Copolymer of fibroin and poly L-lactic acid, solid phase polymerization preparation method and application thereof
A technology of silk protein and solid-state polymerization, which is applied in the field of copolymers of silk protein and poly-L-lactic acid and its preparation, can solve the problems of no research reports, etc., and achieve the effects of simple process, short production cycle and low product cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
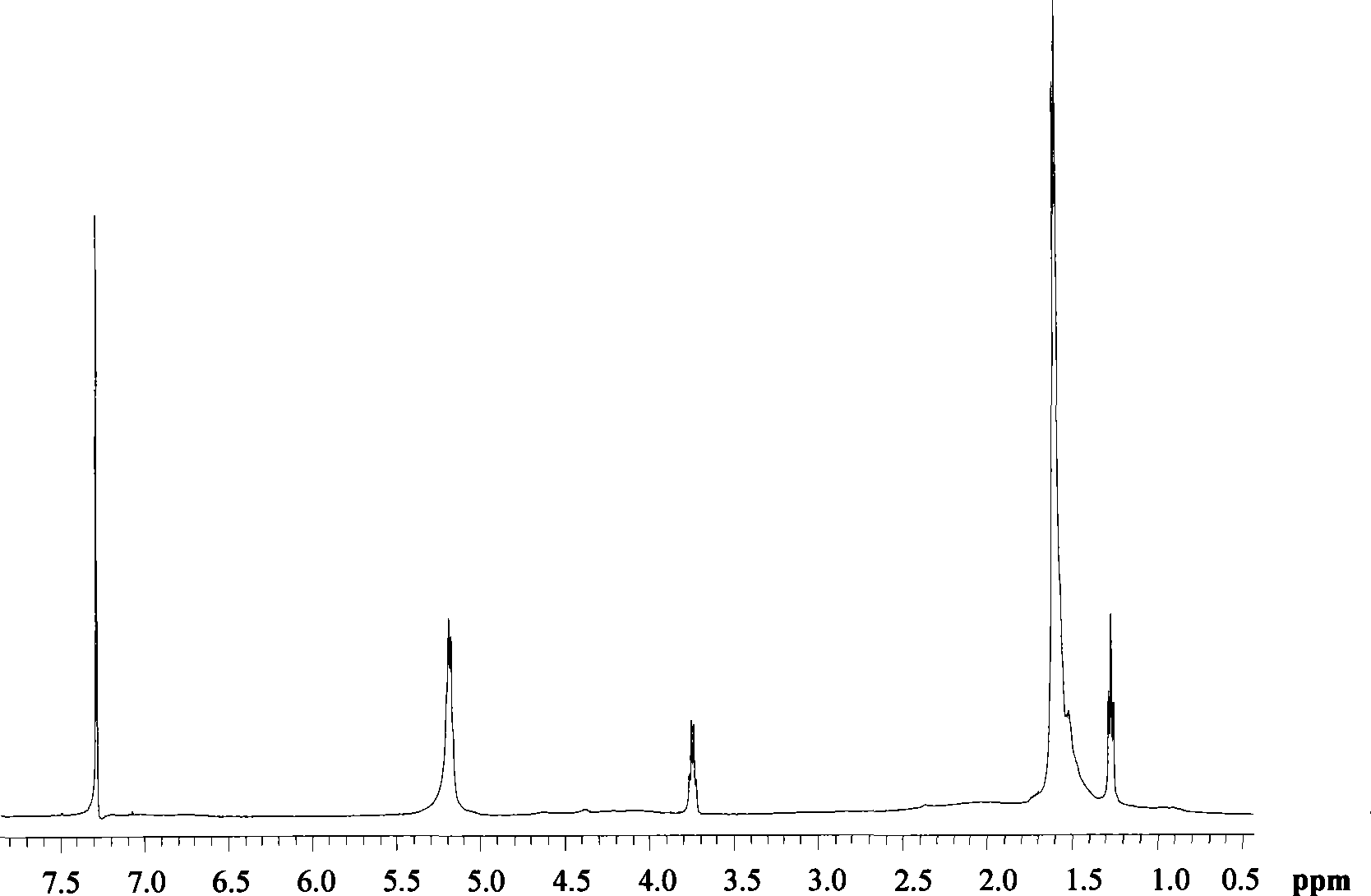
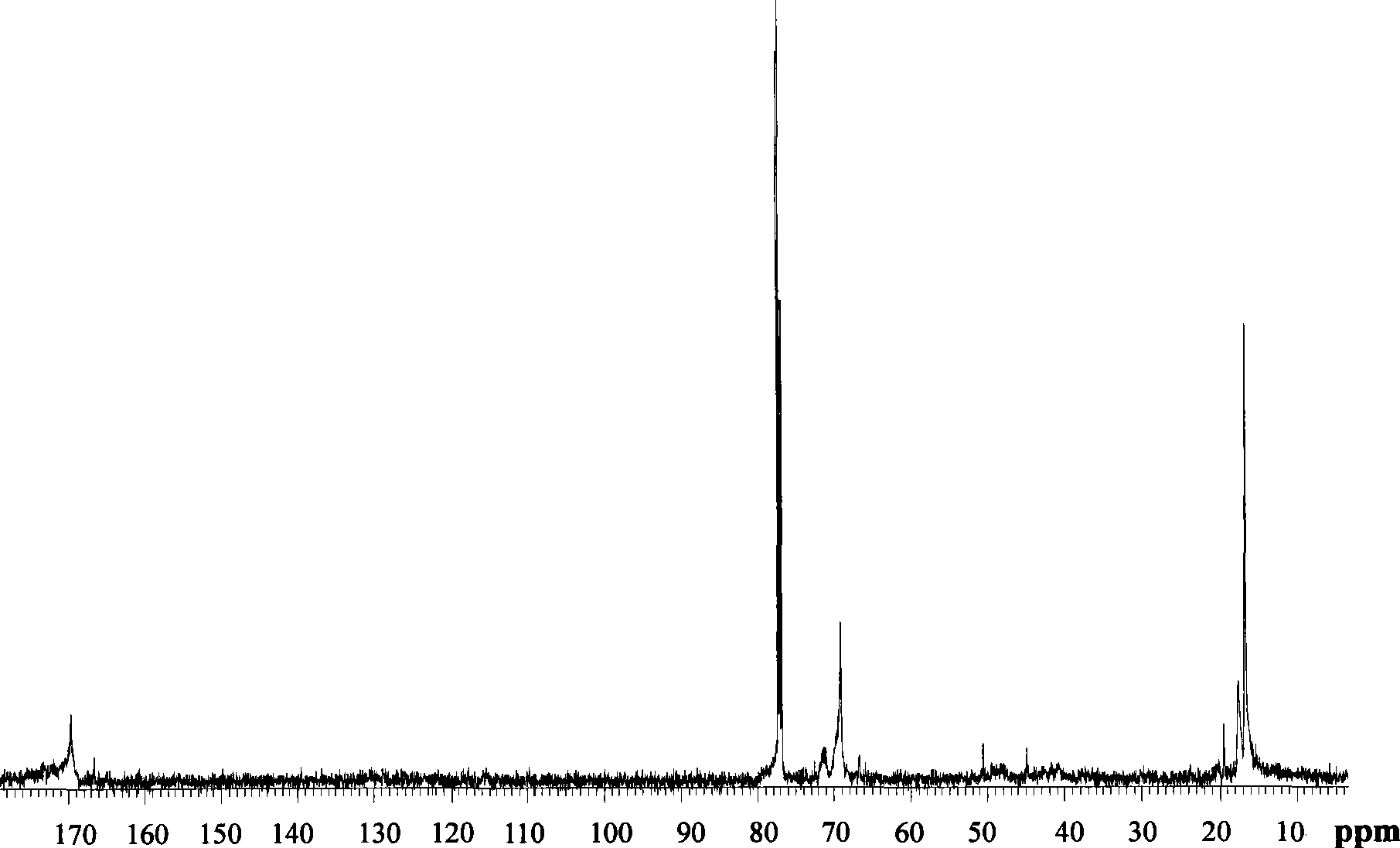
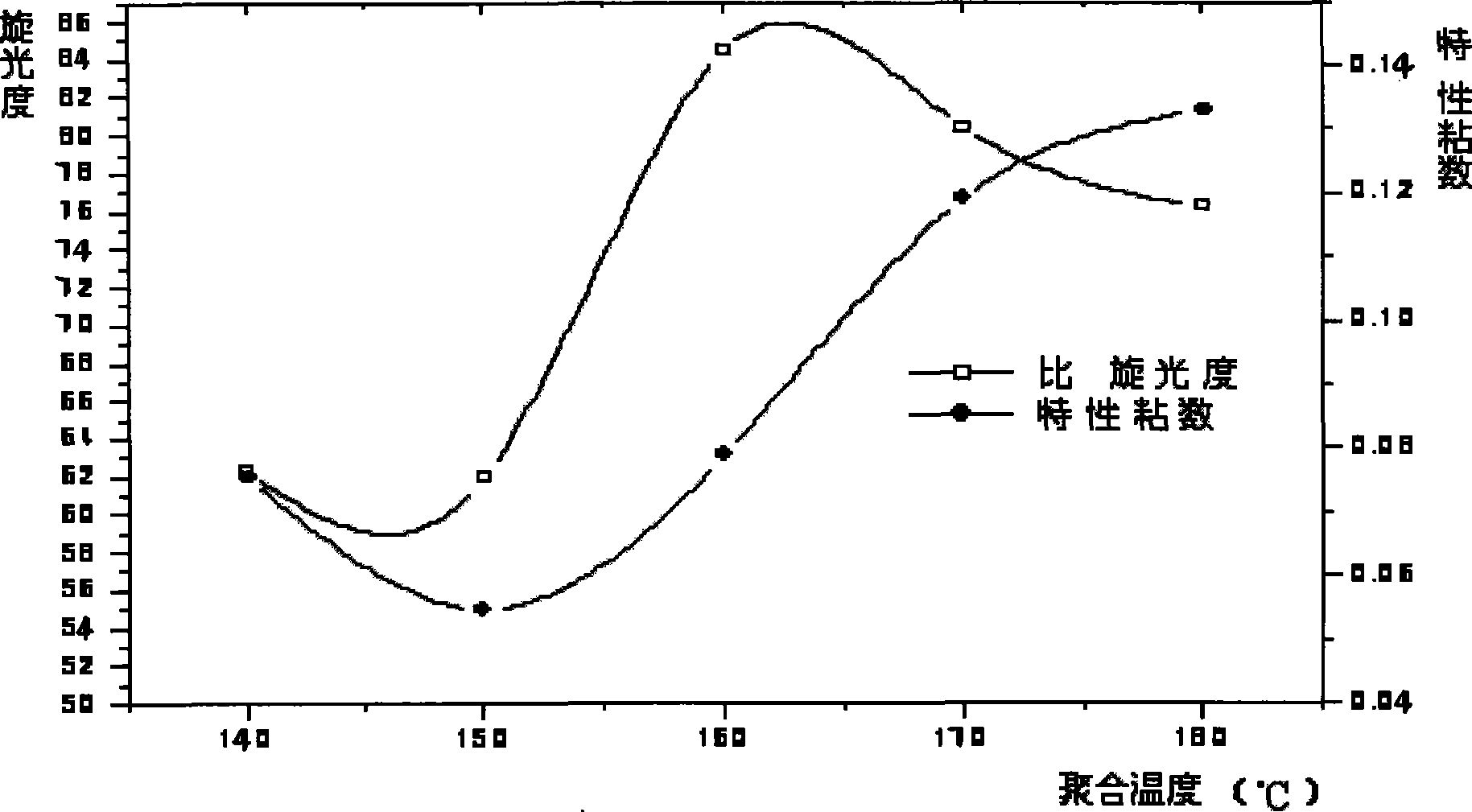
[0051] Add 90% aqueous solution of L-lactic acid into the reaction kettle, dehydrate at 180°C, first dehydrate under normal pressure for 4 hours, then depressurize to 100 mmHg for 4 hours, and finally dehydrate at 10 mmHg for 6 hours to obtain the molecular weight 2000 L-lactic acid oligomers.
[0052] After dehydration, the SnCl 2 2H 2 O / p-toluenesulfonic acid catalyst system (SnCl 2 2H 2 The molar content of O accounts for 50% of the entire catalyst system) into the prepolymer, SnCl 2 2H 2 The amount of O used is 0.4 wt% of the L-lactic acid oligomer. The pressure of the system was gradually reduced to 0 mmHg (manometer reading), and the reaction temperature was raised to 200° C. to carry out the polymerization reaction. As the reaction progressed, lactide monomers began to appear and reflux, the temperature of the condensing reflux device was controlled at 90°C, and the reactant gradually became viscous. The polymerization reaction was stopped after 4 hours to obtain...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Add 85% aqueous solution of L-lactic acid into the reaction kettle and dehydrate at 140°C. First dehydrate the mixed monomers under normal pressure for 1 hour, then reduce the pressure to 100 mmHg for 4 hours, and finally dehydrate for 1 hour at 50 mmHg to obtain L-lactic acid oligomers with a molecular weight of 500.
[0057] After dehydration, the SnCl 2 / p-toluenesulfonic acid catalyst system (SnCl 2 The molar content accounts for 1% of the entire catalyst system) is added to the prepolymer, SnCl 2The dosage is 0.01wt% of the L-lactic acid oligomer. The pressure of the system was gradually reduced to 1 mm Hg, the reaction temperature was raised to 180° C., and the condensing reflux temperature was 50° C. to carry out the polymerization reaction. As the reaction progressed, the lactide monomer was produced and began to reflux, and the reactant gradually became viscous. The reaction time was 20 hours to obtain poly-L-lactic acid with a molecular weight of 13,000. ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Add 90% aqueous solution of L-lactic acid into the reaction kettle, and dehydrate at 150°C. First dehydrate the monomer under normal pressure for 2 hours, then reduce the pressure to 150 mmHg for 2 hours, and finally dehydrate for 6 hours at 10 mmHg to obtain L-lactic acid oligomers with a molecular weight of 1500.
[0062] After dehydration, the SnCl 2 2H 2 O / octanoic acid catalyst system (SnCl 2 2H 2 The molar content of O accounts for 60% of the entire catalyst system) into the prepolymer. SnCl 2 2H 2 The amount of O used is 0.80 wt% of the L-lactic acid oligomer. The pressure of the system was gradually reduced to 10 mm Hg, the reaction temperature was 180° C., and the condensation reflux temperature was 20° C. As the reaction progressed, lactide monomers began to appear and reflux, and the reactant gradually became viscous. The reaction was stopped after 25 hours to obtain poly-L-lactic acid with a molecular weight of 18,000.
[0063] Then add silk protein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com