waste ethanol solution through distillation; Finally the product is dried and pulverized.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Take 9g of the dry coated broken paper pretreated by hydrochloric acid, add 120mL of 85% alcohol, mix well, add 8g of sodium hydroxide solid, stir continuously at 45°C for 90min, then add 11.5g of monochloroacetic acid and 30mL of mass concentration A solution mixed with 95% ethanol was reacted at 40°C for 1.0 hour, and then heated to 60°C for 3.5 hours; the pH value was adjusted to neutral with dilute hydrochloric acid; washed three times with 75% ethanol at a mass concentration of 95% % ethanol for washing once; the product is dried, and the waste ethanol solution is reused through distillation; finally, the product is dried and pulverized.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com