Phase-change memory
A phase-change memory and phase-change memory technology, which is applied in the field of memory and phase-change memory, can solve problems such as difficult DUMMY resistance, data storage error, and resistance value reduction, so as to reduce the read operation voltage or current, and reduce the chip area , The effect of reducing process deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
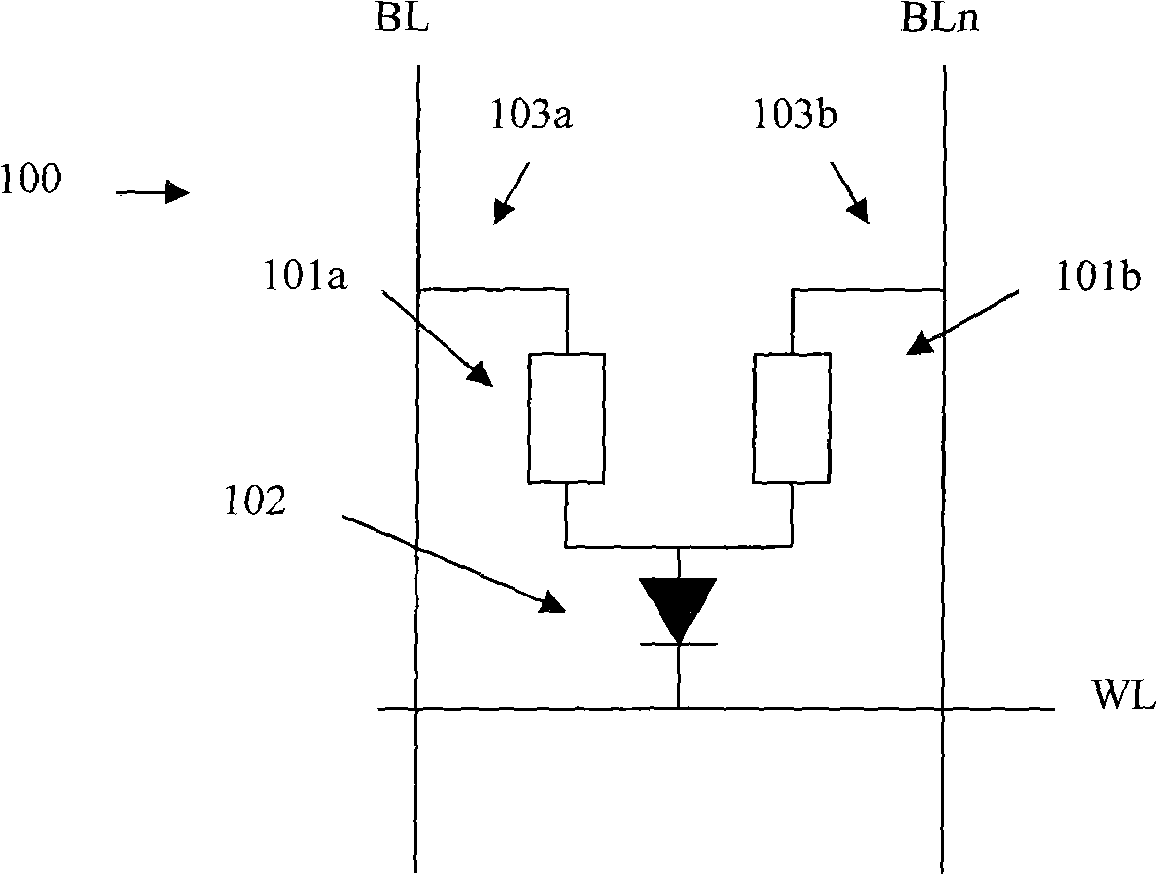
[0031]see figure 1 , figure 2 and Figure 4 , this embodiment introduces a phase change memory 400 in which the storage unit is a 1D2R structure.
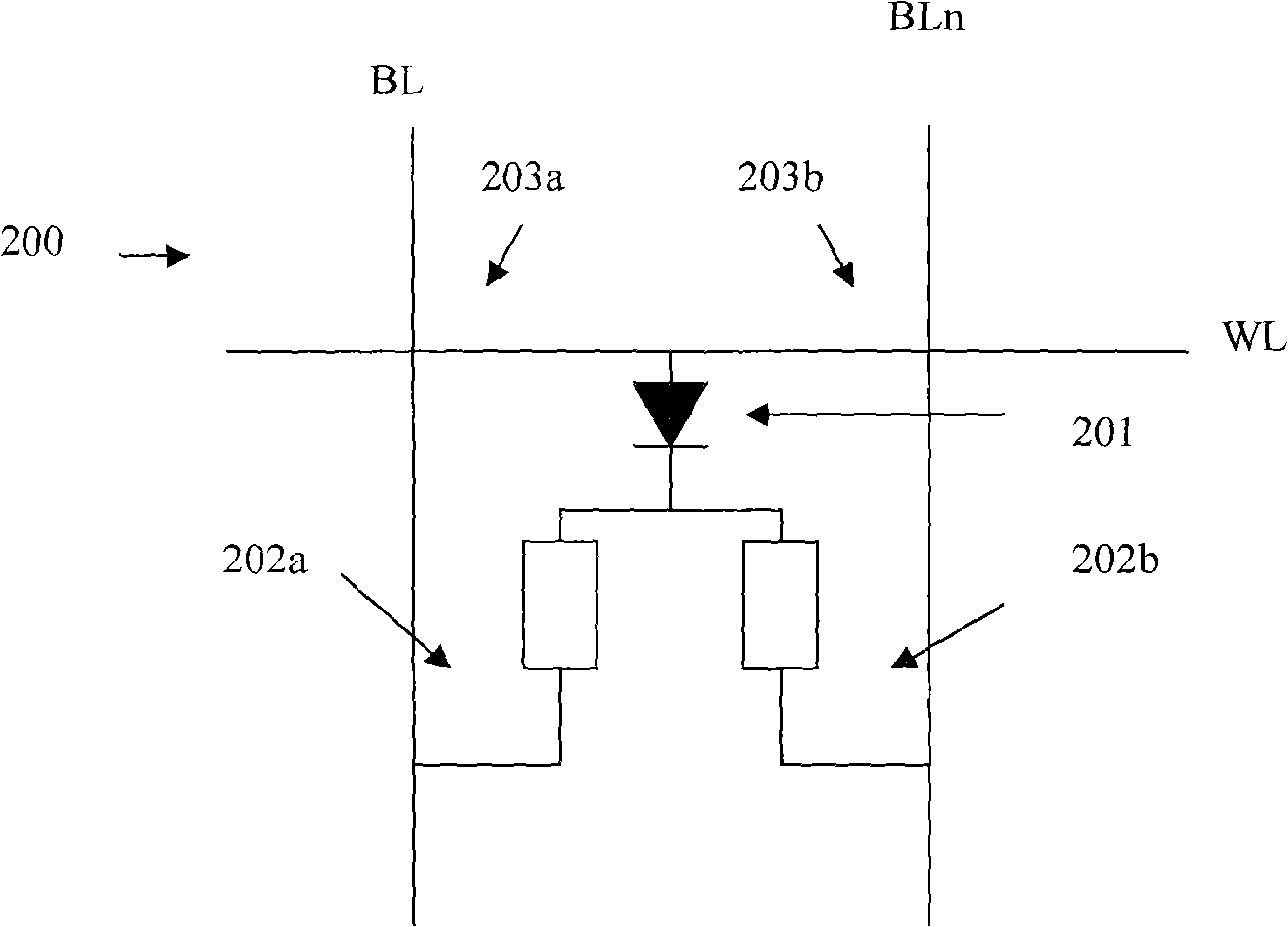
[0032] Firstly, the structure of the storage unit in this embodiment is introduced. Such as figure 1 As shown, the memory cell 100 includes phase change memory cells 101a and 101b, a gate diode 102, phase change material upper electrodes 103a and 103b, a word line WL, and bit lines BL and BLn. Wherein the phase-change memory unit 101a and the phase-change memory unit 101b store two complementary data (so in this embodiment "phase-change memory unit" can also be called "complementary state phase-change unit"), for example, when 101a is "RESET" state, 101b is in the "SET" state, that is, two phase-change units are used to store 1-bit data. In this embodiment, the phase-change memory cells 101a and 101b are connected in parallel and connected to the anode of the gate diode 102 . The storage unit can also be figure 2 The str...
Embodiment 2
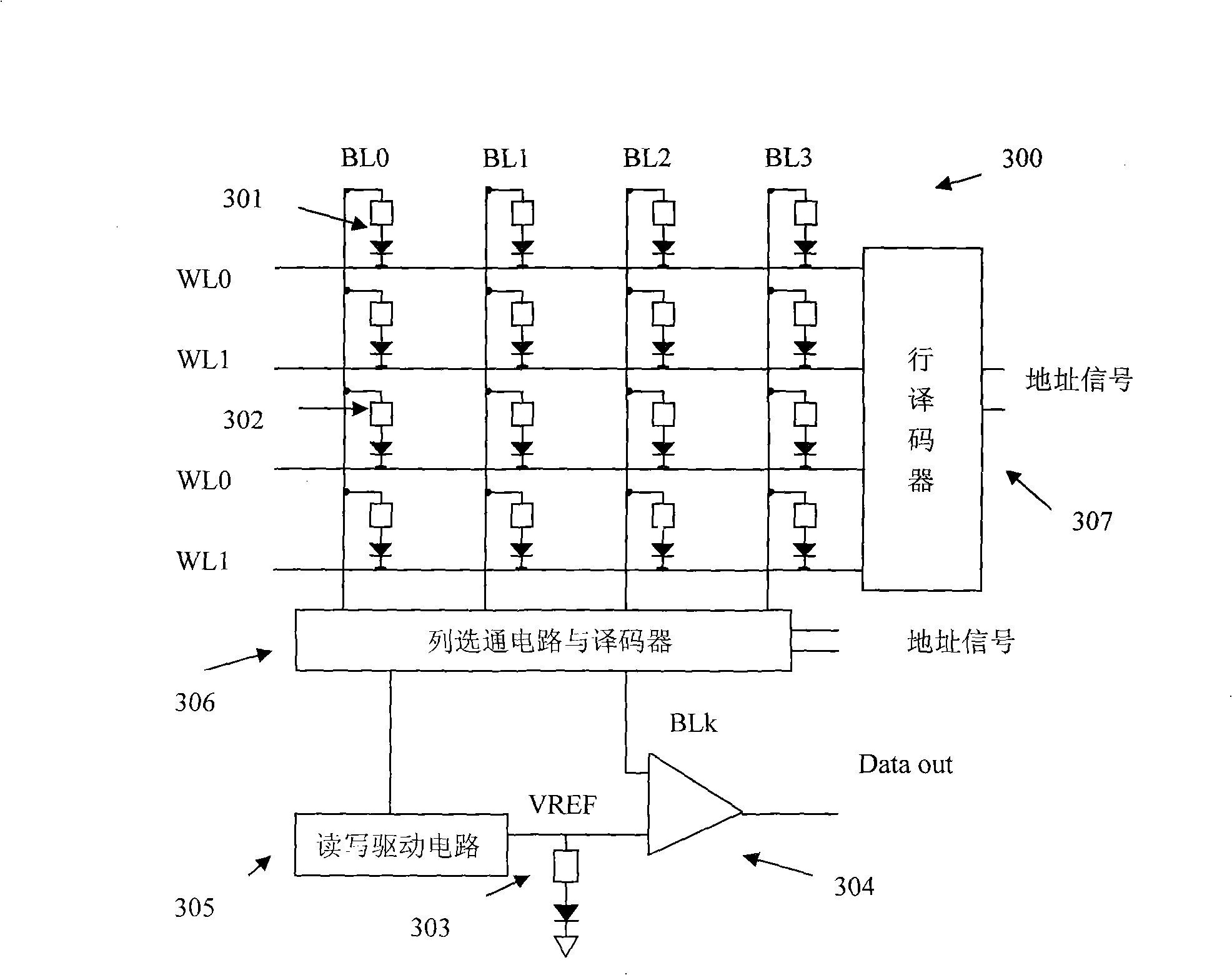
[0040] see Figure 7 , this embodiment introduces a phase change memory 700 in which the storage unit is a 1DnR structure, where n is an integer greater than or equal to 2. In a memory cell with a 1DnR structure, n phase-change resistors share a gate diode to store n-bit data.
[0041] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the present invention discloses a phase-change memory 700, including several storage units 701, a column gate circuit and a decoder 702, a read comparison resistor 703, a sense amplifier 704, a read-write drive circuit 705, and a row decoder 706 . The bit line of each memory cell 701 is connected to the column gate circuit and decoder 702, and the word line of each memory cell 701 is connected to the row decoder 706; the column gate circuit and decoder 702 is connected to the read-write drive circuit 705 and the sense amplifier 704 , and the read-write drive circuit 705 is connected to the sense amplifier 704 through the read comparison resistor 703 . The column g...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that in this embodiment, the number of phase-change memory cells of each memory cell is different or not completely the same. Its implementation principle is the same as that of Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com