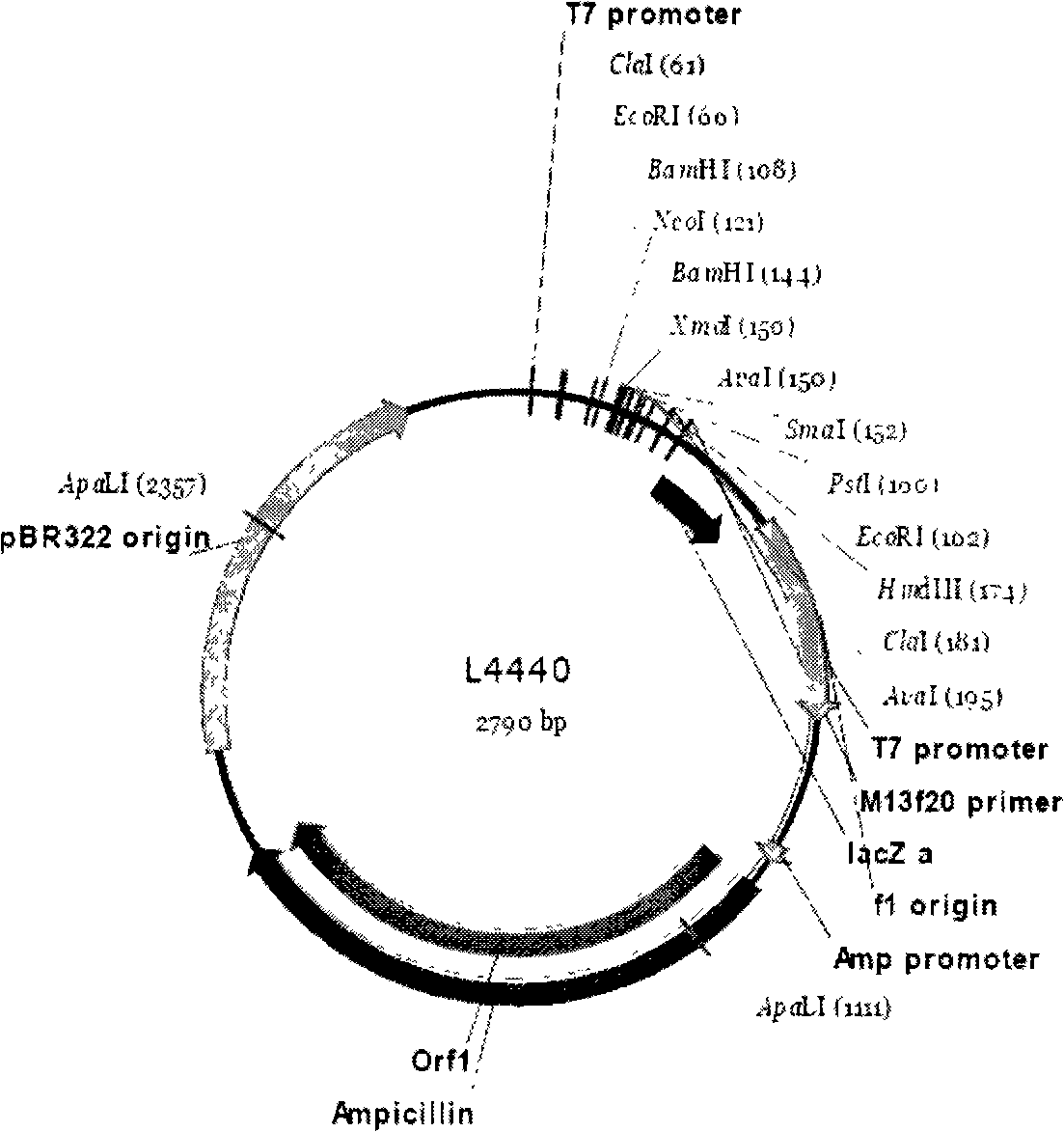
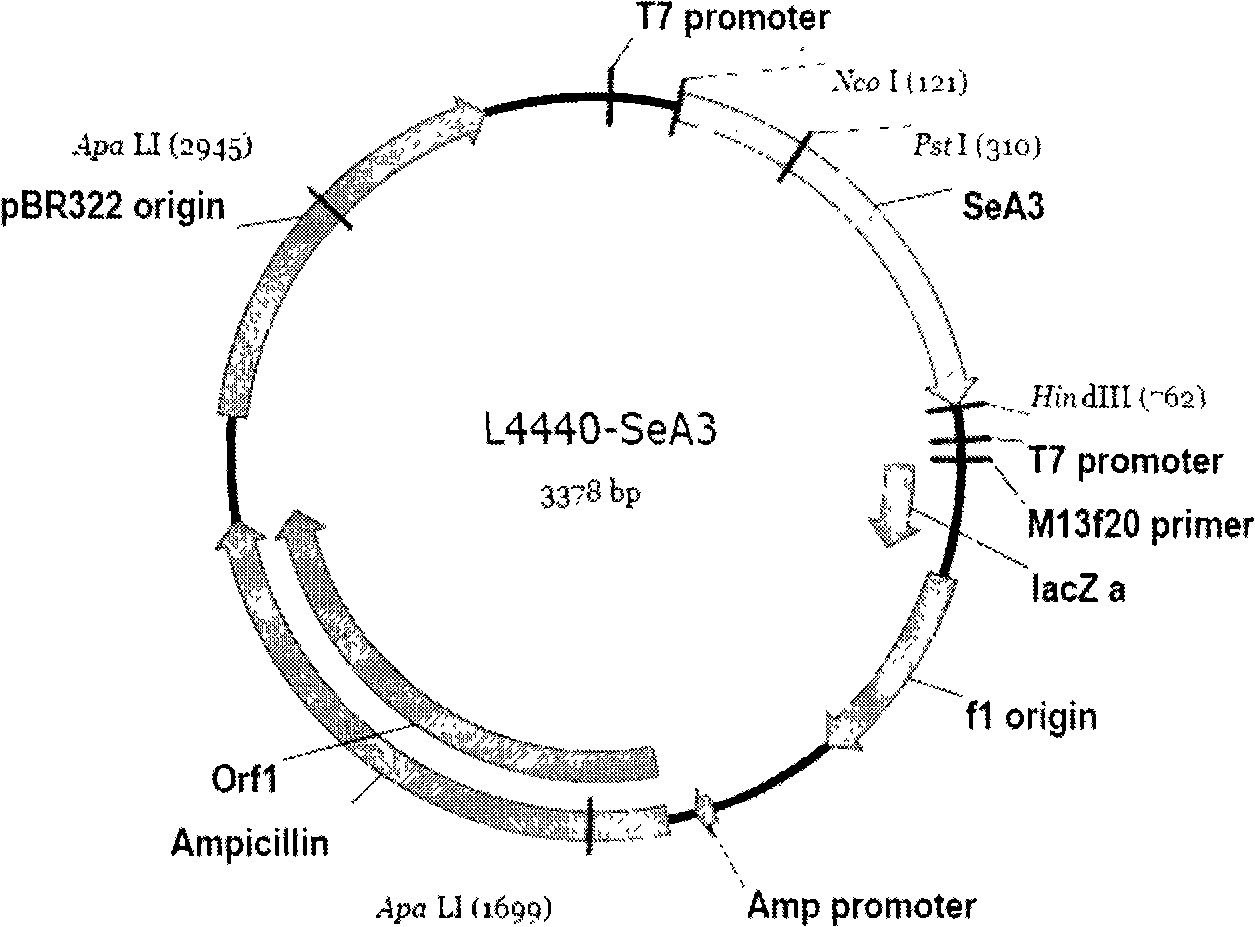
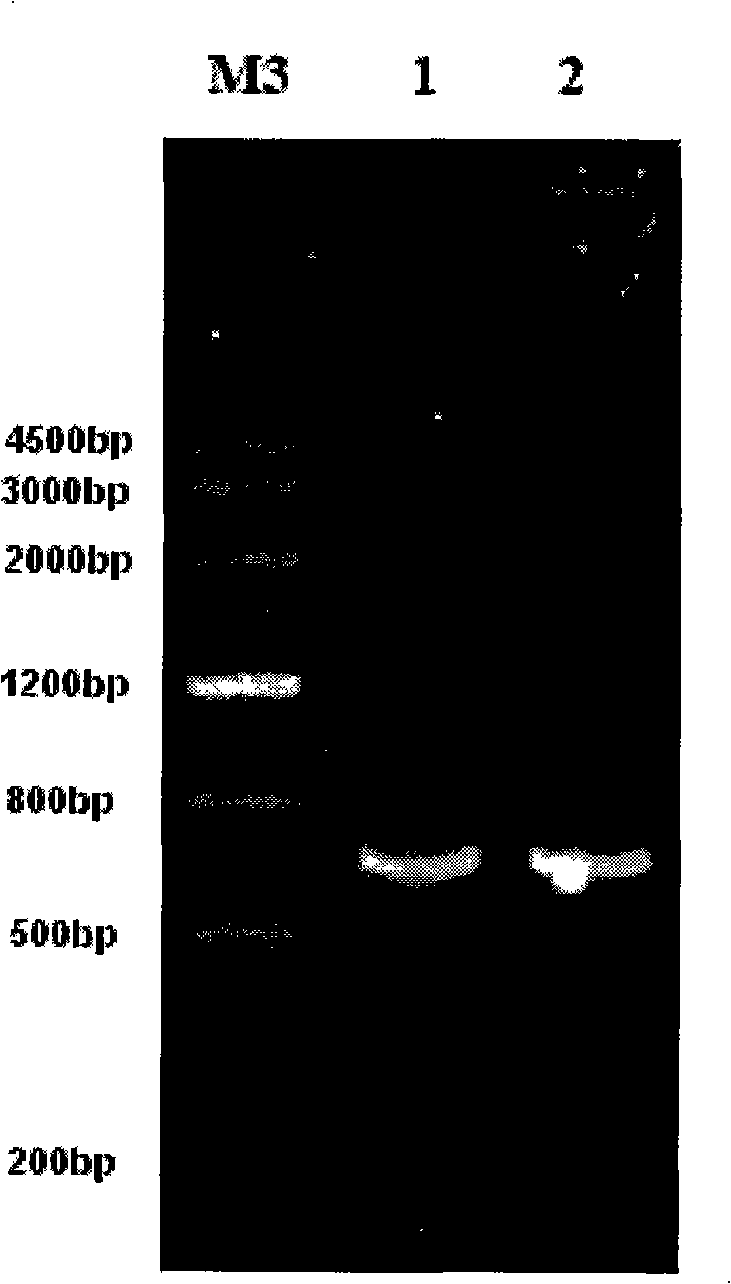Method for feeding dsRNA restraint insect gene expression
A gene expression and insect technology, applied in the field of growth and development regulation of insects, can solve problems such as inability to be directly and widely used, high injection technical requirements, and increased costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Cultivate and prepare the feed that has expressed dsRNA, that is, L4440-SeA3. At the same time, prepare a comparison feed with the same amount of empty vector L4440, and the same amount of deionized water ddH 2 O prepared feed, divided into three contrast groups and fed three batches of larvae of the same fourth instar beet armyworm respectively.
[0054] The specific instructions are as follows:
[0055] Step 1: Acquisition of the SeA3 target gene fragment
[0056] Considering that the insect chitin synthase gene is the key enzyme that catalyzes the formation of chitin in insects, this example selects the chitin synthase gene SeCHS-A, and selects a specific gene segment on the SeCHS-A gene SeA3 is a dsRNA fragment with a specific function. The length of the target gene of the dsRNA fragment SeA3 is 635bp, and its gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO1 (Appendix 2 of the Sequence List).
[0057] Get the fifth instar larvae of beet armyworm and use the Trizol method (Lif...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2: The effect of feeding htLSA3 on the growth and development of beet armyworm
[0080] Adopt the same steps as the first three steps of Example 1. The methods for inducing the expression of SeA3dsRNA and enriching the bacterial solution are the same as the fourth step of Example 1. Beet armyworm larvae were fed daily in the same manner as in Example 1, using third instar beet armyworm larvae. htLSA3 treatment group and L4440, ddH 2 O control group has 35 test worms in each group, single feeding, counting the survival rate every day, and observing and recording the phenotype until the time of pupation.
[0081] After feeding Escherichia coli htLSA3 expressing SeA3dsRNA, the larvae of beet armyworm mainly showed that they could not molt normally at the beginning of each instar, and the skin molted to half of the body. Figure 7 As shown, they finally died because they could not complete the molting; before pupation, they showed that the prepupa could not molt ...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Example 3: Effects of Feeding htLSA3 on Growth and Development of Spodoptera litura
[0087] Adopt the same steps as the first three steps of Example 1. The methods for inducing the expression of SeA3dsRNA and enriching the bacterial solution are the same as the fourth step of Example 1. Spodoptera litura larvae were fed daily in the same manner as in Example 1, using third instar larvae of Spodoptera litura. Also set htLSA3 processing group and L4440, ddH 2 O control group has 35 test worms in each group, single feeding, counting the survival rate every day, and observing and recording the phenotype until the time of pupation.
[0088] After feeding Escherichia coli htLSA3 expressing SeA3dsRNA, the larvae of Spodoptera litura mainly showed that they could not complete the molting normally at the beginning of each instar, and the skin molted to a small part or half of the body, and finally died because they could not complete the molting; It also shows that the prepu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com