NPN (negative-positive-negative) heterojunction bipolar-junction transistor laser
A transistor laser, heterojunction bipolar technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor lasers, lasers, laser components, etc., can solve the problems of material quality degradation in the active area, deterioration of device luminous performance, etc., to improve electrical performance and increase luminescence Performance, the effect of reducing the concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
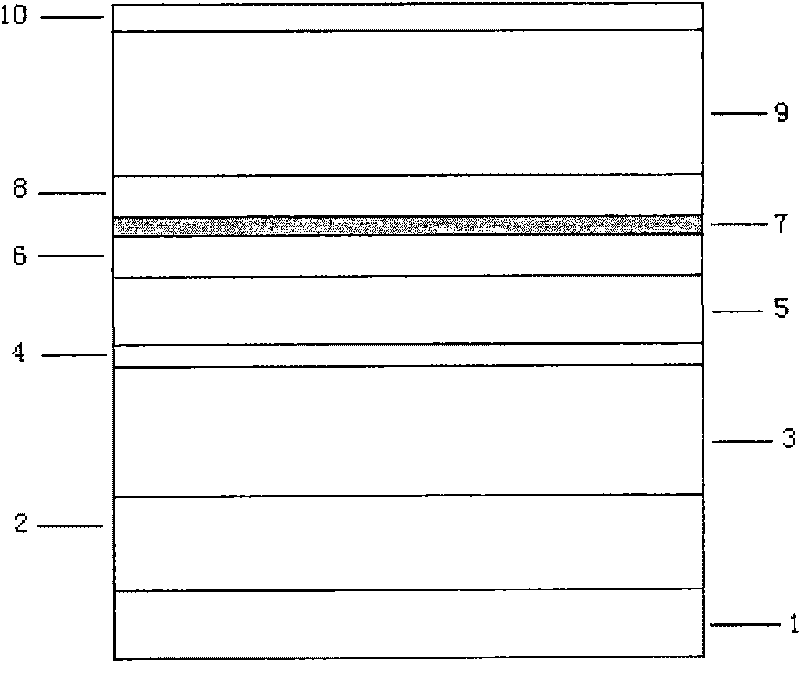
[0044] This embodiment is a specific process method for growing a GaAs-based NPN heterojunction bipolar transistor laser, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0045] 1) growing a gallium arsenide buffer layer 2 with a thickness of about 500 nm on the washed gallium arsenide substrate 1;
[0046] 2) growing InGaP (InGaP) with a thickness of 0.4 to 1.2 microns on the GaAs buffer layer 2 0.49 Ga 0.51 P) or aluminum gallium arsenide (Al x Ga 1-x As (0<x≤1)) lower cladding layer 3, which limits the light field and electric field;
[0047] 3) growing an n layer with a thickness of 30-70 nm on the lower cladding layer 3 + GaAs sub-collector layer 4;
[0048] 4) growing an i-type or weakly n-type doped gallium arsenic collector layer 5 with a thickness of 60-200 nm on the sub-collector layer 4;
[0049] 5) On the gallium arsenic collector layer 5, p + GaAs base layer 6;
[0050] 6) Growing an i-type InGaAs / GaAs quantum well active region 7 on the GaAs base layer ...
no. 2 example
[0055] This embodiment is a specific process method for growing an indium phosphorus-based NPN heterojunction bipolar transistor laser, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0056] 1) growing an indium phosphorus buffer layer 2 with a thickness of about 500 nm on the washed indium phosphorus substrate 1;
[0057] 2) growing an indium phosphorus lower cladding layer 3 with a thickness of 0.4 to 1.2 microns on the indium phosphorus buffer layer 2 to confine the optical field and the electric field;
[0058] 3) On the indium phosphorus lower cladding layer 3, grow n + InP sub-collector layer 4;
[0059] 4) growing an i-type or weakly n-type doped indium phosphorus collector layer 5 with a thickness of 60-200 nm on the sub-collector layer 4;
[0060] 5) On the indium phosphorus collector layer 5, p + InGaAsP or InGaAs base layer 6;
[0061] 6) On the indium phosphorus base layer 6, grow the i-type indium gallium arsenide phosphorus quantum well active region layer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com