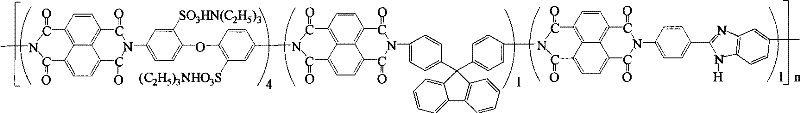
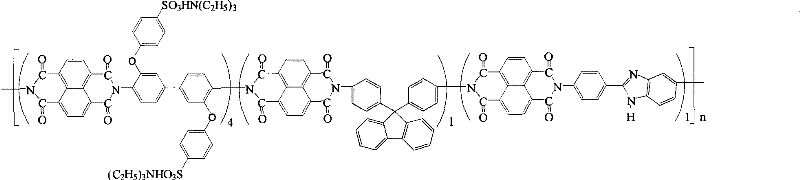
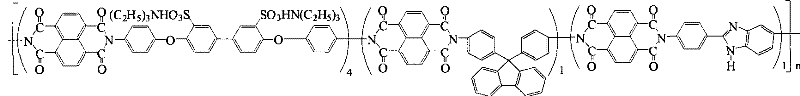
Preparation of glyoxalinyl-containing sulphonation polyimides covalence-ionomer membrane
A technology based on sulfonated polyimide and sulfonated polyimide membrane, which is applied in the field of polymer membrane preparation, can solve the problems of poor compatibility, low proton conductivity, loss, etc., and achieve water resistance and mechanical properties Good, high proton conductivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Add 1.44 g (4.0 mmol) of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether-2,2'-disulfonic acid (English abbreviation: ODADS) to a dry 100 mL three-neck flask equipped with a condenser tube and a nitrogen inlet and outlet , 0.348 grams (1.0mmol) 9,9-two (4-aminophenyl) fluorene (English abbreviation: BAPF), 0.224 grams (1.0mmol) 2- (4-aminophenyl) -5-aminobenzimidazole (English abbreviation name: APABI), 25mL m-cresol and 1.4mL triethylamine. After all the diamine monomers were completely dissolved, 1.608 g (6.0 mmol) of 1,4,5,8-naphthalene dioic anhydride (English abbreviation: NTDA) and 1.04 g of benzoic acid were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 0.5 hours, then heated to 80°C for 4 hours, and then heated to 180°C for 20 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was cooled, and then slowly poured into 250 mL of acetone to obtain a filamentous precipitate. Filter, wash with acetone, dry under vacuum condition, obtain imidazole-containing sulfonated pol...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 2.112 grams (4.0 mmol) of 3,3-bis(4-sulfonic acid phenoxy)benzidine (English abbreviation: BSPOB) to a dry 100 mL three-necked bottle equipped with a condenser tube and a nitrogen inlet and outlet, 0.348 Gram (1.0mmol) 9,9-bis(4-aminophenyl) fluorene (English abbreviation: BAPF), 0.224 gram (1.0mmol) 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole (English Abbreviated name: APABI), 30 mL m-cresol and 1.22 mL triethylamine. After the diamine monomer was completely dissolved, 1.608 g (6.0 mmol) of 1,4,5,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride (English abbreviation: NTDA) and 1.04 g of benzoic acid were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 0.5 hours, then heated to 80°C for 4 hours, and then heated to 180°C for 20 hours. After the reaction, the reaction system was cooled and 20 mL of m-cresol was added to dilute the highly viscous mixture, and then the diluted liquid was slowly poured into 300 mL of acetone to obtain a fibrous precipitate. Filter, wash...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Add 2.112 grams (4.0 mmol) of 4,4'-bis(4-aminophenoxy)biphenyl-3,3'-disulfonic acid ( English abbreviation name: BAPBDS), 0.348 grams (1.0mmol) 9,9-two (4-aminophenyl) fluorene (English abbreviation name: BAPF), 0.224 grams (1.0mmol) 2-(4-aminophenyl)- 5-aminobenzimidazole (English abbreviation name: APABI), 30 mL of m-cresol and 1.22 mL of triethylamine. After the diamine monomer was completely dissolved, 1.608 g (6.0 mmol) of 1,4,5,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride (English abbreviation: NTDA) and 1.04 g of benzoic acid were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 0.5 hours, then heated to 80°C for 4 hours, and then heated to 180°C for 20 hours. After the reaction, the reaction system was cooled and 20 mL of m-cresol was added to dilute the highly viscous mixture, and then the diluted liquid was slowly poured into 300 mL of acetone to obtain a fibrous precipitate. Filter, wash with acetone, and vacuum dry to obtain imidazole-containing sul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com