Clostridium acetobutylicum strain and screening method and application thereof
A technology of Fusobacterium acetobutylicum and acetone butanol, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., to achieve significant social significance and economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
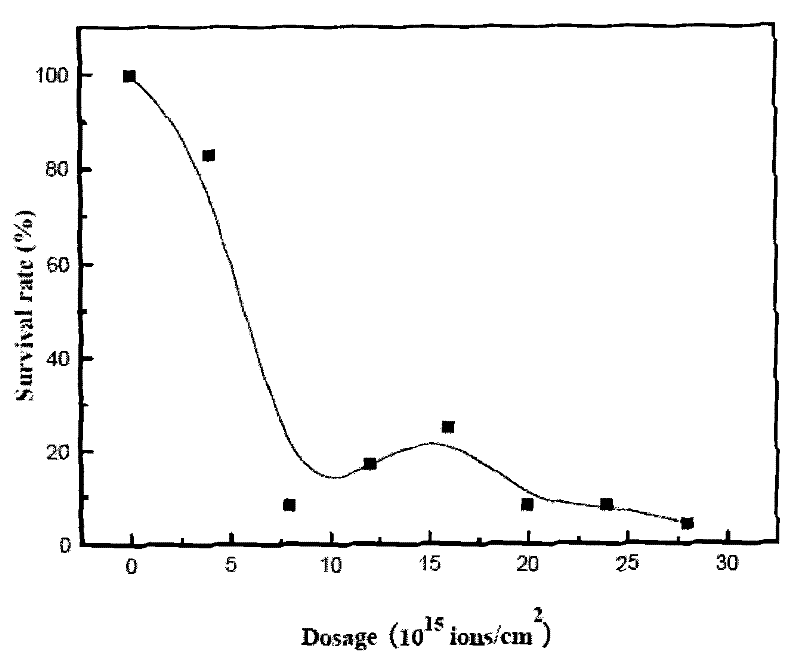
[0031] This example illustrates the method of performing the first step of ion beam mutagenesis on the original strain of Fusobacterium acetobutylicum.
[0032] The original strain of Fusobacterium acetobutylicum came from self-screening, the specific method is as follows:
[0033] 1. Use the fermentation screening medium containing 25g / L butanol to enrich the butanol-resistant microorganisms in the soil samples in Nanjing area, and screen out the strains that can tolerate 25g / L butanol. Streak the bacterial solution in the sample tube capable of growth on the solid plate medium, culture at 37°C for 48 hours, and obtain a single colony.
[0034] Among them, fermentation screening medium: butanol 1%, yeast powder 0.2%, peptone 0.3%, soluble starch 1%, ammonium acetate 0.2%, sodium chloride 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1%, phosphoric acid Dipotassium hydrogen dipotassium 0.1%, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.01%, pH6.
[0035] 2. Pick the singl...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This example illustrates the method for further screening of excellent Fusobacterium acetobutylicum.
[0041] Wherein, the medium formula (% is mass percent) used:
[0042] (1) Solid plate medium: yeast powder 0.2%, peptone 0.3%, soluble starch 1%, ammonium acetate 0.2%, sodium chloride 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1 %, 0.01% ferrous sulfate 7 hydrate, pH6.
[0043] (2) Xylose plate medium: corn steep liquor 0.1% (solid content is 40-50%), xylose 1%, ammonium acetate 0.2%, sodium chloride 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1 %, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1%, ferrous sulfate 7 hydrate 0.01%, agar 1.5%, pH 5-7.
[0044] (3) 2-deoxy-D-glucose plate medium: yeast powder 0.2%, peptone 0.3%, soluble starch 1%, ammonium acetate 0.2%, sodium chloride 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.3%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1% , dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1%, ferrous sulfate he...
Embodiment 3
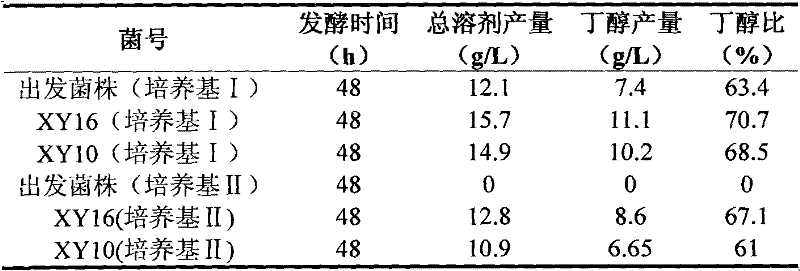
[0065] This example illustrates the passage stability of mutant strains XY16 and XY10.
[0066] The results of the subculture fermentation test of bacterial strain XY16 and XY10 are shown in Table 2:
[0067] Table 2
[0068]
[0069] From the experimental results, it can be seen that after 7 consecutive passages, the total solvent production and butanol production of the two mutant strains are relatively stable, and they have good passage stability, and can be used as production strains for further research and development.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com