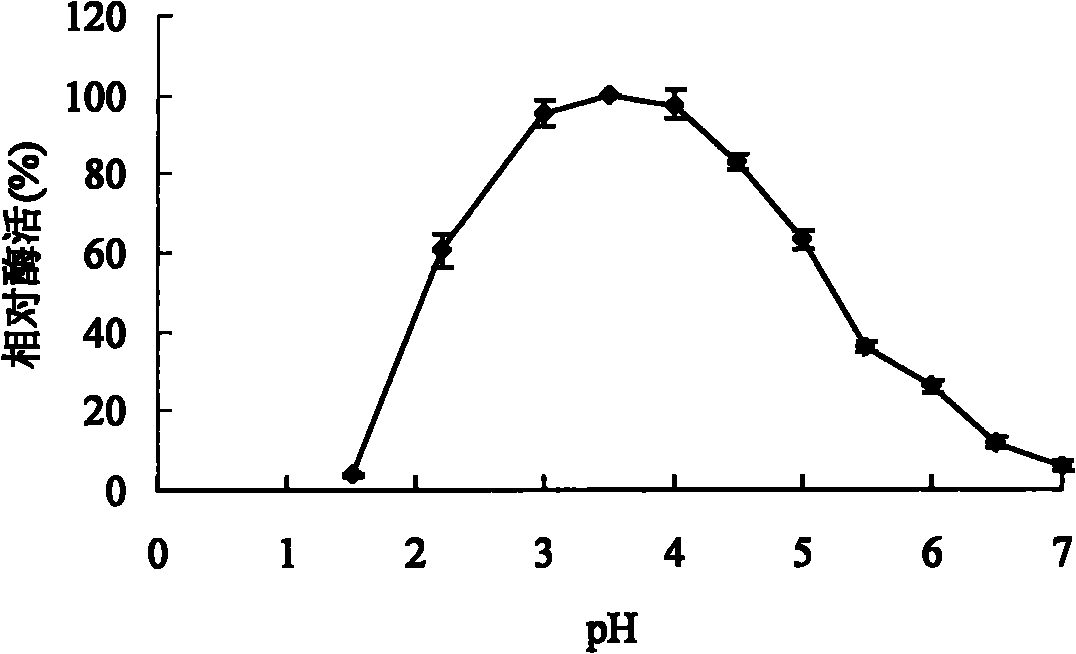
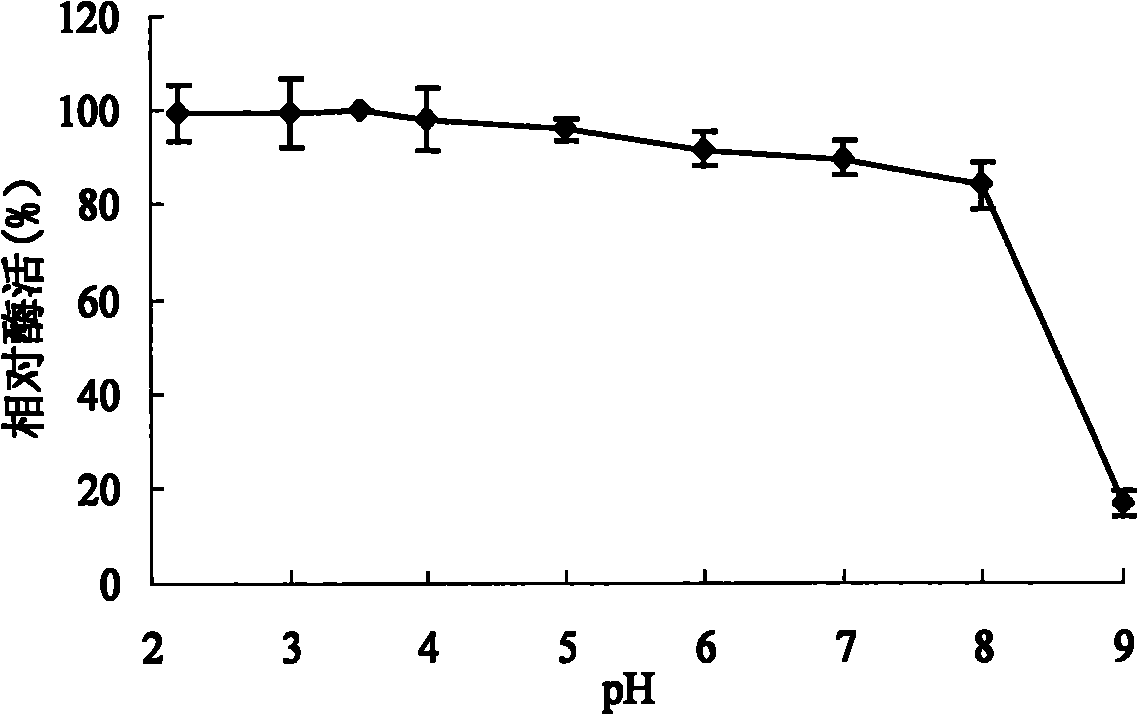
Acidophilic alpha-galactosidase AgalB with galactomannan degradation capability and gene and application thereof
A technology of galactomannan and galactosidase, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as inability to hydrolyze a variety of substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Cloning of the acidophilic fungus Bispora sp.MEY-1α-galactosidase encoding gene AgalB
[0046] Extract genomic DNA from the acidophilic fungus Bispora sp.MEY-1:
[0047] Filter the mycelium cultured for 3 days with sterile filter paper and put it in a mortar, add 2 mL of extract, grind for 5 min, then place the grind in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, lyse in a water bath at 65°C for 20 min, and mix every 10 min. Homogenize once and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 5 min. The supernatant was extracted in phenol / chloroform to remove impurities, and then the supernatant was added to an equal volume of isopropanol. After standing at room temperature for 5 min, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min. The supernatant was discarded, the precipitate was washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried in vacuum, dissolved in an appropriate amount of TE, and placed at -20°C for use.
[0048] Through the construction of cDNA library, EST sequencing and Blast comparison, the partial nu...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 RT-PCR analysis of α-galactosidase gene
[0053] Extract the total RNA of Bispora sp.MEY-1, use reverse transcriptase to obtain a strand of cDNA, and then design the appropriate primers (AgalB F1: 5′-ATGGCGATACTTTTTGCTTGCTTTGCGACGCTTG-3′, AgalB R: 5′-TCATACCGAACATTGATAGTAGAAGGCGCATGTGC-3′) The single-stranded cDNA was amplified to obtain the cDNA sequence of α-galactosidase, and the amplified product was recovered and sent to Shanghai Shenggong for sequencing.
[0054] By comparing the genome sequence and cDNA sequence of α-galactosidase, it was found that the gene has 3 introns. The cDNA is 1281bp long, encoding 426 amino acids and a stop codon, and 17 amino acids at the N-terminal are its predicted signal peptide Sequence, the determined partial nucleotide sequence of the mature protein of the gene AgalB is compared with the α-galactosidase gene sequence on GeneBank. The highest amino acid sequence identity is 35%, and the nucleotide sequence identity is 36%. , ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 Preparation of recombinant α-galactosidase.
[0056] The expression vector pPIC9 was double digested (SnaBI+NotI), and the gene encoding α-galactosidase AgalB was double digested (SnaBI+NotI), and the gene fragment encoding mature α-galactosidase was cut out and expressed The vector pPIC9 was connected to obtain the recombinant plasmid pPIC-AgalB containing the Bispora sp.MEY-1α-galactosidase gene AgalB and transformed into Pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain the recombinant Pichia pastoris strain GS115 / AgalB.
[0057] Take the GS115 strain containing the recombinant plasmid, inoculate it in 400 mL of BMGY culture solution, culture with shaking at 250 rpm at 30°C for 48 hours, and collect the bacteria by centrifugation. Then it was resuspended in 200 mL BMMY medium and cultured with shaking at 250 rpm at 20°C. After 72 hours of induction, the supernatant was collected by centrifugation. Determine the activity of α-galactosidase. The expression level of recombinant α...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com