Method for treating biological laboratory wastewater
A treatment method and laboratory technology, which is applied in the field of biological laboratory wastewater treatment, can solve problems such as unreliability, insufficient treatment efficiency of cancer cells, weak degradation and removal of organic pollutants, etc., to achieve low health risks and avoid toxic The production of disinfection by-products and the effect of low environmental toxicological and ecological risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
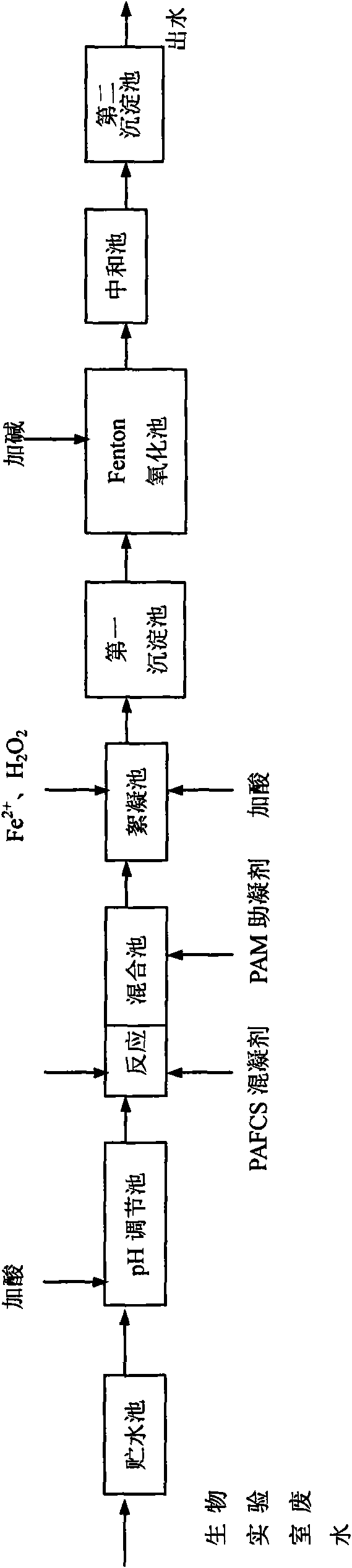
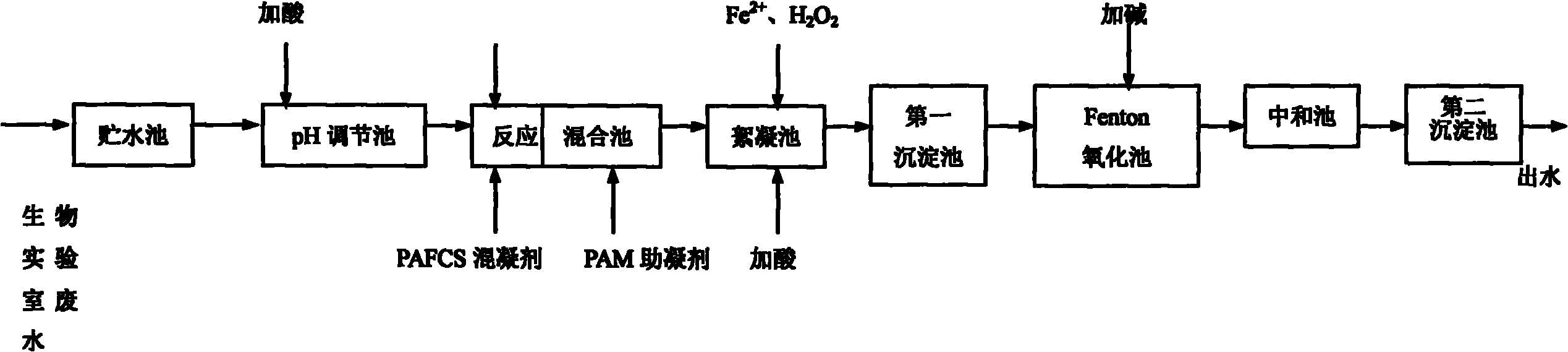
[0025] Wastewater from a biological laboratory in a university, the biological laboratory wastewater first enters the storage tank for flow regulation, and then enters the pH adjustment tank, where dilute H is added 2 SO 4 (30%) is used as a pH regulator to reduce the pH of the waste water to 2, stir for 20 minutes, and carry out preliminary sterilization; after sterilization, the waste water enters the chemical reaction tank, and CaO with a molar concentration of 0.75 times the LAS is added, and the medium speed (150r / min) Mix at high speed for 5 minutes for chemical reaction; the mixed water flows into the mixing tank for coagulation, add PAFCS 40mg / L, stir quickly (300r / min) for 1min, enter the flocculation tank after coagulation, add PAM 1.0mg / L, slowly (60r / min) stirred for 15min, entered the first sedimentation tank, then precipitated for 100min, and after solid-liquid separation, the supernatant continued to enter the Fenton oxidation tank, adding 0.044mol / L of H 2 o ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A biological product development laboratory, water quality parameters COD 1550mg / L, LAS 25mg / L, pH7.5, turbidity 200NTU, SS60mg / L, NH 3 -N 4.3mg / L, T-N 7.1mg / L, T-P 0.36mg / L, the total number of bacteria 2.4×10 5 CFU / mL, ATP9.8×10 3 RLU / mL, biological toxicity is toxic. The water sample of biological laboratory wastewater first enters the storage tank for flow adjustment, and then enters the pH adjustment tank, and dilute H is added to the pH adjustment tank. 2 SO 4 (30%) as a pH regulator to lower the pH of the waste water to 2, stir for 10 minutes, and carry out preliminary sterilization, then enter the chemical reaction tank, add CaO with an amount of 1.0 times the molar concentration of LAS, quickly mix for 10 minutes, and pump the mixed water into Add PAFCS50mg / L to the mixing tank, stir rapidly (300r / min), stir for 1min, enter the flocculation tank after coagulation, add PAM0.5mg / L, stir slowly (60r / min), stir for 15min, and then let it settle 30min. After so...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The laboratory wastewater of the Medicine Valley Building in a high-tech park. The water samples of the laboratory wastewater first enter the storage tank for flow adjustment, and then enter the pH adjustment tank, and add dilute H to the pH adjustment tank. 2 SO 4 (30%) as a pH regulator to reduce the pH of the waste water to 2, stir for 30 minutes, and carry out preliminary sterilization, then enter the chemical reaction tank, add CaO with an amount of 1.0 times the molar concentration of LAS, quickly mix for 10 minutes, and pump the mixed water into In the mixing tank, add PAFCS60mg / L, stir rapidly (300r / min), stir for 1min, stir slowly (60r / min), stir for 15min, enter the flocculation tank after coagulation, add PAM0.8mg / L, and then let it settle 30min. After solid-liquid separation, the supernatant continues to enter the Fenton oxidation pool, adjust the pH of the water body in the oxidation pool to 3.5, react for 4 hours, mol (H 2 o 2 ) / mol(Fe 2+ ) ratio of 20...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com