Method for preparing genetic engineering N-acetylated thymosin alpha1
A technology of genetic engineering and thymosin, which is applied in the field of preparing genetic engineering N-acetylated thymosin α1, can solve the problems of affecting biological activity and immunogenicity, and achieve the effect of convenient purification and reduced complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
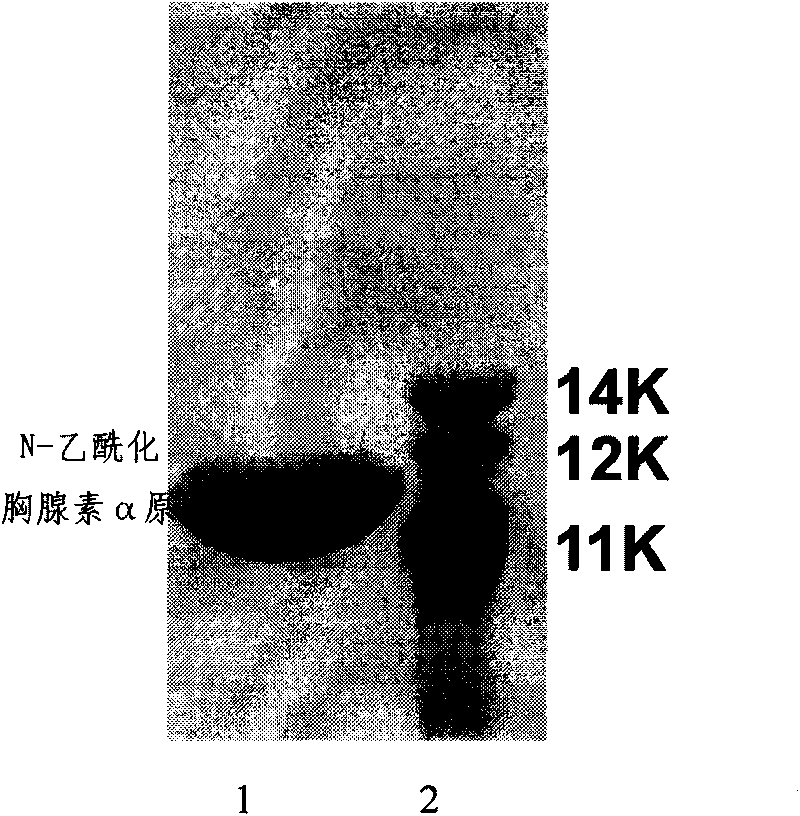
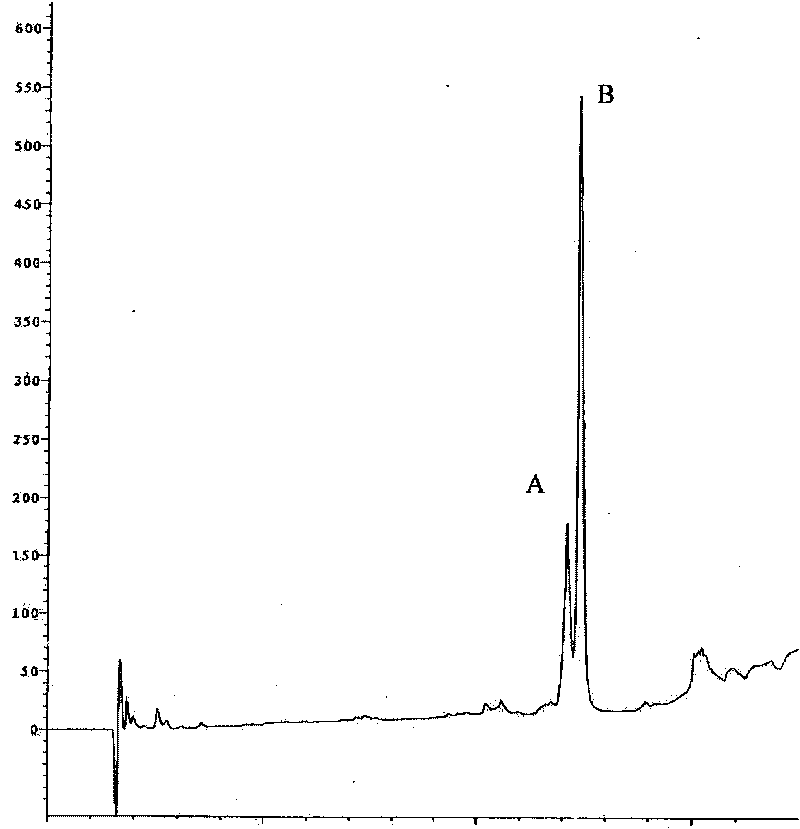
[0048] Example 1. Preparation of N-acetylated thymosin α1 with N-acetylated thymosin α progen
[0049] The pfu enzymes, endonucleases, ligases, and kits used in the experiment were purchased from Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. and Beijing Biotech Biogene Technology Co., Ltd.
[0050] 1. Construction of genetically engineered bacteria expressing N-acetylated prothymosin α
[0051] Take the aborted human fetal thymus, use the total RNA preparation kit, and prepare total RNA according to the method provided by the kit; use the RT-PCR kit, and reverse-transcribe the mRNA into cDNA according to the method provided by the kit; use the cDNA as a template, Using Prot1: 5'-CCCATATGTCTGATGCAGCTGTAGATACC-3' and Prot2: 5'-CGGGATCCCTAGTCATCCACGTCGGTCTTCTG-3' as primers, the cDNA of thymosin was amplified by PCR. Add 1 μl cDNA, 3 μl each of 20 μmol / L Prot1 and Prot2 primers, 10 μl of 2 mmol / L dNTP, 10 μl of 10X reaction buffer, and 5 U of pfu DNA polymerase int...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2, Preparation of N-acetylated thymosin α1 (Ile13) (sequence 2 in the sequence listing)
[0065] Using the recombinant plasmid pET-NproT constructed in the above-mentioned Example 1 as a template, using Prot3: 5'-cccatatgtctgatgcagctgtagataccagctccgaaatcaccatcaaggactta-3' and Prot2 as primers, PCR amplification was carried out, and the amino acid residue encoded by the deoxyribonucleotide sequence obtained was The gene was named NproT(Ile13) from prothymosin alpha prothymosin whose 13th amino-terminal amino acid is isoleucine.
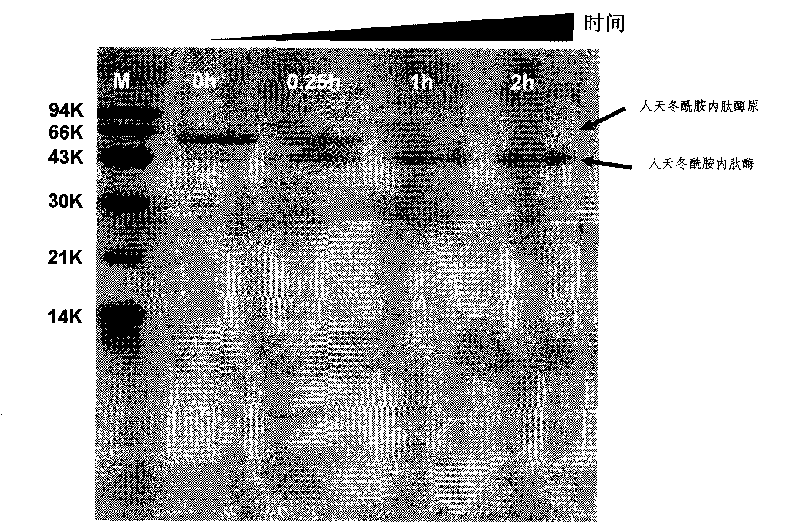
[0066] NproT (Ile13) was inserted between the NdeI and BamHI restriction sites of the vector PET22b using the same method as in Example 1 above to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET-NproT (Ile13); then the recombinant plasmid pET-NproT (Ile13) was transferred into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells, adopt the screening method identical with above-mentioned embodiment 1 to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) (pET-NproT...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3, using natural genes and artificially synthesized genes to express C-terminal deletions and / or substitution of G from the 36th position of the amino terminal to A, and substitution of G to A from the 43rd position of the amino terminal to prothymosin α variants, Preparation of N-acetylated thymosin α1
[0069] 1. Construction of engineering bacteria expressing C-terminal deleted prothymosin α variants
[0070]Using the recombinant plasmid pET-NproT constructed in the above-mentioned Example 1 as a template, and using Prot1 and Prot4: 5'-gtggatccttaATCGACATCGTCATCCTCATC-3' as primers, the gene (NproT- C), its deoxyribonucleotide sequence is shown in sequence 11 in the sequence listing, and its coded amino acid sequence is shown in sequence 4 in the sequence listing.
[0071] Using the same method as in Example 1 above, NproT-C was inserted between the BamHI and NdeI restriction sites of the vector PET22b to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET-NproT-C; then the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com