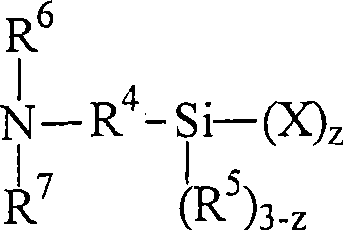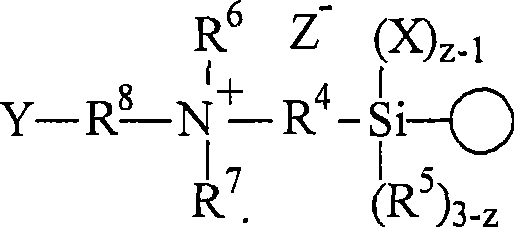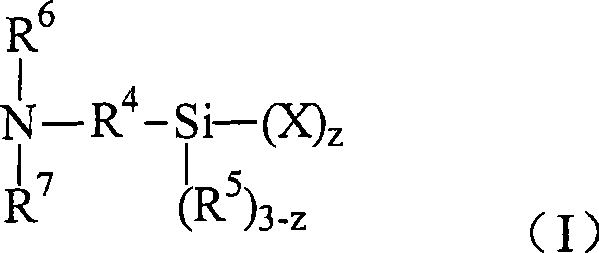Method for nanoparticle surface modification
A nanoparticle and surface modification technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanostructure manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as defects in the physical properties of nanoparticles, achieve efficient processing and adaptability, reduce nanoparticle aggregation, and reduce separation processing Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0074] All solvents and reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company, Milwaukee, WI, unless otherwise noted. Nalco 2326 colloidal silica, commercially available from Nalco Chemical Company (Bedford Park, Illinois, USA). All percentages and amounts are by weight unless otherwise indicated.
[0075] Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy was performed using a 400 MHz Varian NOVA solid state photometer (Palo Alto, CA, USA). Load the sample into a 5mm rotor. Use a 5mm MAS NMR probe to collect 15 N and 13 C CP / MAS. 15 The N spectrum takes liquid ammonia as the reference, and the second reference is 15 N-labeled glycine. The quaternary peak at 55 ppm and the tertiary peak at 45 ppm were used to determine the degree of quaternization.
[0076] Preparation of N-trimethoxysilylpropyl-N,N-dimethylbutylammonium bromide : N,N-dimethylaminopropyltrimethoxysilane (10 g; Gelest, Inc., Morrisville, Pennsylvania, USA), and dissolved in diethyl ether (50 g; butyl bromid...
example 1
[0080] A mixture of Nalco 2326 colloidal silica (100 g), N,N-dimethylaminopropyltrimethoxysilane (5.88 g) and 1-methoxy-2-propanol (117.5 g) was prepared in a Mix in a 3 neck round bottom flask with a mechanical stirrer at 80°C for 1 hour. Lauryl chloride (5.8 g) dissolved in 1-methoxy-2-propanol (20 g) was added to the mixture, which was then stirred at a temperature of 80°C for a further 18 hours. The surface-modified nanoparticles (15.03 g) were then isolated by drying in an oven at 130°C. The surface-modified nanoparticles are soluble in water at levels greater than 20% by weight, resulting in clear solutions with no increase in solution viscosity. according to 15 N NMR spectroscopy showed that the quaternization of the amine was greater than 20%.
example 2
[0082]A mixture of Nalco 2326 colloidal silica (100 g), N,N-dimethylaminopropyltrimethoxysilane (5.88 g) and 1-methoxy-2-propanol (117.5 g) was prepared using a mechanical Mix in a stirrer 3 neck round bottom flask at 80°C for 1 hour. To the mixture was added butyl bromide (3.88 g) dissolved in 1-methoxy-2-propanol (20 g) and stirring was continued for an additional 18 hours while maintaining the reaction temperature at 80°C. The surface-modified nanoparticles (22.3 g) were then isolated by drying in an oven at 130°C. The surface-modified nanoparticles are soluble in water at levels greater than 20% by weight, resulting in clear solutions with no increase in solution viscosity. The surface-modified nanoparticles are soluble in water at levels greater than 20% by weight, and the resulting solution has no increase in solution viscosity. according to 15 N NMR spectroscopy showed that the quaternization of the amine was greater than 20%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com