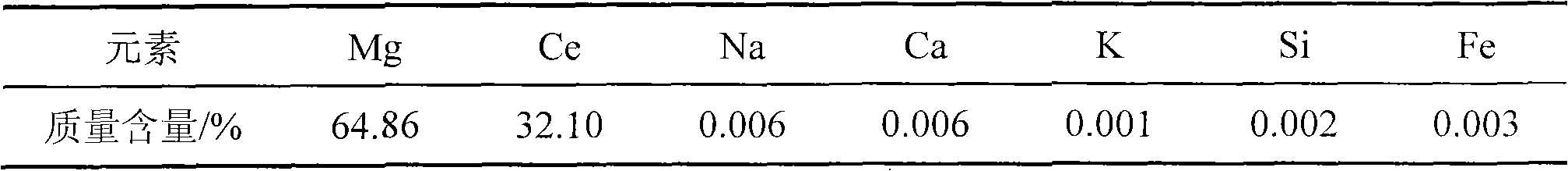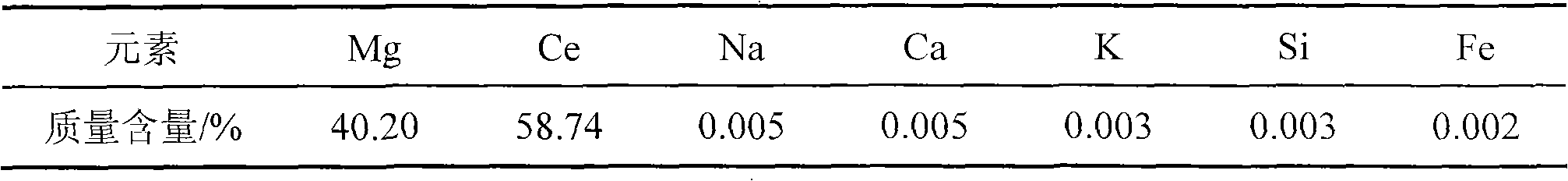Method for electrolytically preparing magnesium-rare earth by using hydrated magnesium chloride and rare earth chloride
A technology for hydrating magnesium chloride and magnesium rare earth alloys, which is applied in the field of producing magnesium rare earth alloys, can solve the problems of high cost, difficult preparation, and high production cost of magnesium or magnesium alloys, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs and simplifying the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
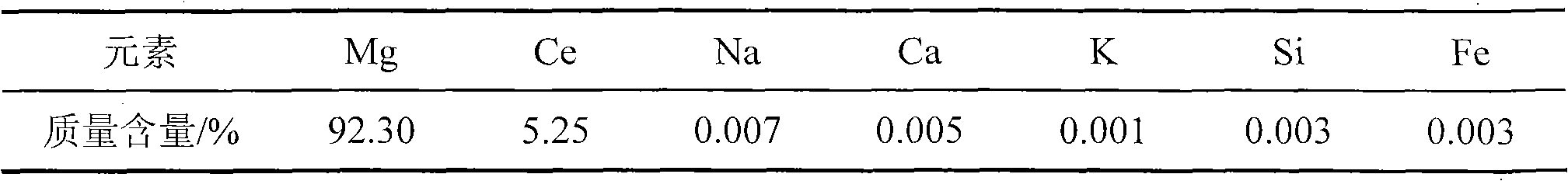
[0032] Example 1 A method for electrolytically preparing magnesium rare earth alloys with hydrated magnesium chloride and rare earth chloride, the electrolytic raw material is MgCl 2 2H 2 O and CeCl 3 ·3H 2 O, its mass ratio is 10:1; the electrolyte is MgCl 2 -NaCl-KCl-CeCl 3 system, where MgCl 2 The mass percentage is 20%, the mass percentage of rare earth chloride is 5%, the mass ratio of sodium chloride to potassium chloride is 1:1; the cathode is a molybdenum rod, and the anode is graphite. Under the condition of 680°C, direct current electrolysis is carried out, and Mg-Ce alloy is obtained at the cathode.
[0033] As determined by EDTA titration, the Mg-Ce alloy contained 5.25% (Wt.%) Ce (see Table 1).
[0034] Table 1: Magnesium-cerium alloy content
[0035]
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 A method for electrolytically preparing magnesium rare earth alloys with hydrated magnesium chloride and rare earth chloride, the electrolytic raw material is MgCl 2 2H 2 O and CeCl 3 ·3H 2 O, its mass ratio is 5:1; the electrolyte is MgCl 2 -NaCl-KCl-CeCl 3 system, where MgCl 2 The mass percentage is 10%, the mass percentage of rare earth chloride is 10%, the mass ratio of sodium chloride to potassium chloride is 3:1; the cathode is a molybdenum rod, and the anode is graphite. Under the condition of 800°C, direct current electrolysis is carried out, and Mg-Ce alloy is obtained at the cathode.
[0037] As determined by EDTA titration, the Mg-Ce alloy contained 32% (Wt.%) Ce (see Table 2).
[0038] Table 2: Magnesium-cerium alloy content
[0039]
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 A method for electrolytically preparing magnesium rare earth alloys with hydrated magnesium chloride and rare earth chloride, the electrolytic raw material is MgCl 2 2H 2 O and CeCl 3 ·3H 2 O, its mass ratio is 1:1; the electrolyte is MgCl 2 -NaCl-KCl-CeCl 3 system, where MgCl2 The mass percentage is 15%, the mass percentage of rare earth chloride is 15%, the mass ratio of sodium chloride to potassium chloride is 2:1; the cathode is a molybdenum rod, and the anode is graphite. When the voltage is 8.0V and the temperature Under the condition of 720°C, direct current electrolysis is carried out, and Mg-Ce alloy is obtained at the cathode.
[0041] As determined by EDTA titration, the Mg-Ce alloy contained 58% (Wt.%) Ce (see Table 3).
[0042] Table 3: Magnesium-cerium alloy content
[0043]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com