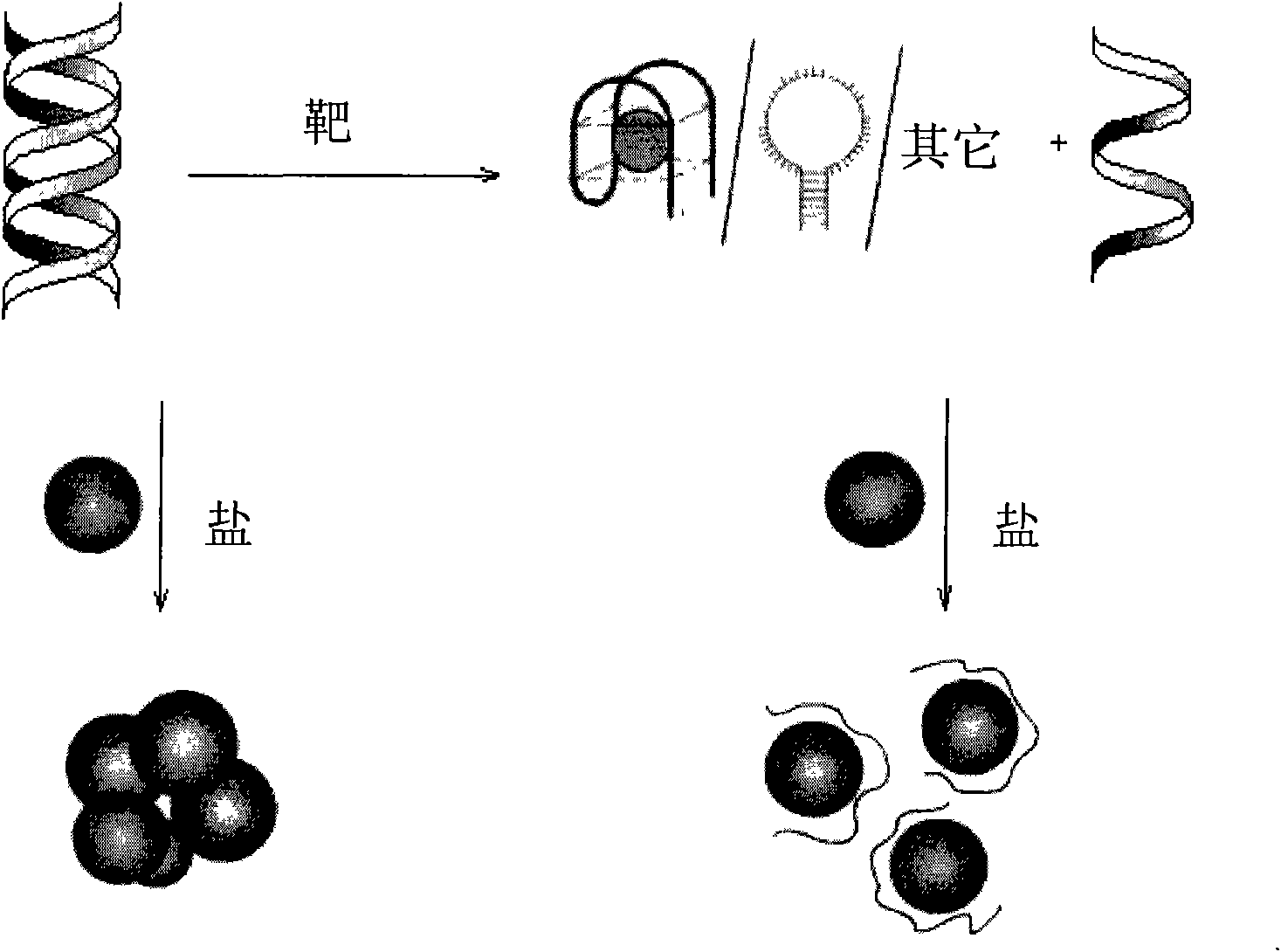
Target molecule detection method based on nano-Au and nucleic acid structure
A detection method and technology of target molecules, which are applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and material analysis by observing the effect on chemical indicators, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable applications, and achieve the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The detection of embodiment 1 thrombin
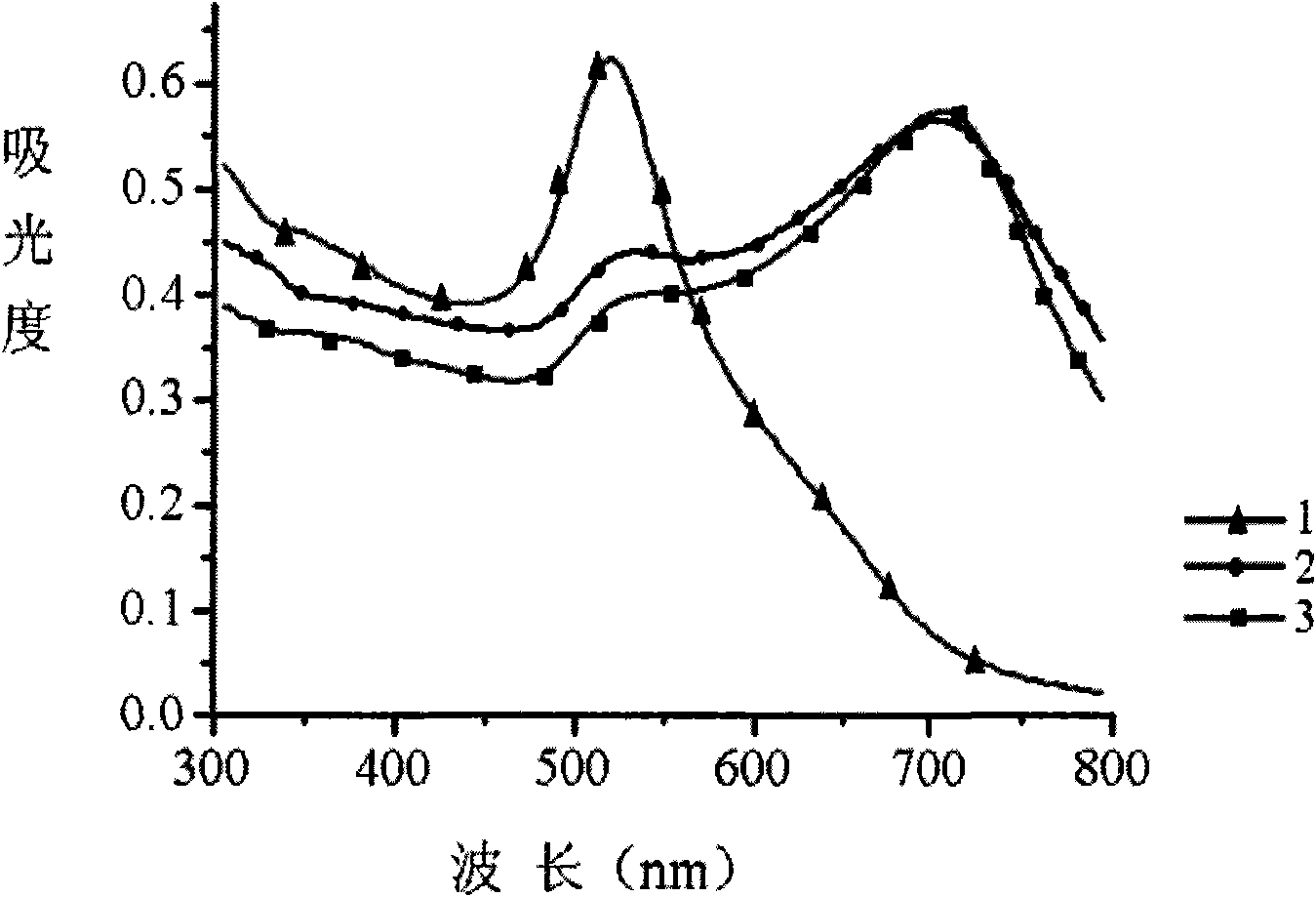
[0042] Steps: Take 2 μL of thrombin aptamer solution with a concentration of 100 μM and 2 μL of a cDNA solution with a concentration of 100 μM, and add 18 μL of buffer solution (20 mM Tris-acetic acid, pH 7.4, 140 mM NaCl, 1 mM CaCl 2 , 1 mM MgCl 2 ), react at room temperature for 30 min to fully hybridize to form double-stranded probes. Then, 2 μL of an aqueous solution of thrombin with a concentration of 0.1 mM was added to the hybridization solution, and the mixture was reacted for 30 min at room temperature to allow a sufficient reaction. At the same time, a group in which 2 μL of water was added without thrombin was used as a blank experiment. And a group to which 2 μL of 1 mM BSA was added was used as a control. Then, 2 μL of the above reaction solution was added to 100 μL of the gold nano-solution (13 nm, 3.5 nM) prepared above, and the molar number of DNA was controlled to be about 50 times that of the gold nano-partic...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The detection of embodiment 2 lysozyme
[0045] Steps: take 2 μL of lysozyme aptamer solution with a concentration of 100 μM and 2 μL of a cDNA solution with a concentration of 100 μM, add 18 μL of buffer solution (10 mM PB, pH 7.0, 0.2M NaCl), and react at room temperature for 30 minutes to make it Sufficient hybridization is performed to form double-stranded probes. Then, 2 μL of an aqueous solution of lysozyme with a concentration of 0.01-1 mM was added to the hybridization solution, and the mixture was reacted at room temperature for 30 minutes to allow a sufficient reaction. At the same time, a group without adding lysozyme and adding 2 μL of water was used as a blank experiment. And a group to which 2 μL of 1 mM BSA was added was used as a control. Then, 2 μL of the above reaction solution was added to 100 μL of the gold nano-solution (13 nm, 3.5 nM) prepared above, and the molar number of DNA was controlled to be about 50 times that of the gold nano-particles. ...
Embodiment 3 2
[0047] The detection of embodiment 3 divalent mercury ions (one)
[0048] Steps: Take 2 μL of MSO (oligonucleotide specifically binding to mercury ions) solution with a concentration of 100 μM and 2 μL of a cDNA solution with a concentration of 100 μM, respectively, and add 18 μL of buffer solution (10 mM arsinic acid-sodium arsinic acid, pH 6.8, 0.3M NaCl), react at room temperature for 30 min to fully hybridize to form double-stranded probes. Then add 2 μL of 0.01 mM Hg to the hybridization solution 2+ aqueous solution, and reacted at room temperature for 5 minutes to make it fully reacted. without adding Hg 2+ , add 2 μL of water to a group as a blank experiment. In addition, selectivity analysis was carried out through two groups of experiments, one group added 2 μL of 25 mM Ca 2+ , Mg 2+ The other group added 0.5mM mixed ions (Fe 2+ , Cu 2+ ,Co 2+ , Mn 2+ , Ni 2+ , Zn 2+ , Cd 2+ ). After the above reaction solution was diluted 60 times with water, 2 μL was ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com