Preparation process of D-mannose
A preparation process and mannose technology, which are applied in the field of six-carbon sugar preparation technology, can solve the problems of high purchase cost, low yield and purity, and high cost of fructose, and achieve full utilization, product purity improvement, and product yield improvement. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
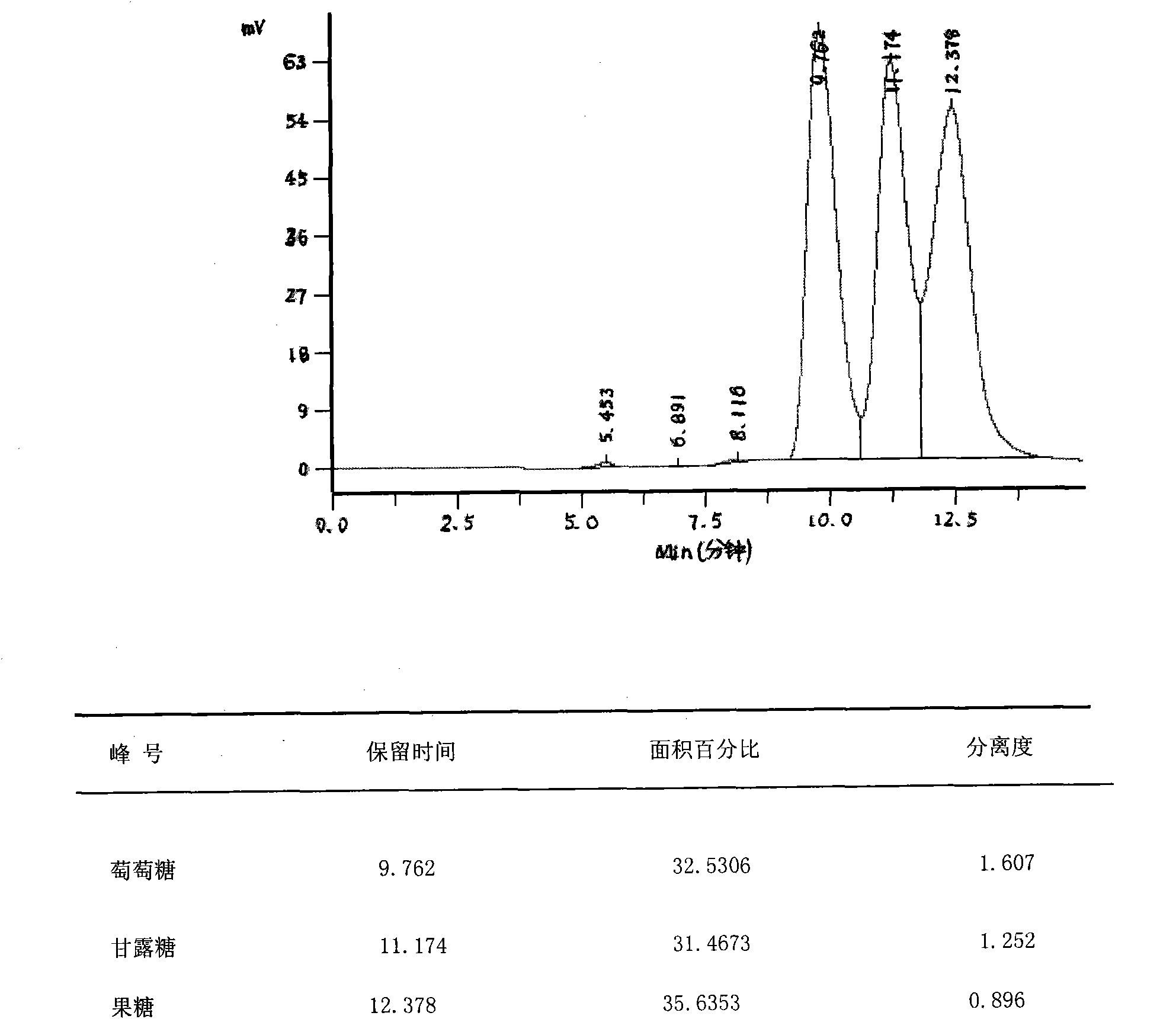
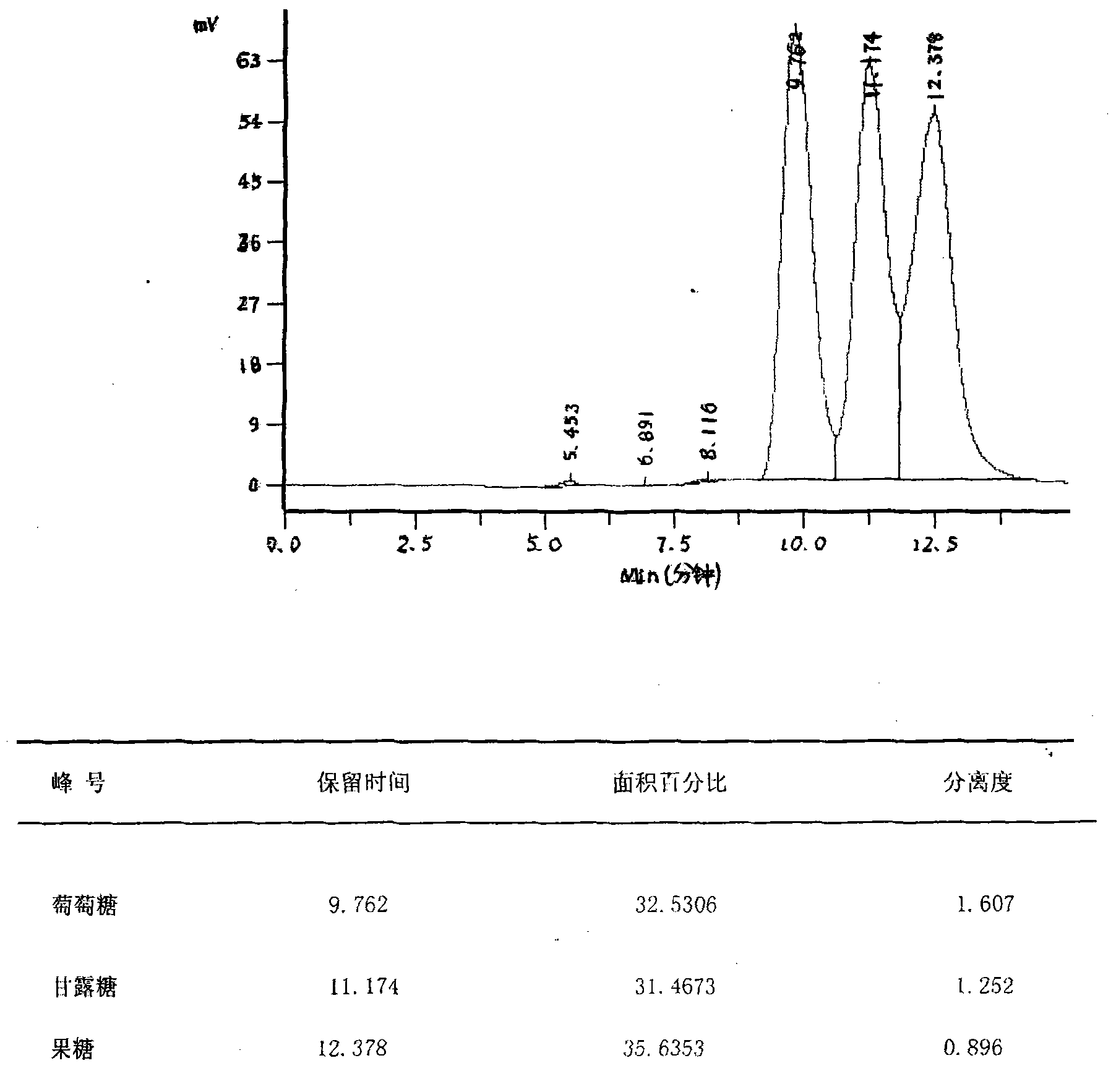
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Dilute 5Kg of crystalline glucose with purified water to a concentration of 45%, add 15g of catalyst molybdate, and carry out epimerization under vacuum at 90°C. The mannose content in the obtained isomerized mixture is 29.2%. After desalting and refining the above-mentioned heterogeneous mixture, it enters a simulated moving bed for separation and purification to obtain mannose-rich component B1 and glucose-rich component A1. Component A1 is returned to the simulated moving bed system for recycling, and the content of mannose in component B1 is 93.2%. Component B1 was evaporated once to a concentration of 55%, and then 14 g of activated carbon was added for decolorization. After decolorization, it was evaporated twice to obtain a feed solution with a concentration of 90%. The feed solution was subjected to aqueous phase crystallization. Gradient temperature control during the crystallization process: 0-12 hours, drop 0.5°C per hour; 13-24 hours, drop 0.8°C per hour; a...
Embodiment 2
[0037]Dilute 5Kg of crystalline glucose with purified water to a concentration of 50%, add 13g of catalyst molybdate, and carry out epimerization under a vacuum condition of 95°C. The content of mannose in the obtained isomerized mixture is 28.5%. After desalting and refining the above-mentioned heterogeneous mixture, it enters a simulated moving bed for separation and purification to obtain mannose-rich component B1 and glucose-rich component A1. Component A1 is returned to the simulated moving bed system for recycling, and the content of mannose in component B1 is 90.6%. Component B1 was evaporated once to a concentration of 60%, and then 15 g of activated carbon was added for decolorization. After decolorization, it was evaporated twice to obtain a feed solution with a concentration of 91%. The feed solution was subjected to aqueous phase crystallization. Gradient temperature control during the crystallization process: 0-12 hours, drop 0.5°C per hour; 13-24 hours, drop 0.8...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Dilute 5Kg of crystalline glucose with purified water to a concentration of 50%, add 14g of catalyst molybdate, and carry out epimerization under a vacuum condition of 100°C. The content of mannose in the obtained isomerized mixture is 29.2%. After desalting and refining the above-mentioned heterogeneous mixture, it enters a simulated moving bed for separation and purification to obtain mannose-rich component B1 and glucose-rich component A1. Component A1 is returned to the simulated moving bed system for recycling, and the content of mannose in component B1 is 91.2%. Component B1 was evaporated once to a concentration of 55%, and then 18 g of activated carbon was added for decolorization. After decolorization, it was evaporated twice to obtain a feed solution with a concentration of 92%. The feed solution was subjected to aqueous phase crystallization. Gradient temperature control during the crystallization process: 0-12 hours, drop 0.5°C per hour; 13-24 hours, drop 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com